Genome Analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the Causal Agent of Wet Bubble Disease of Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strain
2.2. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.3. Functional Annotation of Pathogenicity-Related Genes and Secondary Metabolites
2.4. Orthology and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. De Novo Genome Sequencing of H. perniciosus
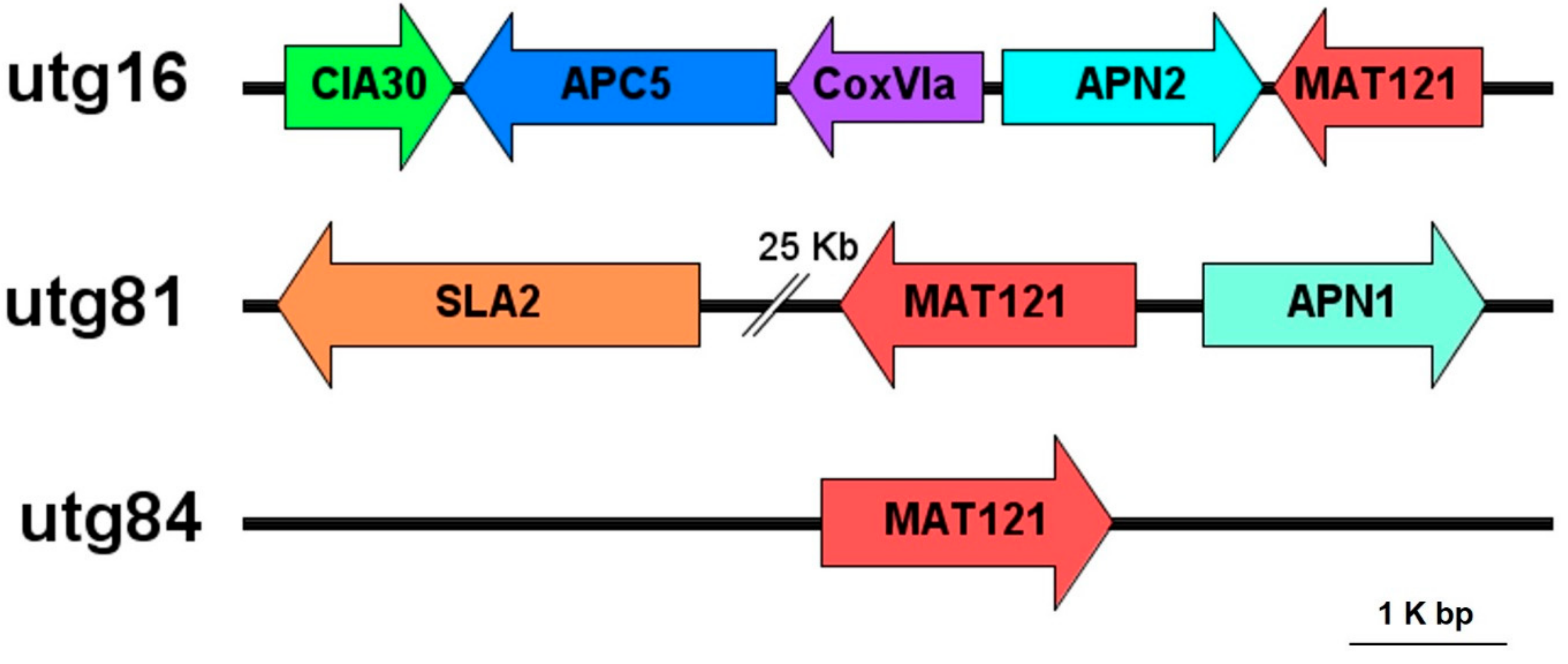
3.2. Identification of Mating-Type Idiomorphs in H. perniciosus
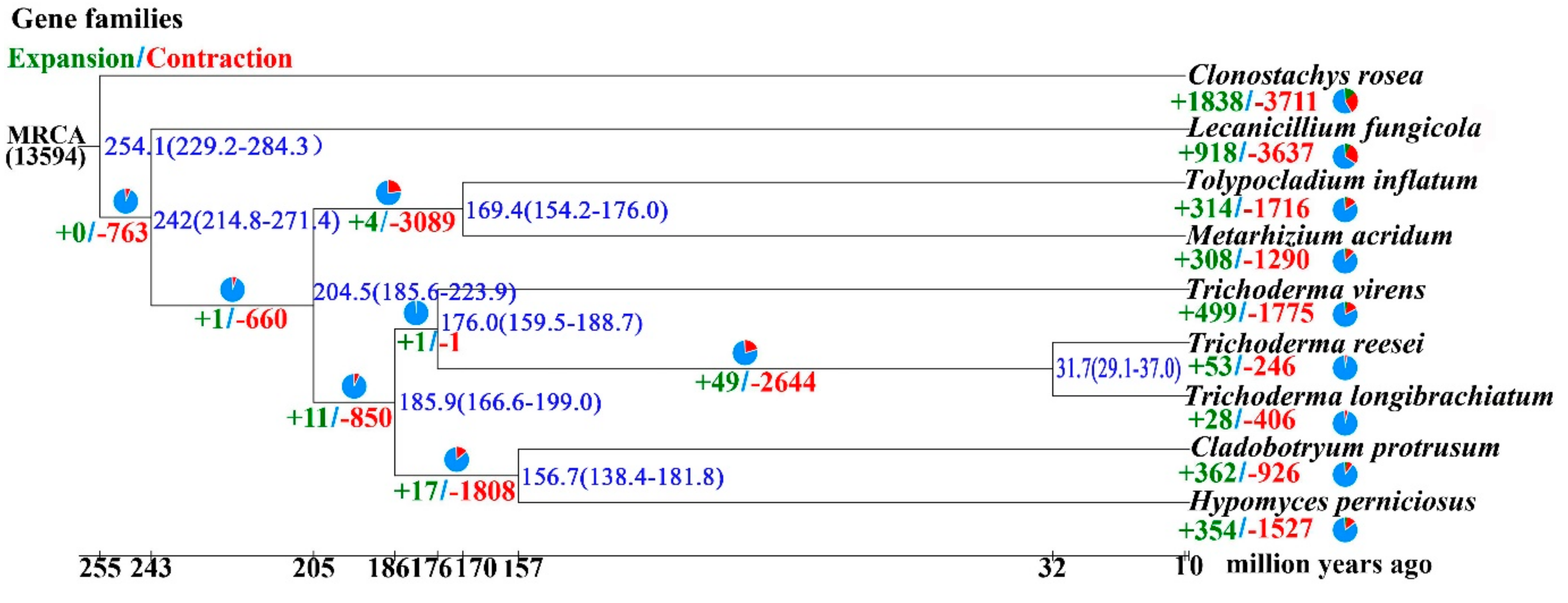
3.3. Genome Evolution and Phylogenomic Analysis of H. perniciosus
3.4. Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme (CAZymes) in H. perniciosus
3.5. Secondary Metabolites in H. perniciosus
3.6. Pathogenicity-Related Genes in H. perniciosus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, J.T.; Jaffe, B.; Muthumeenakshi, S.; Brown, A.E.; Wright, D.M. Variations in isolates of Mycogone perniciosa and in disease symptoms in Agaricus bisporus. Plant Pathol. 1995, 44, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.E.V. Three diseases of cultivated mushrooms. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1924, 10, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.P.; Wang, X.X.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, B.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, Y. Identification of resistance to wet bubble disease and genetic diversity in wild and cultivated strains of Agaricus bisporus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Kakishima, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. The effect of Hypomyces perniciosus on the mycelia and basidiomes of Agaricus bisporus. Microbiology 2017, 163, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, B.Z.; Wang, S.; Li, C.H.; Wen, Z.Q. Analysis of genetic diversity and development of SCAR Markers in a Mycogone perniciosa population. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, D.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Genetic diversity analysis of Mycogone perniciosa causing wet bubble disease of Agaricus bisporus in China using SRAP. J. Phytopathol. 2016, 164, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.Q.; Wu, X.H.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.S.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Liu, X.G. Evaluation of the safe use and dietary risk of beta-cypermethrin, pyriproxyfen, avermectin, diflubenzuron and chlorothalonil in button mushroom. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandy, D.G.; Spencer, D.M. Fungicides for the control of Mycogone perniciosa (Magn.), the cause of wet bubble on the cultivated mushroom. Sci. Hortic. 1978, 8, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamoclija, J.; Soković, M.; Ljaljević-Grbić, M.; Vukojević, J.; Milenković, I.; Van Griensven, L. Morphological characteristics and mycelial compatibility of different Mycogone perniciosa isolates. J. Microsc. 2008, 232, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.M.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Farrer, R.; van Dam, P.; Bertoldo, C.; Rep, M. Comparative genomics of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis reveals the secreted protein recognized by the Fom-2 resistance gene in melon. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossah, F.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, C.T.; Okorley, B.A.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.P.; Li, Y. Genome sequencing of Cladobotryum protrusum provides insights into the evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the cobweb disease pathogen on cultivated mushroom. Genes 2019, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Baars, J.J.P.; Kalkhove, S.I.C.; Lugones, L.G.; Wösten, H.A.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Lecanicillium fungicola: causal agent of dry bubble disease in white-button mushroom. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Reid, I.D.; Yanke, J.L.; Wang, P.; Abbott, D.W.; Tsang, A.; McAllister, T. Application of transcriptomics to compare the Carbohydrate Active Enzymes that are expressed by diverse genera of anaerobic Fungi to degrade plant cell wall carbohydrates. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.; Bradnam, K.; Korf, I. CEGMA: a pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriventseva, E.V.; Simão, F.A.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Seppey, M.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO Applications from quality assessments to gene prediction and phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Simao, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Chen, N. Using repeatMasker to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2009, 25, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birney, E.; Clamp, M.; Durbin, R. GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanke, M.; Keller, O.; Gunduz, I.; Hayes, A.; Waack, S.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: ab initio prediction of alternative transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majoros, W.H.; Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: two open source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2878–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, C.; Karlin, S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA11Edited by F.E. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 268, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsik, C.G.; Mackey, A.J.; Reese, J.T.; Milshina, N.V.; Roos, D.S.; Weinstock, G.M. Creating a honey bee consensus gene set. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Nikolskaya, A.N.; et al. The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrane, M.; Consortium, U. UniProt Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data. Database 2011, 2011, bar009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank and its new supplement TREMBL. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Chang, H.-Y.; Daugherty, L.; Fraser, M.; Hunter, S.; Lopez, R.; McAnulla, C.; McMenamin, C.; Nuka, G.; Pesseat, S.; et al. The InterPro protein families database: the classification resource after 15 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Stærfeldt, H.-H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, P.P.; Eldai, H. Annotating RNA motifs in sequences and alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, 691–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, Y.; Khatri, I.; Subramanian, S.; Shenoy, B.D. Genome sequence, comparative analysis, and evolutionary insights into chitinases of entomopathogenic Fungus Hirsutella thompsonii. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, M.H.; Reddy, V.S.; Tsu, B.V.; Ahmed, M.S.; Li, C.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G. The transporter classification database (TCDB): recent advances. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Ahn, K.; Park, B.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Lee, Y.H. Fungal cytochrome P450 database. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R. The cytochrome p450 homepage. Hum. Genom. 2009, 4, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: signalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierleoni, A.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. PredGPI: a GPI-anchor predictor. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Nielsen, H.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, M.; Cuzick, A.; Rutherford, K.; Irvine, A.; Pedro, H.; Pant, R.; Sadanadan, V.; Khamari, L.; Billal, S.; Mohanty, S.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E. PHI-base: a new interface and further additions for the multi-species pathogen–host interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Yao, B.; Zhang, C. DFVF: database of fungal virulence factors. Database 2012, 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Weber, T.; Chevrette, M.G.; Lu, X.; Schwalen, C.J.; Kautsarsa, S.A.; Suarez Duran, H.G.; de Los Santos, E.L.C.; Kim, H.U.; Nave, M.; et al. antiSMASH 4.0-improvements in chemistry prediction and gene cluster boundary identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemert, N.; Podell, S.; Penn, K.; Badger, J.H.; Allen, E.; Jensen, P.R. The natural product domain seeker NaPDoS: a phylogeny based bioinformatic tool to classify secondary metabolite gene diversity. Plos ONE 2012, 7, e34064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Stoeckert, C.J.; Roos, D.S. OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, S.B.; Marin, J.; Suleski, M.; Paymer, M.; Kumar, S. Tree of life reveals clock-like speciation and diversification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bie, T.; Cristianini, N.; Demuth, J.P.; Hahn, M.W. CAFE: a computational tool for the study of gene family evolution. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floudas, D.; Binder, M.; Riley, R.; Barry, K.; Blanchette, R.A.; Henrissat, B.; Martínez, A.T.; Otillar, R.; Spatafora, J.W.; Yadav, J.S.; et al. The paleozoic origin of enzymatic Lignin decomposition reconstructed from 31 Fungal genomes. Science 2012, 336, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.Z.; Yang, Z.Q.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.B. dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, V. Chitinases of filamentous fungi: a large group of diverse proteins with multiple physiological functions. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2008, 22, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, M.A.; Thai, M. Compost bacteria and fungi that influence growth and development of Agaricus bisporus and other commercial mushrooms. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018, 102, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, C.F. Microbial ecology of the Agaricus bisporus mushroom cropping process. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018, 102, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, S.; Ahmed, M.; Shah, S. Disease status and yield losses due to wet bubble disease (Mycogone perniciosa) associated with the cultivation of white button mushroom at different mushroom units of Kashmir valley. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 12, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, A.; Salamov, A.; Korzeniewski, F.; Nordberg, H.; Shabalov, I.; Dubchak, I.; Otillar, R.; Riley, R.; Ohm, R.; Nikitin, R.; et al. MycoCosm portal: gearing up for 1000 fungal genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev, I.V.; Cullen, D.; Goodwin, S.B.; Hibbett, D.; Jeffries, T.; Kubicek, C.P.; Kuske, C.R.; Magnuson, J.K.; Martin, F.M.; Spatafora, J.W.; et al. Fueling the future with fungal genomics. Mycology 2011, 2, 192–209. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev, I.V.; Nordberg, H.; Shabalov, I.; Aerts, A.; Cantor, M.; Goodstein, D.; Kuo, A.; Minovitsky, S.; Nikitin, R.; Ohm, R.A.; et al. The genome portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, E.; Kohler, A.; Baker, A.R.; Foulongne-Oriol, M.; Lombard, V.; Nagy, L.G.; Ohm, R.A.; Patyshakuliyeva, A.; Brun, A.; Aerts, A.L.; et al. Genome sequence of the button mushroom Agaricus bisporus reveals mechanisms governing adaptation to a humic-rich ecological niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17501–17506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.G.; Hu, S.N.; Yao, N.; Dean, R.A.; Zhao, W.S.; Shen, M.; Zhang, H.W.; Li, C.; et al. Comparative analysis of the genomes of two field isolates of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plos Genet. 2012, 8, e1002869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Ke, X.; Dou, D.; Gao, X.; Song, N.; Dai, Q.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.R.; et al. Genome sequence of Valsa canker pathogens uncovers a potential adaptation of colonization of woody bark. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Fang, A.; Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Xue, M.; Bao, J.; Hu, D.; Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Specific adaptation of Ustilaginoidea virens in occupying host florets revealed by comparative and functional genomics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duplessis, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Lin, Y.C.; Aerts, A.; Tisserant, E.; Veneault-Fourrey, C.; Joly, D.L.; Hacquard, S.; Amselem, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; et al. Obligate biotrophy features unraveled by the genomic analysis of rust fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9166–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, F.; Kohler, A.; Murat, C.; Balestrini, R.; Coutinho, P.M.; Jaillon, O.; Montanini, B.; Morin, E.; Noel, B.; Percudani, R.; et al. Périgord black truffle genome uncovers evolutionary origins and mechanisms of symbiosis. Nature 2010, 464, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, P.D.; Abbott, J.C.; Amselem, J.; Burgis, T.A.; Soanes, D.M.; Stuber, K.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Brown, J.K.; Butcher, S.A.; Gurr, S.J.; et al. Genome expansion and gene loss in powdery mildew fungi reveal tradeoffs in extreme parasitism. Science 2010, 330, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.H.; Yang, D.R.; Jiang, J.J.; Zhang, Q.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Shi, C.; Tong, Y.; et al. The caterpillar fungus, Ophiocordyceps sinensis, genome provides insights into highland adaptation of fungal pathogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faino, L.; Seidl, M.F.; Shi-Kunne, X.; Pauper, M.; van den Berg, G.C.; Wittenberg, A.H.; Thomma, B.P. Transposons passively and actively contribute to evolution of the two-speed genome of a fungal pathogen. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffaele, S.; Kamoun, S. Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, G.H.; Poinar, G.J.; Spatafora, J.W. The oldest fossil evidence of animal parasitism by fungi supports a Cretaceous diversification of fungal-arthropod symbioses. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druzhinina, I.S.; Chenthamara, K.; Zhang, J.; Atanasova, L.; Yang, D.; Miao, Y.; Rahimi, M.J.; Grujic, M.; Cai, F.; Pourmehdi, S.; et al. Massive lateral transfer of genes encoding plant cell wall-degrading enzymes to the mycoparasitic fungus Trichoderma from its plant-associated hosts. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Atanasova, L.; Jensen, D.F.; Zeilinger, S. Necrotrophic mycoparasites and their genomes. Microbiolspectrum 2017, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, L.; et al. Whole genome sequencing revealed host adaptation-focused genomic plasticity of pathogenic Leptospira. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, L.; Tripathy, S.; Ishaque, N.; Boot, N.; Cabral, A.; Kemen, E.; Thines, M.; Ah-Fong, A.; Anderson, R.; Badejoko, W.; et al. Signatures of adaptation to obligate biotrophy in the Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis genome. Science 2010, 330, 1549–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguileta, G.; Refrégier, G.; Yockteng, R.; Fournier, E.; Giraud, T. Rapidly evolving genes in pathogens: Methods for detecting positive selection and examples among fungi, bacteria, viruses and protists. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, G.; Münch, K.; Mannhaupt, G.; Schirawski, J.; Kahmann, R.; Dutheil, J.Y. Positively selected effector genes and their contribution to virulence in the smut fungus Sporisorium reilianum. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 629–645. [Google Scholar]
- Seidl, V.; Song, L.; Lindquist, E.; Gruber, S.; Koptchinskiy, A.; Zeilinger, S.; Schmoll, M.; Martínez, P.; Sun, J.; Grigoriev, I.; et al. Transcriptomic response of the mycoparasitic fungus Trichoderma atroviride to the presence of a fungal prey. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Heitman, J. Mechanisms of homothallism in Fungi and transitions between heterothallism and homothallism. In Sex in Fungi; Heitman, J., Ed.; American Society of Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Seidl, V.; Seibel, C.; Kubicek, C.P.; Schmoll, M. Sexual development in the industrial workhorse Trichoderma reesei. Proc. Nat. L Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1390–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Feretzaki, M.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Heitman, J. Sex in Fungi. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, P.N.; Rafiqi, M.; Gan, P.H.P.; Hardham, A.R.; Jones, D.A.; Ellis, J.G. Effectors of biotrophic fungi and oomycetes: pathogenicity factors and triggers of host resistance. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.; Kishore, A.; Ballester, A.R.; Raphael, G.; Feigenberg, O.; Liu, Y.; Norelli, J.; Gonzalez-Candelas, L.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S. Identification of pathogenicity-related genes and the role of a subtilisin-related peptidase S8 (PePRT) in authophagy and virulence of Penicillium expansum on apples. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2019, 149, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, W.; Xie, B.-B.; Sun, C.-Y.; Li, D.; Rong, J.-C.; Chen, L.-L.; Shi, M.; Qin, Q.-L.; Wang, X.-W.; et al. Comparative genomics provide insights into evolution of Trichoderma nutrition style. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 379–390. [Google Scholar]


| HP10 | |
|---|---|
| Total scaffold number | 23 |
| Total length of sequences | 44,006,492 bp |
| N50 | 5,099,276 bp |
| N90 | 2,013,553 bp |
| GC content | 44.39% |
| Annotated protein-coding genes | 10,077 |
| Repeat sequences proportion | 25.27% |
| ncRNA proportion | 0.27% |
| CEGMA | 97.98% |
| BUSCO | 99.3% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Sossah, F.L.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. Genome Analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the Causal Agent of Wet Bubble Disease of Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Genes 2019, 10, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060417
Li D, Sossah FL, Sun L, Fu Y, Li Y. Genome Analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the Causal Agent of Wet Bubble Disease of Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Genes. 2019; 10(6):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060417
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Frederick Leo Sossah, Lei Sun, Yongping Fu, and Yu Li. 2019. "Genome Analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the Causal Agent of Wet Bubble Disease of Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus)" Genes 10, no. 6: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060417
APA StyleLi, D., Sossah, F. L., Sun, L., Fu, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Genome Analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the Causal Agent of Wet Bubble Disease of Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Genes, 10(6), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060417





