SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Subtyping Algorithm of Single Cells and Bulk Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
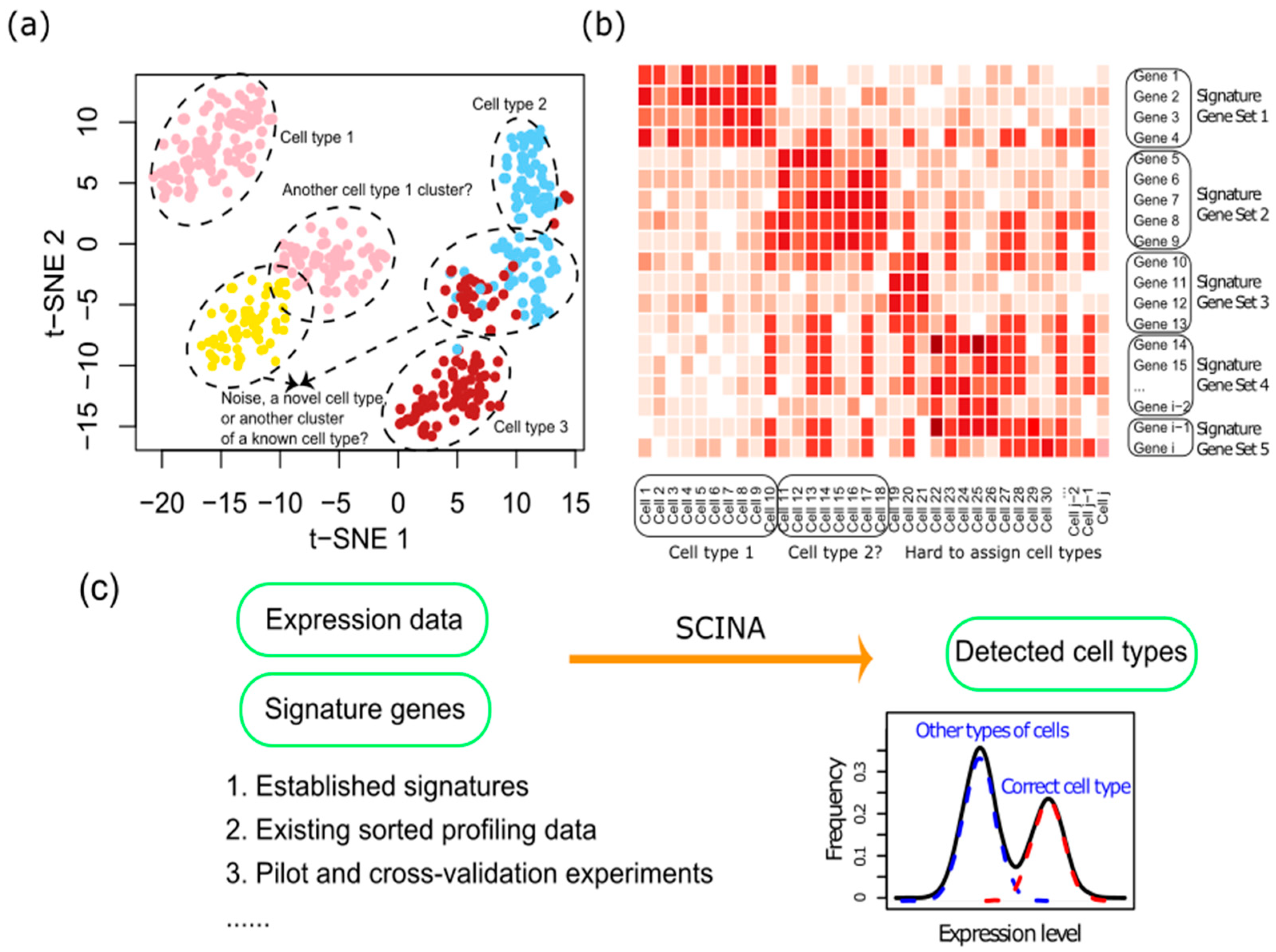
2.1. The SCINA Algorithm
2.2. Simulation Data Generation and Adding Noise to the Prior Information
2.3. Stk4 KO Mouse Related Experiments
2.4. UTSW FHD/FHD-Like Patient Cohort
2.5. Genomics Analysis Pipelines
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Availability of Data and Material
3. Results
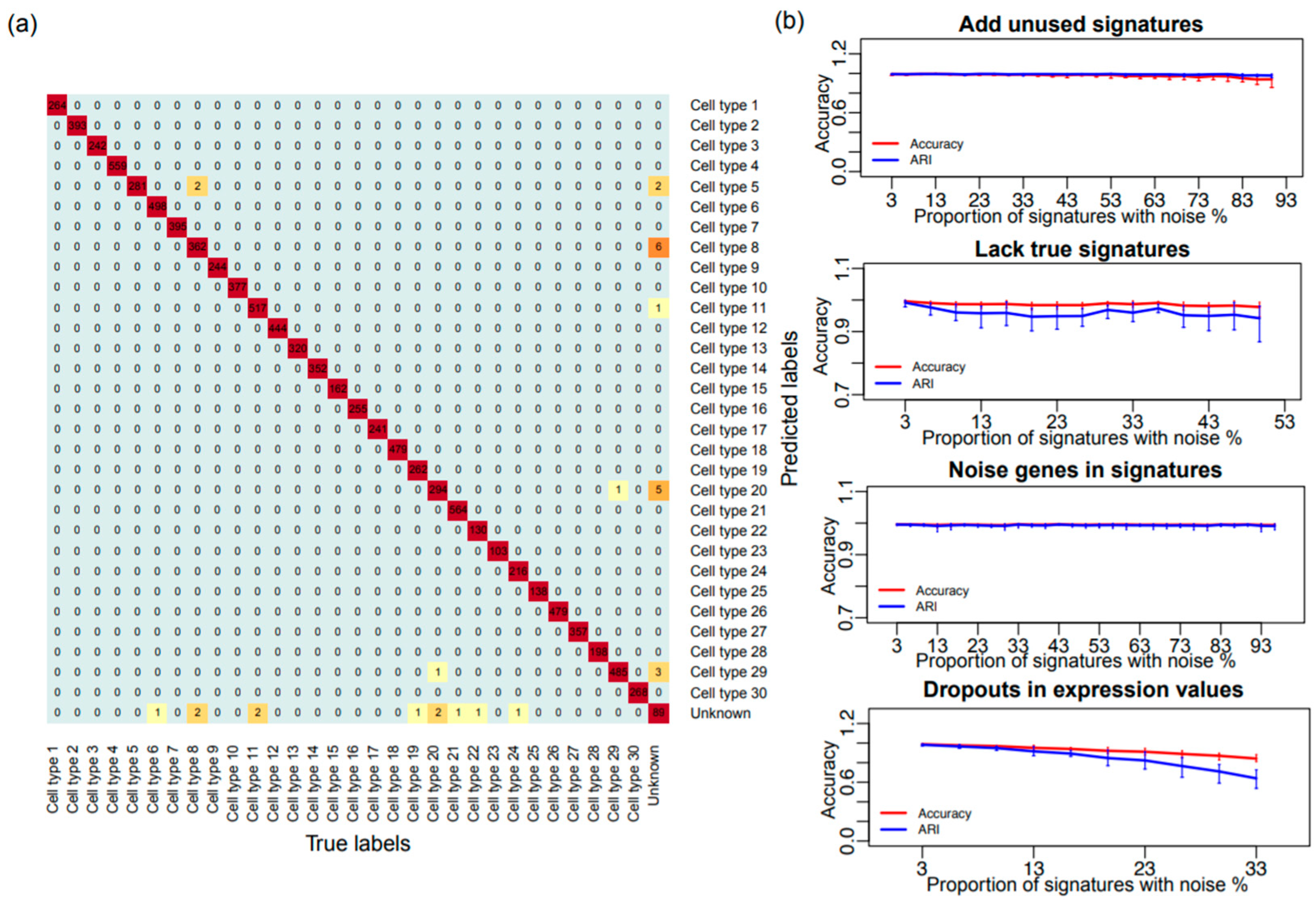
3.1. Validation of the SCINA Model by Simulation Data
3.2. Validation of the SCINA Model by Real Data
3.3. Discovery of a New Stage of Oligodendrocyte Development in Mouse Brain
3.4. SCINA Detected Immune Cell Population Alterations in Stk4 Knock-Out Mice
3.5. SCINA Identified a Novel Tumor Clade Based on Patient Bulk RNA-Seq Profiles
3.6. The SCINA R Package and SCINA on the Cloud
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Picelli, S.; Faridani, O.R.; Björklund, A.K.; Winberg, G.; Sagasser, S.; Sandberg, R. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.X.Y.; Terry, J.M.; Belgrader, P.; Ryvkin, P.; Bent, Z.W.; Wilson, R.; Ziraldo, S.B.; Wheeler, T.D.; McDermott, G.P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, R.K.; Utz, P.J. Screening: CyTOF-the next generation of cell detection. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Smibert, P.; Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Potter, S.S.; Whitsett, J.A.; Xu, Y. SINCERA: A Pipeline for Single-Cell RNA-Seq Profiling Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.H.; Simonds, E.F.; Bendall, S.C.; Davis, K.L.; Amir, E.D.; Tadmor, M.D.; Litvin, O.; Fienberg, H.G.; Jager, A.; Zunder, E.R.; et al. Data-Driven Phenotypic Dissection of AML Reveals Progenitor-like Cells that Correlate with Prognosis. Cell 2015, 162, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Su, Z. Identification of cell types from single-cell transcriptomes using a novel clustering method. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, A.B.; Roco, C.M.; Muscat, R.A.; Kuchina, A.; Sample, P.; Yao, Z.; Graybuck, L.T.; Peeler, D.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Chen, W.; et al. Single-cell profiling of the developing mouse brain and spinal cord with split-pool barcoding. Science 2018, 360, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intratumoral Immune Cells Reveal the Immune Landscape in Human Cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Lu, R.; Kapur, P.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Hannan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Pedrosa, I.; Luke, J.J.; Zhang, H.; Goldstein, L.D.; et al. An Empirical Approach Leveraging Tumorgrafts to Dissect the Tumor Microenvironment in Renal Cell Carcinoma Identifies Missing Link to Prognostic Inflammatory Factors. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Zhan, X.; Bu, C.-H.; Lyon, S.; Pratt, D.; Hildebrand, S.; Choi, J.H.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, K.-W.; et al. Real-time resolution of point mutations that cause phenovariance in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E440–E449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durinck, S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Pavía-Jiménez, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Kapur, P.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Toffessi-Tcheuyap, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pahuja, K.B.; et al. Spectrum of diverse genomic alterations define non-clear cell renal carcinoma subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.K.; Jain, M. NGS QC Toolkit: A Toolkit for Quality Control of Next Generation Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows—Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ Data to High-Confidence Variant Calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit Best Practices Pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar]
- Cibulskis, K.; Lawrence, M.S.; Carter, S.L.; Sivachenko, A.; Jaffe, D.; Sougnez, C.; Gabriel, S.; Meyerson, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Zhang, Q.; Larson, D.E.; Shen, D.; McLellan, M.D.; Lin, L.; Miller, C.A.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Wilson, R.K. VarScan 2: Somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Stuart, T.; Hafemeister, C.; Zheng, S. Available online: https://satijalab.org/seurat/ (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Guo, M. SINCERA: A Pipeline for Single-Cell RNA-Seq Profiling Analysis. Available online: https://rdrr.io/github/minzheguo/SINCERA/ (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Chen, H.; Lau, M.C.; Wong, M.T.; Newell, E.W.; Poidinger, M. Cytofkit: A Bioconductor Package for an Integrated Mass Cytometry Data Analysis Pipeline. PLoS Comput. Biol 2016, 12, e1005112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, E.; Navon, R.; Steinfeld, I.; Lipson, D.; Yakhini, Z. GOrilla: A tool for discovery and visualization of enriched GO terms in ranked gene lists. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, E.; Lipson, D.; Yogev, S.; Yakhini, Z.; Fraenkel, E. Discovering Motifs in Ranked Lists of DNA Sequences. PLoS Comput. Boil. 2007, 3, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Wang, T.; Deng, K.; Li, B.; Hu, S.; Qin, Q.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, S.; Meyer, C.A.; He, H.H.; et al. High-dimensional genomic data bias correction and data integration using MANCIE. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilworth, D.; Gudavicius, G.; Xu, X.; Boyce, A.K.J.; O’Sullivan, C.; Serpa, J.J.; Bilenky, M.; Petrochenko, E.V.; Borchers, C.H.; Hirst, M.; et al. The prolyl isomerase FKBP25 regulates microtubule polymerization impacting cell cycle progression and genomic stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2459–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLellan, A.D.; Kämpgen, E. Functions of myeloid and lymphoid dendritic cells. Immunol. Lett. 2000, 72, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, D.; Ding, J.; Thotakura, S.; Haskett, S.; Aluri, H.; Kublin, C.; Michel, A.; Clapisson, L.; Mingueneau, M.; Zoukhri, D. RNA-Seq and CyTOF immuno-profiling of regenerating lacrimal glands identifies a novel subset of cells expressing muscle-related proteins. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, M.C.; Craddock, N.; Norton, N.; Williams, H.; Peirce, T.; Moskvina, V.; Nikolov, I.; Hamshere, M.; Carroll, L.; Georgieva, L.; et al. Identification of loci associated with schizophrenia by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, A.C.; Whitfield, J.B.; Martin, N.G.; Pergadia, M.L.; Goate, A.M.; Lind, P.A.; McEvoy, B.P.; Schrage, A.J.; Grant, J.D.; Chou, Y.-L.; et al. A quantitative-trait genome-wide association study of alcoholism risk in the community: Findings and implications. Boil. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Lei, Q.-Y.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo–YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An updated version. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Huang, L.; Niu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, H.; Tao, W.; et al. Mst1 positively regulates B-cell receptor signaling via CD19 transcriptional levels. Blood Adv. 2016, 1, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdollahpour, H.; Appaswamy, G.; Kotlarz, D.; Diestelhorst, J.; Beier, R.; Schäffer, A.A.; Gertz, E.M.; Schambach, A.; Kreipe, H.H.; Pfeifer, D.; et al. The phenotype of human STK4 deficiency. Blood 2012, 119, 3450–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, I.P.M.; Alam, N.A.; Rowan, A.J.; Barclay, E.; Jaeger, E.E.; Kelsell, D.; Leigh, I.; Gorman, P.; Lamlum, H.; Rahman, S.; et al. Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.J.; De Cubas, A.A.; Smith, C.C.; Lang, M.; Gibb, E.A.; Bottaro, D.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Haake, S.; Hakimi, A.A.; Henske, E.P.; et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Linehan, W.M.; Spellman, P.T.; Ricketts, C.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Fei, S.S.; Davis, C.; Wheeler, D.A.; Murray, B.A.; Schmidt, L.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Papillary Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Category Identification and Assignment Tool. R package version 1.1.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SCINA (accessed on 26 December 2018).
- Zhang, Z. SCINA: Automatic Cell Type Detection and Assignment for Single Cell RNA-Seq (ScRNA-seq) and Cytof/FACS Data. Available online: https://github.com/jcao89757/SCINA (accessed on 26 December 2018).
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T. SCINA: Automatic Cell Type Detection and Assignment for Single Cell RNA-Seq (ScRNA-seq) and Cytof/FACS Data. Available online: http://lce.biohpc.swmed.edu/scina/ (accessed on 21 December 2018).





| SCINA-predicted Tumor Subtypes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromophobe | Clear Cell | FHD | Normal | Papillary | Unknown | Sum | ||
| Pathologic review | Chromophobe | 44 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 45 |
| Clear cell | 16 | 492 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 528 | |
| FHD | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | |
| Normal | 0 | 1 | 1 | 156 | 2 | 1 | 161 | |
| Papillary | 3 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 278 | 23 | 323 | |
| Sum | 63 | 501 | 20 | 163 | 287 | 34 | 1068 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Luo, D.; Zhong, X.; Choi, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Mahrt, E.; Guo, W.; Stawiski, E.W.; Modrusan, Z.; et al. SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Subtyping Algorithm of Single Cells and Bulk Samples . Genes 2019, 10, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070531
Zhang Z, Luo D, Zhong X, Choi JH, Ma Y, Wang S, Mahrt E, Guo W, Stawiski EW, Modrusan Z, et al. SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Subtyping Algorithm of Single Cells and Bulk Samples . Genes. 2019; 10(7):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070531
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ze, Danni Luo, Xue Zhong, Jin Huk Choi, Yuanqing Ma, Stacy Wang, Elena Mahrt, Wei Guo, Eric W Stawiski, Zora Modrusan, and et al. 2019. "SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Subtyping Algorithm of Single Cells and Bulk Samples " Genes 10, no. 7: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070531
APA StyleZhang, Z., Luo, D., Zhong, X., Choi, J. H., Ma, Y., Wang, S., Mahrt, E., Guo, W., Stawiski, E. W., Modrusan, Z., Seshagiri, S., Kapur, P., Hon, G. C., Brugarolas, J., & Wang, T. (2019). SCINA: A Semi-Supervised Subtyping Algorithm of Single Cells and Bulk Samples . Genes, 10(7), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070531





