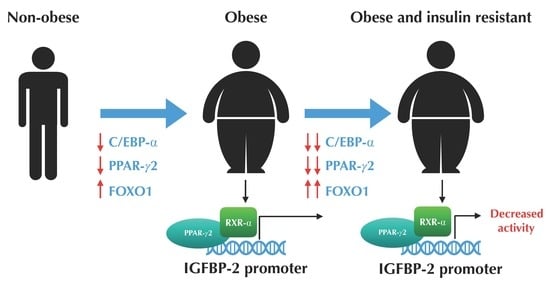
Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP-? and PPAR-?2 Genes and Their Association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Designs and Participants
2.2. Analytical Methods and Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and qPCR
2.4. Protein Isolation, Specific Detection and Quantification
2.5. PPAR-γ2 Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for PPAR-γ2
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristic Data of the Participants
3.2. The Expression Profile of C/EBP-α and FOXO1 are Altered in VAT from Morbidly Obese Individuals and Associated with Insulin Resistance
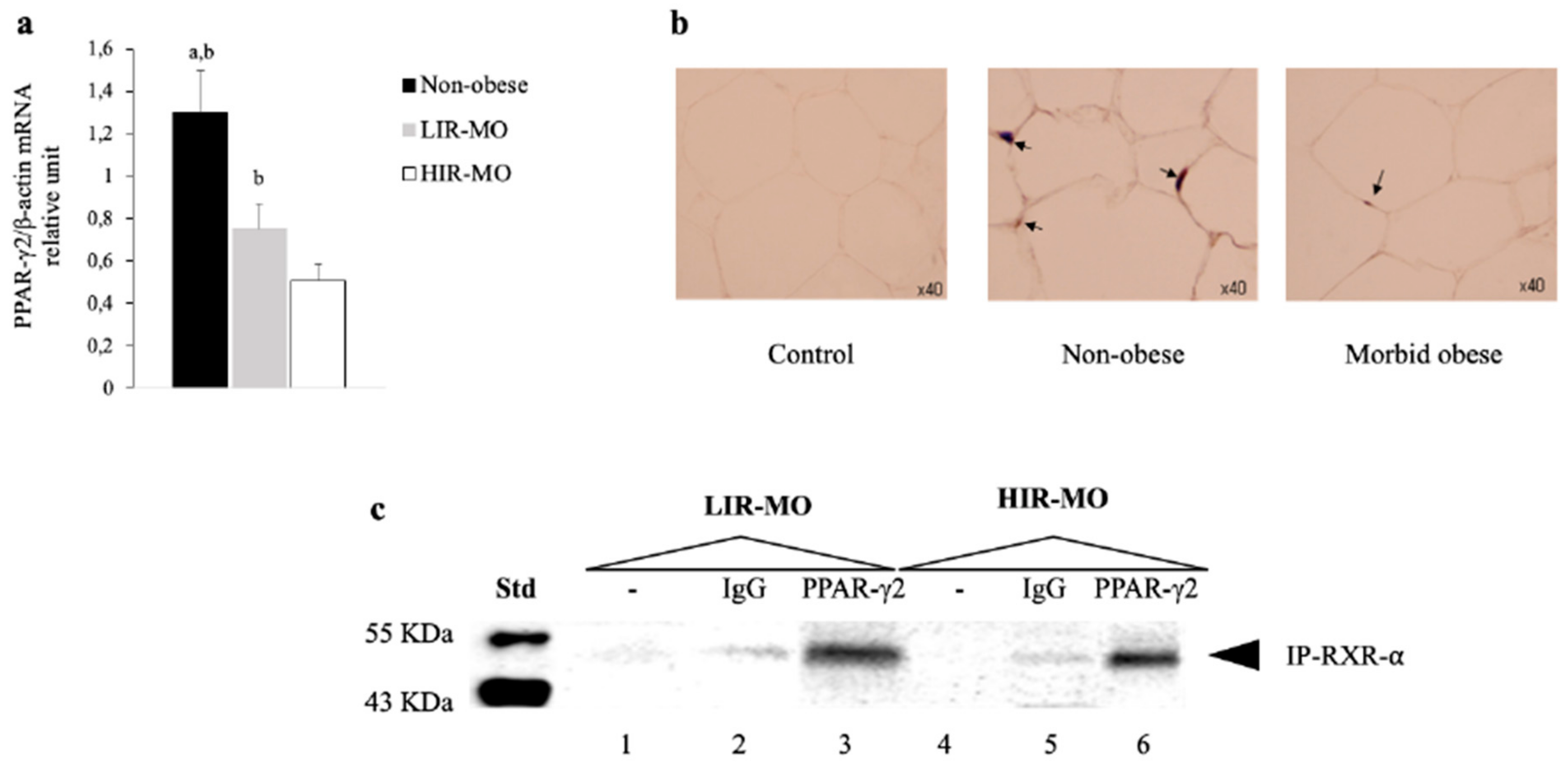
3.3. The Expression of PPAR-γ2 is Decreased and Related to Insulin Resistance in VAT from Morbidly Obese Individuals
3.4. PPAR-γ2 Activity is Reduced in VAT from Morbidly Obese Individuals and Associated with Insulin Resistance
3.5. PPAR-γ2–RXR-α Physically Interact with the IGFBP-2 Promoter through the Functional PPRE Domain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight: Fact Sheet; WHO Media Centre: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Andolfi, C.; Fisichella, P.M. Epidemiology of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2018, 28, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, T.; Mullins, R.; Kapogiannis, D. Insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Peters, S.A.; Woodward, M.; Mejia Arango, S.; Batty, G.D.; Beckett, N.; Beiser, A.; Borenstein, A.R.; Crane, P.K.; Haan, M.; et al. Type 2diabetes as a risk factor for dementia in women compared with men: A pooled analysis of 2.3 million people comprising more than 100,000 cases of dementia. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, S.R. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Santos, I.; Garcia-Serrano, S.; Boughanem, H.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Tinahones, F.J.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. The Antagonist Effect of Arachidonic Acid on GLUT4 Gene Expression by Nuclear Receptor Type II Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Rosen, E.D.; Brun, R.; Hauser, S.; Adelmant, G.; Troy, A.E.; McKeon, C.; Darlington, G.J.; Spiegelman, B.M. Cross-regulation of C/EBPα and PPARγ controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Puig, A.; Jimenez-Liñan, M.; Lowell, B.B.; Hamann, A.; Hu, E.; Spiegelman, B.; Flier, J.S.; Moller, D.E. Regulation of PPAR γ gene expression by nutrition and obesity in rodents. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Sarraf, P.; Troy, A.E.; Bradwin, G.; Moore, K.; Milstone, D.S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Mortensen, R.M. PPARγ is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugii, S.; Olson, P.; Sears, D.D.; Saberi, M.; Atkins, A.R.; Barish, G.D.; Hong, S.H.; Castro, G.L.; Yin, Y.Q.; Nelson, M.C.; et al. PPAR activation in adipocytes is sufficient for systemic insulin sensitization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22504–22509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlington, G.J.; Ross, S.E.; MacDougald, O.A. The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30057–30060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytag, S.O.; Paielli, D.L.; Gilbert, J.D. Ectopic expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α promotes the adipogenic program in a variety of mouse fibroblastic cells. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Biggs, W.H.; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The forkhead transcription factor Fox01 regulates adipocyte differentiation. Dev. Cell. 2003, 4, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, K.; Sakamoto, K. Forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 is essential for adipocyte differentiation. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2009, 45, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, S.R. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1: A possible link between obesity and insulin resistance. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armoni, M.; Harel, C.; Karni, S.; Chen, H.; Bar-Yoseph, F.; Ver, M.; Quon, M.; Karnieli, E. FOXO1 represses peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ1 and -γ2 gene promoters in primary adipocytes: A novel paradigm to increase insulin sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, K.; Chen, Y.R.; Kojima, N.; Ogata, K.; Fukamizu, A.; Miyajima, A. Foxo1 links insulin signaling to C/EBPα and regulates gluconeogenesis during liver development. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3607–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.M.; Oh, Y.; Gargosky, S.E.; Gucev, Z.; Matsumoto, T.; Hwa, V.; Ng, L.; Simpson, D.M.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory dynamics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boney, C.M.; Moats-Staats, B.M.; Stiles, A.D.; D’ercole, A.J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins during adipogenesis. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T.; Shah, A.M.; Ezzat, V.A.; Miell, J.R.; Modo, M.; Williams, S.C.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. IGF-binding protein-2 protects against the development of obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughanem, H.; Cabrera-Mulero, A.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) family and its role in obesity and cancer. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, A.H.; Kaushal, K.; Siddals, K.W.; Rudenski, A.S.; Anderson, S.G.; Gibson, J.M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) is a marker for the metabolic syndrome. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2006, 114, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Picard, F. Modulation of IGFBP2 mRNA expression in white adipose tissue upon aging and obesity. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Vendrell, J.; Chacon, M.R.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; García-Fuentes, E.; Macias-González, M. The retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor γ1 (RORγ1): A novel player determinant of insulin sensitivity in morbid obesity. Obesity 2012, 20, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Santos, I.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Lara, M.F.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.C.; Tinahones, F.J.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. IGFBP-3 Interacts with the Vitamin D Receptor in Insulin Signaling Associated with Obesity in Visceral Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinahones, F.J.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Macias-Gonzalez, M.; Ceperuelo, V.; Gluckmann, E.; Rivas-Marin, J.; Vendrell, J.; García-Fuentes, E. Obesity and insulin resistance-related changes in the expression of lipogenic and lipolytic genes in morbidly obese subjects. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Roca-Rodríguez Mdel, M.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Vendrell, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; García-Fuentes, E.; Tinahones, F.J. CCNG2 and CDK4 is associated with insulin resistance in adipose tissue. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2014, 10, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIas-Gonzalez, M.; Moreno-Santos, I.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Garcia-Fuentes, E. PPARγ2 protects against obesity by means of a mechanism that mediates insulin resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Martínez, G.; Esteva, I.; de Adana, S.R.; Catalá, M.; Merelo, M.J.; Tinahones, F.; Gómez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Cuesta, A.L.; Cardona, F.; Soriguer, F. Patterns of insulin resistance in the general population of southeast Spain. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 65, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Serrano, S.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; García-Almeida, J.M.; García-Arnés, J.; Rivas-Marín, J.; Gallego-Perales, J.L.; García-Escobar, E.; Rojo-Martinez, G.; et al. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 is associated with insulin resistance in morbidly obese subjects. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Birerdinc, A.; Hossain, N.; Afendy, A.; Chandhoke, V.; Younossi, Z.; Baranova, A. Validation of endogenous reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis of human visceral adipose samples. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschke, K.; Fishbein, L.; Dietrich, A.; Klöting, N.; Tönjes, A.; Oberbach, A.; Fasshauer, M.; Jenkner, J.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Gene expression of PPARγ and PGC-1α in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues is related to insulin resistance markers and mediates beneficial effects of physical training. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, L.E.; Orho-Melander, M.; William-Olsson, L.; Sjöholm, K.; Sjöström, L.; Groop, L.; Carlsson, B.; Carlsson, L.M.; Olsson, B. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) in adipose tissue regulates genes in lipid and glucose metabolism and a genetic variation in C/EBPα is associated with serum levels of triglycerides. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4880–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Inoue, J.; Lambert, G.; Yim, S.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. Disruption of hepatic C/EBPα results in impaired glucose tolerance and age-dependent hepatosteatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44740–44748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusler, R.A.; Hartil, K.; Vaitheesvaran, B.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Knight, C.M.; Cook, J.R.; Kammoun, H.L.; Febbraio, M.A.; Gutierrez-Juarez, R.; Kurland, I.J.; et al. Integrated control of hepatic lipogenesis versus glucose production requires FoxO transcription factors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T. The role of FOXO1 in β-cell failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.Q.; Imamura, T.; Sonoda, N.; Sears, D.D.; Patsouris, D.; Kim, J.J.; Olefsky, J.M. FOXO1 transrepresses peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ transactivation, coordinating an insulin-induced feed-forward response in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, P.; Otto, T.C.; Adi, S.; Lane, M.D. Convergence of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ and Foxo1 Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45485–45491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgino, F.; Leonardini, A.; Laviola, L.; Perrini, S.; Natalicchio, A. Cross-Talk between PPARγ and insulin signaling and modulation of Insulin Sensitivity. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 818945. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Myers, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Fenyk-Melody, J.; Wu, M.; Ventre, J.; Doebber, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, T.M.; Lambert, M.H.; Kliewer, S.A. Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor γ and Metabolic Disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 341–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, S.W.; Harcourt, B.E.; Kao, K.T.; Alexander, E.J.; Russo, V.C.; Werther, G.A.; Sabin, M.A. Serum IGFBP-2 levels are associated with reduced insulin sensitivity in obese children. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.; Li, Z.; Lemieux, I.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Poirier, P.; Deshaies, Y.; Després, J.P.; Picard, F. Circulating IGFBP-2 levels are incrementally linked to correlates of the metabolic syndrome and independently associated with VLDL triglycerides. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedbacker, K.; Birsoy, K.; Wysocki, R.W.; Asilmaz, E.; Ahima, R.S.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M. Antidiabetic Effects of IGFBP2, a Leptin-Regulated Gene. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, M.; Kang, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Bae, J.H.; Song, D.K.; Im, S.S. Recent Insights into Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 Transcriptional Regulation. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 32, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variables | Non-obese | LIR-MO | HIR-MO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 15 (8/7) | 11 (5/6) | 12 (5/7) |
| Age (years) | 47.0 ± 15.6 | 45.6 ± 11.7 | 37.8 ± 9.6 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.2 ± 11.8 a,b | 150.0 ± 26.9 | 156.2 ± 18.7 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 83.3 ± 10.5 a,b | 141.0 ± 16.3 | 143.7 ± 20.2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 ± 2.45 a,b | 56.5 ± 7.1 | 55.4 ± 3.9 |
| Insulin (µIU/mL) | 9.2 ± 3.9 a,b | 14.1 ± 4.0 c | 44.5 ± 7.8 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 84.6 ± 14.7 b | 93.0 ± 10.1 c | 102.3 ± 10.9 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.99 ± 0.09 a,b | 3.27 ± 0.94 c | 11.28 ± 2.43 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 193.2 ± 44.0 | 204.5 ± 39.8 | 200.4 ± 23.5 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 90.3 ± 50.4 | 111.3 ± 35.2 | 136.4 ± 91.2 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.5 ± 17.2 | 46.8 ± 14.8 | 42.2 ± 17.9 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 119.6 ± 37.2 | 135.4 ± 29.9 | 130,9 ± 44.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boughanem, H.; Cabrera-Mulero, A.; Millán-Gómez, M.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Macías-González, M. Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP-? and PPAR-?2 Genes and Their Association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Genes 2019, 10, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090706
Boughanem H, Cabrera-Mulero A, Millán-Gómez M, Garrido-Sánchez L, Cardona F, Tinahones FJ, Moreno-Santos I, Macías-González M. Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP-? and PPAR-?2 Genes and Their Association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Genes. 2019; 10(9):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090706
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoughanem, Hatim, Amanda Cabrera-Mulero, Mercedes Millán-Gómez, Lourdes Garrido-Sánchez, Fernando Cardona, Francisco José Tinahones, Inmaculada Moreno-Santos, and Manuel Macías-González. 2019. "Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP-? and PPAR-?2 Genes and Their Association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance" Genes 10, no. 9: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090706
APA StyleBoughanem, H., Cabrera-Mulero, A., Millán-Gómez, M., Garrido-Sánchez, L., Cardona, F., Tinahones, F. J., Moreno-Santos, I., & Macías-González, M. (2019). Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP-? and PPAR-?2 Genes and Their Association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Genes, 10(9), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090706