Genetic-Based Hypertension Subtype Identification Using Informative SNPs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
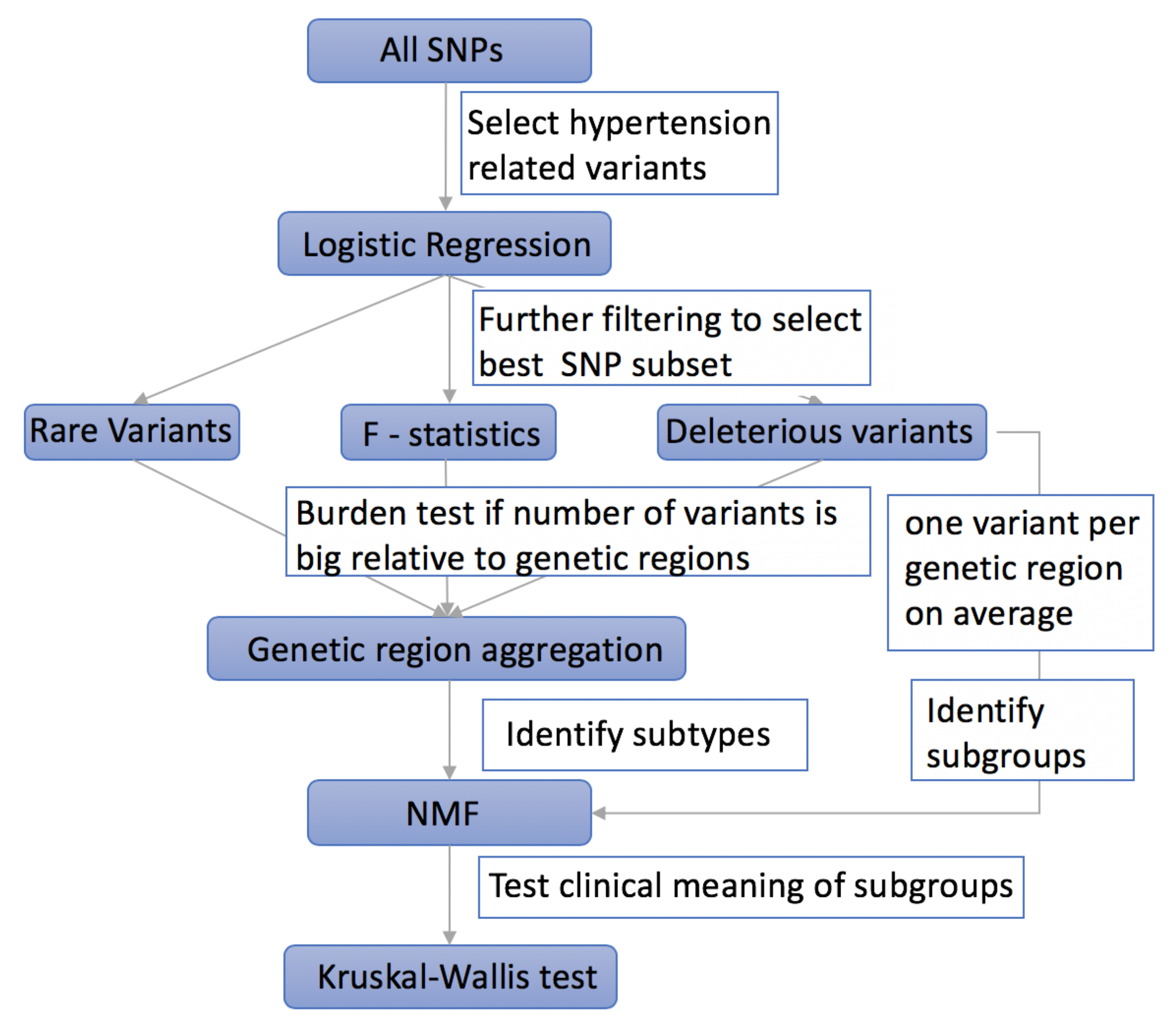
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Using Logistic Regression to Filter Hypertension Related Variants
2.2. Using F-Statistics to Rank the Selected Variants
2.3. Taking into Account the Impact of Rare Variants on Complex Diseases
2.4. Aggregating Variants within the Same Genetic Region to Increase Power
2.5. Selecting Deleterious Variants
2.6. Using NMF to Cluster Hypertensive Patients into Subgroups
2.7. Using Kruskal–Wallis Test to Evaluate the Efficiency of Different Methods
3. Results
3.1. Population of Study
3.2. Comparisons of Clustering Results for Different Methods
3.3. Summary
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farasat, S.M.; Morrell, C.H.; Scuteri, A.; Ting, C.T.; Yin, C.P.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Chen, C.-H.; Lakatta, E.G.; Najjar, S.S. Do hypertensive individuals have enlarged aortic root diameters? Insights from studying the various subtypes of hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.A.K.E.E.V.; Sharma, A.K. Prevalence of hypertension and subtypes in an Indian rural population: Clinical and electrocardiographic correlates. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1994, 8, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, L. Effective selection of informative SNPs and classification on the HapMap genotype data. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.C.; Lee, S.; Cai, T.; Li, Y.; Boehnke, M.; Lin, X. Rare-variant association testing for sequencing data with the sequence kernel association test. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunet, J.P.; Tamayo, P.; Golub, T.R.; Mesirov, J.P. Metagenes and molecular pattern discovery using matrix factorization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4164–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Huang, H.; Blackshaw, S.; Liu, J.S.; Cepko, C.; Wong, W.H. Clustering analysis of SAGE data using a Poisson approach. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.J.; Katz, D.H.; Selvaraj, S.; Burke, M.A.; Yancy, C.W.; Gheorghiade, M.; Bonow, R.O.; Huang, C.-C.; Deo, R.C. Phenomapping for novel classification of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 2015, 131, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S. The interpretation of population structure by F-statistics with special regard to systems of mating. Evolution 1965, 19, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, C.P.; Ng, F.L.; Nicholls, H.L.; Gupta, A.; Barnes, M.R.; Munroe, P.B.; Caulfield, M.J. Over 1000 genetic loci influencing blood pressure with multiple systems and tissues implicated. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R151–R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, B.E.; Browning, S.R. A groupwise association test for rare mutations using a weighted sum statistic. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Leal, S.M. Methods for detecting associations with rare variants for common diseases: Application to analysis of sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, A.L.; Kryukov, G.V.; de Bakker, P.I.; Purcell, S.M.; Staples, J.; Wei, L.J.; Sunyaev, S.R. Pooled association tests for rare variants in exon-resequencing studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgenthaler, S.; Thilly, W.G. A strategy to discover genes that carry multi-allelic or mono-allelic risk for common diseases: A cohort allelic sums test (CAST). Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2007, 615, 28–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Leal, S.M. Discovery of rare variants via sequencing: Implications for the design of complex trait association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, F.; Pan, W. A Data-Adaptive Sum Test for Disease Association with Multiple Common or Rare Variants. Hum. Hered. 2010, 70, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.R.; Rao, D.C.; Ellison, R.C.; Arnett, D.K.; Heiss, G.; Oberman, A.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Leppert, M.F.; Province, M.A.; Mockrin, S.C.; et al. NHLBI family blood pressure program: Methodology and recruitment in the HyperGEN network. Ann. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.G.; Selvaraj, S.; Martinez, E.E.; Katz, D.H.; Beussink, L.; Kim, K.-Y.A.; Ping, J.; Rasmussen-Torvik, L.; Goyal, A.; Sha, J.; et al. Archeological Echocardiography: Digitization and Speckle Tracking Analysis of Archival Echocardiograms in the Hyper GEN Study. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.J.; Aistrup, G.L.; Gupta, D.K.; O’Toole, M.J.; Nahhas, A.F.; Schuster, D.; Chirayil, N.; Bassi, N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Beussink, L.; et al. Ultrastructural and cellular basis for the development of abnormal myocardial mechanics during the transition from hypertension to heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 306, H88–H100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraj, S.; Martinez, E.E.; Aguilar, F.G.; Kim, K.Y.A.; Peng, J.; Sha, J.; Irvin, M.R.; Lewis, C.E.; Hunt, S.C.; Arnett, D.K.; et al. Association of central adiposity with adverse cardiac mechanics: Findings from the hypertension genetic epidemiology network study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e004396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraj, S.; Aguilar, F.G.; Martinez, E.E.; Beussink, L.; Kim, K.Y.A.; Peng, J.; Rasmussen-Torvik, L.; Sha, J.; Irvin, M.R.; Gu, C.C.; et al. Association of comorbidity burden with abnormal cardiac mechanics: Findings from the HyperGEN study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sárközy, M.; Zvara, A.; Gyémánt, N.; Fekete, V.; Kocsis, G.; Pipis, J.; Szűcs, G.; Csonka, C.; Puskás, L.G.; Ferdinandy, P.; et al. Metabolic syndrome influences cardiac gene expression pattern at the transcript level in male ZDF rats. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, S.; Wu, C.; Yoshida, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, P.; Wu, F.; Duffen, J.P.; Yao, R.; Jardin, B.; Adham, I.M.; et al. Relaxin Family Member Insulin-Like Peptide 6 Ameliorates Cardiac Fibrosis and Prevents Cardiac Remodeling in Murine Heart Failure Models. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartels, E.; Nielsen, J.; Hellgren, L.; Ploug, T.; Nielsen, L. Cardiac expression of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein is increased in obesity and serves to attenuate cardiac triglyceride accumulation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.; Murphy, S.; Kishore, R.; Vaughan, D. Global gene expression profiling in PAI-1 knockout murine heart and kidney: Molecular basis of cardiac-selective fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, G.; O’Seaghdha, C.; Hwang, S.; Meigs, J.; Fox, C. The association of a single-nucleotide polymorphism in CUBN and the risk of albuminuria and cardiovascular disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Yan, M.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Chen, C. Association between TNIP1, MPHOSPH6 and ZNF208 genetic polymorphisms and the coronary artery disease risk in Chinese Han population. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, E.; Heimiller, J.; Leinwand, L.A. Distinct cardiac transcriptional profiles defining pregnancy and exercise. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J.; Caballero, R.; Gómez, R.; Valenzuela, C.; Delpón, E. Pharmacology of cardiac potassium channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Cui, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Tian, X.; Jin, C.; Dong, Q.; Huang, P.; Xu, J. Quantitative proteomics analysis of ischemia/reperfusion injury-modulated proteins in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells and the protective role of Tongxinluo. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.; Larson, M.; Tanriverdi, K.; O’Donnell, C.; Morin, K.; Hakanson, A.; Vasan, R.S.; Johnson, A.D.; Iafrati, M.D.; Benjamin, E.J. The relation of platelet and leukocyte inflammatory transcripts to body mass index in the Framingham heart study. Circulation 2010, 122, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glessner, J.; Li, J.; Desai, A.; Palmer, M.; Kim, D.; Lucas, A.; Chang, X.; Connolly, J.J.; Almoguera, B.; Harley, J.B.; et al. CNV Association of Diverse Clinical Phenotypes from eMERGE reveals novel disease biology underlying cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 298, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| SNP Array | ANNOVAR Gene-Based Annotation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AA | refGene | knownGene | ensGene |
| nonsynonymous SNP | 10,554 | 11,073 | 11,404 |
| stopgain | 90 | 110 | 117 |
| stoploss | 12 | 17 | 17 |
| synonymous SNP | 17,802 | 18,231 | 18,511 |
| unknown | 553 | 10 | 9 |
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| elateral | Lateral e’ velocity | Left ventricular early diastolic relaxation velocity, measured at the lateral mitral annnulus in the apical 4-chamber view |
| eseptal | Septal e’ velocity | Left ventricular early diastolic relaxation velocity, measured at the septal mitral annnulus in the apical 4-chamber view |
| gcs | Global circumferential strain | Left ventricular circumferential strain, measured in the parasternal short axis view |
| gls | Global longitudinal strain | Left ventricular longitudinal strain, measured in the apical 4-chamber view |
| grs | Global radial strain | Left ventricular radial strain, measured in the parasternal short axis view |
| sr_a | strain rate-atrial | Left ventricular late (atrial) diastolic strain rate, measured in the apical 4-chamber view |
| sr_e | strain rate-early diastlic | Left ventricular early diastolic strain rate, measured in the apical 4-chamber view |
| sr_s | strain rate-early systolic | Left ventricular systolic strain rate, measured in the apical 4-chamber view |
| sseptal | Septal s’ velocity | Left ventricular systolic longitudinal velocity, measured at the septal mitral annulus in the apical 4-chamber view |
| slateral | Lateral s’ velocity | Left ventricular systolic longitudinal velocity, measured at the lateral mitral annulus in the apical 4-chamber view |
| Methods p-Value (AA/Caucasian) | Phenotypic Variables | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elateral | Eseptal | gcs | gls | grs | sr_a | sr_e | sr_s | Sseptal | |
| Logistic (0.05) + F + Rare + geneaggr | 0.11 />0.1 | 0.07 />0.1 | 0.97 />0.1 | 0.02 />0.1 | 0.80 />0.1 | 0.07 />0.1 | 0.06 />0.1 | 0.01 />0.1 | 0.00 />0.1 |
| Logistic (0.05) + F + All + geneaggr | 0.51 /0.04 | 0.32 /0.00 | 0.05 /0.03 | 0.07 /0.01 | 0.18 /0.28 | 0.04 /0.44 | 0.11 /0.05 | 0.08 /0.18 | 0.16 /0.02 |
| Logistic (0.05) + del + geneaggr | 0.97 /0.04 | 0.68 /0.01 | 0.73 /0.65 | 0.01 /0.03 | 0.76 /0.39 | 0.19 /0.02 | 0.62 /0.10 | 0.01 /0.08 | 0.11 /0.09 |
| Logistic (0.05) + del | 0.76 /0.05 | 0.30 /0.01 | 0.42 /0.65 | 0.02 /0.03 | 0.74 /0.39 | 0.48 /0.02 | 0.64 /0.10 | 0.01 /0.08 | 0.29 /0.09 |
| Logistic (0.1) + del + geneaggr | 0.49 /0.07 | 0.11 /0.02 | 0.97 /0.63 | 0.16 /0.03 | 0.72 /0.37 | 0.13 /0.01 | 0.29 /0.14 | 0.30 /0.09 | 0.39 /0.11 |
| Logistic (0.1) + del | 0.77 /0.03 | 0.82 /0.02 | 0.89 /0.73 | 0.02 /0.02 | 0.65 /0.32 | 0.21 /0.02 | 0.45 /0.08 | 0.02 /0.06 | 0.15 /0.06 |
| Methods/Number of Significant Phenotypic Variables | Number of Significant Phenotypic Variables (Number of Variants; Number of Genetic Regions If with Geneagg) | Number of Hypertensive Patients in Each Cluster | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African American | Caucasian | African American | Caucasian | |
| Logistic (0.05) + F + Rare + geneaggr | 6 (472) | 0 | ||
| Logistic (0.05) + F + All + geneaggr | 4 (12,555) | 6 (675) | 430/145 | 583/29 |
| Logistic (0.05) + del + geneaggr | 2 (370; 339) | 6 (217; 213) | 318/257 | 485/127 |
| Logistic (0.05) + del | 2 (370) | 6 (217) | 445/130 | 485/127 |
| Logistic (0.1) + del + geneaggr | 0 (735, 643) | 6 (467, 379) | 398/177 | 486/126 |
| Logistic (0.1) + del | 2 (735) | 7 (467) | 273/302 | 484/128 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Jiang, H.; Shah, S.J.; Arnett, D.; Irvin, M.R.; Luo, Y. Genetic-Based Hypertension Subtype Identification Using Informative SNPs. Genes 2020, 11, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111265
Ma Y, Jiang H, Shah SJ, Arnett D, Irvin MR, Luo Y. Genetic-Based Hypertension Subtype Identification Using Informative SNPs. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111265
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuanjing, Hongmei Jiang, Sanjiv J Shah, Donna Arnett, Marguerite R Irvin, and Yuan Luo. 2020. "Genetic-Based Hypertension Subtype Identification Using Informative SNPs" Genes 11, no. 11: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111265
APA StyleMa, Y., Jiang, H., Shah, S. J., Arnett, D., Irvin, M. R., & Luo, Y. (2020). Genetic-Based Hypertension Subtype Identification Using Informative SNPs. Genes, 11(11), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111265





