Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Tomato GIF Genes
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3. Identification of CAREs in the Promoter
2.4. Plant Materials and Hormone Treatment
2.5. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.6. Subcellular Localization
2.7. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
2.8. Expression Profiles and the Correlation Coefficients Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of GIF Genes in Tomatoes
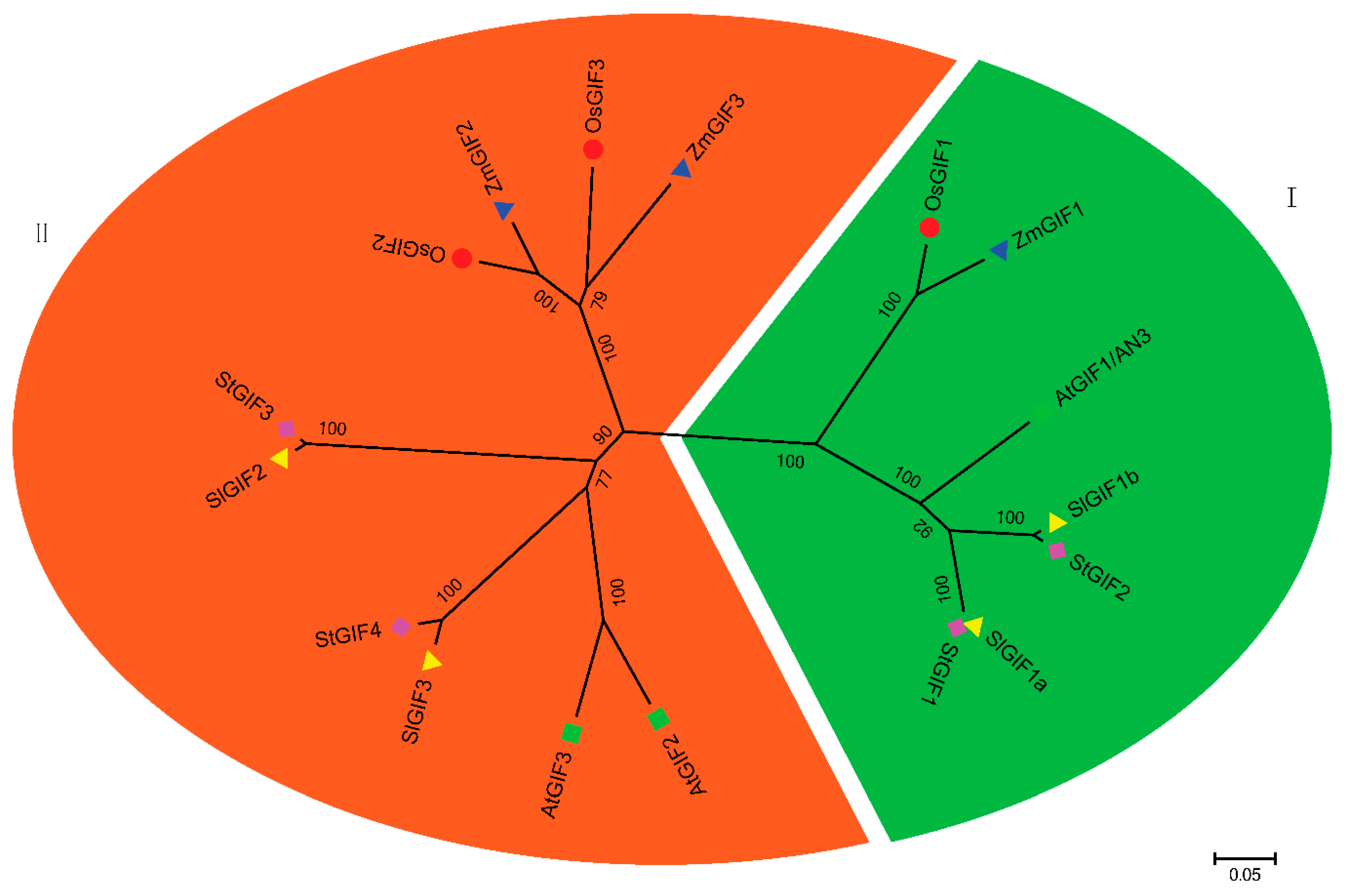
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the SlGIF Family Genes
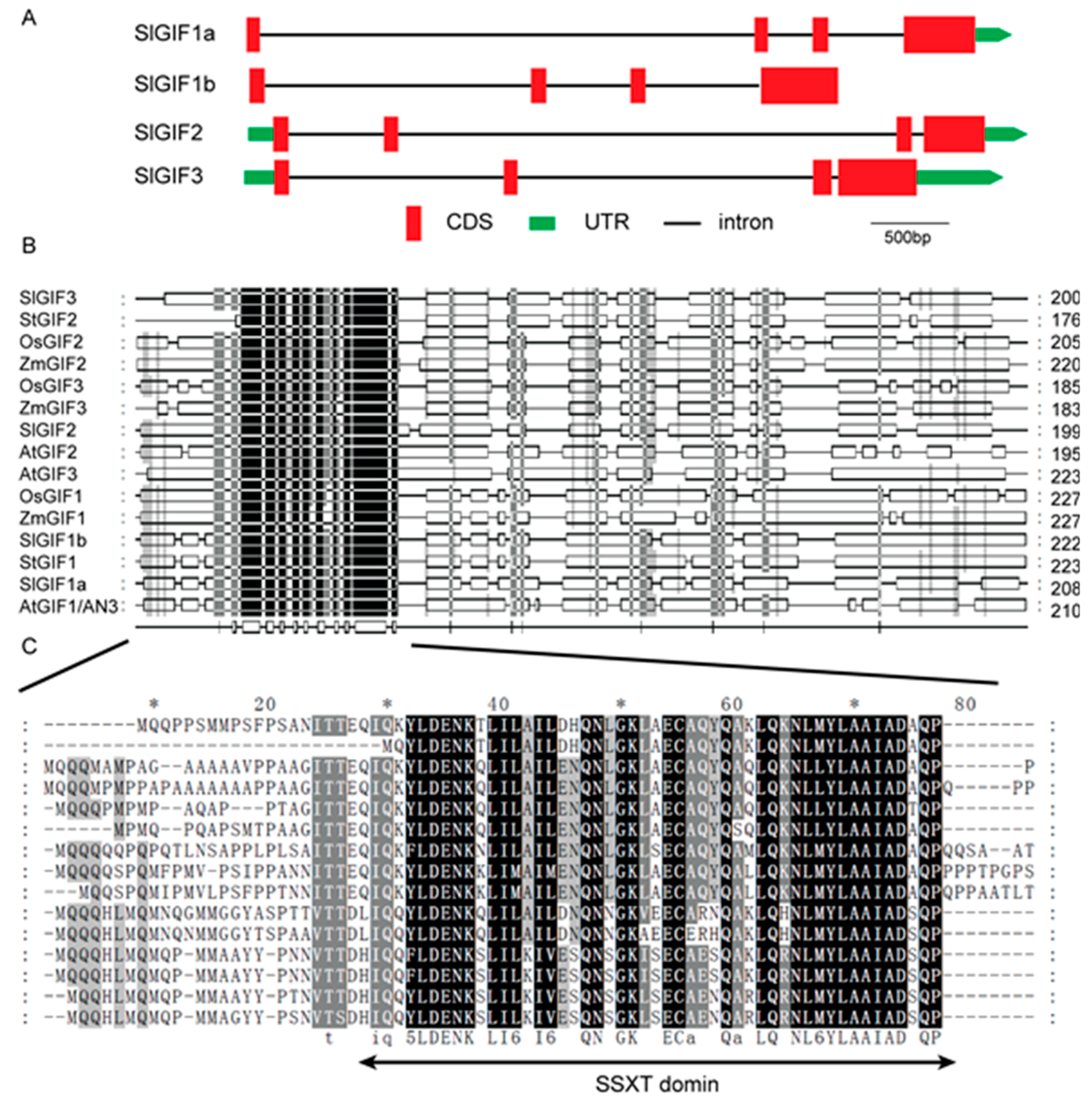
3.3. Gene Structures, Conserved Domains, and CAREs in the Promoters of SlGIF Genes in Tomatoes
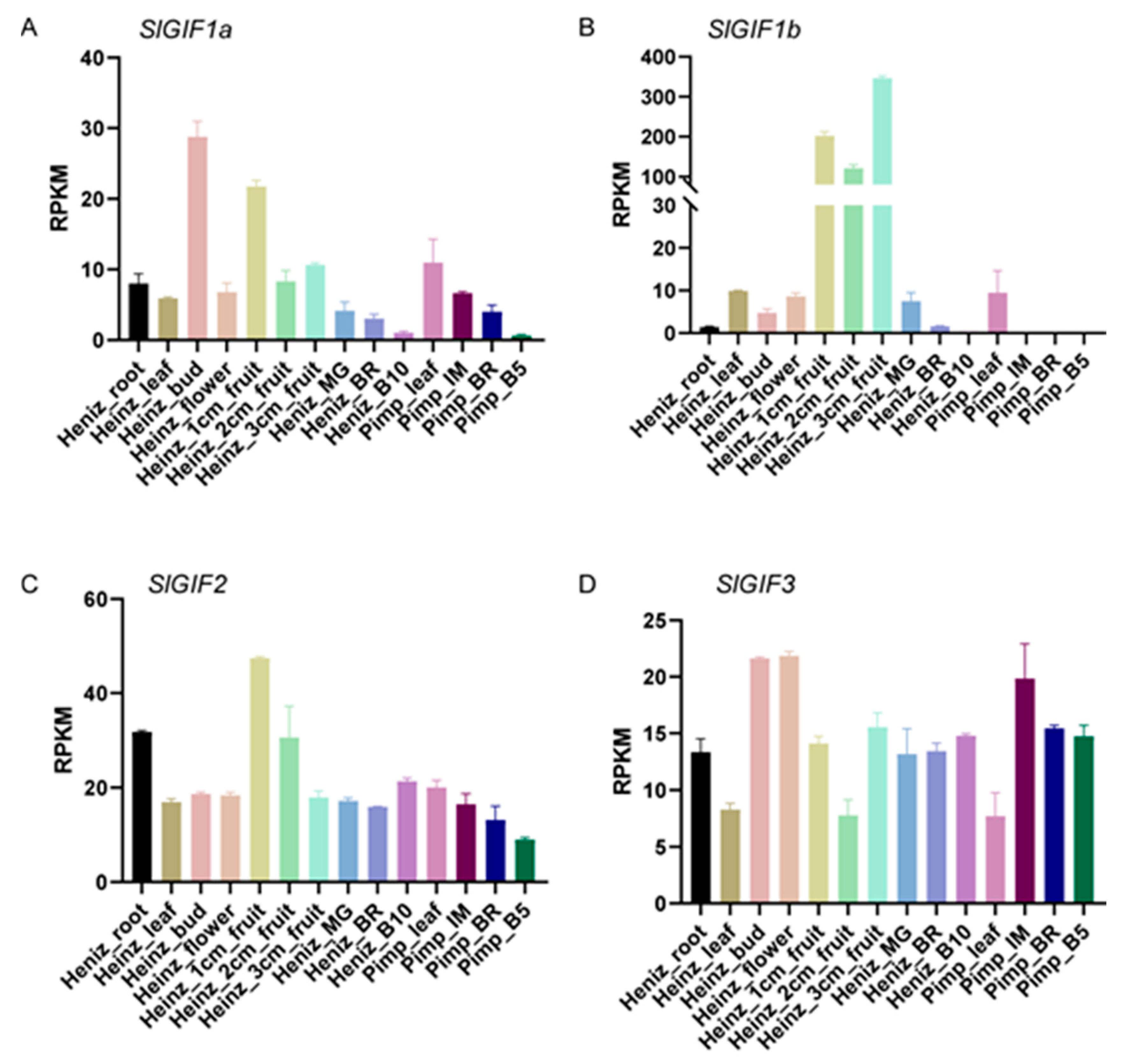
3.4. Expression Patterns of the SlGIFs in Different Tomato Tissues
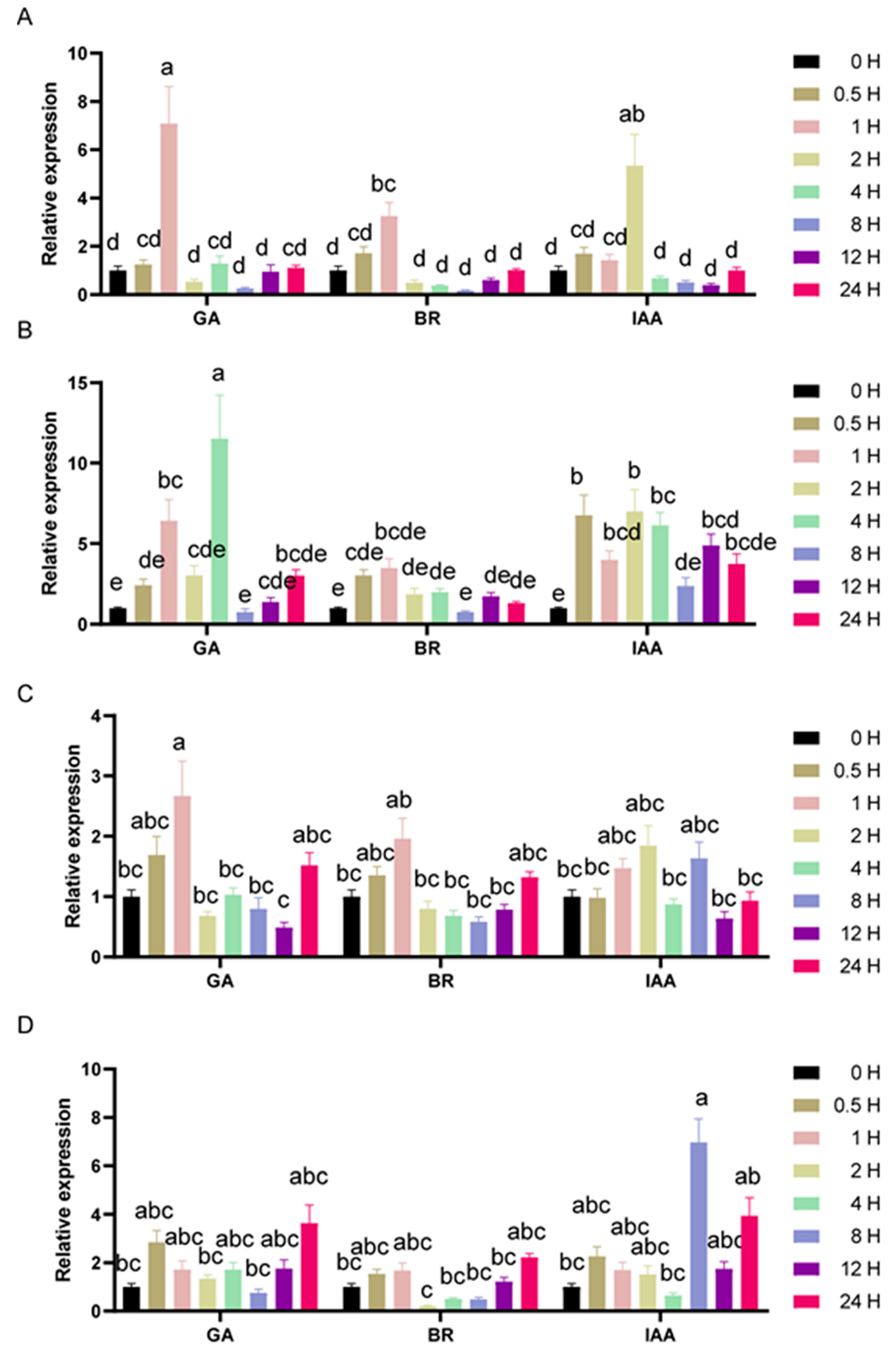
3.5. Expression Profiles of the SlGIF Genes under Phytohormone Treatments
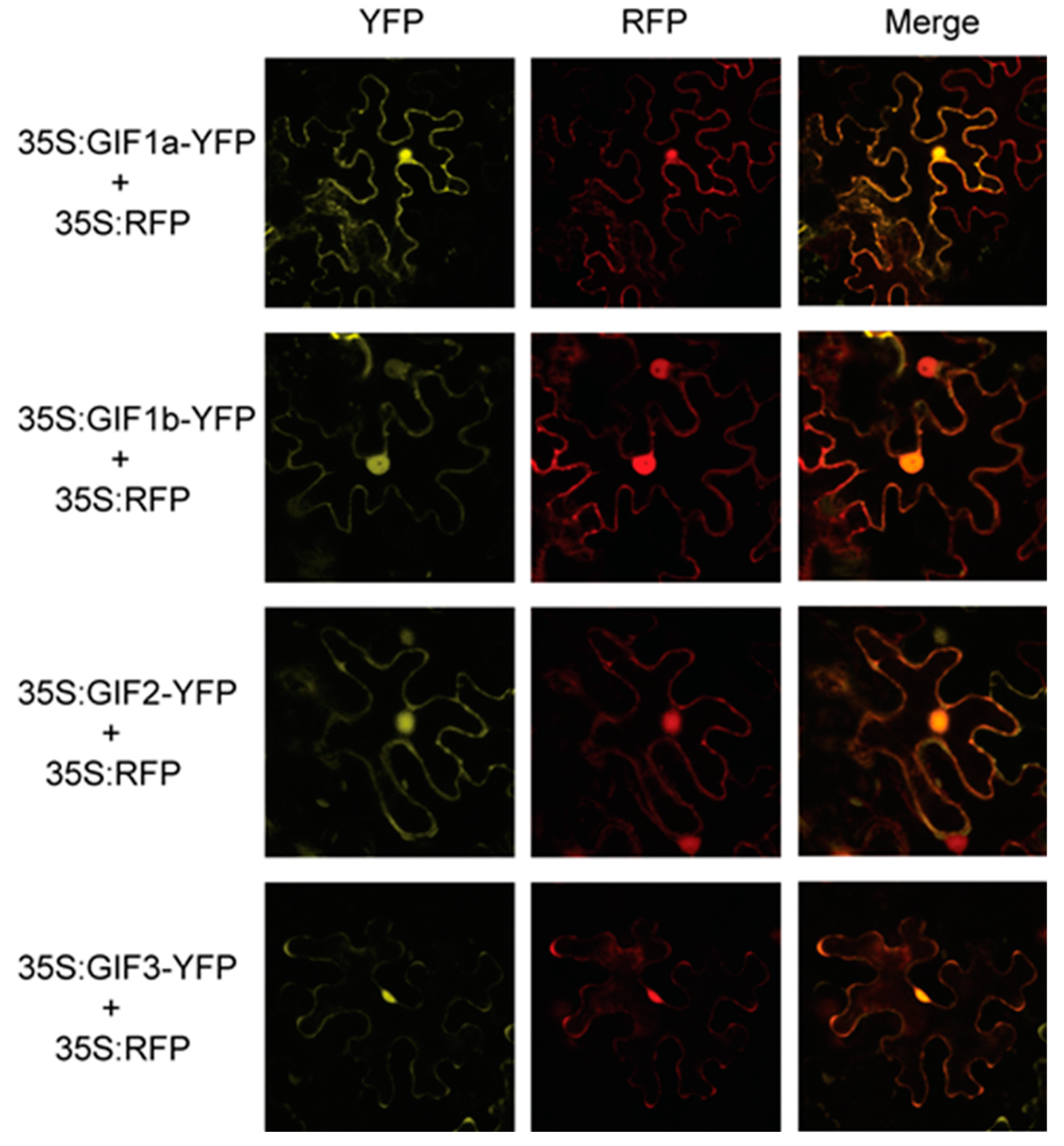
3.6. Subcellular Localization of the SlGIF Proteins
3.7. Interactions between the SlGIF Proteins and the SlGRF Proteins
3.8. Relative Expression between SlGIF and SlGRF Genes and SlGIF Protein
4. Discussion
4.1. Phylogenetic Relationships and Structures of the SlGIF Gene Families
4.2. Different Expression Patterns Shown by SlGIFs
4.3. Multifunctions in Tomatoes Played by the SlGIF Gene Family
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levine, M.; Tjian, R. Transcription regulation and animal diversity. Nature 2003, 424, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Dommel, M.; Mou, Z. Abscisic acid promotes proteasome-mediated degradation of the transcription coactivator NPR1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2016, 86, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ouyang, X.H.; Yang, P.Y.; Lau, O.S.; Li, G.; Li, J.G.; Chen, H.D.; Deng, X.W. Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 Positively Mediate Induction of COP1 Transcription in Response to Photomorphogenic UV-B Light. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4590–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.S. Transcription coactivator Arabidopsis ANGUSTIFOLIA3 modulates anthocyanin accumulation and light-induced root elongation through transrepression of Constitutive Photomorphogenic1. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoel, S.H.; Mou, Z.; Tada, Y.; Spivey, N.W.; Genschik, P.; Dong, X. Proteasome-mediated turnover of the transcription coactivator NPR1 plays dual roles in regulating plant immunity. Cell 2009, 137, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoe Kim, J.; Tsukaya, H. Regulation of plant growth and development by the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR duo. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6093–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): A Small Transcription Factor Family with Important Functions in Plant Biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukaya, H. Yield increase: GRFs provide the key. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.G.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, B.L.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, H.Q.; Zhu, X.D.; Li, Y.H. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. Whole genome analysis of the OsGRF gene family encoding plant-specific putative transcription activators in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.C.; Gao, F.Y.; Xie, K.L.; Zeng, X.H.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.S.; Ren, Y.; Li, W.B.; Deng, Q.M.; et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, R.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Debernardi, J.M.; Palatnik, J.F.; Casati, P. Repression of Growth Regulating Factors by the MicroRNA396 Inhibits Cell Proliferation by UV-B Radiation in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3570–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13374–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, G.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Molecular Mechanism of microRNA396 Mediating Pistil Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Chong, K. OsmiR396d-Regulated OsGRFs Function in Floral Organogenesis in Rice through Binding to Their Targets OsJMJ706 and OsCR4. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.H.; Wynn, A.N.; Franks, R.G.; Hwang, Y.S.; Lim, J.; Kim, J.H. The Arabidopsis thaliana GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR gene family plays an essential role in control of male and female reproductive development. Dev. Biol. 2014, 386, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.H.; Ko, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Pak, J.-H.; Kim, J.H. The Arabidopsis GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR Gene Family Performs an Overlapping Function in Determining Organ Size as Well as Multiple Developmental Properties. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horiguchi, G.; Kim, G.T.; Tsukaya, H. The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005, 43, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikura, U.; Horiguchi, G.; Ponce, M.R.; Micol, J.L.; Tsukaya, H. Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion mediated by ribosome-related processes in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2009, 59, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawade, K.; Horiguchi, G.; Usami, T.; Hirai, M.Y.; Tsukaya, H. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Signaling Coordinates Proliferation between Clonally Distinct Cells in Leaves. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanei, M.; Horiguchi, G.; Tsukaya, H. Stable establishment of cotyledon identity during embryogenesis in Arabidopsis by ANGUSTIFOLIA3 and HANABA TARANU. Development 2012, 139, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horiguchi, G.; Nakayama, H.; Ishikawa, N.; Kubo, M.; Demura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Tsukaya, H. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Plays Roles in Adaxial/Abaxial Patterning and Growth in Leaf Morphogenesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debernardi, J.M.; Mecchia, M.A.; Vercruyssen, L.; Smaczniak, C.; Kaufmann, K.; Inze, D.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity. Plant J. 2014, 79, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.H.; Wu, K.; Ye, Y.F.; Yu, J.P.; Zhang, J.Q.; Liu, Q.; Hu, M.Y.; Li, H.; Tong, Y.P.; et al. Modulating plant growth-metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture. Nature 2018, 560, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruyssen, L.; Verkest, A.; Gonzalez, N.; Heyndrickx, K.S.; Eeckhout, D.; Han, S.-K.; Jegu, T.; Archacki, R.; Van Leene, J.; Andriankaja, M.; et al. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Binds to SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Complexes to Regulate Transcription during Arabidopsis Leaf Development. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelissen, H.; Eeckhout, D.; Demuynck, K.; Persiau, G.; Walton, A.; van Bel, M.; Vervoort, M.; Candaele, J.; De Block, J.; Aesaert, S.; et al. Dynamic Changes in ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Complex Composition Reveal a Growth Regulatory Mechanism in the Maize Leaf. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, W.; Singh, R.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, M.F.; Lunde, C.; Hake, S.; Zhang, Z.X. GRF-interacting factor1 Regulates Shoot Architecture and Meristem Determinacy in Maize. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercoli, M.F.; Ferela, A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Perrone, A.P.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F. GIF Transcriptional Co-regulators Control Root Meristem Homeostasis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Transcriptional repression of GIF1 by the KIX-PPD-MYC repressor complex controls seed size in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lin, T.; Qin, M.; Peng, M.; Yang, C.; et al. Rewiring of the Fruit Metabolome in Tomato Breeding. Cell 2018, 172, 249–261.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consortium, T.G. The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 2012, 485, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, G.T.; Zhang, J.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Yu, Q.H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; Lun, Y.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.X.; et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.D.; He, Q.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, C.H. The Potato ERF Transcription Factor StERF3 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Phytophthora infestans and Salt Tolerance in Potato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Pozo, N.; Zheng, Y.; Snyder, S.I.; Nicolas, P.; Shinozaki, Y.; Fei, Z.J.; Catala, C.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Rose, J.K.C.; Mueller, L.A. The Tomato Expression Atlas. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2397–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Z.; Xie, Y.B.; Ma, J.Y.; Luo, X.T.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.X.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, S.M.; Huang, S.H.; Wang, S.F.; Cheng, D.D.; Liu, J.W.; Lv, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.F. Enhancing Brassinosteroid Signaling via Overexpression of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) SlBRI1 Improves Major Agronomic Traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.J.; Chen, X.J.; Guo, X.; Yin, L.L.; Ahammed, G.J.; Xu, C.J.; Chen, K.S.; Liu, C.C.; Xia, X.J.; Shi, K.; et al. DWARF overexpression induces alteration in phytohormone homeostasis, development, architecture and carotenoid accumulation in tomato. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Qiao, S.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, X. Brassinosteroid signaling regulates leaf erectness in Oryza sativa via the control of a specific U-type cyclin and cell proliferation. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Che, R.; Tong, H.; Shi, B.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Liu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.H.; Israeli, A.; Ori, N.; Sun, T.P. The Interaction between DELLA and ARF/IAA Mediates Crosstalk between Gibberellin and Auxin Signaling to Control Fruit Initiation in Tomato. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1710–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khatun, K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Park, J.I.; Nath, U.K.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, K.B.; Nou, I.S.; Chung, M.Y. Molecular Characterization and Expression Profiling of Tomato GRF Transcription Factor Family Genes in Response to Abiotic Stresses and Phytohormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.Y.; Wang, J.; Ju, Z.; Liu, Q.Q.; Li, S.; Tian, H.Q.; Fu, D.Q.; Zhu, H.L.; Luo, Y.B.; Zhu, B.Z. Regulations on growth and development in tomato cotyledon, flower and fruit via destruction of miR396 with short tandem target mimic. Plant Sci. 2016, 247, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.T.; Franz, M.; Kazi, F.; Donaldson, S.L.; Morris, Q.; Bader, G.D. Cytoscape Web: An interactive web-based network browser. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2347–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkel, G.R.; Tracy, J.A.; Jalufka, F.L.; Lekven, A.C. CHD8short, a naturally-occurring truncated form of a chromatin remodeler lacking the helicase domain, is a potent transcriptional coregulator. Gene 2018, 641, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulten, H.J.; Bakhashab, S. Meta-Analysis of Microarray Expression Studies on Metformin in Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, W.P.; Guo, Y.Y.; Yang, G.P.; Lai, H.L.; Sun, T.T.; Zhang, Z.W.; Ouyang, L.L.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, L.M.; Li, X.H.; et al. CHD1L promotes EOC cell invasiveness and metastasis via the regulation of METAP2. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frary, A.; Nesbitt, T.C.; Grandillo, S.; Knaap, E.; Cong, B.; Liu, J.; Meller, J.; Elber, R.; Alpert, K.B.; Tanksley, S.D. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 2000, 289, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.P.; Van Eck, J.; Cong, B.; Tanksley, S.D. A new class of regulatory genes underlying the cause of pear-shaped tomato fruit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13302–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Jiang, N.; Schaffner, E.; Stockinger, E.J.; van der Knaap, E. A retrotransposon-mediated gene duplication underlies morphological variation of tomato fruit. Science 2008, 319, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, M.; Zhang, N.; Sauvage, C.; Munos, S.; Blanca, J.; Canizares, J.; Diez, M.J.; Schneider, R.; Mazourek, M.; McClead, J.; et al. A cytochrome P450 regulates a domestication trait in cultivated tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17125–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Clevenger, J.P.; Sun, L.; Visa, S.; Kamiya, Y.; Jikumaru, Y.; Blakeslee, J.; van der Knaap, E. The control of tomato fruit elongation orchestrated by sun, ovate and fs8.1 in a wild relative of tomato. Plant Sci. 2015, 238, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Chakrabarti, M.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ramos, A.; van der Knaap, E. Fruit weight is controlled by Cell Size Regulator encoding a novel protein that is expressed in maturing tomato fruits. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, B.Y.; Keyhaninejad, N.; Rodriguez, G.R.; Kim, H.J.; Chakrabarti, M.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Taitano, N.K.; Gonzalo, M.J.; Diaz, A.; et al. A common genetic mechanism underlies morphological diversity in fruits and other plant organs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.S.; Zeng, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, W.J.; Gao, F.Y.; Cao, Y.; Luo, T.; Yuan, G.Q.; Wu, X.H.; et al. OsGIF1 Positively Regulates the Sizes of Stems, Leaves, and Grains in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Z.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Tang, K.; Tang, D.G.; Datsenka, T.; Cheng, J.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Handa, A.K.; Zhu, J.K. Critical roles of DNA demethylation in the activation of ripening-induced genes and inhibition of ripening-repressed genes in tomato fruit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4511–E4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Gene Name | Gene Loci | Chromosome Location (Strand) | aa | pIs/Mw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlGIF1a | Solyc04g009820.2.1 | SL2.50ch04:3139217-3143959 (+) | 208 | 6.60/22.74 KDa |
| SlGIF1b | Solyc11g006230.1.1 | SL2.50ch11:981174-984561 (−) | 222 | 6.41/23.59 KDa |
| SlGIF2 | Solyc03g082480.2.1 | SL2.50ch03:45948144-45952630 (+) | 199 | 5.85/21.83 KDa |
| SlGIF3 | Solyc10g009280.2.1 | SL2.50ch10:3267235-3271023 (−) | 200 | 6.51/21.74 KDa |
| Cis-Element | Members of GIFs | Functions of Cis-Element |
|---|---|---|
| ABRE | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness |
| ACA-motif | SlGIF3 | part of gapA in (gapA-CMA1) involved with light responsiveness |
| ACE | SlGIF1a, SlGIF2, and SlGIF3 | cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness |
| AE-box | SlGIF3 | part of a module for light response |
| ARE | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction |
| AT1-motif | SlGIF1b | part of a light responsive module |
| ATCT-motif | SlGIF1b | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| AT-rich sequence | SlGIF1b and SlGIF3 | element for maximal elicitor-mediated activation |
| AuxRR-core | SlGIF1a | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Box 4 | SlGIF1a, SlGIF2, and SlGIF3 | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| CAAT-box | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| CAT-box | SlGIF1b and SlGIF2 | cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression |
| CGTCA-motif | SlGIF1a and SlGIF2 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness |
| chs-CMA1a | SlGIF1b and SlGIF2 | part of a light responsive element |
| circadian | SlGIF1a and SlGIF1b | cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control |
| GARE-motif | SlGIF1a and SlGIF2 | gibberellin-responsive element |
| G-box | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| GCN4_motif | SlGIF1b | cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression |
| GT1-motif | SlGIF1a and SlGIF2 | Light-responsive element |
| LAMP-element | SlGIF1a | part of a light-responsive element |
| LAMP-element | SlGIF3 | part of a light-responsive element |
| LTR | SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SlGIF3 | cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| MBS | SlGIF3 | MYB-binding site involved in drought inducibility |
| MRE | SlGIF1a and SlGIF3 | MYB-binding site involved in light responsiveness |
| O2-site | SlGIF1a and SlGIF1b | cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation |
| Sp1 | SlGIF1b | Light-responsive element |
| TATA-box | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | core promoter element around –30 of transcription start |
| TATC-box | SlGIF1a | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| TCA-element | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, SlGIF2, and SiGIF3 | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| TC-rich repeats | SlGIF1a, SlGIF1b, and SlGIF3 | cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| TGA-box | SlGIF2 | part of an auxin-responsive element |
| TGACG-motif | SlGIF1b and SlGIF3 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA responsiveness |
| TGA-element | SlGIF3 | auxin-responsive element |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ai, G.; Zhang, D.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Ahiakpa, J.K.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato. Genes 2020, 11, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121435
Ai G, Zhang D, Huang R, Zhang S, Li W, Ahiakpa JK, Zhang J. Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato. Genes. 2020; 11(12):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121435
Chicago/Turabian StyleAi, Guo, Dedi Zhang, Rong Huang, Shiqi Zhang, Wangfang Li, John K. Ahiakpa, and Junhong Zhang. 2020. "Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato" Genes 11, no. 12: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121435
APA StyleAi, G., Zhang, D., Huang, R., Zhang, S., Li, W., Ahiakpa, J. K., & Zhang, J. (2020). Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato. Genes, 11(12), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121435




