The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of TtAP2/ERF Genes in the Genome of Durum Wheat
2.2. Chromosomal Mapping, Gene Duplications, and Estimation of Ka/Ks Values of the Duplicated Pairs
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Motif Recognition
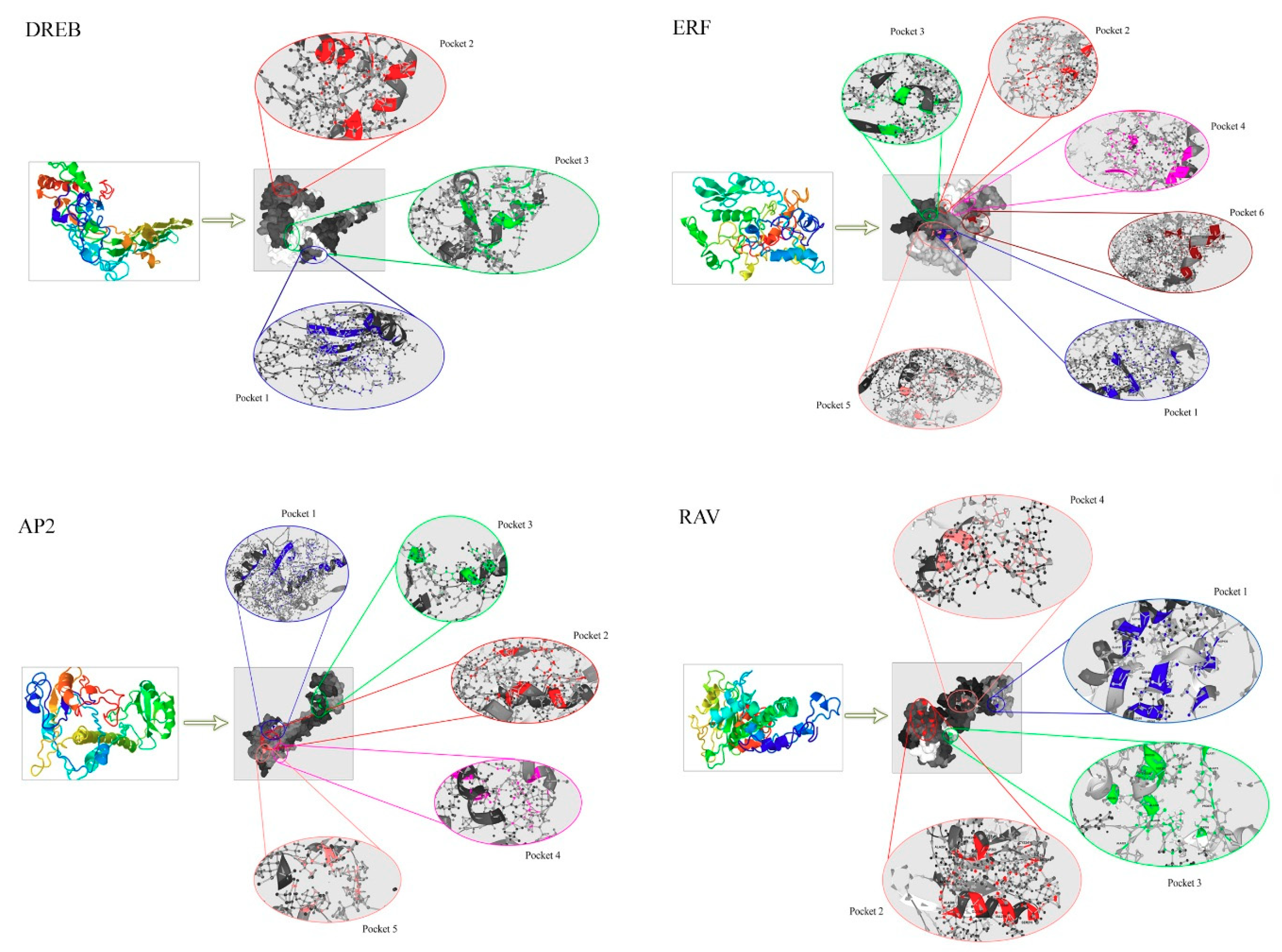
2.4. Three-Dimensional Protein Modeling and Molecular Docking via Protein Pocket Sites
2.5. In Silico Expression Analysis of TtAP2/ERF Genes through RNA-seq Data
2.6. Plant Materials and Stress Treatments
2.7. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR-Based Expression Assays of TtAP2s/ERFs
3. Results
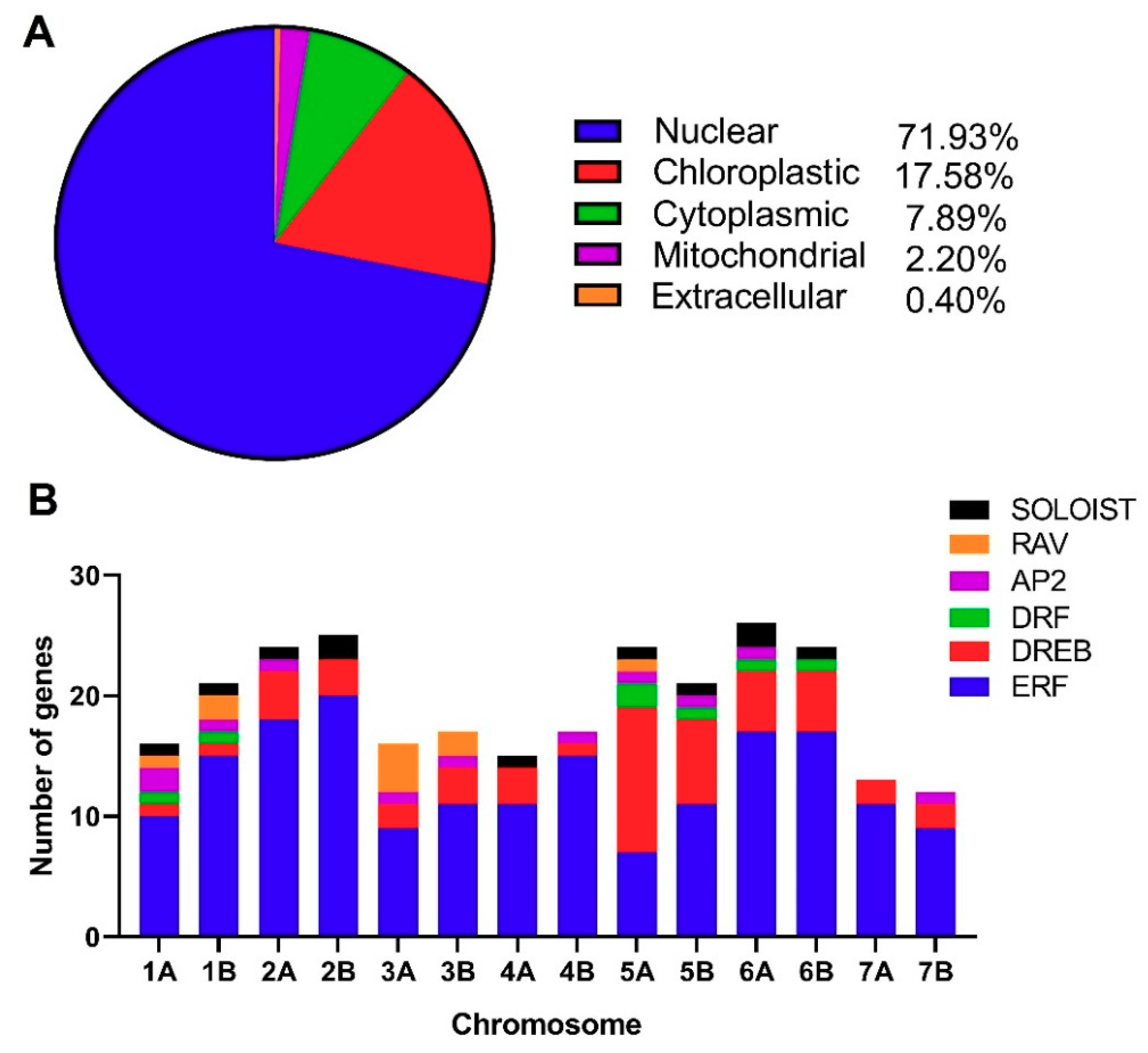
3.1. Identification of TtAP2/ERF Genes and Their Chromosomal Positions in the Durum Wheat Genome
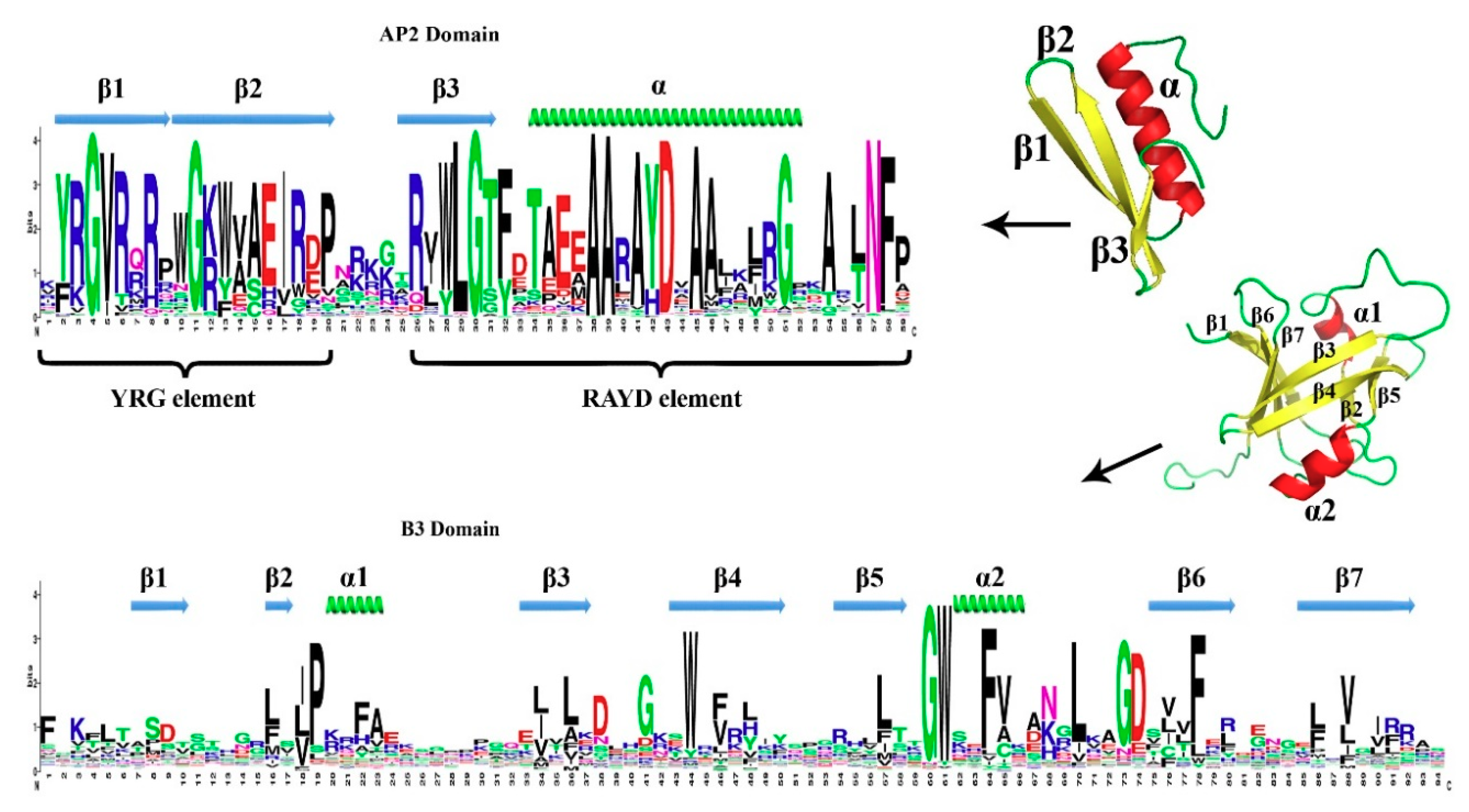
3.2. Conserved Amino Acid Residues in the DNA-Binding Domains of TtAP2/ERF Proteins
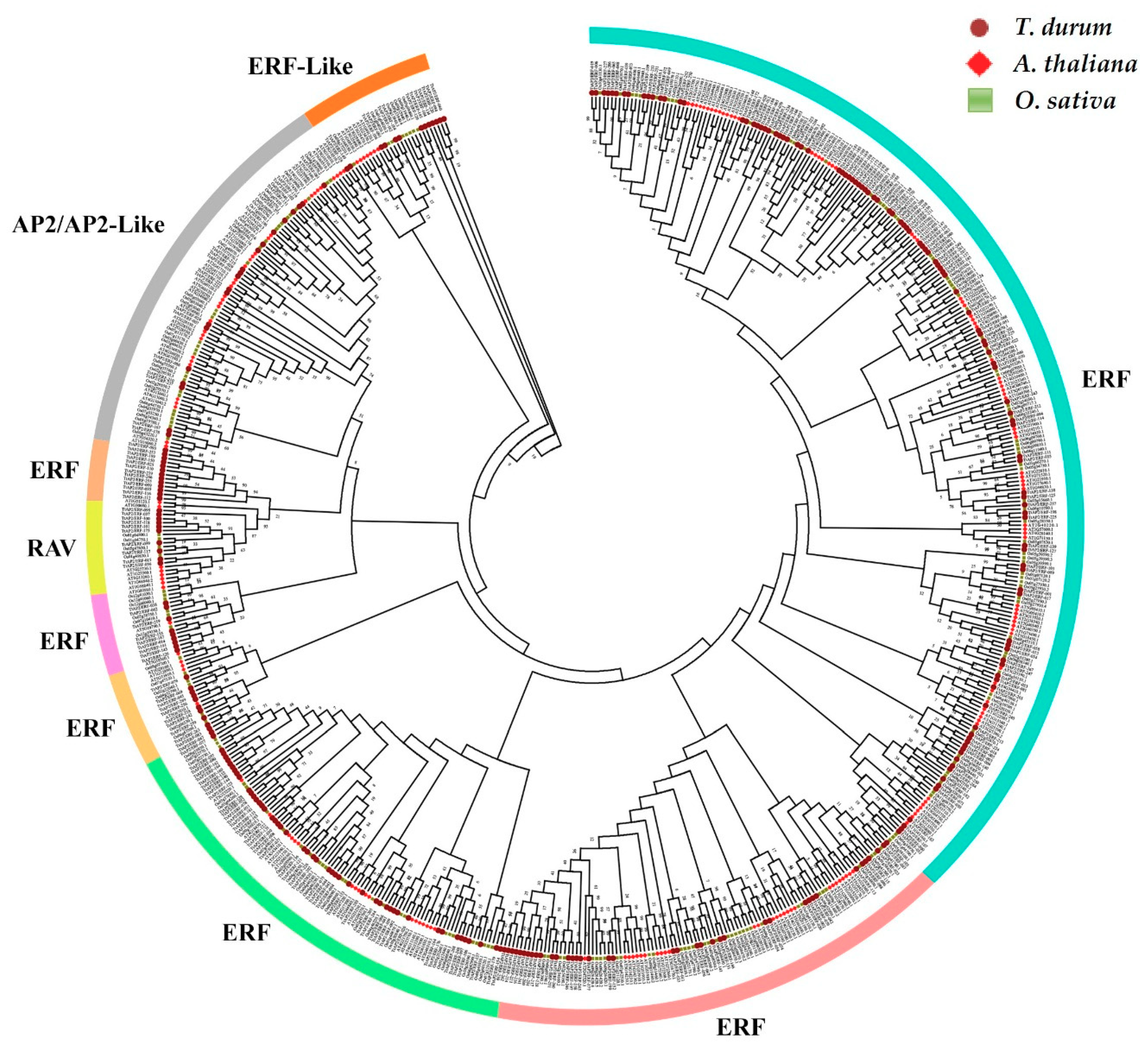
3.3. Phylogenetic Relationships and Conserved Motifs
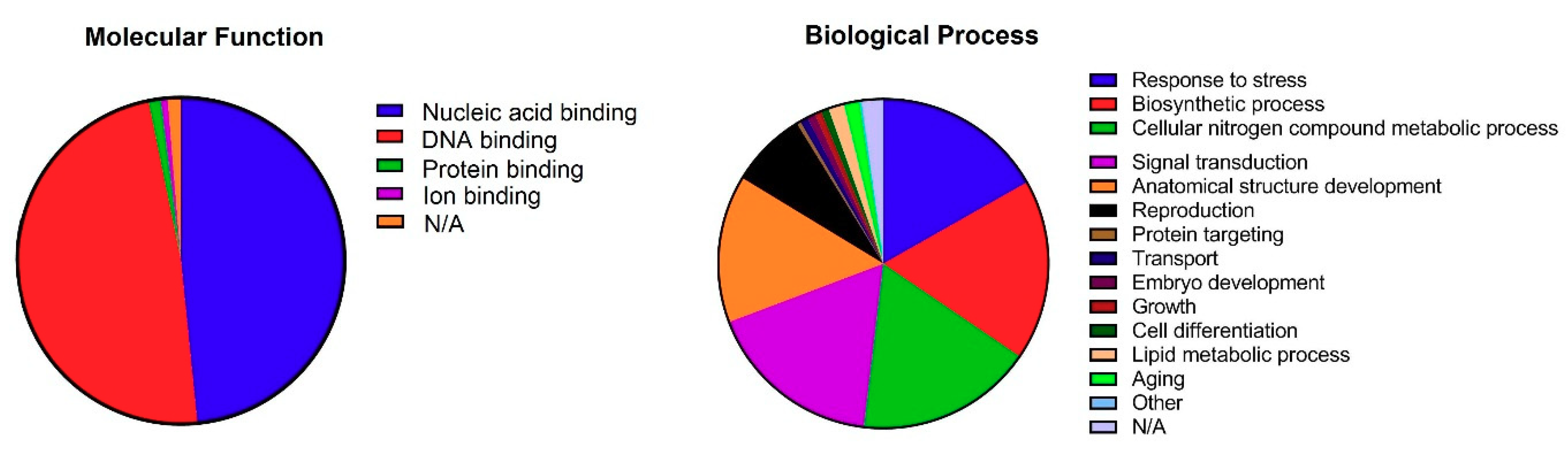
3.4. Gene Ontology Annotations
3.5. Identification of Duplicated Gene Pairs with Estimation of Ka/Ks Ratios
3.6. Homology Modeling of TtAP2/ERF Proteins and Docking Assays of Their Pocket Sites
3.7. Assay of TtAP2s/ERFs Expression in Multiple Tissues and under Abiotic Stimuli via RNA-Seq
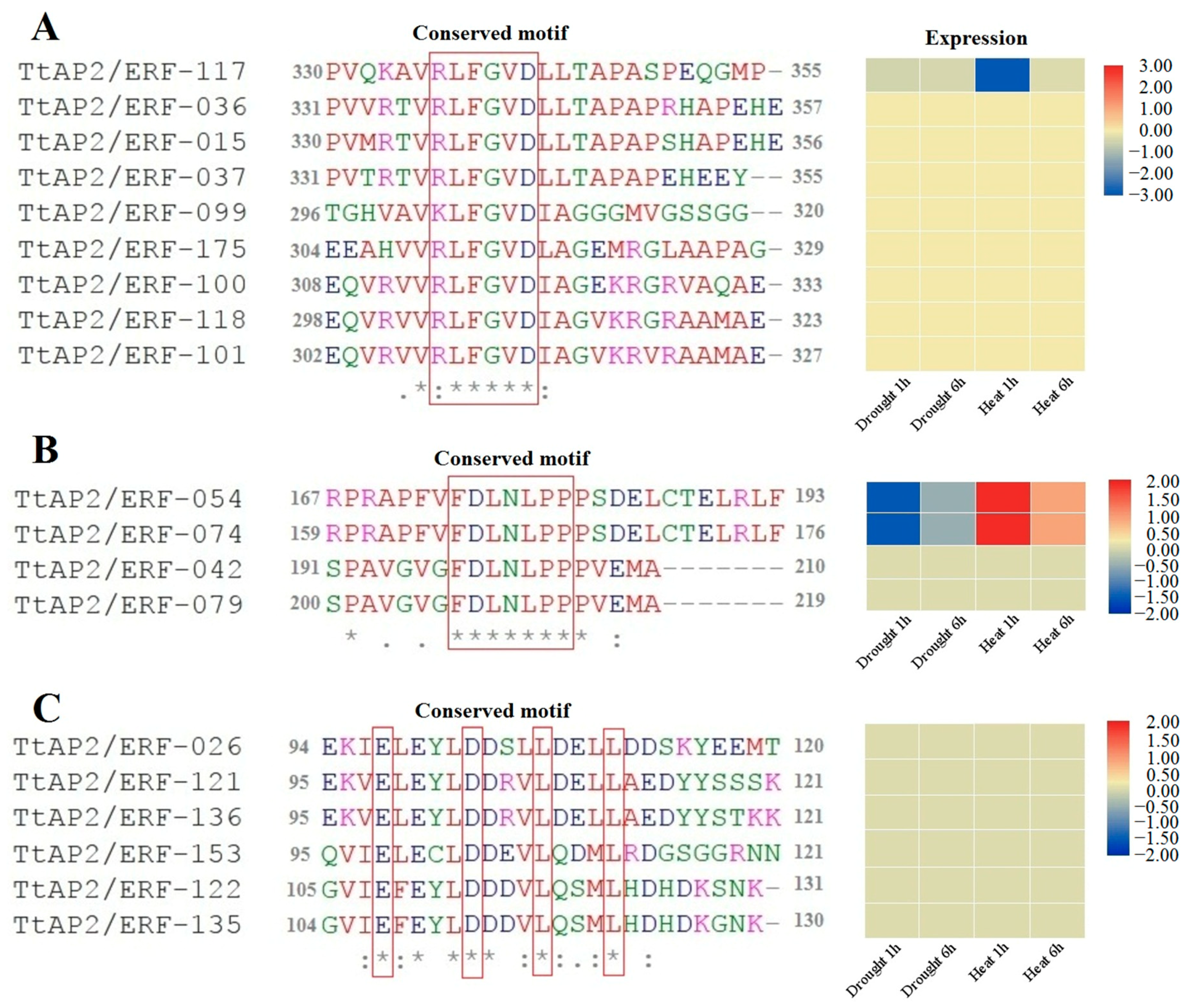
3.8. Identification Repression Motifs in TtAP2/ERFs
3.9. Expression Levels of TtAP2s/ERFs after Stimulus Exposure According to RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 781–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, P.; Mazloomi, F.; Nussbaumer, T.; Barcaccia, G. Insights into the SAM Synthetase Gene Family and Its Roles in Tomato Seedlings under Abiotic Stresses and Hormone Treatments. Plants 2020, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lata, C.; Prasad, M. Role of DREBs in regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4731–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadizadeh, M.; Heidari, P. Bioinformatics study of transcription factors involved in cold stress. Biharean Biol. 2014, 8, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Han, J.; Deng, X.; Tan, S.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Peng, H.; Yang, G.; He, G. Expansion and stress responses of AP2/EREBP superfamily in Brachypodium distachyon. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, S.; Ahmadizadeh, M.; Heidari, P. Genome-wide characterization, expression profiling, and post- transcriptional study of GASA gene family. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Hou, X.-L.; Xing, G.-M.; Liu, J.-X.; Duan, A.-Q.; Xu, Z.-S.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Katsura, K.; Maruyama, K.; Taji, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharoni, A.M.; Nuruzzaman, M.; Satoh, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kondoh, H.; Sasaya, T.; Choi, I.-R.; Omura, T.; Kikuchi, S. Gene structures, classification and expression models of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, B.K.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, M.; Muleke, E.M.; Dong, J.; Liu, L. Genome-wide characterization of the AP2/ERF gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.): Unveiling evolution and patterns in response to abiotic stresses. Gene 2019, 718, 144048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-X.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y.; Gong, W.; Ma, L.-G.; Luo, J.-C.; Deng, X.W.; Zhu, Y.-X. An annotation update via cDNA sequence analysis and comprehensive profiling of developmental, hormonal or environmental responsiveness of the Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP transcription factor gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, J.-M.; Yao, Q.-H.; Xiong, F.; Sun, C.-C.; Zhou, X.-R.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Discovery and expression profile analysis of AP2/ERF family genes from Triticum aestivum. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Guan, S.; Li, L.-C.; Li, A.; Guo, J.; Mao, L.; Ma, Y. Phylogeny, gene structures, and expression patterns of the ERF gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4095–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owji, H.; Hajiebrahimi, A.; Seradj, H.; Hemmati, S. Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2017, 71, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yin, X.; Ndayambaza, B.; Zhang, Z.; Min, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the ERF gene family in Medicago sativa L. under various abiotic stresses. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Jakada, B.H.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Jin, X.; Cai, H. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ERF transcription factor family in pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.). PeerJ 2020, 8, e10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya-Ting, H.U.; Zhi-Chao, X.U.; Ya, T.; Ran-Ran, G.A.O.; Ai-Jia, J.I.; Xiang-Dong, P.U.; Yu, W.; Xia, L.I.U.; Jing-Yuan, S. Genome-wide identification and analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors related to camptothecin biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 582–593. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Feng, G.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X. Genome-wide AP2/ERF gene family analysis reveals the classification, structure, expression profiles and potential function in orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 5225–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, C.; Mishra, A.K.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Bonthala, V.S.; Khan, Y.; Prasad, M. Genome-wide investigation and expression profiling of AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Priyadarshini, S.S.; Singh, V.; Vashisht, I.; Jung, K.-H.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, M.K. Comprehensive phylogenomic analysis of ERF genes in sorghum provides clues to the evolution of gene functions and redundancy among gene family members. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, H. Structural variation, functional differentiation and expression characteristics of the AP2/ERF gene family and its response to cold stress and methyl jasmonate in Panax ginseng CA Meyer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yao, S.; Huang, R.; Tan, Y.; Huang, D. Transcriptome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor gene family involved in the regulation of gypenoside biosynthesis in Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jofuku, K.D.; Omidyar, P.K.; Gee, Z.; Okamuro, J.K. Control of seed mass and seed yield by the floral homeotic gene APETALA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketa, S.; Amano, S.; Tsujino, Y.; Sato, T.; Saisho, D.; Kakeda, K.; Nomura, M.; Suzuki, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Sato, K. Barley grain with adhering hulls is controlled by an ERF family transcription factor gene regulating a lipid biosynthesis pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4062–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, X.F.; Li, J.Y. Arabidopsis RAV1 is down-regulated by brassinosteroid and may act as a negative regulator during plant development. Cell Res. 2004, 14, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Jung, H.W.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of the DREB Subfamily in Saccharum spontaneum Reveals Their Functional Divergence During Cold and Drought Stresses. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, A.; Sperandei, M.; Cantale, C.; Arcangeli, C.; Ammar, K.; Galeffi, P. Variability and expression profile of the DRF1 gene in four cultivars of durum wheat and one triticale under moderate water stress conditions. Planta 2013, 237, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, A.; Rasi, C.; Sperandei, M.; Cantale, C.; Iannetta, M.; Dettori, M.; Ammar, K.; Galeffi, P. Identification of a DREB-related gene in Triticum durum and its expression under water stress conditions. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, Y. Characterization of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family and Expression Profiling of DREB Subfamily under Cold and Osmotic Stresses in Ammopiptanthus nanus. Plants 2020, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhloufi, E.; Yousfi, F.-E.; Marande, W.; Mila, I.; Hanana, M.; Bergès, H.; Mzid, R.; Bouzayen, M. Isolation and molecular characterization of ERF1, an ethylene response factor gene from durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. subsp. durum), potentially involved in salt-stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6359–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.-M.; Zhou, M.-L.; Xiao, X.-G.; Tang, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.-M. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF family genes from Lotus corniculatus shows LcERF054 enhances salt tolerance. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2014, 14, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Feng, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Deng, P.; Song, W.; Nie, X. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors family in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavas, M.; Kizildogan, A.; Gökdemir, G.; Baloglu, M.C. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis of AP2-ERF gene family in salt tolerant common bean. EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 1187–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Wu, T.; Huang, K.; Jin, Y.-M.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Yun, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, H. A Novel AP2/ERF Transcription Factor, OsRPH1, Negatively Regulates Plant Height in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Ci, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Ma, W.; Jiang, L. A Novel ERF Transcription Factor, ZmERF105, Positively Regulates Maize Resistance to Exserohilum turcicum. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Singh, S.K.; Patra, B.; Liu, X.; Pattanaik, S.; Yuan, L. Mutually regulated AP2/ERF gene clusters modulate biosynthesis of specialized metabolites in plants. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, M.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Lu, S.; Tang, B.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Kai, G. The AP2/ERF transcription factor SmERF1L1 regulates the biosynthesis of tanshinones and phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morran, S.; Eini, O.; Pyvovarenko, T.; Parent, B.; Singh, R.; Ismagul, A.; Eliby, S.; Shirley, N.; Langridge, P.; Lopato, S. Improvement of stress tolerance of wheat and barley by modulation of expression of DREB/CBF factors. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolser, D.M.; Staines, D.M.; Perry, E.; Kersey, P.J. Ensembl plants: Integrating tools for visualizing, mining, and analyzing plant genomic data. In Plant Genomics Databases; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Tate, J.; Coggill, P.; Heger, A.; Pollington, J.E.; Gavin, O.L.; Gunasekaran, P.; Ceric, G.; Forslund, K. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D211–D222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Copley, R.R.; Doerks, T.; Ponting, C.P.; Bork, P. SMART: A web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Hwang, J. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In Nucleic Acids Symposium Series; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1999; Volume 41, pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Matsui, K.; Hiratsu, K.; Shinshi, H.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Ohme-Takagi, M. A novel group of transcriptional repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.B.; Belachew, A.; Ma, S.F.; Young, M.; Ade, J.; Shen, Y.; Marion, C.M.; Holtan, H.E.; Bailey, A.; Stone, J.K. The EDLL motif: A potent plant transcriptional activation domain from AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant J. 2012, 70, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Nowotny, J.; Cao, R.; Cheng, J. 3Drefine: An interactive web server for efficient protein structure refinement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W406–W409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, S.C.; Davis, I.W.; Arendall, W.B., III; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Word, J.M.; Prisant, M.G.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Structure validation by Cα geometry: ϕ, ψ and Cβ deviation. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2003, 50, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendele, L.; Krivak, R.; Skoda, P.; Novotny, M.; Hoksza, D. PrankWeb: A web server for ligand binding site prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Gao, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, F.; Lai, L.; Pei, J. CavityPlus: A web server for protein cavity detection with pharmacophore modelling, allosteric site identification and covalent ligand binding ability prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W374–W379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools-an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. bioRxiv 2020, 289660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.-J.; Liu, J.-M.; Liu, W.-Q.; Liu, Q.; Yan, Y.-B.; Zhou, H.-M. The conserved Ala37 in the ERF/AP2 domain is essential for binding with the DRE element and the GCC box. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbowicz-Matuk, A. Involvement of plant C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factors in stress responses. Plant Sci. 2012, 185, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, S.V.; Borunova, V.V.; Maksimenko, O.G.; Kantidze, O.L. Cys2His2 zinc finger protein family: Classification, functions, and major members. Biochemisty 2012, 77, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.K.; Rai, S.; Kaushik, M.; Sinha, S.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Mahendru, A. Transcriptome data of cultivated tetraploid and hexaploid wheat variety during grain development. Data Br. 2019, 22, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.; Paciorek, T.; Benková, E.; Friml, J. Immunocytochemical techniques for whole-mount in situ protein localization in plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.-J.; Vogel, M.O.; Viehhauser, A. AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling. Protoplasma 2010, 245, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, V. Small family, big impact: In silico analysis of DREB2 transcription factor family in rice. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 65, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Qin, F.; Osakabe, Y.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Dual function of an Arabidopsis transcription factor DREB2A in water-stress-responsive and heat-stress-responsive gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18822–18827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. Cell polarity signaling in Arabidopsis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 24, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, P.; Ahmadizadeh, M.; Izanlo, F.; Nussbaumer, T. In silico study of the CESA and CSL gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa: Focus on post-translation modifications. Plant Gene 2019, 19, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretic, N.; Hoen, D.R.; Huynh, M.L.; Harrison, P.M.; Bureau, T.E. The evolutionary fate of MULE-mediated duplications of host gene fragments in rice. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, L.; Gao, H.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ren, F. Genome-wide characterization of bHLH genes in grape and analysis of their potential relevance to abiotic stress tolerance and secondary metabolite biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kanwar, P.; Pandey, A.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sopory, S.K.; Kapoor, S.; Pandey, G.K. Comprehensive genomic analysis and expression profiling of phospholipase C gene family during abiotic stresses and development in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Guo, C. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their responses to abiotic stress in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Hai, M.; Guo, Y.; Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Ding, X.; Yan, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C. The ERF transcription factor family in cassava: Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses against drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamuro, J.K.; Caster, B.; Villarroel, R.; Van Montagu, M.; Jofuku, K.D. The AP2 domain of APETALA2 defines a large new family of DNA binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7076–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stank, A.; Kokh, D.B.; Fuller, J.C.; Wade, R.C. Protein binding pocket dynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Berne, B.J.; Friesner, R.A. Ligand binding to protein-binding pockets with wet and dry regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormoz, S. Amino acid composition of proteins reduces deleterious impact of mutations. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Hotta, Y. Glycine-rich proteins. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauregard, M.; Hefford, M.A. Enhancement of essential amino acid contents in crops by genetic engineering and protein design. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 4, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, G.; Höfgen, R. Metabolic engineering of amino acids and storage proteins in plants. Metab. Eng. 2002, 4, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Q. Connections Between Amino Acid Metabolisms in Plants: Lysine as an Example. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwell, J.R.; Rath, V.L.; Rasmussen, J.; Cabrilo, Z.; Bertozzi, C.R. Characterization and mutagenesis of Gal/GlcNAc-6-O-sulfotransferases. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 15590–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K.; Fukunaga, S.; Bednarek, P.; Piślewska-Bednarek, M.; Watanabe, S.; Narusaka, Y.; Shirasu, K.; Takano, Y. Glutathione and tryptophan metabolism are required for Arabidopsis immunity during the hypersensitive response to hemibiotrophs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Bonthala, V.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Khandelwal, R.; Khan, Y.; Roy, R.; Prasad, M. C2H2 type of zinc finger transcription factors in foxtail millet define response to abiotic stresses. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2014, 14, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigyo, M.; Hasebe, M.; Ito, M. Molecular evolution of the AP2 subfamily. Gene 2006, 366, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, P. Comparative Analysis of C-repeat Binding Factors (CBFs) in Tomato and Arabidopsis. Brazilian Arch. Biol. Technol. 2019, 62, e19180715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, C.; Kobayashi, F.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.; Takumi, S. Differential regulation of transcript accumulation and alternative splicing of a DREB2 homolog under abiotic stress conditions in common wheat. Genes Genet. Syst. 2006, 81, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-C.; Hsieh, E.-J.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-P. Arabidopsis RGLG2, functioning as a RING E3 ligase, interacts with AtERF53 and negatively regulates the plant drought stress response. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration-and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-G.; Zhang, W.-K.; He, S.-J.; Zhang, J.-S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.-Y. An EREBP/AP2-type protein in Triticum aestivum was a DRE-binding transcription factor induced by cold, dehydration and ABA stress. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yang, W.-W.; Liao, P.; Guo, Y.-W.; Kumar, A.; Gao, W. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed ERF transcription factors associated with salt response in cotton. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Nong, Q.; Jian, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Xia, K. An AP2/ERF Gene, HuERF1, from Pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) Positively Regulates Salt Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hsieh, E.; Cheng, M.; Chen, C.; Hwang, S.; Lin, T. ORA47 (octadecanoid-responsive AP2/ERF-domain transcription factor 47) regulates jasmonic acid and abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling through binding to a novel cis-element. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehrig, E.M.; Appel, H.M.; Jones, A.D.; Schultz, J.C. Roles for jasmonate-and ethylene-induced transcription factors in the ability of Arabidopsis to respond differentially to damage caused by two insect herbivores. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Jasmonate regulates the inducer of CBF expression–c-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2907–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Boon, N.J.; Webb, A.A.R.; Tanaka, R.J. Synergistic activation of RD29A via integration of salinity stress and abscisic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.R.; da Cunha, B.A.D.B.; Martins, P.K.; Martins, M.T.B.; Alekcevetch, J.C.; Chalfun-Júnior, A.; Andrade, A.C.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Qin, F.; Mizoi, J. Induced over-expression of AtDREB2A CA improves drought tolerance in sugarcane. Plant Sci. 2014, 221, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, A.; Sperandei, M.; Sharma, S.; Cantale, C.; Iannetta, M.; Dettori, M.; Ammar, K.; Galeffi, P. Molecular analyses of a dehydration-related gene from the DREB family in durum, wheat and triticale. In Biosaline Agriculture and High Salinity Tolerance; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Rashotte, A.M.; Goertzen, L.R. The CRF domain defines cytokinin response factor proteins in plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faraji, S.; Filiz, E.; Kazemitabar, S.K.; Vannozzi, A.; Palumbo, F.; Barcaccia, G.; Heidari, P. The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses. Genes 2020, 11, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121464
Faraji S, Filiz E, Kazemitabar SK, Vannozzi A, Palumbo F, Barcaccia G, Heidari P. The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses. Genes. 2020; 11(12):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121464
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaraji, Sahar, Ertugrul Filiz, Seyed Kamal Kazemitabar, Alessandro Vannozzi, Fabio Palumbo, Gianni Barcaccia, and Parviz Heidari. 2020. "The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses" Genes 11, no. 12: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121464
APA StyleFaraji, S., Filiz, E., Kazemitabar, S. K., Vannozzi, A., Palumbo, F., Barcaccia, G., & Heidari, P. (2020). The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses. Genes, 11(12), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121464








