Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical History
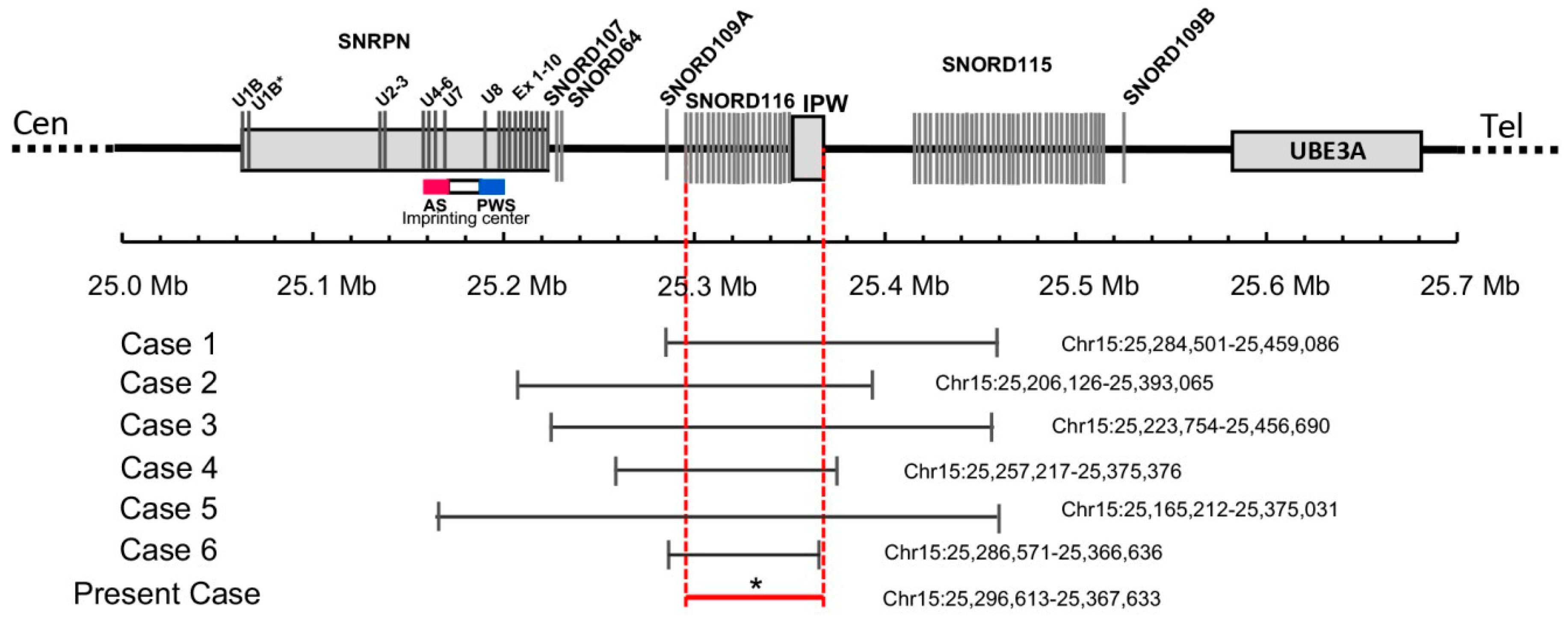
3.2. Genetic Findings
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Diagnostic Testing
References
- Butler, M.G. Prader-Willi syndrome: Current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1990, 35, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irizarry, K.A.; Miller, M.; Freemark, M.; Haqq, A.M. Prader-Willi syndrome: Genetics, metabolomics, hormonal function, and new approaches to therapy. Adv. Pediatr. 2016, 63, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Miller, J.L.; Kuipers, P.J.; German, J.R.; Beaudet, A.L.; Sahoo, T.; Driscoll, D.J. Unique and atypical deletions in Prader-Willi syndrome reveal distinct phenotypes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, S.C.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Birch, R.; Buiting, K. Practice guidelines for the molecular analysis of Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, T.; del Gaudio, D.; German, J.R.; Shinawi, M.; Peters, S.U.; Person, R.E.; Garnica, A.; Cheung, S.W.; Beaudet, A.L. Prader-Willi phenotype caused by paternal deficiency for the HBII-85 C/D box small nucleolar RNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Smith, A.J.; Purmann, C.; Walters, R.G.; Ellis, R.J.; Holder, S.E.; Van Haelst, M.M.; Brady, A.F.; Fairbrother, U.L.; Dattani, M.; Keogh, J.M. A deletion of the HBII-85 class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is associated with hyperphagia, obesity and hypogonadism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3257–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duker, A.L.; Ballif, B.C.; Bawle, E.V.; Person, R.E.; Mahadevan, S.; Alliman, S.; Thompson, R.; Traylor, R.; Bejjani, B.A.; Shaffer, L.G. Paternally inherited microdeletion at 15q11.2 confirms a significant role for the SNORD116 C/D box snoRNA cluster in Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieth, E.; Eddiry, S.; Gaston, V.; Lorenzini, F.; Buffet, A.; Conte Auriol, F.; Molinas, C.; Cailley, D.; Rooryck, C.; Arveiler, B. Highly restricted deletion of the SNORD116 region is implicated in Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Butler, M.G. Prader-Willi syndrome and atypical submicroscopic 15q11-q13 deletions with or without imprinting defects. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, P.; Grasso, M.; Acquaviva, F.; Gennaro, E.; Galli, M.L.; Falco, M.; Scarano, F.; Scarano, G.; Lonardo, F. SNORD116 deletions cause Prader-Willi syndrome with a mild phenotype and macrocephaly. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgent Genetics. Clinical Exome. Available online: https://fulgentdiagnostics.com/Clinical-Exome (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Richards, C.S.; Bale, S.; Bellissimo, D.B.; Das, S.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.R.; Lyon, E.; Ward, B.E.; Molecular Subcommittee of the ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. ACMG recommendations for standards for interpretation and reporting of sequence variations: Revisions 2007. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/ Height-For-Age, Weight-For-Age, Weight-For-Height and Body Mass Index- For-Age: Methods and Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/technical_report/en/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Butler, M.G.; Miller, J.L.; Forster, J.L. Prader-Willi syndrome—Clinical genetics, diagnosis and treatment approaches: An update. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grugni, G.; Sartorio, A.; Crinò, A. Growth hormone therapy for Prader-Willi syndrome: Challenges and solutions. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Copping, N.A.; Onaga, B.; Pride, M.C.; Coulson, R.L.; Yang, M.; Yasui, D.H.; LaSalle, J.M.; Silverman, J.L. Cognitive deficits in the Snord116 deletion mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, S.; Solomon, N.M.; Camper, S.A.; Cohen, P.; Francke, U. SnoRNA Snord116 (Pwcr1/MBII-85) deletion causes growth deficiency and hyperphagia in mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.; Larder, R.; Tadross, J.; Rimmington, D.; Bosch, F.; Cenzano, V.J.; Ayuso, E.; Ma, M.K.; Rainbow, K. Hypothalamic loss of Snord116 recapitulates the hyperphagia of Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spikol, E.D.; Laverriere, C.E.; Robnett, M.; Carter, G.; Wolfe, E.M.; Glasgow, E. Zebrafish models of Prader-Willi syndrome: Fast track to pharmacotherapeutics. Diseases 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case 1 [5] | Case 2 [6] | Case 3 [7] | Case 4 [8] | Case 5 [9] | Case 6 [10] | Present case | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deletion size (kbp) | 175 | 187 | 236 | 118 | 210 | 80 | 71 |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian | South Asian Indian | African-American | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian |
| Gender | Male | Male | Male | Female | Female | Male | Male |
| Birth weight (g) | 3218 | 2800 | 3020 | 2780 | 3334 | 2710 | 3140 |
| Birth length (cm) | 54.5 | N/A | 53 | 48 | 54.6 | 49 | 51 |
| Age at examination (years) | 4.8 | 19.5 | 11 | 23 | 26 | 18 | 17 |
| Clinical features | |||||||
| Hypotonia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Infantile feeding problems/FTT | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Tube feeding | + | − | + | + | − | − | + |
| Start of excess weight gain (months) | 18 | 24 | 6 | 18 | 30 | Between 48–72 | 36 |
| Hyperphagia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Overweight/Obesity | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Distinctive facial features | + | N/A | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hypogonadism | + | + | + | + | N/A | + | − |
| Developmental delay | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Mental retardation | + | + | + | + | N/A | − | − |
| Behavioral problems | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Skin picking | + | + | − | + | + | − | + |
| Sleep disturbances/ apnea | + | N/A | + | + | N/A | − | + |
| Short stature | − | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Small hands/feet for height | + | + | − | N/A | + | − | − |
| Eye abnormalities | − | N/A | + | N/A | N/A | + | − |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Q.; Potter, K.J.; Burnett, L.C.; Orsso, C.E.; Inman, M.; Ryman, D.C.; Haqq, A.M. Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes 2020, 11, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
Tan Q, Potter KJ, Burnett LC, Orsso CE, Inman M, Ryman DC, Haqq AM. Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes. 2020; 11(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Qiming, Kathryn J. Potter, Lisa Cole Burnett, Camila E. Orsso, Mark Inman, Davis C. Ryman, and Andrea M. Haqq. 2020. "Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion" Genes 11, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
APA StyleTan, Q., Potter, K. J., Burnett, L. C., Orsso, C. E., Inman, M., Ryman, D. C., & Haqq, A. M. (2020). Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes, 11(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128





