Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical History
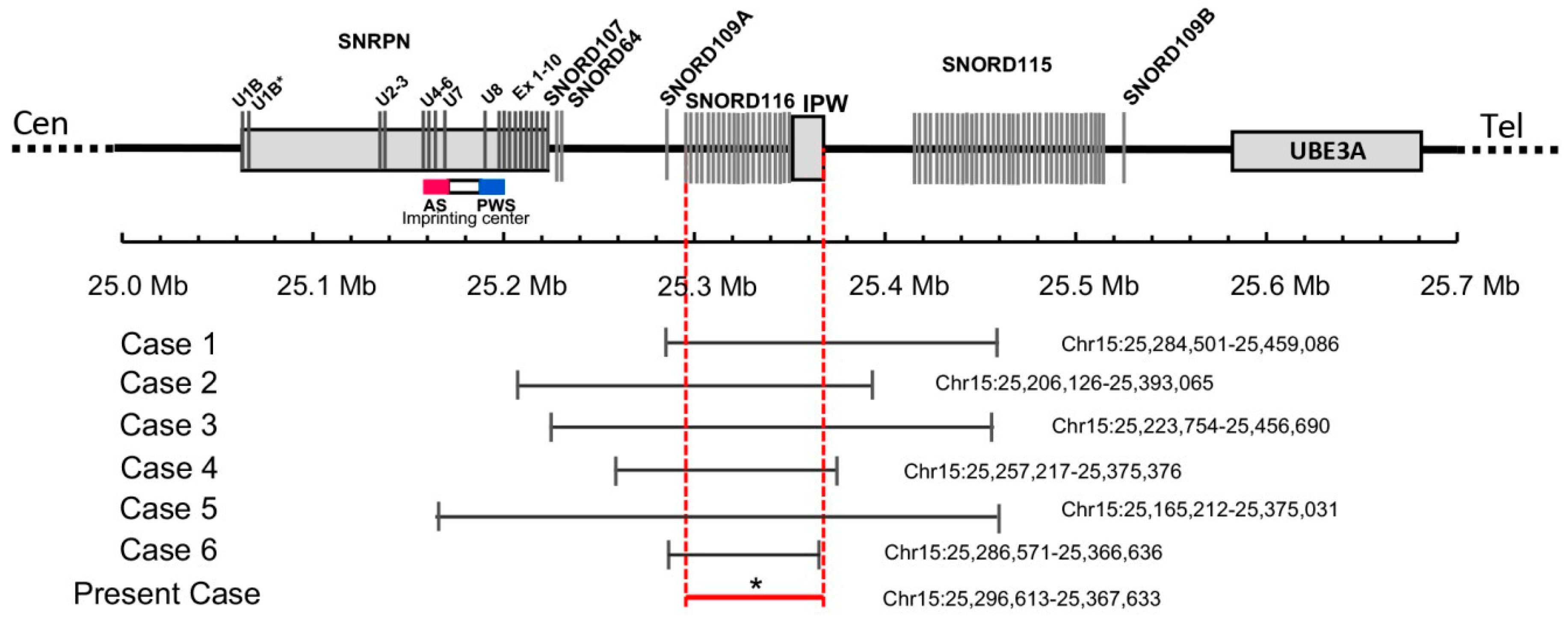
3.2. Genetic Findings
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Diagnostic Testing
References
- Butler, M.G. Prader-Willi syndrome: Current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1990, 35, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irizarry, K.A.; Miller, M.; Freemark, M.; Haqq, A.M. Prader-Willi syndrome: Genetics, metabolomics, hormonal function, and new approaches to therapy. Adv. Pediatr. 2016, 63, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Miller, J.L.; Kuipers, P.J.; German, J.R.; Beaudet, A.L.; Sahoo, T.; Driscoll, D.J. Unique and atypical deletions in Prader-Willi syndrome reveal distinct phenotypes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, S.C.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Birch, R.; Buiting, K. Practice guidelines for the molecular analysis of Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahoo, T.; del Gaudio, D.; German, J.R.; Shinawi, M.; Peters, S.U.; Person, R.E.; Garnica, A.; Cheung, S.W.; Beaudet, A.L. Prader-Willi phenotype caused by paternal deficiency for the HBII-85 C/D box small nucleolar RNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Smith, A.J.; Purmann, C.; Walters, R.G.; Ellis, R.J.; Holder, S.E.; Van Haelst, M.M.; Brady, A.F.; Fairbrother, U.L.; Dattani, M.; Keogh, J.M. A deletion of the HBII-85 class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is associated with hyperphagia, obesity and hypogonadism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3257–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duker, A.L.; Ballif, B.C.; Bawle, E.V.; Person, R.E.; Mahadevan, S.; Alliman, S.; Thompson, R.; Traylor, R.; Bejjani, B.A.; Shaffer, L.G. Paternally inherited microdeletion at 15q11.2 confirms a significant role for the SNORD116 C/D box snoRNA cluster in Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieth, E.; Eddiry, S.; Gaston, V.; Lorenzini, F.; Buffet, A.; Conte Auriol, F.; Molinas, C.; Cailley, D.; Rooryck, C.; Arveiler, B. Highly restricted deletion of the SNORD116 region is implicated in Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.; Butler, M.G. Prader-Willi syndrome and atypical submicroscopic 15q11-q13 deletions with or without imprinting defects. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, P.; Grasso, M.; Acquaviva, F.; Gennaro, E.; Galli, M.L.; Falco, M.; Scarano, F.; Scarano, G.; Lonardo, F. SNORD116 deletions cause Prader-Willi syndrome with a mild phenotype and macrocephaly. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgent Genetics. Clinical Exome. Available online: https://fulgentdiagnostics.com/Clinical-Exome (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Richards, C.S.; Bale, S.; Bellissimo, D.B.; Das, S.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.R.; Lyon, E.; Ward, B.E.; Molecular Subcommittee of the ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. ACMG recommendations for standards for interpretation and reporting of sequence variations: Revisions 2007. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/ Height-For-Age, Weight-For-Age, Weight-For-Height and Body Mass Index- For-Age: Methods and Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/technical_report/en/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Butler, M.G.; Miller, J.L.; Forster, J.L. Prader-Willi syndrome—Clinical genetics, diagnosis and treatment approaches: An update. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grugni, G.; Sartorio, A.; Crinò, A. Growth hormone therapy for Prader-Willi syndrome: Challenges and solutions. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, A.; Copping, N.A.; Onaga, B.; Pride, M.C.; Coulson, R.L.; Yang, M.; Yasui, D.H.; LaSalle, J.M.; Silverman, J.L. Cognitive deficits in the Snord116 deletion mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, S.; Solomon, N.M.; Camper, S.A.; Cohen, P.; Francke, U. SnoRNA Snord116 (Pwcr1/MBII-85) deletion causes growth deficiency and hyperphagia in mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.; Larder, R.; Tadross, J.; Rimmington, D.; Bosch, F.; Cenzano, V.J.; Ayuso, E.; Ma, M.K.; Rainbow, K. Hypothalamic loss of Snord116 recapitulates the hyperphagia of Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spikol, E.D.; Laverriere, C.E.; Robnett, M.; Carter, G.; Wolfe, E.M.; Glasgow, E. Zebrafish models of Prader-Willi syndrome: Fast track to pharmacotherapeutics. Diseases 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Case 1 [5] | Case 2 [6] | Case 3 [7] | Case 4 [8] | Case 5 [9] | Case 6 [10] | Present case | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deletion size (kbp) | 175 | 187 | 236 | 118 | 210 | 80 | 71 |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian | South Asian Indian | African-American | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian |
| Gender | Male | Male | Male | Female | Female | Male | Male |
| Birth weight (g) | 3218 | 2800 | 3020 | 2780 | 3334 | 2710 | 3140 |
| Birth length (cm) | 54.5 | N/A | 53 | 48 | 54.6 | 49 | 51 |
| Age at examination (years) | 4.8 | 19.5 | 11 | 23 | 26 | 18 | 17 |
| Clinical features | |||||||
| Hypotonia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Infantile feeding problems/FTT | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Tube feeding | + | − | + | + | − | − | + |
| Start of excess weight gain (months) | 18 | 24 | 6 | 18 | 30 | Between 48–72 | 36 |
| Hyperphagia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Overweight/Obesity | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Distinctive facial features | + | N/A | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hypogonadism | + | + | + | + | N/A | + | − |
| Developmental delay | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Mental retardation | + | + | + | + | N/A | − | − |
| Behavioral problems | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Skin picking | + | + | − | + | + | − | + |
| Sleep disturbances/ apnea | + | N/A | + | + | N/A | − | + |
| Short stature | − | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Small hands/feet for height | + | + | − | N/A | + | − | − |
| Eye abnormalities | − | N/A | + | N/A | N/A | + | − |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Q.; Potter, K.J.; Burnett, L.C.; Orsso, C.E.; Inman, M.; Ryman, D.C.; Haqq, A.M. Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes 2020, 11, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
Tan Q, Potter KJ, Burnett LC, Orsso CE, Inman M, Ryman DC, Haqq AM. Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes. 2020; 11(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Qiming, Kathryn J. Potter, Lisa Cole Burnett, Camila E. Orsso, Mark Inman, Davis C. Ryman, and Andrea M. Haqq. 2020. "Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion" Genes 11, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128
APA StyleTan, Q., Potter, K. J., Burnett, L. C., Orsso, C. E., Inman, M., Ryman, D. C., & Haqq, A. M. (2020). Prader–Willi-Like Phenotype Caused by an Atypical 15q11.2 Microdeletion. Genes, 11(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020128





