Genetic Differentiation in Hatchery and Stocked Populations of Sea Trout in the Southern Baltic: Selection Evidence at SNP Loci
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Genomic DNA Isolation
2.2. SNP Genotyping and SNP Validation
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Polymorphism and Diversity
3.2. Genetic Structure and Relationships
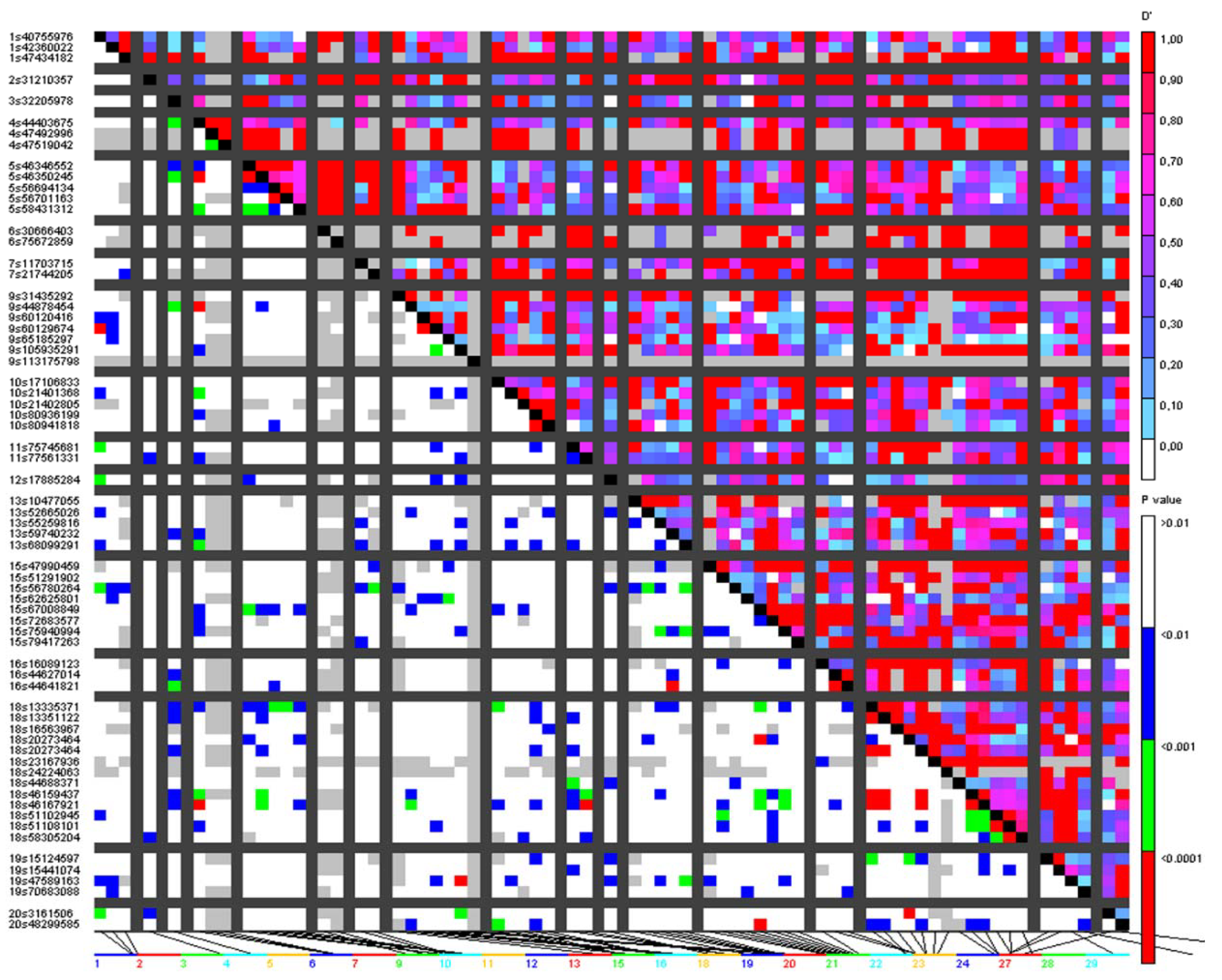
3.3. Analysis of Putative Outliers and Linkage Disequilibrium
4. Discussion
4.1. Stocking History and Evidence From Alternative Non-Genetic Methods
4.2. Vistulian Clade and the Breeding Lines
4.3. Outlier Loci and Potential Selection Pressure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradbury, I.R.; Hamilton, L.C.; Rafferty, S.; Meerburg, D.; Poole, R.; Dempson, J.B.; Robertson, M.J.; Reddin, D.G.; Bourret, V.; Dionne, M.; et al. Genetic evidence of local exploitation of Atlantic salmon in a coastal subsistence fishery in the Northwest Atlantic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 72, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, T.F.; Legault, C.M.; King, T.L.; Spidle, A.P. Probabilistic-based genetic assignment model: Assignments to subcontinent of origin of the West Greenland Atlantic salmon harvest. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekkevold, D.; Worsøe Clausen, L.; Mariani, S.; André, C.; Hatfield, E.M.C.; Torstensen, E.; Ryman, N.; Carvalho, G.R.; Ruzzante, D.E. Genetic mixed-stock analysis of Atlantic herring populations in a mixed feeding area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 442, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vähä, J.-P.; Erkinaro, J.; Falkegård, M.; Orell, P.; Niemelä, E. Genetic stock identification of Atlantic salmon and its evaluation in a large population complex. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 74, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annual changes in the proportions of wild and hatchery Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) caught in the Baltic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 1274–1285. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koljonen, M.-L.; Gross, R.; Koskiniemi, J. Wild Estonian and Russian sea trout (Salmo trutta) in Finnish coastal sea trout catches: Results of genetic mixed-stock analysis. Hereditas 2014, 151, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potter, T.; Ó’Maoiléidigh, N. Review of mixed stock fisheries for atlantic salmon in european community waters, excluding the Baltic sea. Preparatory paper for the European Commission. 2006; 51p. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. Salmon and sea trout populations and rivers in the Baltic Sea—HELCOM assessment of salmon (Salmo salar) and sea trout (Salmo trutta) populations and habitats in rivers flowing to the Baltic Sea. Proc No 2011. [Google Scholar]
- BACC II Author Team. Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic; Regional Climate Studies, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-16005-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kołder, W. Stocking of the upper Vistula River system with salmon and sea trout from 1879 to 1954. Rocz. Nauk. Rol. 1958, 215–267. [Google Scholar]
- Dębowski, P. The largest Baltic population of sea trout (Salmo trutta L.): Its decline, restoration attempts, and current status. Fish. Amp. Aquat. Life 2018, 26, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, R. Present situation of the Vistula sea trout. Arch. Pol. Fish. 1993, 101–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, R.; Wisniewolski, W.; Prus, P. Impact of the Włocławek dam on migratory fish in the Vistula River. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2007, 15, 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Report of the Baltic Salmon and Trout Assessment Working Group (WGBAST), 30 March–6 April 2016, Klaipeda, Lithuania. ICES CM 2016/ACOM:09. 2016; 257p.
- Dębowski, P.; Bartel, R. Homing of tagged sea trout (Salmo trutta L.) smolts released into polish rivers. Arch. Rybactwa. Pol. 1995, 03, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, R.; Pachur, M.; Bernaś, R. Distribution, migrations, and growth of tagged sea trout released into the Vistula River. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2010, 18, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Berejikian, B.A.; Ford, M.J.; Blouin, M.S. Fitness of hatchery-reared salmonids in the wild. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einum, S.; Fleming, I.A. Implications of Stocking: Ecological Interactions Between Wild and Released Salmonids. Nord. J. Freshw. Res. 2001, 75, 56–70. [Google Scholar]
- Naish, K.A.; Taylor, J.E.; Levin, P.S.; Quinn, T.P.; Winton, J.R.; Huppert, D.; Hilborn, R. An evaluation of the effects of conservation and fishery enhancement hatcheries on wild populations of salmon. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2007, 53, 61–194. [Google Scholar]
- Chaput, G.J. Understanding the Risks and Benefits of Hatchery and Stocking Activities to Wild Atlantic Salmon Populations; North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization: Edinburgh, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-9514129-7-8. [Google Scholar]
- Łuczyński, M.; Bartel, R.; Vuorinen, J.A.; Domagała, J.; Zolkiewicz, L.; Brzuzan, P. Biochemical genetic characteristics of four Polish sea trout (Salmo trutta trutta L.) populations. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2000, 47, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Włodarczyk, E.; Wenne, R. Mitochondrial DNA variation in sea trout from coastal rivers in the southern Baltic region. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2001, 58, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wąs, A.; Wenne, R. Genetic differentiation in hatchery and wild sea trout (Salmo trutta) in the Southern Baltic at microsatellite loci. Aquaculture 2002, 204, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wąs, A.; Wenne, R. Microsatellite DNA polymorphism in intensely enhanced populations of sea trout (Salmo trutta) in the Southern Baltic. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drywa, A.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Wąs, A.; Dobosz, S.; Kent, M.P.; Lien, S.; Bernaś, R.; Wenne, R. Genotyping of two populations of Southern Baltic Sea trout Salmo trutta m. trutta using an Atlantic salmon derived SNP-array. Mar. Genom. 2013, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenne, R.; Bernaś, R.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Drywa, A.; Wąs, A. Recent genetic changes in enhanced populations of sea trout (Salmo trutta m. trutta) in the southern Baltic rivers revealed with SNP analysis. Aquat. Living Resour. 2016, 29, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Wąs, A.; Bernaś, R. Long-term and seasonal genetic differentiation in wild and enhanced stocks of sea trout (Salmo trutta m. trutta L.) from the Vistula River, in the southern Baltic—Management implications. Fish. Res. 2016, 175, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rengmark, A.H.; Slettan, A.; Skaala, Ø.; Lie, Ø.; Lingaas, F. Genetic variability in wild and farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) strains estimated by SNP and microsatellites. Aquaculture 2006, 253, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoneking, M. From the evolutionary past. Nature 2001, 409, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linløkken, A.N.; Haugen, T.O.; Kent, M.P.; Lien, S. Genetic differences between wild and hatchery-bred brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) in single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to selective traits. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nei, M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 1978, 89, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takezaki, N.; Nei, M.; Tamura, K. POPTREE2: Software for constructing population trees from allele frequency data and computing other population statistics with Windows interface. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rannala, B.; Mountain, J.L. Detecting immigration by using multilocus genotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9197–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piry, S.; Alapetite, A.; Cornuet, J.-M.; Paetkau, D.; Baudouin, L.; Estoup, A. GENECLASS2: A software for genetic assignment and first-generation migrant detection. J. Hered. 2004, 95, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.A.; Nichols, R.A. Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 263, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Foll, M.; Gaggiotti, O. A Genome-Scan Method to Identify Selected Loci Appropriate for Both Dominant and Codominant Markers: A Bayesian Perspective. Genetics 2008, 180, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, R.; Hellmann, I.; Hubisz, M.; Bustamante, C.; Clark, A.G. Recent and ongoing selection in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, A.P.; Yáñez, J.M.; Davidson, W.S. Evidence of recent signatures of selection during domestication in an Atlantic salmon population. Mar. Genom. 2016, 26, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, S.; Gidskehaug, L.; Moen, T.; Hayes, B.J.; Berg, P.R.; Davidson, W.S.; Omholt, S.W.; Kent, M.P. A dense SNP-based linkage map for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) reveals extended chromosome homeologies and striking differences in sex-specific recombination patterns. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lien, S.; Koop, B.F.; Sandve, S.R.; Miller, J.R.; Kent, M.P.; Nome, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Leong, J.S.; Minkley, D.R.; Zimin, A.; et al. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 2016, 533, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yates, A.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Billis, K.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Cummins, C.; Clapham, P.; Fitzgerald, S.; Gil, L.; et al. Ensembl 2016. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D710–D716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voight, B.F.; Kudaravalli, S.; Wen, X.; Pritchard, J.K. A map of recent positive selection in the human genome. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e72. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M. Linkage disequilibrium--understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaunt, T.R.; Rodriguez, S.; Zapata, C.; Day, I.N.M. MIDAS: Software for analysis and visualisation of interallelic disequilibrium between multiallelic markers. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating f-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1984, 38, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Borzęcka, I. Classifying Vistula and Pomeranian sea trout populations using discriminant functions based on selected scale characters. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2010, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degerman, E.; Leonardsson, K.; Lundqvist, H. Coastal migrations, temporary use of neighbouring rivers, and growth of sea trout (Salmo trutta) from nine northern Baltic Sea rivers. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernaś, R.; Burzyński, A.; Dębowski, P.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Wenne, R. Genetic diversity within sea trout population from an intensively stocked southern Baltic river, based on microsatellite DNA analysis. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2014, 21, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narum, S.R.; Hess, J.E. Comparison of FST outlier tests for SNP loci under selection. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petereit, C.; Bekkevold, D.; Nickel, S.; Dierking, J.; Hantke, H.; Hahn, A.; Reusch, T.; Puebla, O. Population genetic structure after 125 years of stocking in sea trout (Salmo trutta L.). Conserv. Genet. 2018, 19, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, G.W.; Chopp, T.; Qi, S.-M.; Cutler, M.L. The Ras suppressor Rsu-1 binds to the LIM 5 domain of the adaptor protein PINCH1 and participates in adhesion-related functions. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 306, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymchuk, W.E.; Beckman, B.; Devlin, R.H. Altered expression of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis hormones in domesticated fish. Endocrinology 2009, 4, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moghadam, H.K.; Johnsen, H.; Robinson, N.; Andersen, Ø.; Jørgensen, E.H.; Johnsen, H.K.; Bæhr, V.J.; Tveiten, H. Impacts of early life stress on the methylome and transcriptome of Atlantic salmon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna-Hansen, S.; Li, J.; Kent, M.P.; Boulding, E.G.; Dominik, S.; Davidson, W.S.; Lien, S. Chromosomal differences between European and North American Atlantic salmon discovered by linkage mapping and supported by fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, R.; Ráb, P. Chromosome evolution in the Salmonidae (Pisces): An update. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2001, 76, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitwein, M.; Guinand, B.; Pouzadoux, J.; Desmarais, E.; Berrebi, P.; Gagnaire, P.-A. A Dense Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) Linkage Map Reveals Recent Chromosomal Rearrangements in the Salmo Genus and the Impact of Selection on Linked Neutral Diversity. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, B.J.G.; Gosselin, T.; Normandeau, E.; Lamothe, M.; Isabel, N.; Audet, C.; Bernatchez, L. Salmonid Chromosome Evolution as Revealed by a Novel Method for Comparing RADseq Linkage Maps. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3600–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Stock | N | NPL | MNA | Ho | He | DHWE | FIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS9 | 25 | 3706 | 1.949 | 0.339 | 0.324 | 4 | −0.034 |
| TS8 | 18 | 3657 | 1.931 | 0.332 | 0.319 | 7 | −0.011 |
| TVS | 28 | 3780 | 1.961 | 0.345 | 0.333 | 3 | −0.024 |
| TVR | 21 | 3560 | 1.906 | 0.328 | 0.314 | 12 | −0.019 |
| TVA | 19 | 3640 | 1.927 | 0.326 | 0.324 | 13 | 0.020 |
| Among Populations | Within Populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance component | % variation | Variance component | % variation | |
| All samples | 22.74 | 3.40 | 646.83 | 96.60 |
| Sampled in wild | 13.31 | 1.98 | 655.90 | 98.01 |
| Hatchery stocks | 42.49 | 6.19 | 643.54 | 93.80 |
| Stock | TS9 | TS8 | TVS | TVR | TVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS9 | 1281.257 | 6.032 | 33.938 | 64.040 | 51.076 |
| TS8 | 0.004 | 1292.351 | 34.579 | 64.132 | 50.736 |
| TVS | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1316.761 | 67.770 | 15.800 |
| TVR | 0.047 | 0.047 | 0.049 | 1255.973 | 84.902 |
| TVA | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.011 | 0.061 | 1315.641 |
| Stock | TS9 | TS8 | TVS | TVR | TVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS9 | 56.02 | 43.98 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TS8 | 52.63 | 47.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TVS | 17.41 | 11.17 | 60.71 | 0.00 | 10.71 |
| TVR | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 |
| TVA | 0.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 | 0.00 | 80.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernaś, R.; Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; Árnyasi, M.; Kent, M.P.; Lien, S.; Wenne, R. Genetic Differentiation in Hatchery and Stocked Populations of Sea Trout in the Southern Baltic: Selection Evidence at SNP Loci. Genes 2020, 11, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020184
Bernaś R, Poćwierz-Kotus A, Árnyasi M, Kent MP, Lien S, Wenne R. Genetic Differentiation in Hatchery and Stocked Populations of Sea Trout in the Southern Baltic: Selection Evidence at SNP Loci. Genes. 2020; 11(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernaś, Rafał, Anita Poćwierz-Kotus, Mariann Árnyasi, Matthew Peter Kent, Sigbjørn Lien, and Roman Wenne. 2020. "Genetic Differentiation in Hatchery and Stocked Populations of Sea Trout in the Southern Baltic: Selection Evidence at SNP Loci" Genes 11, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020184
APA StyleBernaś, R., Poćwierz-Kotus, A., Árnyasi, M., Kent, M. P., Lien, S., & Wenne, R. (2020). Genetic Differentiation in Hatchery and Stocked Populations of Sea Trout in the Southern Baltic: Selection Evidence at SNP Loci. Genes, 11(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020184





