Evolutionary Dynamics of the POTE Gene Family in Human and Nonhuman Primates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval of POTE Gene Entries in Human and Nonhuman Primates
2.2. Features and Domain Prediction of POTE Transcripts
2.3. FISH Analysis
2.4. Radioactive Screening on High-Density Filters
2.5. PacBio Callithrix Jacchus BAC Sequencing and Assembly
2.6. Phylogenetic and LINE Analyses
2.7. Gene Expression
2.8. Estimating the Timing of Human-Specific POTE Duplications
3. Results
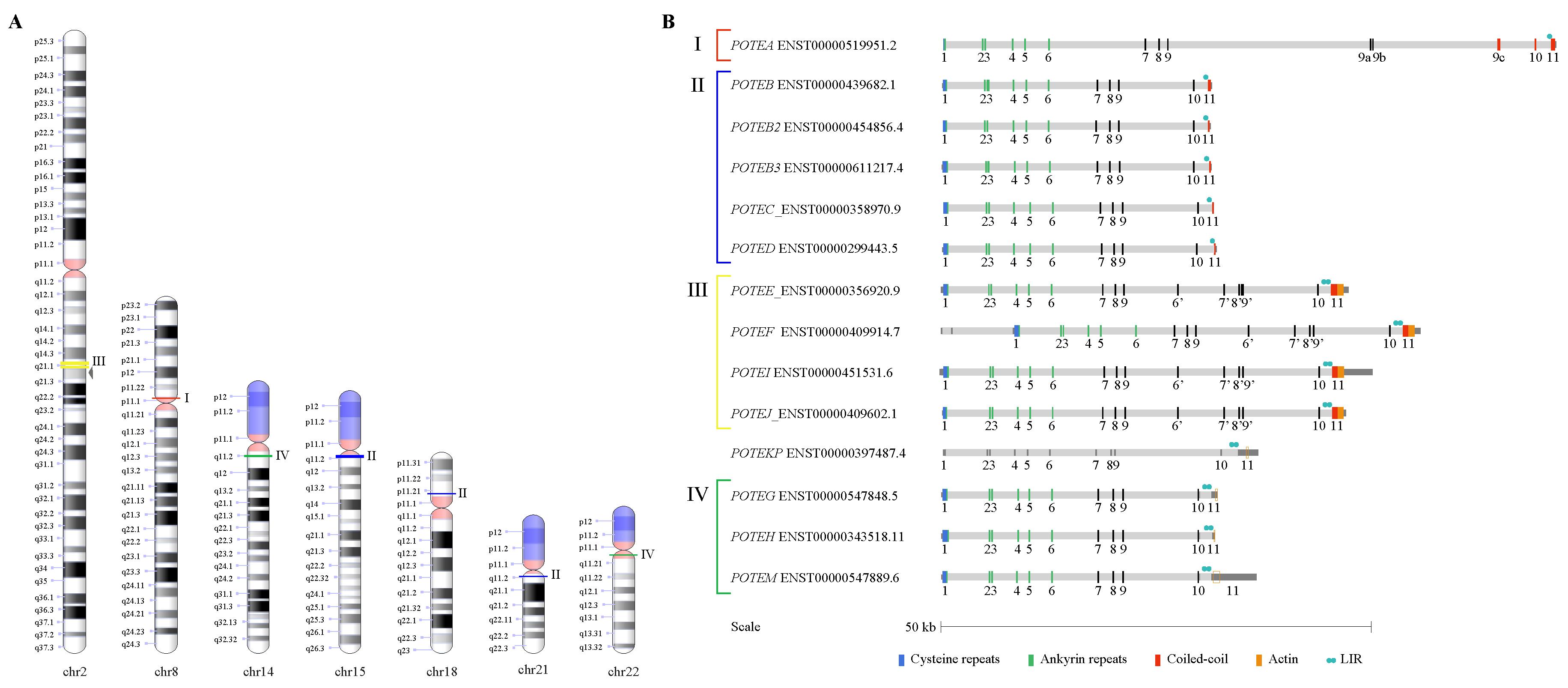
3.1. POTE Gene Family in the Human Genome
3.2. POTE Expression Levels in Cancer
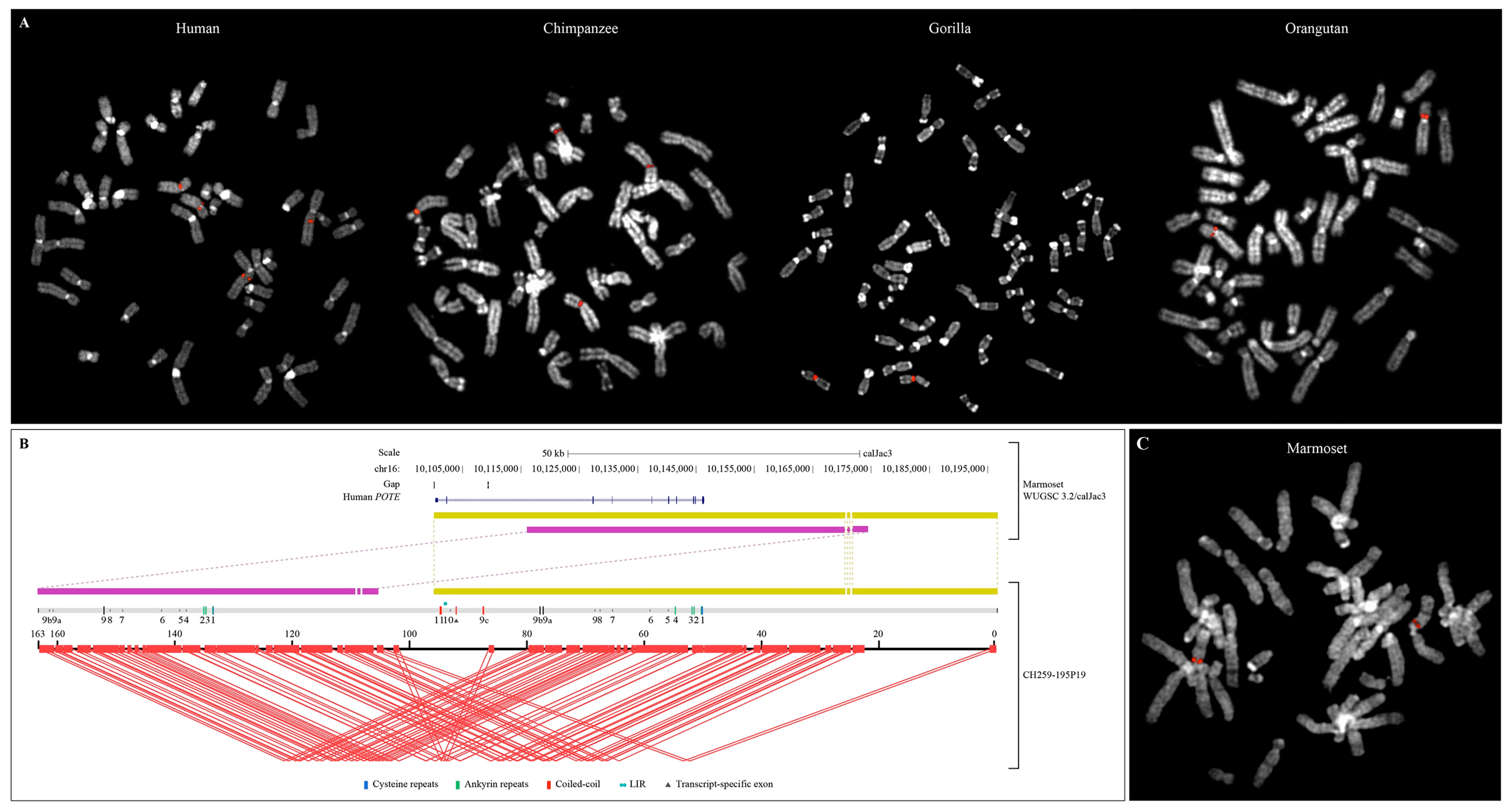
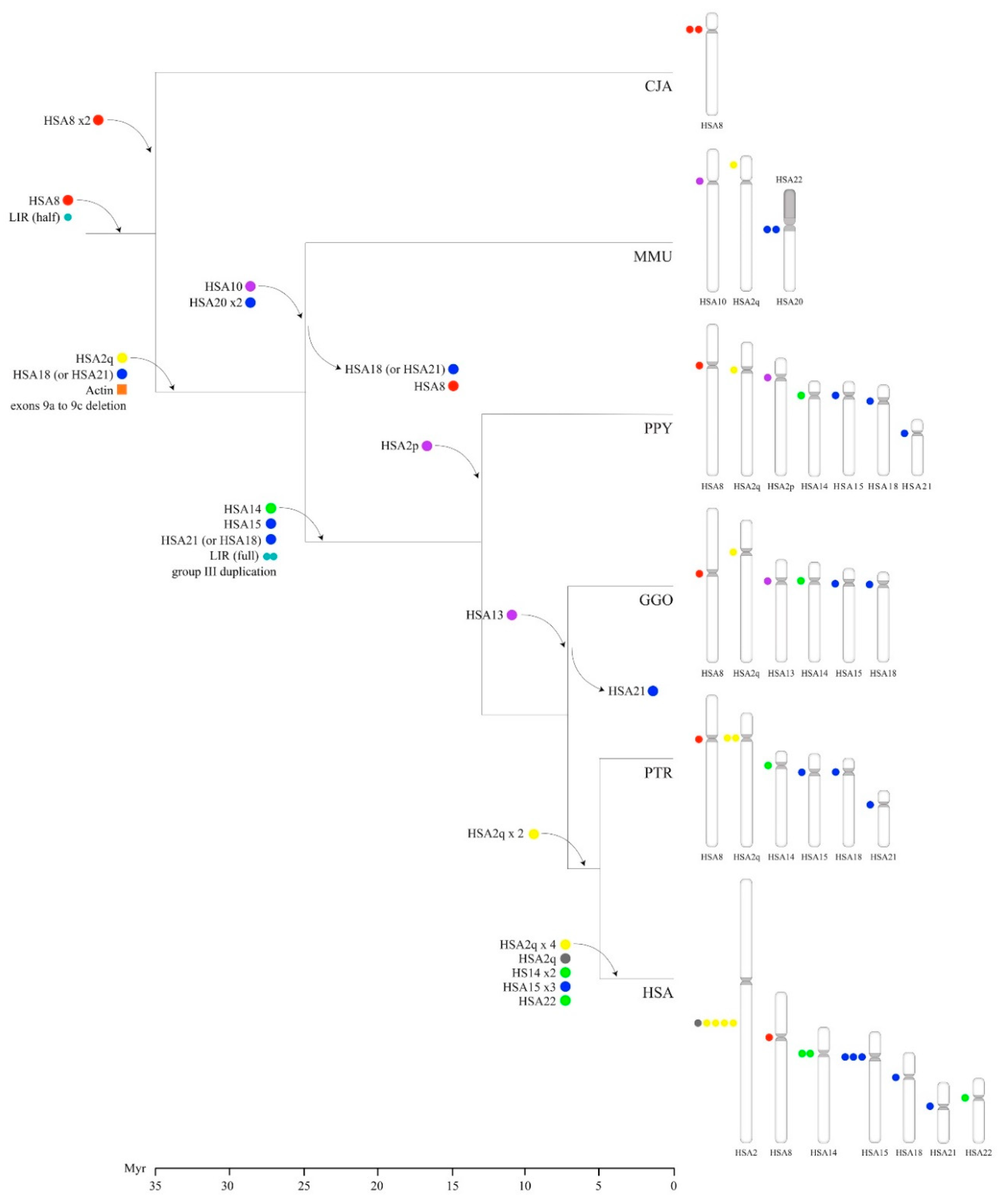
3.3. POTE Gene Family in Primate Genomes
3.4. Structure of the Intraduplication of POTE Genes
3.5. Repetitive Elements in POTE Genes
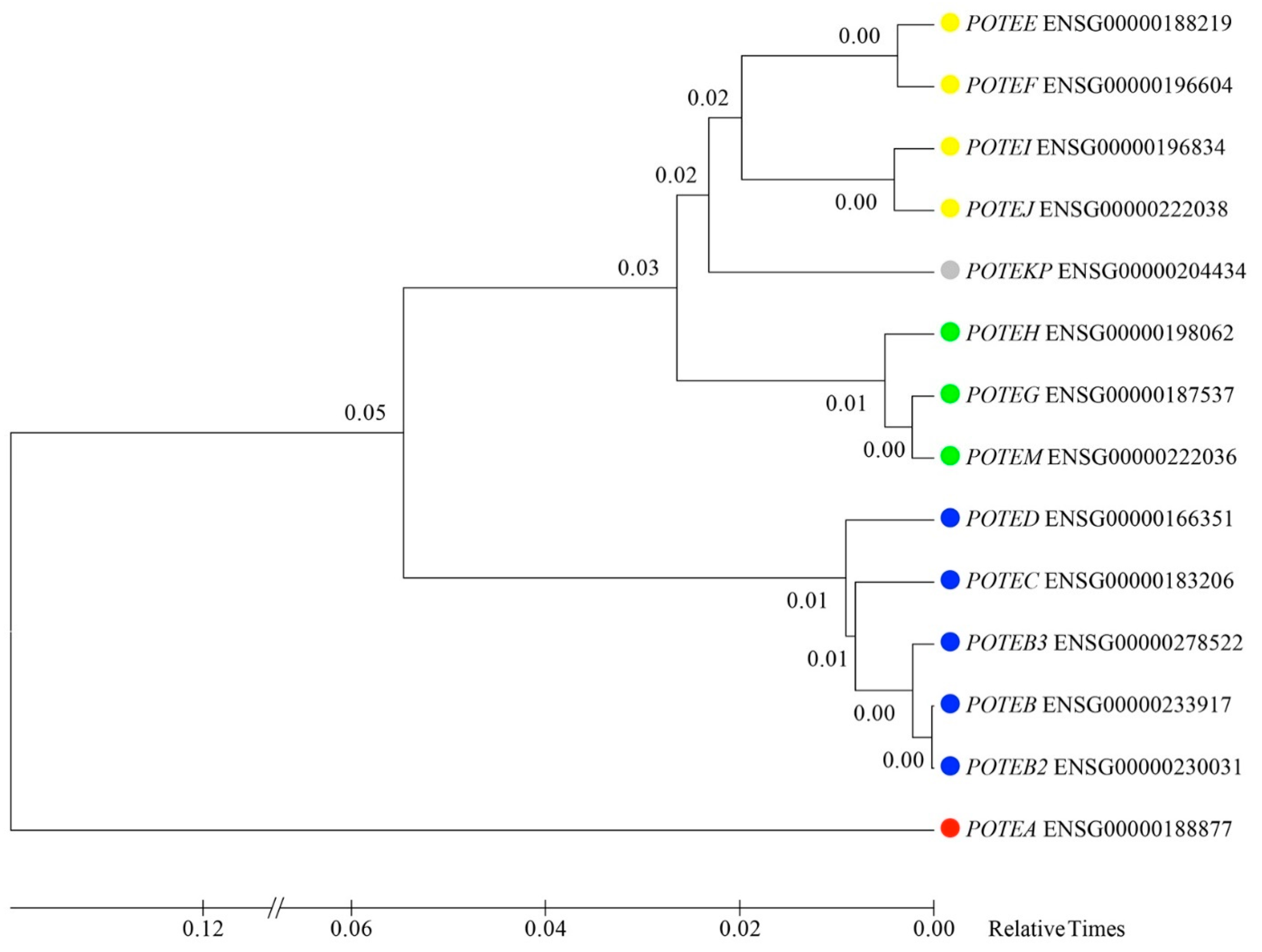
3.6. Inferring the Evolutionary Relationships of POTE Paralogs
3.7. Timing of Human-Specific POTE Duplications
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Access
References
- Alkan, C.; Kidd, J.M.; Marques-Bonet, T.; Aksay, G.; Antonacci, F.; Hormozdiari, F.; Kitzman, J.O.; Baker, C.; Malig, M.; Mutlu, O.; et al. Personalized copy number and segmental duplication maps using next-generation sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.A.; Yavor, A.M.; Massa, H.F.; Trask, B.J.; Eichler, E.E. Segmental duplications: Organization and impact within the current human genome project assembly. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafrate, A.J.; Feuk, L.; Rivera, M.N.; Listewnik, M.L.; Donahoe, P.K.; Qi, Y.; Scherer, S.W.; Lee, C. Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itsara, A.; Cooper, G.M.; Baker, C.; Girirajan, S.; Li, J.; Absher, D.; Krauss, R.M.; Myers, R.M.; Ridker, P.M.; Chasman, D.I.; et al. Population analysis of large copy number variants and hotspots of human genetic disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catacchio, C.R.; Maggiolini, F.A.M.; D’Addabbo, P.; Bitonto, M.; Capozzi, O.; Lepore Signorile, M.; Miroballo, M.; Archidiacono, N.; Eichler, E.E.; Ventura, M.; et al. Inversion variants in human and primate genomes. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolini, F.A.M.; Cantsilieris, S.; D’Addabbo, P.; Manganelli, M.; Coe, B.P.; Dumont, B.L.; Sanders, A.D.; Pang, A.W.C.; Vollger, M.R.; Palumbo, O.; et al. Genomic inversions and GOLGA core duplicons underlie disease instability at the 15q25 locus. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.Y.; Eichler, E.E. Human adaptation and evolution by segmental duplication. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 41, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.Y.; Nuttle, X.; Sudmant, P.H.; Antonacci, F.; Graves, T.A.; Nefedov, M.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Sajjadian, S.; Malig, M.; Kotkiewicz, H.; et al. Evolution of human-specific neural SRGAP2 genes by incomplete segmental duplication. Cell 2012, 149, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, G.; Siswara, P.; Malig, M.; Marques-Bonet, T.; Mullikin, J.C.; Ventura, M.; Eichler, E.E.; Program, N.C.S. Evolutionary dynamism of the primate LRRC37 gene family. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, I.K.; Gacquer, D.; Van Heurck, R.; Kumar, D.; Wojno, M.; Bilheu, A.; Herpoel, A.; Lambert, N.; Cheron, J.; Polleux, F.; et al. Human-specific NOTCH2NL genes expand cortical neurogenesis through delta/notch regulation. Cell 2018, 173, 1370–1384.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddes, I.T.; Pollen, A.A.; Davis, J.M.; Sikela, J.M. Paired involvement of human-specific Olduvai domains and NOTCH2NL genes in human brain evolution. Hum. Genet. 2019, 138, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, A.J.; Caballero, O.L.; Jungbluth, A.; Chen, Y.T.; Old, L.J. Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulie, P.G.; Van den Eynde, B.J.; van der Bruggen, P.; Boon, T. Tumour antigens recognized by T lymphocytes: At the core of cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Albahrani, M.; Zhang, W.; Kufel, C.N.; James, S.R.; Odunsi, K.; Klinkebiel, D.; Karpf, A.R. Epigenetic activation of POTE genes in ovarian cancer. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Popescu, N.C.; Sathyanarayana, B.K.; Kumar, V.; Lee, B.; Pastan, I. POTE, a highly homologous gene family located on numerous chromosomes and expressed in prostate, ovary, testis, placenta, and prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16975–16980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, C.J.; Zhang, W.; Sharma, A.; Chee, L.; James, S.R.; Kufel, C.N.; Miller, A.; Meza, J.; Drapkin, R.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Expression of the POTE gene family in human ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K.; Saint Fleur, A.; Lee, Y.; Kydd, A.; Hahn, Y.; Popescu, N.C.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Lee, B.; Pastan, I. POTE paralogs are induced and differentially expressed in many cancers. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, S.M.; Mao, J.; Zhu, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bigler, S.A.; Zhou, X. The C-terminal common to group 3 POTES (CtG3P): A newly discovered nucleolar marker associated with malignant progression and metastasis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, T.K.; Saint Fleur, A.; Ha, D.; Yamada, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, B.; Hahn, Y.; Kaufman, D.S.; Pera, M.; Pastan, I. Selective POTE paralogs on chromosome 2 are expressed in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, Y.; Bera, T.K.; Pastan, I.H.; Lee, B. Duplication and extensive remodeling shaped POTE family genes encoding proteins containing ankyrin repeat and coiled coil domains. Gene 2006, 366, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, G.; Pazienza, M.; Huddleston, J.; Antonacci, F.; Malig, M.; Vives, L.; Eichler, E.E.; Ventura, M. Hominoid fission of chromosome 14/15 and the role of segmental duplications. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Ise, T.; Ha, D.; Saint Fleur, A.; Hahn, Y.; Liu, X.F.; Nagata, S.; Lee, B.; Bera, T.K.; Pastan, I. Evolution and expression of chimeric POTE-actin genes in the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17885–17890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, T.K.; Huynh, N.; Maeda, H.; Sathyanarayana, B.K.; Lee, B.; Pastan, I. Five POTE paralogs and their splice variants are expressed in human prostate and encode proteins of different lengths. Gene 2004, 337, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Leung, F.C. Discovery of a long inverted repeat in human POTE genes. Genomics 2009, 94, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J. BLAT—The BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, P.; Jauch, A.; Cremer, T.; Ward, D.C. Detection of Down syndrome by in situ hybridization with chromosome 21 specific DNA probes. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1990, 360, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Vollger, M.R.; Logsdon, G.A.; Audano, P.A.; Sulovari, A.; Porubsky, D.; Peluso, P.; Wenger, A.M.; Concepcion, G.T.; Kronenberg, Z.N.; Munson, K.M.; et al. Improved assembly and variant detection of a haploid human genome using single-molecule, high-fidelity long reads. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Battistuzzi, F.U.; Billing-Ross, P.; Murillo, O.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. Estimating divergence times in large molecular phylogenies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19333–19338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, R.; Cantor, C.; Jukes, T. Improved procedures for comparing homologous sequences in molecules of proteins and nucleic acids. J. Mol. Biol. 1972, 64, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, H.; Bray, N.L.; Puente, S.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Differential analysis of RNA-seq incorporating quantification uncertainty. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, B.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.A.; Seal, R.L.; Tweedie, S.; Bruford, E.A. Genenames.org: The HGNC and VGNC resources in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D619–D625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Copley, R.R.; Doerks, T.; Ponting, C.P.; Bork, P. SMART: A web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupas, A.; Van Dyke, M.; Stock, J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 1991, 252, 1162–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.; Chaisson, M.J.P.; Steinberg, K.M.; Warren, W.; Hoekzema, K.; Gordon, D.; Graves-Lindsay, T.A.; Munson, K.M.; Kronenberg, Z.N.; Vives, L.; et al. Discovery and genotyping of structural variation from long-read haploid genome sequence data. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, M.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: A web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W465–W467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Smit, A.; Boissinot, S. Molecular evolution and tempo of amplification of human LINE-1 retrotransposons since the origin of primates. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.; Garcia, R.; Shelledy, W.; Kaplan, J.; Arya, A.; Johnson, Z.; Bergstrom, M.; Novakowski, L.; Nair, P.; Vinson, A.; et al. An initial genetic linkage map of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) genome using human microsatellite loci. Genomics 2006, 87, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marques-Bonet, T.; Kidd, J.M.; Ventura, M.; Graves, T.A.; Cheng, Z.; Hillier, L.W.; Jiang, Z.; Baker, C.; Malfavon-Borja, R.; Fulton, L.A.; et al. A burst of segmental duplications in the genome of the African great ape ancestor. Nature 2009, 457, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, A.; Marmoset, G.S. The common marmoset genome provides insight into primate biology and evolution. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.A.; Church, D.M.; Ventura, M.; Rocchi, M.; Eichler, E.E. Analysis of segmental duplications and genome assembly in the mouse. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Bera, T.K.; Liu, L.J.; Pastan, I. A primate-specific POTE-actin fusion protein plays a role in apoptosis. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Antonacci, F.; Cardone, M.F.; Stanyon, R.; D’Addabbo, P.; Cellamare, A.; Sprague, L.J.; Eichler, E.E.; Archidiacono, N.; Rocchi, M. Evolutionary formation of new centromeres in macaque. Science 2007, 316, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunis, J.J.; Prakash, O. The origin of man: A chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science 1982, 215, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienberg, J.; Jauch, A.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Senger, G.; Horsthemke, B.; Claussen, U.; Cremer, T.; Arnold, N.; Lengauer, C. The origin of human chromosome 2 analyzed by comparative chromosome mapping with a DNA microlibrary. Chromosome Res. 1994, 2, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Archidiacono, N.; Antonacci, R.; Marzella, R.; Finelli, P.; Lonoce, A.; Rocchi, M. Comparative mapping of human alphoid sequences in great apes using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics 1995, 25, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, I.A.; Mitkevich, S.P.; Yurov, Y.B. The phylogeny of human chromosome specific alpha satellites. Chromosoma 1988, 96, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catacchio, C.R.; Ragone, R.; Chiatante, G.; Ventura, M. Organization and evolution of Gorilla centromeric DNA from old strategies to new approaches. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Mudge, J.M.; Palumbo, V.; Burn, S.; Blennow, E.; Pierluigi, M.; Giorda, R.; Zuffardi, O.; Archidiacono, N.; Jackson, M.S.; et al. Neocentromeres in 15q24-26 map to duplicons which flanked an ancestral centromere in 15q25. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, E.E.; Lu, F.; Shen, Y.; Antonacci, R.; Jurecic, V.; Doggett, N.A.; Moyzis, R.K.; Baldini, A.; Gibbs, R.A.; Nelson, D.L. Duplication of a gene-rich cluster between 16p11.1 and Xq28: A novel pericentromeric-directed mechanism for paralogous genome evolution. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandepoele, K.; Van Roy, N.; Staes, K.; Speleman, F.; van Roy, F. A novel gene family NBPF: Intricate structure generated by gene duplications during primate evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.E.; Viggiano, L.; Bailey, J.A.; Abdul-Rauf, M.; Goodwin, G.; Rocchi, M.; Eichler, E.E. Positive selection of a gene family during the emergence of humans and African apes. Nature 2001, 413, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, E.E.; Budarf, M.L.; Rocchi, M.; Deaven, L.L.; Doggett, N.A.; Baldini, A.; Nelson, D.L.; Mohrenweiser, H.W. Interchromosomal duplications of the adrenoleukodystrophy locus: A phenomenon of pericentromeric plasticity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Hedges, S.B. TimeTree: A resource for timelines, timetrees, and divergence times. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.s; Rooney, A.P. Concerted and birth-and-death evolution of multigene families. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HGNC ID | Approved Symbol | Approved Name | Ensembl ID | Synonyms | Genomic Localization | Gene Size (bp) | Transcript Variants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33893 | POTEA | POTE ankyrin domain family member A | ENSG00000188877 | POTE8, POTE-8, CT104.3 | 8p11.1 | 71,036 | 2 |
| 33734 | POTEB | POTE ankyrin domain family member B | ENSG00000233917 | POTE15, POTE-15, CT104.5 | 15q11.2 | 31,375 | 4 |
| 48327 | POTEB2 | POTE ankyrin domain family member B2 | ENSG00000230031 | 15q11.2 | 30,943 | 2 | |
| 51240 | POTEB3 | POTE ankyrin domain family member B3 | ENSG00000278522 | 15q11.2 | 32,209 | 3 | |
| 33894 | POTEC | POTE ankyrin domain family member C | ENSG00000183206 | POTE18, POTE-18, DKFZp686J0529, CT104.6 | 18p11.21 | 36,247 | 4 |
| 23822 | POTED | POTE ankyrin domain family member D | ENSG00000166351 | POTE, POTE-21, POTE21, CT104.1 | 21q11.2 | 31,728 | 2 |
| 33895 | POTEE | POTE ankyrin domain family member E | ENSG00000188219 | POTE2, POTE-2, A26C1, POTE2gamma, CT104.2 | 2q21.1 | 47,212 | 5 |
| 33905 | POTEF | POTE ankyrin domain family member F | ENSG00000196604 | POTEACTIN, POTE2alpha | 2q21.1 | 55,688 | 2 |
| 33896 | POTEG | POTE ankyrin domain family member G | ENSG00000187537 | POTE14, POTE-14, POTE14alpha, CT104.4 | 14q11.2 | 31,856 | 3 |
| 133 | POTEH | POTE ankyrin domain family member H | ENSG00000198062 | POTE22, CT104.7 | 22q11.1 | 31,606 | 3 |
| 37093 | POTEI | POTE ankyrin domain family member I | ENSG00000196834 | POTE2beta | 2q21.1 | 50,253 | 3 |
| 37094 | POTEJ | POTE ankyrin domain family member J | ENSG00000222038 | POTE2beta | 2q21.1 | 46,611 | 1 |
| 30182 | POTEKP | POTE ankyrin domain family member K, pseudogene | ENSG00000204434 | FKSG30, POTE2delta | 2q21.1 | 36,396 | NA |
| 37096 | POTEM | POTE ankyrin domain family member M | ENSG00000222036 | POTE14beta, P704P, ACT | 14q11.2 | 36,319 | 3 |
| Ensembl Gene ID | Approved SYMBOL | Gene Exons # | LIR | β-Actin Retrogene | Cysteine Repeats # | Ankyrin Repeats # | Coiled Coils # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group1 | |||||||
| ENSG00000188877 | POTEA | 14 | half (low similarity) | no | 1 | 7 * | 4 |
| Group2 | |||||||
| ENSG00000233917 | POTEB | 11 | half | no | 2 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000230031 | POTEB2 | 11 | half | no | 2 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000278522 | POTEB3 | 11 | half | no | 3 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000183206 | POTEC | 11 | half | no | 3 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000166351 | POTED | 11 | half | no | 3 | 7 * | 2 |
| Group3 | |||||||
| ENSG00000188219 | POTEE | 15 | full | yes | 3 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000196604 | POTEF | 17 | full | yes | 3 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000196834 | POTEI | 15 | full | yes | 3 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000222038 | POTEJ | 15 | full | yes | 2 | 7 * | 1 |
| ENSG00000204434 | POTEKP | 11 | full | yes (out of the CDS) | NA | NA | NA |
| Group4 | |||||||
| ENSG00000187537 | POTEG | 12 | full | yes (out of the CDS) | 3 | 7 * | 0 |
| ENSG00000198062 | POTEH | 12 | full | yes (out of the CDS) | 3–4 | 7 * | 0 |
| ENSG00000222036 | POTEM | 12 | full | yes (out of the CDS) | 3 | 7 * | 0 |
| Species/Assembly | Ensembl Gene ID, Approved Symbol | Retrieved as Ortholog of Human | Mapping | Gene Exons # | Ensemble Transcript IDs | LIR | β-Actin Retrogene Position (aa) | Cysteine Repeats # | Ankyrin Repeats # | Coiled Coils # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes)/Pan_tro 3.0/panTro5 | ENSPTRG00000022971, POTEA | POTEA | 8p (HSA8p) | 12 | ENSPTRT00000042301.5 | no 1 | no | 1 | 7 | 1 |
| ENSPTRG00000006815, POTEB | Group II genes | 15q (HSA15q) | 11 | ENSPTRT00000042433.5 | half | no | 3 | 7 | 1 | |
| ENSPTRT00000100986.1 | no | no | 3 | 7 | 0 | |||||
| ENSPTRG00000022897 | POTEE/F | 2Bp (HSA2q) | 16 | ENSPTRT00000037475.5 | full | 708-1078 | 3 | 7 | 1 | |
| ENSPTRT00000050738.5 | no | no | 3 | 7 | 0 | |||||
| ENSPTRG00000024151 | POTEI/POTEJ | 2Bp (HSA2q) | 13 | ENSPTRT00000092585.1 | no | no | 3 | 7 | 0 | |
| ENSPTRT00000089094.1 | no | no | 3 | 7 | 0 | |||||
| ENSPTRT00000078184.1 | no | no | 3 | 7 | 0 | |||||
| ENSPTRG00000050347 | Group IV genes | 14q (HSA14q) | 8 | ENSPTRT00000092958.1 | full 1 | NA | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla)/gorGor4.1/gorGor4 | ENSGGOG00000028525 | POTEA | 8q (HSA8p) | 11 | ENSGGOT00000024046.2 | no | NA | 1 | 7 | 1 |
| ENSGGOG00000015216 | Group II genes | 15 (HSA15q) | 7 | ENSGGOT00000015273.3 | half 1 | NA | 1 | 7 | 0 | |
| ENSGGOG00000007645 | Group III genes | 2Bq (HSA2q) | 9 | ENSGGOT00000029469.2 | full 1 | yes 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | |
| Orangutan (Pongo abelii)/WUGSC 2.0.2/ponAbe2 | ENSPPYG00000018567, POTEA | POTEA | 8 (HSA8p) | 14 | ENSPPYT00000021656.1 | half | no | 1 | 7 | 2 |
| ENSPPYG00000019944 | Group II genes | Un (HSA15q) | 5 | ENSPPYT00000023266.1 | NA | no | 3 | 5 | 0 | |
| ENSPPYT00000023267.1 | NA | no | 2 | 5 | 0 | |||||
| ENSPPYG00000005548 | Group III genes | 14 (HSA14q) | 11 | ENSPPYT00000006570.1 | full 1 | yes 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| ENSPPYG00000012746 | Group IV genes | 2B (HSA2q) | 11 | ENSPPYT00000014802.1 | full | yes 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | |
| Macaque (Macaca mulatta)/BCM Mmul_8.0.1/rheMac8 | ENSMMUG00000031128 | POTEA2 | 10q (HSA20) | 7 | ENSMMUT00000044360.3 | no | NA | 3 | 7 | 0 |
| ENSMMUG00000001813 | Group III-IV genes | 10q (HSA20) | 6 | ENSMMUT00000047624.3 | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | 0 | |
| ENSMMUG00000041125 | Group III-IV genes | 12 (HSA2q) | 6 | ENSMMUT00000044359.3 | no | NA | 1 | 6 | 0 | |
| Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus)/ASM275486v1 | ENSCJAG00000033335 | Group II-III-IV genes | Contig NTIC01007779.1 | 7 | ENSCJAT00000063391.3 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| ENSCJAT00000098614.1 | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | 0 | |||||
| CH259-195P19_g1 3 | NA | 16p (HSA8p) | 9 4 | NA | half | no | 1 | 5 | 2 | |
| CH259-195P19_g2 3 | NA | 16p (HSA8p) | 4 4 | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| HSA2p | HSA2q | HSA8 | HSA10 | HSA13 | HSA14 | HSA15 | HSA18 | HSA20 | HSA21 | HSA22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | yes | yes 1 | yes 2 | yes 2 | yes 2 | yes 2 | yes 2 | ||||
| Chimpanzee | yes (PTR13) | yes (PTR7) 1 | yes (PTR15) 2 | yes (PTR16) 2 | yes (PTR17) 2 | yes (PTR22) 2 | |||||
| Gorilla | yes (GGO11) 2 | yes (GGO7) 1 | yes (GGO14) 3 | yes (GGO18) 2 | yes (GGO15) 2 | yes (GGO16) 2 | |||||
| Orangutan | yes (PPY12) 2 | yes (PPY11) 2 | yes (PPY6) 1 | yes (PPY15) 2 | yes (PPY16) 2 | yes (PPY17) 2 | yes (PPY 22) 2 | ||||
| Macaque | yes (MMU12) 2 | yes (MMU9) 2 | yes (MMU10) 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maggiolini, F.A.M.; Mercuri, L.; Antonacci, F.; Anaclerio, F.; Calabrese, F.M.; Lorusso, N.; L’Abbate, A.; Sorensen, M.; Giannuzzi, G.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. Evolutionary Dynamics of the POTE Gene Family in Human and Nonhuman Primates. Genes 2020, 11, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020213
Maggiolini FAM, Mercuri L, Antonacci F, Anaclerio F, Calabrese FM, Lorusso N, L’Abbate A, Sorensen M, Giannuzzi G, Eichler EE, et al. Evolutionary Dynamics of the POTE Gene Family in Human and Nonhuman Primates. Genes. 2020; 11(2):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaggiolini, Flavia Angela Maria, Ludovica Mercuri, Francesca Antonacci, Fabio Anaclerio, Francesco Maria Calabrese, Nicola Lorusso, Alberto L’Abbate, Melanie Sorensen, Giuliana Giannuzzi, Evan E. Eichler, and et al. 2020. "Evolutionary Dynamics of the POTE Gene Family in Human and Nonhuman Primates" Genes 11, no. 2: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020213
APA StyleMaggiolini, F. A. M., Mercuri, L., Antonacci, F., Anaclerio, F., Calabrese, F. M., Lorusso, N., L’Abbate, A., Sorensen, M., Giannuzzi, G., Eichler, E. E., Catacchio, C. R., & Ventura, M. (2020). Evolutionary Dynamics of the POTE Gene Family in Human and Nonhuman Primates. Genes, 11(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020213







