Differential Responses of LINE-1 in the Dentate Gyrus, Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex to Chronic Neurotoxic Methamphetamine: A Study in Rat Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
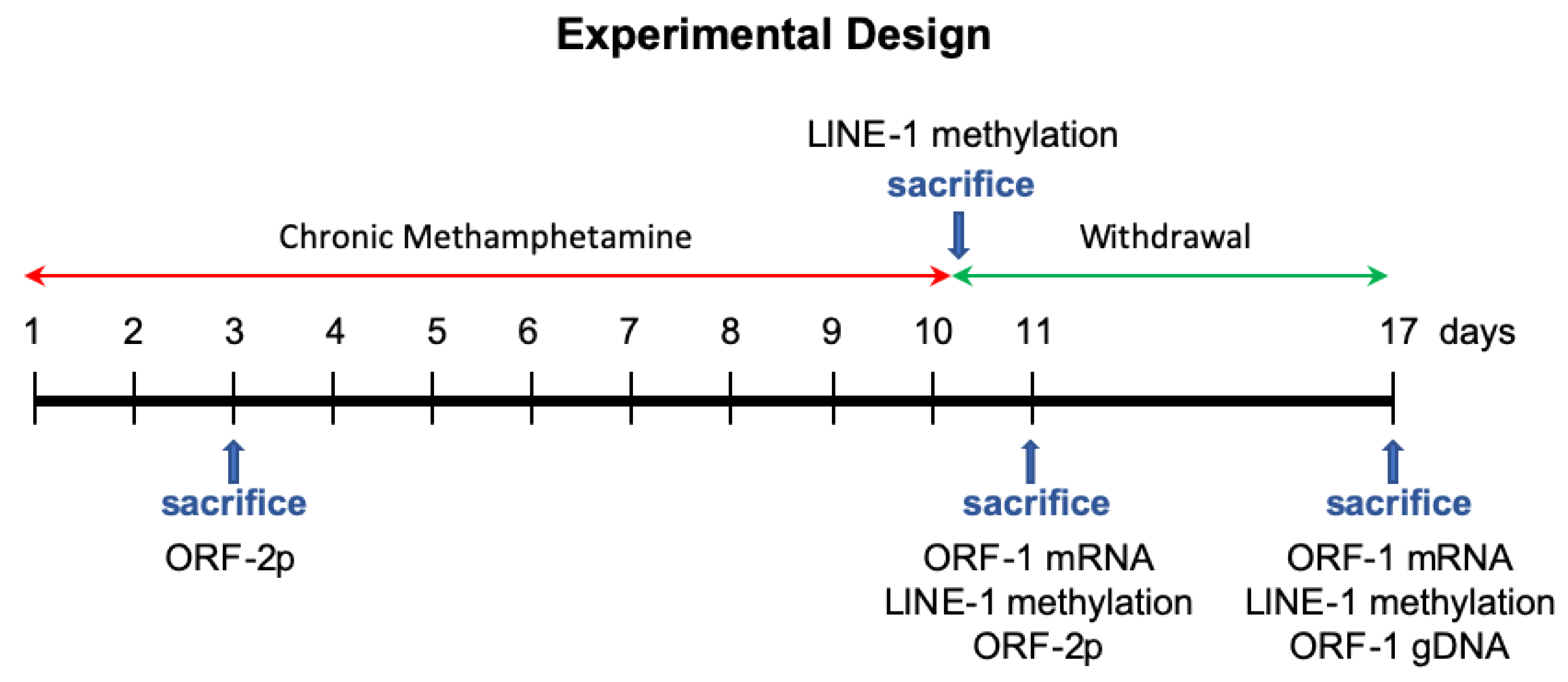
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Administration of Methamphetamine
2.3. Tissue Collection
2.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Pyrosequencing
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
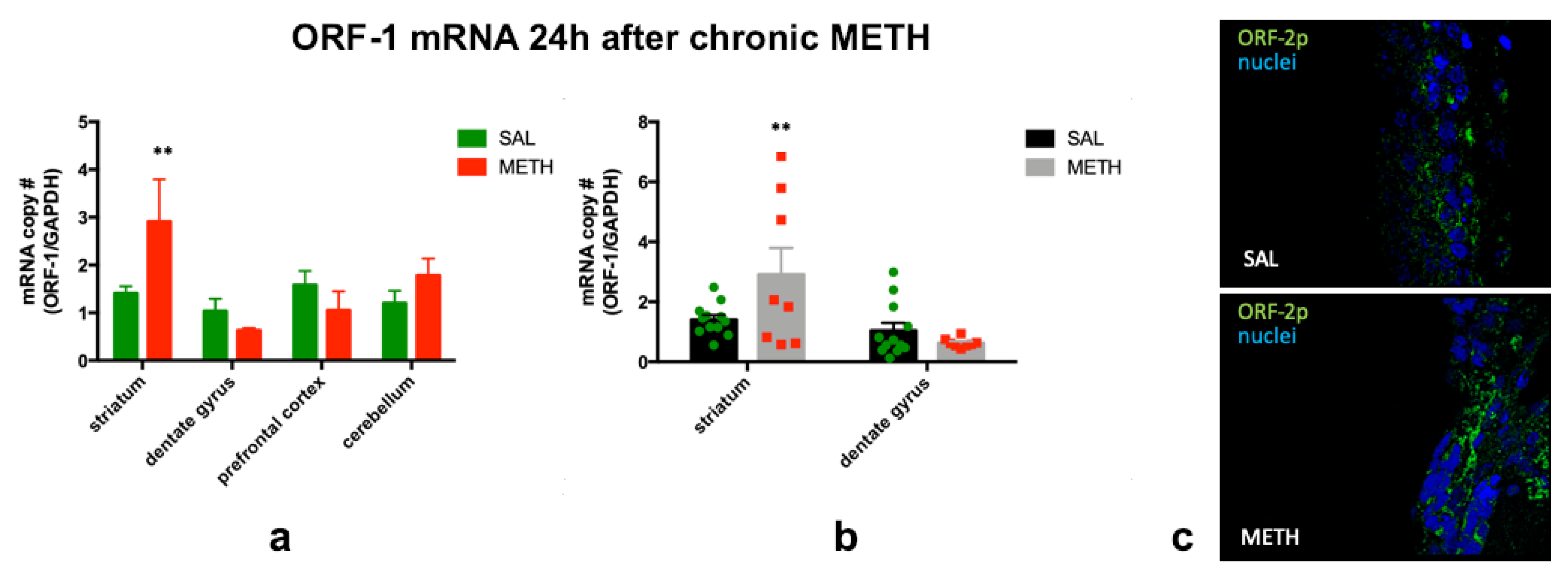
3.1. Chronic METH Treatment Increases ORF-1 mRNA Levels in the Striatum of Adult Rat Brain
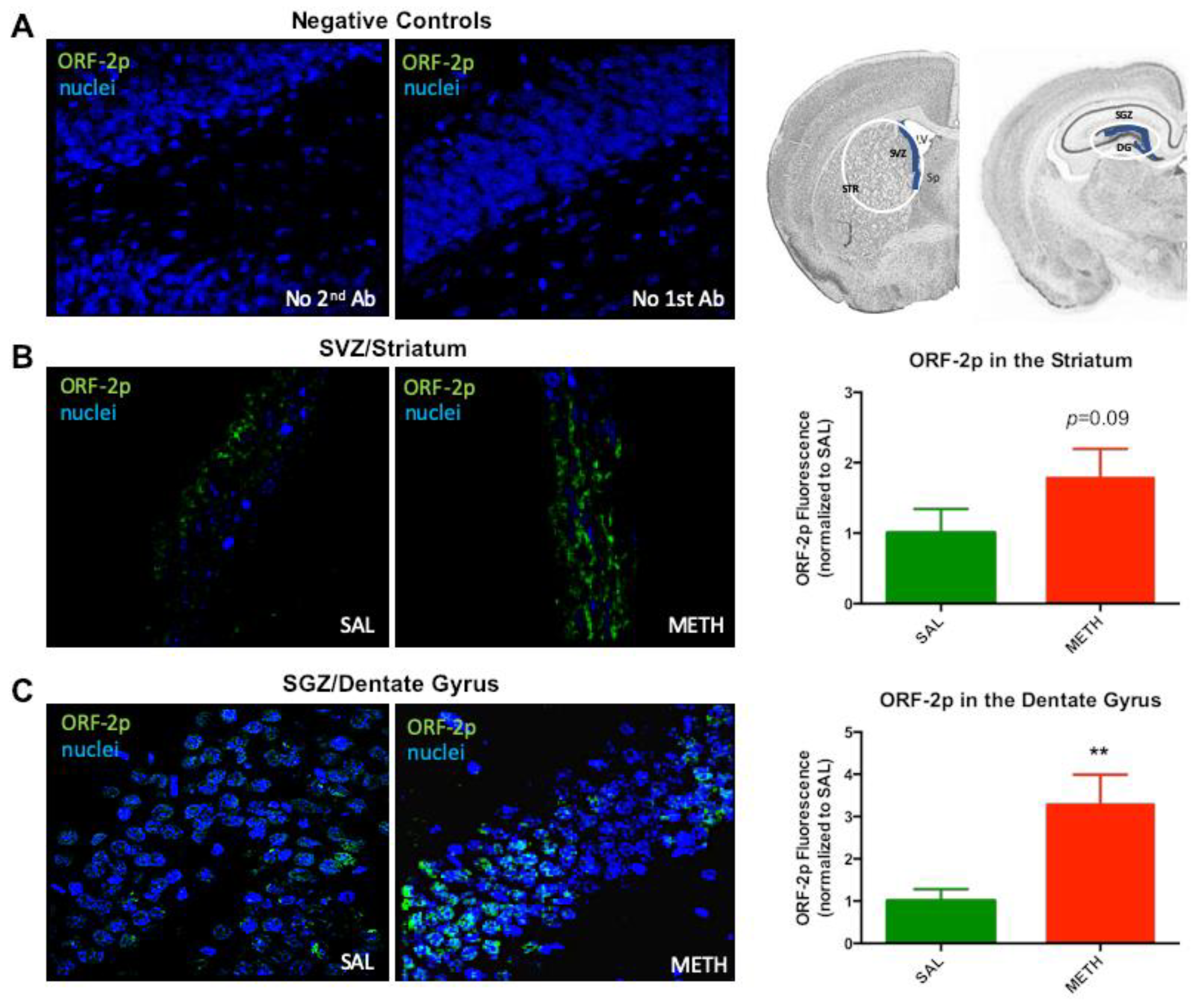
3.2. Expression of ORF-2p is Increased on the Third Day of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment
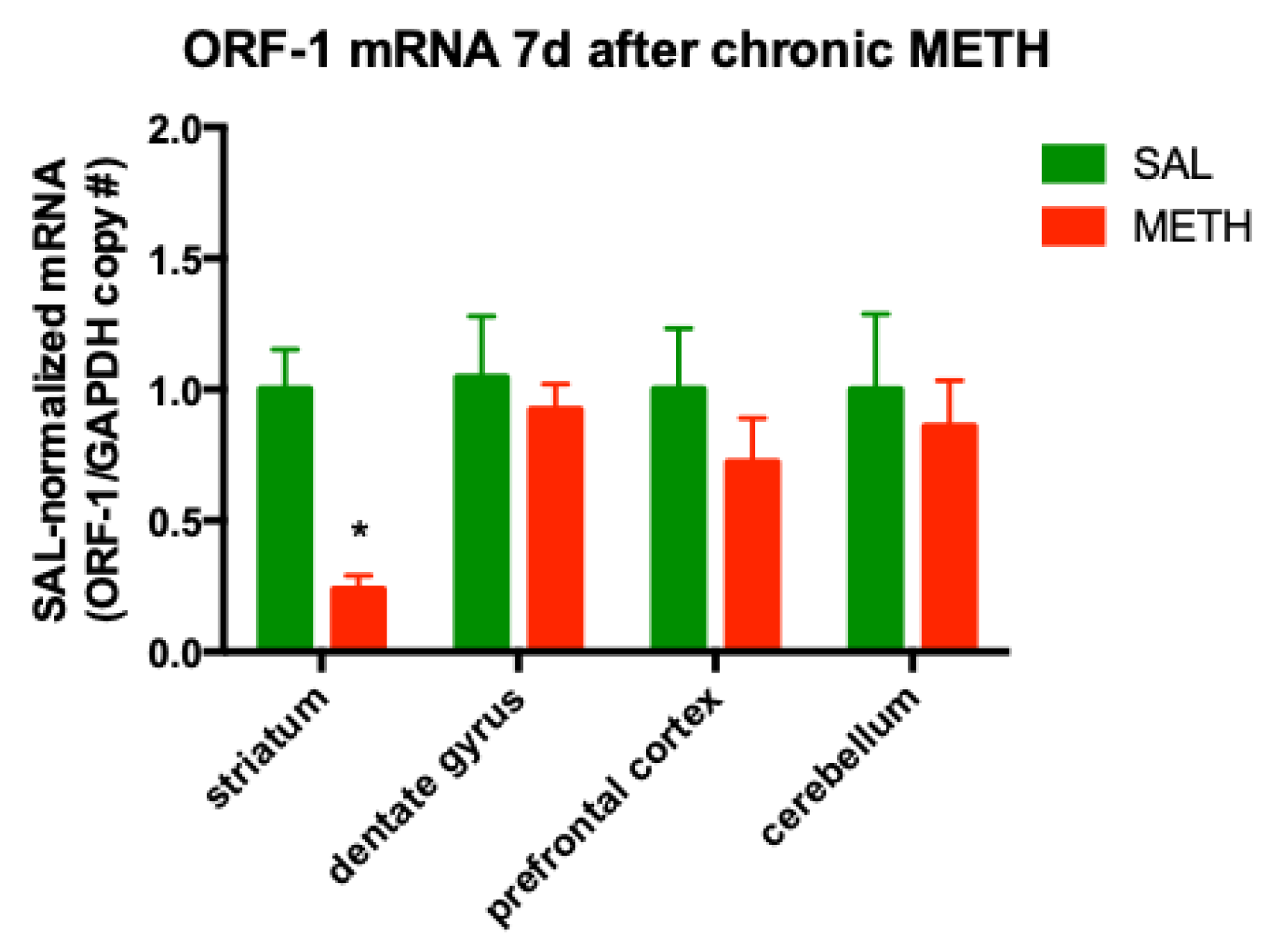
3.3. Chronic METH Treatment Leads to a Persistent Decrease in ORF-1 mRNA Levels in the Striatum of Adult Rat Brain
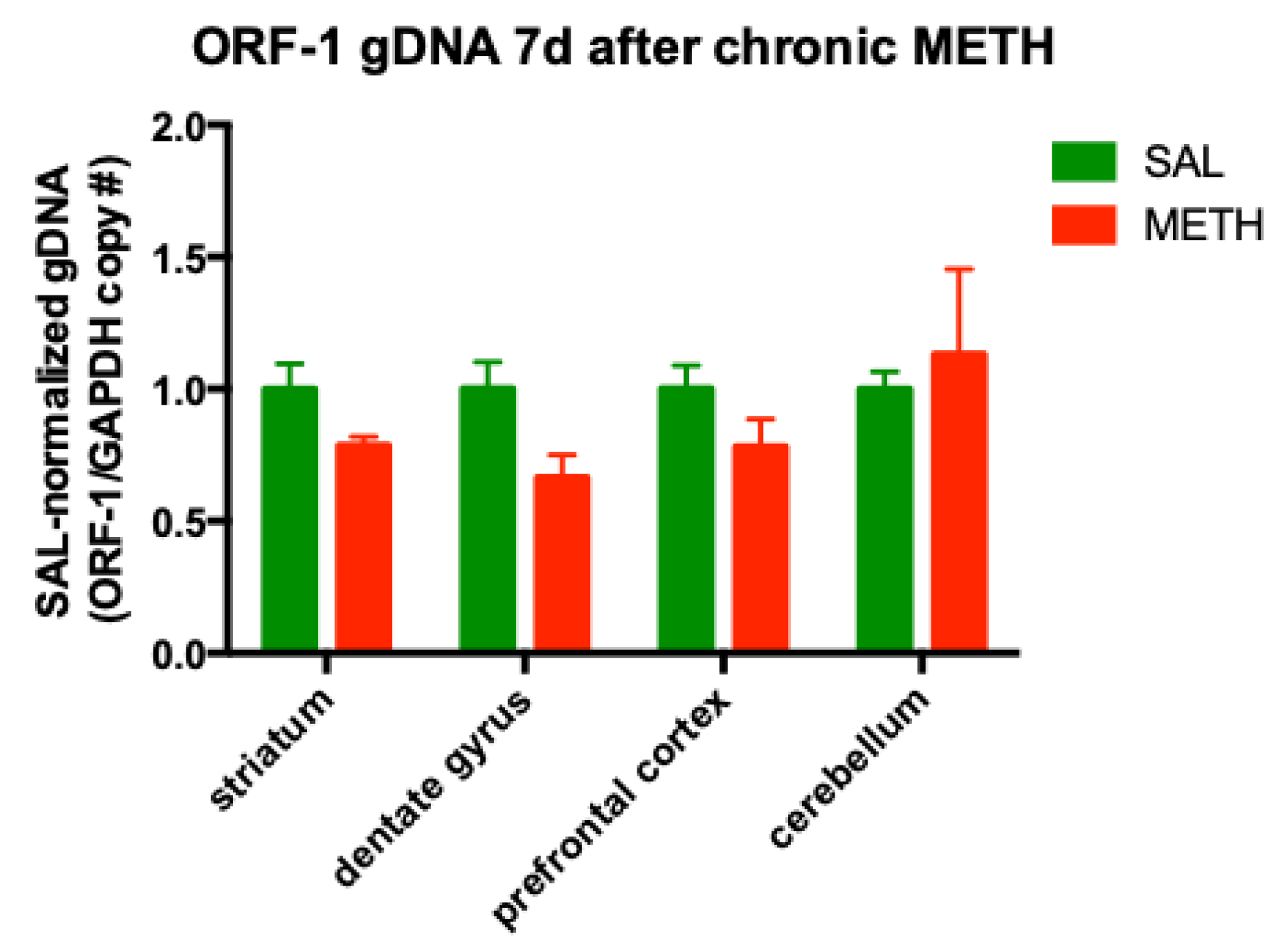
3.4. Chronic METH Has no Significant Effect on the ORF-1 gDNA Levels in the Striatum and Dentate Gyrus of Adult Rat Brain
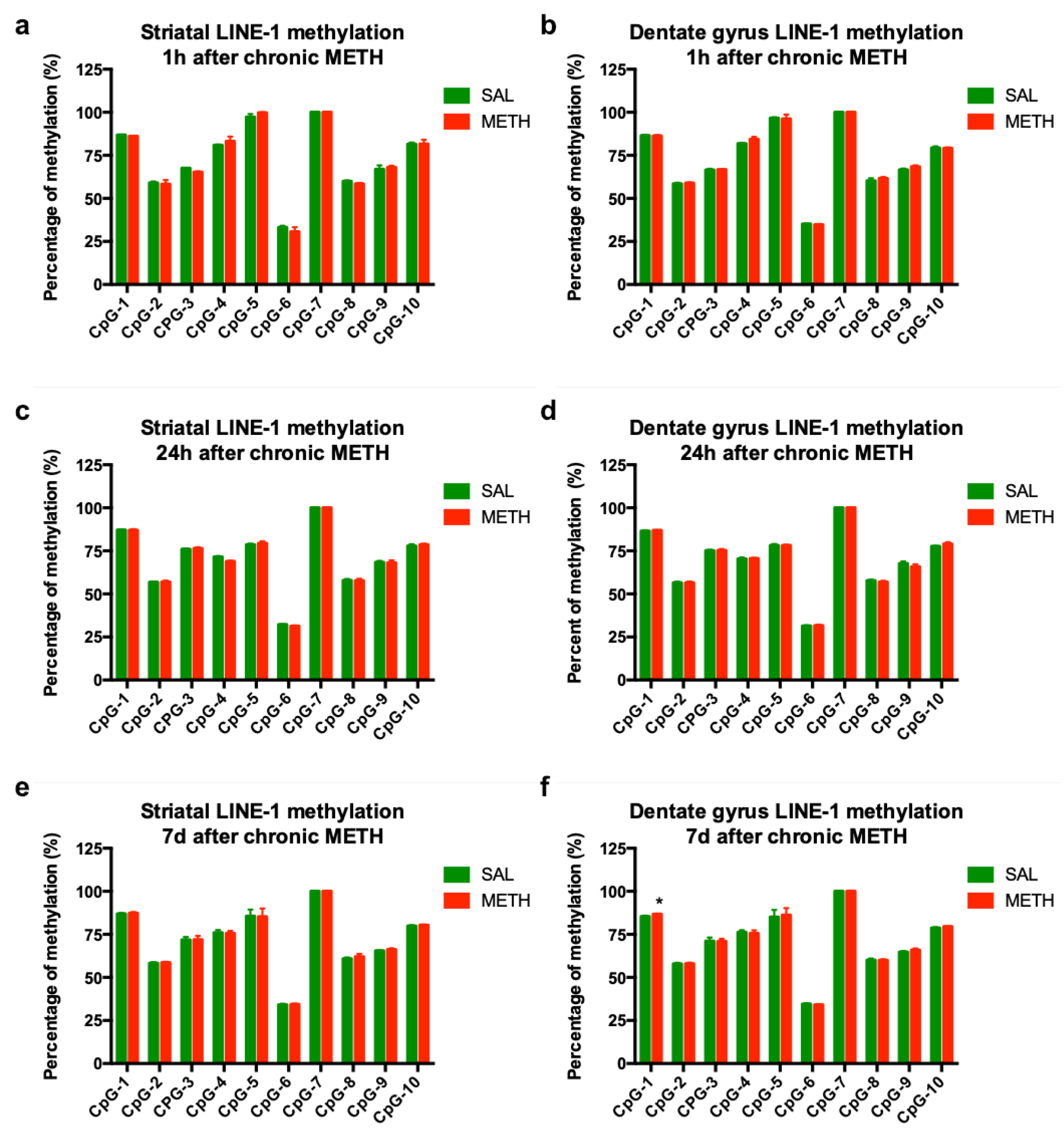
3.5. Chronic METH-Triggered Activation of LINE-1 Is Not Accompanied by Hypomethylation of LINE-1 Promoter
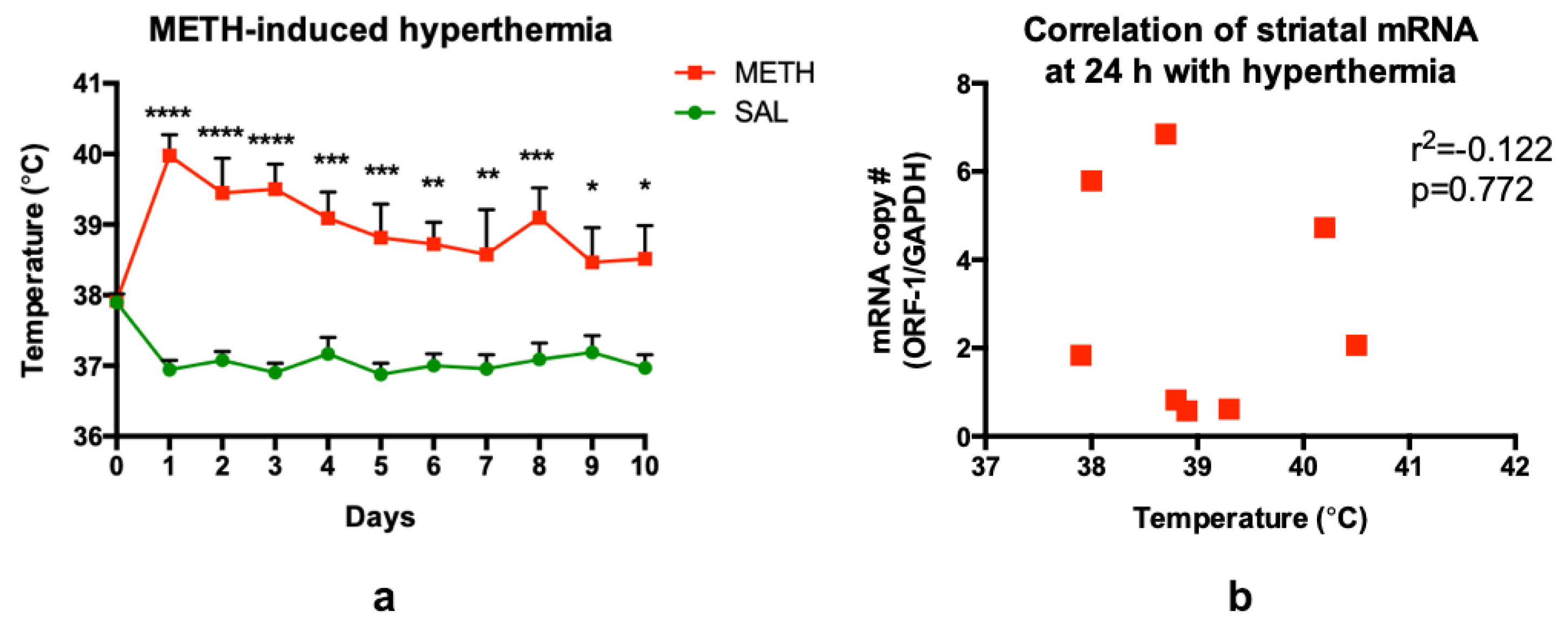
3.6. Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperthermia Does Not Contribute to LINE-1 Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jalal, H.; Buchanich, J.M.; Roberts, M.S.; Balmert, L.C.; Zhang, K.; Burke, D.S. Changing dynamics of the drug overdose epidemic in the United States from 1979 through 2016. Science 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIDA. Overdose Death Rates; National Institute on Drug Abuse: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018.
- Hart, C.L.; Marvin, C.B.; Silver, R.; Smith, E.E. Is cognitive functioning impaired in methamphetamine users? A critical review. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 586–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.R.; Bretz, S.W.; Johnson, E.B.; Turnipseed, S.D.; Brofeldt, B.T.; Derlet, R.W. Methamphetamine abuse and emergency department utilization. West. J. Med. 1999, 170, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, R.C.; Cunningham, J.K.; Sajeev, G.; Kish, S.J. Incidence of Parkinson’s disease among hospital patients with methamphetamine-use disorders. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, R.C.; Cunningham, J.K.; Sykes, J.; Kish, S.J. Increased risk of Parkinson’s disease in individuals hospitalized with conditions related to the use of methamphetamine or other amphetamine-type drugs. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012, 120, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, G.; Pearson-Dennett, V.; Wilcox, R.A.; Chau, M.T.; Thoirs, K.; Thewlis, D.; Vogel, A.P.; White, J.M. Adults with a history of illicit amphetamine use exhibit abnormal substantia nigra morphology and parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 25, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarone, D. Stimulant abuse: Pharmacology, cocaine, methamphetamine, treatment, attempts at pharmacotherapy. Prim. Care 2011, 38, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, K.E.; Ray, L.A. Methamphetamine: An update on epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical phenomenology, and treatment literature. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 143, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.K. Methamphetamine—Effects on human performance and behavior. Forensic. Sci. Rev. 2002, 14, 133–151. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, A.K.; Radle, M.; Beste, C. Methamphetamine-associated difficulties in cognitive control allocation may normalize after prolonged abstinence. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 88, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusyniak, D.E. Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Neurol. Clin. 2011, 29, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecht, M.L.; Lovinger, K.; Herbeck, D.M.; Urada, D. Patterns of treatment utilization and methamphetamine use during first 10 years after methamphetamine initiation. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2013, 44, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report; UN Office on Drugs and Crime: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte, G.A.; Guillery, R.W.; Seiden, L.S.; Schuster, C.R.; Moore, R.Y. Dopamine nerve terminal degeneration produced by high doses of methylamphetamine in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1982, 235, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Kalasinsky, K.S.; Levey, A.I.; Bergeron, C.; Reiber, G.; Anthony, R.M.; Schmunk, G.A.; Shannak, K.; Haycock, J.W.; Kish, S.J. Striatal dopamine nerve terminal markers in human, chronic methamphetamine users. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.C.; Ricaurte, G.A.; Seiden, L.S.; Schuster, C.R.; Miller, R.J.; Westley, J. Long-lasting depletions of striatal dopamine and loss of dopamine uptake sites following repeated administration of methamphetamine. Brain Res. 1980, 181, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, A.J.; Gibb, J.W. Long-term effects of multiple doses of methamphetamine on tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980, 214, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Moszczynska, A.; Turenne, S.; Kish, S.J. Rat striatal levels of the antioxidant glutathione are decreased following binge administration of methamphetamine. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 255, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Chang, L.; Wang, G.J.; Fowler, J.S.; Leonido-Yee, M.; Franceschi, D.; Sedler, M.J.; Gatley, S.J.; Hitzemann, R.; Ding, Y.S.; et al. Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloch, I.; Afanador, L.; Mexhitaj, I.; Ghazaryan, N.; Garzagongora, A.G.; Angulo, J.A. A single high dose of methamphetamine induces apoptotic and necrotic striatal cell loss lasting up to 3 months in mice. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloch, I.K.; Afanador, L.; Zhu, J.; Angulo, J.A. Methamphetamine induces striatal cell death followed by the generation of new cells and a second round of cell death in mice. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, I.; Ishigami, A.; Kubo, S.; Gotohda, T.; Kitamura, O. The peroxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in methamphetamine-treated rat brain. J. Med. Investig. 2008, 55, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.; Deng, X.; Noailles, P.A.; Ladenheim, B.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine induces neuronal apoptosis via cross-talks between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria-dependent death cascades. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, O.; Tokunaga, I.; Gotohda, T.; Kubo, S. Immunohistochemical investigation of dopaminergic terminal markers and caspase-3 activation in the striatum of human methamphetamine users. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2007, 121, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, G.; Atwell, K.; Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; Cadet, J.L. Involvement of dopamine receptors in binge methamphetamine-induced activation of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial stress pathways. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandyam, C.D.; Wee, S.; Crawford, E.F.; Eisch, A.J.; Richardson, H.N.; Koob, G.F. Varied access to intravenous methamphetamine self-administration differentially alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.M.; Hayashi, K.M.; Simon, S.L.; Geaga, J.A.; Hong, M.S.; Sui, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Toga, A.W.; Ling, W.; London, E.D. Structural abnormalities in the brains of human subjects who use methamphetamine. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6028–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Chou, J.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine causes widespread apoptosis in the mouse brain: Evidence from using an improved TUNEL histochemical method. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 93, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, N.; Kadota, M.T.; Watanabe, M.; Ito, Y.; Akaike, N.; Carpenter, D.O. Neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine on rat hippocampus pyramidal neurons. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuchert-Noodt, G.; Dawirs, R.R.; Hildebrandt, K. Adult treatment with methamphetamine transiently decreases dentate granule cell proliferation in the gerbil hippocampus. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochman, L.J.; Fornal, C.A.; Jacobs, B.L. Suppression of hippocampal cell proliferation by short-term stimulant drug administration in adult rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczenski, R.; Everall, I.P.; Crews, L.; Adame, A.; Grant, I.; Masliah, E. Escalating dose-multiple binge methamphetamine exposure results in degeneration of the neocortex and limbic system in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 207, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanos, P.K.; Kim, R.; Delis, F.; Ananth, M.; Chachati, G.; Rocco, M.J.; Masad, I.; Muniz, J.A.; Grant, S.C.; Gold, M.S.; et al. Chronic methamphetamine effects on brain structure and function in rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinto, P.; Samant, A.R.; Chavez, G.; Kim, A.; Yuan, C.J.; Soleiman, M.; Grant, Y.; Edwards, S.; Wee, S.; Koob, G.F.; et al. Levels of neural progenitors in the hippocampus predict memory impairment and relapse to drug seeking as a function of excessive methamphetamine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, N.; O’Dell, S.J.; Marshall, J.F. Neurotoxic methamphetamine regimen severely impairs recognition memory in rats. Synapse 2003, 49, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladenheim, B.; Krasnova, I.N.; Deng, X.; Oyler, J.M.; Polettini, A.; Moran, T.H.; Huestis, M.A.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity is attenuated in transgenic mice with a null mutation for interleukin-6. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.C.; Woods, S.P.; Matt, G.E.; Meyer, R.A.; Heaton, R.K.; Atkinson, J.H.; Grant, I. Neurocognitive effects of methamphetamine: A critical review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maze, I.; Feng, J.; Wilkinson, M.B.; Sun, H.; Shen, L.; Nestler, E.J. Cocaine dynamically regulates heterochromatin and repetitive element unsilencing in nucleus accumbens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, I.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene coexpression networks in human brain identify epigenetic modifications in alcohol dependence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.; Shah, J.; Hodgson, N.; Byun, H.M.; Deth, R. Morphine induces redox-based changes in global DNA methylation and retrotransposon transcription by inhibition of excitatory amino acid transporter type 3-mediated cysteine uptake. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Badge, R.M.; Moran, J.V. LINE-1 elements in structural variation and disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2011, 12, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodic, N. LINE-1 activity and regulation in cancer. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, D.M.; Devine, S.E. Aberrantly High Levels of Somatic LINE-1 Expression and Retrotransposition in Human Neurological Disorders. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszczynska, A.; Flack, A.; Qiu, P.; Muotri, A.R.; Killinger, B.A. Neurotoxic methamphetamine doses increase LINE-1 expression in the neurogenic zones of the adult rat brain. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, G.; Marcantonio, P.; Del Re, B. LINE-1 retrotransposition in human neuroblastoma cells is affected by oxidative stress. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 346, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszczynska, A.; Callan, S.P. Molecular, behavioral, and physiological consequences of methamphetamine neurotoxicity: Implications for treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.M.; Metzker, M.L.; Muzny, D.M.; Sodergren, E.J.; Scherer, S.; Scott, G.; Steffen, D.; Worley, K.C.; Burch, P.E.; et al. Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 2004, 428, 493–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, J.A.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mobile DNA elements in the generation of diversity and complexity in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L. The ORF1 protein encoded by LINE-1: Structure and function during L1 retrotransposition. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 45621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodier, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Vetter, M.R.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. LINE-1 ORF1 protein localizes in stress granules with other RNA-binding proteins, including components of RNA interference RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 6469–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B. Relationships between stress granules, oxidative stress, and neurodegenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1809592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, N.A.; Belancio, V.P.; Deininger, P.L. L1 mobile element expression causes multiple types of toxicity. Gene 2008, 419, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Wu, C.; Jin, L. A possible role for long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1) in huntington’s disease progression. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3644–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, K.; Sakaki, Y. Identification of critical CpG sites for repression of L1 transcription by DNA methylation. Gene 1997, 189, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, I.; Pascale, E.; Furano, A.V. The left end of rat L1 (L1Rn, long interspersed repeated) DNA which is a CpG island can function as a promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 9233–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cost, G.J.; Feng, Q.; Jacquier, A.; Boeke, J.D. Human L1 element target-primed reverse transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5899–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaurte, G.A.; Schuster, C.R.; Seiden, L.S. Long-term effects of repeated methylamphetamine administration on dopamine and serotonin neurons in the rat brain: A regional study. Brain Res. 1980, 193, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, T.; Kadota, K. Neurotoxic morphological changes induced in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats behaviorally sensitized to methamphetamine. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2004, 67, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.D.; Noguchi, K.K. The neurotoxic effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and methamphetamine on serotonin, dopamine, and GABA-ergic terminals: An in-vitro autoradiographic study in rats. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Liao, H.; Long, L.; Ding, Y.; Huang, J.; Yan, J. Necroptosis contributes to methamphetamine-induced cytotoxicity in rat cortical neurons. Toxicol. Vitro 2016, 35, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abekawa, T.; Ito, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Nakato, Y.; Koyama, T. Olanzapine and risperidone block a high dose of methamphetamine-induced schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities and accompanied apoptosis in the medial prefrontal cortex. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 101, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Huang, E.; Tai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, R.; Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Nupr1 modulates methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neuronal apoptosis and autophagy through CHOP-Trib3-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaudin de The, F.X.; Rekaik, H.; Peze-Heidsieck, E.; Massiani-Beaudoin, O.; Joshi, R.L.; Fuchs, J.; Prochiantz, A. Engrailed homeoprotein blocks degeneration in adult dopaminergic neurons through LINE-1 repression. EMBO J. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.F.; Newport, R.R.; Holson, W.; Slikker, W., Jr.; Bowyer, J.F. Low environmental temperatures or pharmacologic agents that produce hyperthermia decrease methamphetamine neurotoxicity in mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 765, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, S.; Zahmatkesh, M.; Tavoosidana, G.; Karimian, M.; Hassanzadeh, G. Simvastatin enhances the hippocampal klotho in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive decline. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, N.; Goodier, J.L.; Cheung, L.E.; Wang, Y.J.; Kajikawa, M.; Kazazian, H.H.; Okada, N. In Vitro screening for compounds that enhance human L1 mobilization. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Cheng, V.; Xu, X.; Qiao, W.; Guo, F.; Liang, C.; Cen, S. The MOV10 helicase inhibits LINE-1 mobility. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21148–21160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.P.; Liu, X.; Whangbo, J.; McCrossan, G.; Sanborn, K.B.; Basar, E.; Walch, M.; Lieberman, J. Apoptosis triggers specific, rapid, and global mrna decay with 3’ uridylated intermediates degraded by DIS3L2. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkocki, Z.; Krawczyk, P.S.; Adamska, D.; Bijata, K.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Dziembowski, A. Uridylation by TUT4/7 restricts retrotransposition of human LINE-1s. Cell 2018, 174, 1537–1548.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okudaira, N.; Ishizaka, Y.; Nishio, H. Retrotransposition of long interspersed element 1 induced by methamphetamine or cocaine. J. Biol. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Killian, J.K.; Yang, M.; Walker, R.L.; Hong, J.A.; Zhang, M.; Davis, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, M.; Xi, S.; et al. Epigenomic alterations and gene expression profiles in respiratory epithelia exposed to cigarette smoke condensate. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3650–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, G.A.; Doucet-O’Hare, T.T.; Hammond, M.J.; Crist, R.C.; Ewing, A.D.; Ferraro, T.N.; Mash, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr.; Berrettini, W.H. Reading LINEs within the cocaine addicted brain. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erichsen, L.; Beermann, A.; Arauzo-Bravo, M.J.; Hassan, M.; Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Hafiz, T.A.; Fischer, J.C.; Santourlidis, S. Genome-wide hypomethylation of LINE-1 and Alu retroelements in cell-free DNA of blood is an epigenetic biomarker of human aging. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Zaher, A.O.; Mostafa, M.G.; Farghaly, H.S.; Hamdy, M.M.; Abdel-Hady, R.H. Role of oxidative stress and inducible nitric oxide synthase in morphine-induced tolerance and dependence in mice. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 247, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy-Feitosa, E.; Okuro, R.T.; Pinho Ribeiro, V.; Lanzetti, M.; Barroso, M.V.; Zin, W.A.; Porto, L.C.; Brito-Gitirana, L.; Valenca, S.S. Eucalyptol attenuates cigarette smoke-induced acute lung inflammation and oxidative stress in the mouse. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchinetti, E.; Feng, J.; Silva, R.; Tolstonog, G.V.; Schaub, M.C.; Schumann, G.G.; Zaugg, M. Inhibition of LINE-1 expression in the heart decreases ischemic damage by activation of Akt/PKB signaling. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 25, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Narasimhan, P.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Park, E.H.; Chan, P.H. The role of Akt signaling in oxidative stress mediates NF-kappaB activation in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, M. The epigenetic alterations of endogenous retroelements in aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 174, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Davis, K.L.; Fleckenstein, A.E.; Wilkins, D.G. The role of hyperthermia and metabolism as mechanisms of tolerance to methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 482, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephans, S.; Yamamoto, B. Methamphetamines pretreatment and the vulnerability of the striatum to methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 1996, 72, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.J.; Hulme, A.E.; Sahinovic, E.; Kulpa, D.A.; Moldovan, J.B.; Kopera, H.C.; Athanikar, J.N.; Hasnaoui, M.; Bucheton, A.; Moran, J.V.; et al. Characterization of LINE-1 ribonucleoprotein particles. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudiasl, G.R.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Niknazar, S.; Darabi, S.; Roozbahany, N.A. Nod-like receptor protein 3 and nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome activation in the hippocampal region of postmortem methamphetamine chronic user. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2019, 120, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, S.N. Corticostriatal circuitry. Dialog. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Leranth, C.; Hajszan, T. Extrinsic afferent systems to the dentate gyrus. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 163, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Yu, S.P.; Mohamad, O.; Cao, W.; Wei, Z.Z.; Gu, X.; Jiang, M.Q.; Wei, L. Optogenetic stimulation of glutamatergic neuronal activity in the striatum enhances neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of normal and stroke mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 98, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.F.; Yamamoto, B.K. Methamphetamine neurotoxicity and striatal glutamate release: Comparison to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Brain Res. 1992, 581, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudensky, J.; Yamamoto, B.K. Effects of chronic unpredictable stress and methamphetamine on hippocampal glutamate function. Brain Res. 2007, 1135, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, M.R.; Moy, L.Y.; Jayatilleke, E.; Hogan, K.A.; Manzino, L.; Sonsalla, P.K. Parallel increases in lipid and protein oxidative markers in several mouse brain regions after methamphetamine treatment. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, G.; Lee, Y.W.; Nath, A.; Maragos, W.; Hennig, B.; Toborek, M. Methamphetamine-induced TNF-alpha gene expression and activation of AP-1 in discrete regions of mouse brain: Potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. Neuromol. Med. 2002, 2, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.; Bento, A.R.; Goncalves, J.; Bernardino, L.; Summavielle, T.; Lobo, A.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Malva, J.O.; Agasse, F.; Silva, A.P. Neuropeptide Y promotes neurogenesis and protection against methamphetamine-induced toxicity in mouse dentate gyrus-derived neurosphere cultures. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, J.; Ribeiro, C.F.; Malva, J.O.; Silva, A.P. Protective role of neuropeptide Y Y(2) receptors in cell death and microglial response following methamphetamine injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 36, 3173–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephans, S.E.; Yamamoto, B.K. Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity: Roles for glutamate and dopamine efflux. Synapse 1994, 17, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdsan, W.; Thanoi, S.; Nudmamud-Thanoi, S. Changes in the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT3 in rat brain after exposure to methamphetamine. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.H.; Yang, P.; Wan, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.H.; Feng, Z.T.; Li, L.H.; Yew, D.T. Expression of dopamine transporter in the different cerebral regions of methamphetamine-dependent rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, K.A.; Quinton, M.S.; Russek, S.J.; Yamamoto, B.K. Dynamic changes in vesicular glutamate transporter 1 function and expression related to methamphetamine-induced glutamate release. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6823–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.W.; Collins, C.A.; Gelfand, M.V.; Dant, J.; Brooks, E.S.; Krantz, D.E.; DiAntonio, A. Increased expression of the Drosophila vesicular glutamate transporter leads to excess glutamate release and a compensatory decrease in quantal content. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10466–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolozin, B.; Ivanov, P. Stress granules and neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Ko, J.S.; Heidmann, T.; Medzhitov, R. Trex1 prevents cell-intrinsic initiation of autoimmunity. Cell 2008, 134, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.A.; Tejwani, L.; Trujillo, C.A.; Negraes, P.D.; Herai, R.H.; Mesci, P.; Macia, A.; Crow, Y.J.; Muotri, A.R. Modeling of TREX1-Dependent Autoimmune Disease using Human Stem Cells Highlights L1 Accumulation as a Source of Neuroinflammation. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 319–331.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Song, H.; Xu, Y.; Garrison, K.E.; Buzdin, A.A.; Anwar, N.; Hunter, D.V.; Mujib, S.; Mihajlovic, V.; Martin, E.; et al. LINE-1 retrotransposable element DNA accumulates in HIV-1-infected cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13307–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, G.J.; Billon, V. L1 retrotransposition in the soma: A field jumping ahead. Mob. DNA 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.; Rath, P.C. Long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) show tissue-specific, mosaic genome and methylation-unrestricted, widespread expression of noncoding RNAs in somatic tissues of the rat. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1380–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.L.; Brannock, C.; Krasnova, I.N.; Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Walther, D.; Godino, A.; Pirooznia, M.; Lee, R.S. Genome-wide DNA hydroxymethylation identifies potassium channels in the nucleus accumbens as discriminators of methamphetamine addiction and abstinence. Mol. Psychiatry 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omonijo, O.; Wongprayoon, P.; Ladenheim, B.; McCoy, M.T.; Govitrapong, P.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Differential effects of binge methamphetamine injections on the mRNA expression of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in the rat striatum. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Durango, D.E.; Liu, Y.; Teneng, I.; Kalbfleisch, T.; Lacy, M.E.; Steffen, M.C.; Ramos, K.S. Epigenetic control of mammalian LINE-1 retrotransposon by retinoblastoma proteins. Mutat. Res. 2009, 665, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soifer, H.S.; Zaragoza, A.; Peyvan, M.; Behlke, M.A.; Rossi, J.J. A potential role for RNA interference in controlling the activity of the human LINE-1 retrotransposon. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetto, M.C.; Narvaiza, I.; Denli, A.M.; Benner, C.; Lazzarini, T.A.; Nathanson, J.L.; Paquola, A.C.; Desai, K.N.; Herai, R.H.; Weitzman, M.D.; et al. Differential L1 regulation in pluripotent stem cells of humans and apes. Nature 2013, 503, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, T.; Hsieh, J.; Muotri, A.; Yeo, G.; Warashina, M.; Lie, D.C.; Moore, L.; Nakashima, K.; Asashima, M.; Gage, F.H. Wnt-mediated activation of NeuroD1 and retro-elements during adult neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godino, A.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents. Epigenetics 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Kraijak, K.; Mutirangura, A.; Maes, M. Paranoid schizophrenia and methamphetamine-induced paranoia are both characterized by a similar LINE-1 partial methylation profile, which is more pronounced in paranoid schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 208, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Kraijak, K.; Maes, M.; Mutirangura, A. Methamphetamine (MA) use induces specific changes in LINE-1 partial methylation patterns, which are associated with MA-induced paranoia: A multivariate and neuronal network study. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4258–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Brain Area | Dorsal Striatum | Dentate Gyrus | Prefrontal Cortex |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINE-1 activity (binge METH) | ⇑ ⇑ [45] | ⇑ ⇑ [45] | = [45] |
| Extracellular DA after binge METH | ⇑ ⇑ [44] | ⇑ [44] | ⇑ [44] |
| Extracellular GLU after binge METH | ⇑ ⇑ [76] | ⇑ [81] | = [76] |
| LINE-1 activity (chronic METH) | ⇑⇑ | = | = |
| LINE-1 “tolerance” (chronic METH) | No | Yes | NA |
| GLU transporter after chronic METH | ⇓ ⇓ [87] | ⇑ [87] | ⇓ [87] |
| DAT transporter after chronic METH | ⇓ ⇓ [88] | = [88] | ⇓ [88] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moszczynska, A. Differential Responses of LINE-1 in the Dentate Gyrus, Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex to Chronic Neurotoxic Methamphetamine: A Study in Rat Brain. Genes 2020, 11, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040364
Moszczynska A. Differential Responses of LINE-1 in the Dentate Gyrus, Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex to Chronic Neurotoxic Methamphetamine: A Study in Rat Brain. Genes. 2020; 11(4):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040364
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoszczynska, Anna. 2020. "Differential Responses of LINE-1 in the Dentate Gyrus, Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex to Chronic Neurotoxic Methamphetamine: A Study in Rat Brain" Genes 11, no. 4: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040364
APA StyleMoszczynska, A. (2020). Differential Responses of LINE-1 in the Dentate Gyrus, Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex to Chronic Neurotoxic Methamphetamine: A Study in Rat Brain. Genes, 11(4), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040364





