Interpreting Mixture Profiles: Comparison Between Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 and Traditional Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 20 expanded Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) core loci: TPOX, D3S1358, FGA, D5S818, CSF1PO, D7S820, D8S1179, TH01, vWA, D13S317, D16S539, D18S51, D21S11, D1S1656, D2S1338, D2S441, D10S1248, D12S391, D19S433 and D22S1045;
- 11 non-CODIS loci: D1S1677, D2S1776, D3S4529, D4S2408, D5S2800, D6S1043, D6S474, D12ATA63, D14S1434, Penta E and Penta D;
- 4 gender determination loci: Amelogenin, DYS391, SRY and Y-indel (rs2032678) [2].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Sample
2.2. Purification and Quantification
2.3. Traditional Method
2.4. NGS Method
2.5. Statistical Approach and Semi-Continuous Method
2.6. Quality Control
3. Results
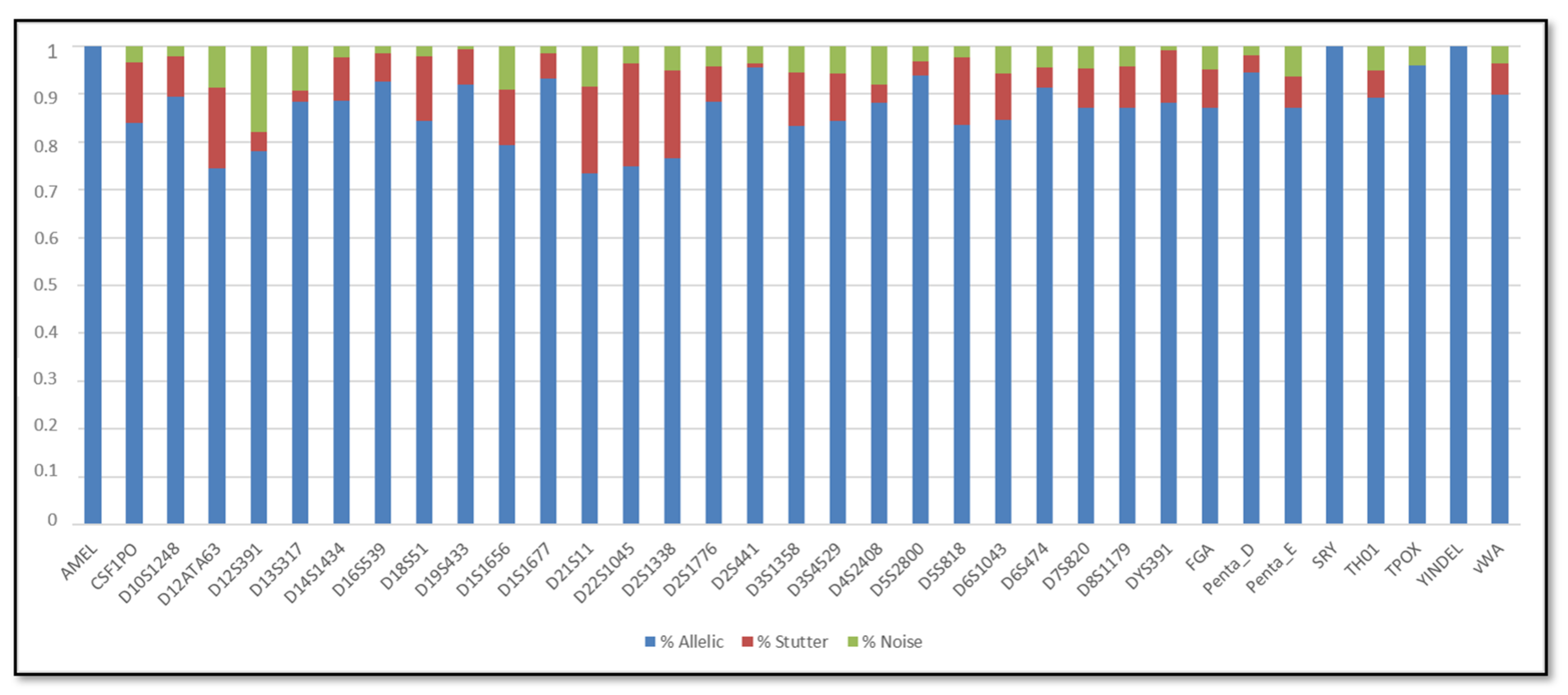
3.1. Single DNA Profiles
3.2. Mixed DNA Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butler, J.M.; Willis, S. Interpol review of forensic biology and forensic DNA typing 2016–2019. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2020, in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Qi, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Pilot study for forensic evaluations of the Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 with the Ion S5™ system. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 43, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strafella, C.; Caputo, V.; Pagliaroli, G.; Iozzo, N.; Campoli, G.; Carboni, S.; Peconi, C.; Galota, R.M.; Zampatti, S.; Minozzi, G.; et al. NGS Analysis for Molecular Diagnosis of Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP): Detection of a Novel Variant in PRPH2 Gene. Genes 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Hou, Y. Characterization of sequence variation at 30 autosomal STRs in Chinese Han and Tibetan populations. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, E.; Spinella, A.; Novelli, G. Past, present and future of forensic DNA typing. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, J.; Carleton, H.A.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Lindsey, R.L.; Trees, E. Next-generation sequencing technologies and their application to the study and control of bacterial infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jäger, A.C.; Alvarez, M.L.; Davis, C.P.; Guzmán, E.; Han, Y.; Way, L.; Walichiewicz, P.; Silva, D.; Pham, N.; Caves, G.; et al. Developmental validation of the MiSeq FGx Forensic Genomics System for Targeted Next Generation Sequencing in Forensic DNA Casework and Database Laboratories. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 28, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devesse, L.; Ballard, D.; Davenport, L.; Riethorst, I.; Mason-Buck, G.; Court, D.S. Concordance of the ForenSeq™ system and characterisation of sequence-specific autosomal STR alleles across two major population groups. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giardina, E.; Pietrangeli, I.; Martone, C.; Asili, P.; Predazzi, I.; Marsala, P.; Gabriele, L.; Pipolo, C.; Ricci, O.; Solla, G.; et al. In silico and in vitro comparative analysis to select, validate and test SNPs for human identification. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvoro, C.; Faccinetto, C.; Zucchelli, L.; Porto, M.; Marino, A.; Occhi, G.; de Los Campos, G.; Vazza, G. Performance of four models for eye color prediction in an Italian population sample. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 40, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Sell, C.; Hadrys, T.; Hedman, J.; Bredemeyer, S.; Laurent, F.X.; Roewer, L.; Achtruth, S.; Sidstedt, M.; Sijen, T.; et al. SeqForSTR-Consortium. Inter-laboratory study on standardized MPS libraries: Evaluation of performance, concordance, and sensitivity using mixtures and degraded DNA. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strafella, C.; Campoli, G.; Galota, R.M.; Caputo, V.; Pagliaroli, G.; Carboni, S.; Zampatti, S.; Peconi, C.; Mela, J.; Sancricca, C.; et al. Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies (LGMDs): The Clinical Application of NGS Analysis, a Family Case Report. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meghnani, V.; Mohammed, N.; Giauque, C.; Nahire, R.; David, T. Performance Characterization and Validation of Saliva as an Alternative Specimen Source for Detecting Hereditary Breast Cancer Mutations by Next Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Genomics 2016, 2016, 2059041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lepre, T.; Cascella, R.; Missiroli, F.; De Felici, C.; Taglia, F.; Zampatti, S.; Cusumano, A.; Ricci, F.; Giardina, E.; Eandi, C.M.; et al. Polymorphisms in ARMS2 (LOC387715) and LOXL1 genes in the Japanese with age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, B.R.; Buel, E. Capillary Electrophoresis in Forensic Genetics. In Encyclopaedia of Forensic Sciences, 2nd ed.; Siegel, J., Saukko, P., Eds.; Academic Press Books—Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Turingan, R.S.; Brown, J.; Kaplun, L.; Smith, J.; Watson, J.; Boyd, D.A.; Steadman, D.W.; Selden, R.F. Identification of human remains using Rapid DNA analysis. Int. J. Legal Med. 2019, 134, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, J.M. The future of forensic DNA analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 with the HID Ion S5™/HID Ion GeneStudio™ S5 System. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/MAN0016129_PrecisionIDSTRIonS5_UG.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Bregu, J.; Conklin, D.; Coronado, E.; Terrill, M.; Cotton, R.W.; Grgicak, C.M. Analytical thresholds and sensitivity: Establishing RFU thresholds for forensic DNA analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Puch-Solis, R.; Curran, J. The low-template-DNA (stochastic) threshold—Its determination relative to risk analysis for national DNA databases. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2009, 3, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Sheng, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Separation/extraction, detection, and interpretation of DNA mixtures in forensic science (review). Int. J. Legal Med. 2018, 132, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, J.M.; Gill, P.; Bill, M.R. Interpretation of repeat measurement DNA evidence allowing for multiple contributors and population substructure. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 148, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haned, H.; Egeland, T.; Pontier, D.; Pène, L.; Gill, P. Estimating drop-out probabilities in forensic DNA samples: A simulation approach to evaluate different models. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haned, H.; Slooten, K.; Gill, P. Exploratory data analysis for the interpretation of low template DNA mixtures. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2012, 6, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Haned, H. A new methodological framework to interpret complex DNA profiles using likelihood ratios. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2013, 7, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Databanks/Testing Laboratories. Available online: https://www.accredia.it/ (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Tytgat, O.; Gansemans, Y.; Weymaere, J.; Rubben, K.; Deforce, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F. Nanopore Sequencing of a Forensic STR Multiplex Reveals Loci Suitable for Single-Contributor STR Profiling. Genes 2020, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, P.; Hicks, T.; Butler, J.M.; Connolly, E.; Gusmão, L.; Kokshoorn, B.; Morling, N.; van Oorschot, R.A.H.; Parson, W.; Prinz, M.; et al. DNA commission of the International society for forensic genetics: Assessing the value of forensic biological evidence—Guidelines highlighting the importance of propositions: Part I: Evaluation of DNA profiling comparisons given (sub-) source propositions. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 36, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coble, M.D.; Buckleton, J.; Butler, J.M.; Egeland, T.; Fimmers, R.; Gill, P.; Gusmão, L.; Guttman, B.; Krawczak, M.; Morling, N.; et al. DNA Commission of the International Society for Forensic Genetics: Recommendations on the validation of software programs performing biostatistical calculations for forensic genetics applications. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 25, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Brenner, C.H.; Buckleton, J.S.; Carracedo, A.; Krawczak, M.; Mayr, W.R.; Morling, N.; Prinz, M.; Schneider, P.M.; Weir, B.S. DNA commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics. DNA commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics: Recommendations on the interpretation of mixtures. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 160, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robino, C.; Ralf, A.; Pasino, S.; De Marchi, M.R.; Ballantyne, K.N.; Barbaro, A.; Bini, C.; Carnevali, E.; Casarino, L.; Di Gaetano, C.; et al. Development of an Italian RM Y-STR haplotype database: Results of the 2013 GEFI collaborative exercise. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 15, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, H.H.; Ang, H.C.; Hoe, S.Y.; Lim, M.L.; Tai, H.E.; Soh, R.C.H.; Syn, C.K. Simple DNA extraction of urine samples: Effects of storage temperature and storage time. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 287, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, M.D.; Bright, J.A. Probabilistic genotyping software: An overview. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 38, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LRmix Studio 2.1. Available online: https://lrmixstudio.org/download/manual.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Castella, V.; Dimo-Simonin, N.; Brandt-Casadevall, C.; Robinson, N.; Saugy, M.; Taroni, F.; Mangin, P. Forensic identification of urine samples: A comparison between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA markers. Int. J. Legal Med. 2006, 120, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aoki, K.; Tanaka, H.; Ueki, M. DNA typing for personal identification of urine after long-term preservation for testing in doping control. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Massively parallel sequencing of forensic STRs and SNPs using the illumina® ForenSeq DNA signature prep kit on the MiSeq FGx forensic genomics system. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 31, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Locus | Average DoC Buccal Swab | Average DoC Urine Sample |
|---|---|---|
| D3S1358 | 38.7 | 28.7 |
| VWA | 48.6 | 40.5 |
| D16S539 | 64.1 | 63.1 |
| CSF1PO | 68.5 | 46.5 |
| TPOX | 66.2 | 66.8 |
| AMEL | / | / |
| D8S1179 | 32.8 | 28.7 |
| D21S11 | 52.5 | 37.9 |
| DYS391 | 16.3 | 18.3 |
| D2S441 | 53.7 | 55.0 |
| D19S433 | 24.1 | 22.8 |
| TH01 | 75.9 | 106.4 |
| FGA | 29.0 | 20.7 |
| D22S1045 | 46.6 | 55.4 |
| D5S818 | 36.2 | 53.9 |
| D13S317 | 52.0 | 57.2 |
| D7S820 | 51.2 | 42.2 |
| D10S1248 | 25.6 | 26.8 |
| D1S1656 | 34.1 | 31.0 |
| D12S391 | 49.4 | 48.7 |
| D2S1338 | 23.8 | 25.8 |
| YINDEL | / | / |
| D18S51 | 42.8 | 29.3 |
| CE Global Filer Mixture DNA Profiles (Buccal Swabs) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | TB_1-2 | TB_1-4 | TB_1-6 | TB_1-8 | TB_1-10 | TB_1-20 | |
| Locus | |||||||
| D3S1358 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17 | 14-17 | |
| VWA | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | |
| D16S539 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 10-11 | 9-10-11 | 10-11 | |
| CSF1PO | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10 | |
| TPOX | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| AMEL | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | |
| D8S1179 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | |
| D21S11 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | |
| DYS391 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| D2S441 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | |
| D19S433 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | |
| TH01 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6 | |
| FGA | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22 | |
| D22S1045 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | |
| D5S818 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 10-13 | |
| D13S317 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11 | 8-11-13 | 8-11 | 8-11 | |
| D7S820 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11 | |
| D10S1248 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | |
| D1S1656 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 15-17.3 | |
| D12S391 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22 | 17.3-22 | |
| D2S1338 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-25 | |
| YINDEL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| D18S51 | 12-13 | 13 | 12-13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | |
| NGS Global Filer Mixture DNA Profiles (Buccal Swabs) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | TB_1-2 | TB_1-4 | TB_1-6 | TB_1-8 | TB_1-10 | TB_1-20 | |
| Locus | |||||||
| D3S1358 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | |
| VWA | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | |
| D16S539 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | |
| CSF1PO | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10 | |
| TPOX | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| AMEL | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | |
| D8S1179 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | |
| D21S11 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | |
| DYS391 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| D2S441 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | |
| D19S433 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | |
| TH01 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | |
| FGA | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22 | |
| D22S1045 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | |
| D5S818 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 10-13 | |
| D13S317 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | |
| D7S820 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | |
| D10S1248 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | |
| D1S1656 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | |
| D12S391 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | |
| D2S1338 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-25 | |
| YINDEL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| D18S51 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | |
| CE Global Filer Mixture DNA Profiles (Urine) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | UR_1-2 | UR_1-4 | UR_1-6 | UR_1-8 | UR_1-10 | UR_1-20 | |
| Locus | |||||||
| D3S1358 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-17 | |
| VWA | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | |
| D16S539 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 10-11 | |
| CSF1PO | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10 | 10-12 | 10 | |
| TPOX | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| AMEL | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | |
| D8S1179 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | |
| D21S11 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | |
| DYS391 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| D2S441 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | |
| D19S433 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | |
| TH01 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | |
| FGA | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22 | |
| D22S1045 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | |
| D5S818 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 10-13 | 10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | |
| D13S317 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | |
| D7S820 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | |
| D10S1248 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | |
| D1S1656 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | |
| D12S391 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22 | 17.3-22 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17.3-22-23 | |
| D2S1338 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | |
| YINDEL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| D18S51 | 12-13 | 13 | 12-13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | |
| NGS Global Filer Mixture DNA Profiles (Urine) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | UR_1-2 | UR_1-4 | UR_1-6 | UR_1-8 | UR_1-10 | UR_1-20 | |
| Locus | |||||||
| D3S1358 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | 14-16-17-18 | |
| VWA | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | 14-17-18 | |
| D16S539 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | 9-10-11 | |
| CSF1PO | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | |
| TPOX | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| AMEL | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | X-Y | |
| D8S1179 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | 13-16 | |
| D21S11 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | 28-29-30 | |
| DYS391 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| D2S441 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | |
| D19S433 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | 13-14 | |
| TH01 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | 6-9 | |
| FGA | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22 | 20-22-23 | 20-22-23 | 20-22 | |
| D22S1045 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | 15-17 | |
| D5S818 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | 9-10-13 | |
| D13S317 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | 8-11-13 | |
| D7S820 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | 9-11-12 | |
| D10S1248 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | 13-14-15 | |
| D1S1656 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | 12-15-17.3 | |
| D12S391 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | 17-17.3-22-23 | |
| D2S1338 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | 17-21-25 | |
| YINDEL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| D18S51 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | 12-13 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragazzo, M.; Carboni, S.; Caputo, V.; Buttini, C.; Manzo, L.; Errichiello, V.; Puleri, G.; Giardina, E. Interpreting Mixture Profiles: Comparison Between Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 and Traditional Methods. Genes 2020, 11, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060591
Ragazzo M, Carboni S, Caputo V, Buttini C, Manzo L, Errichiello V, Puleri G, Giardina E. Interpreting Mixture Profiles: Comparison Between Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 and Traditional Methods. Genes. 2020; 11(6):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060591
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagazzo, Michele, Stefania Carboni, Valerio Caputo, Carlotta Buttini, Laura Manzo, Valeria Errichiello, Giulio Puleri, and Emiliano Giardina. 2020. "Interpreting Mixture Profiles: Comparison Between Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 and Traditional Methods" Genes 11, no. 6: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060591
APA StyleRagazzo, M., Carboni, S., Caputo, V., Buttini, C., Manzo, L., Errichiello, V., Puleri, G., & Giardina, E. (2020). Interpreting Mixture Profiles: Comparison Between Precision ID GlobalFiler™ NGS STR Panel v2 and Traditional Methods. Genes, 11(6), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060591





