Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Highlights Key Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Nutrient Metabolism and Digestion in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) Fed Terrestrial Animal and Plant Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Experimental Diets and Animals
2.3. Tissue Sampling
2.4. Histology
2.5. RNA Extraction, Library Construction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatics
2.7. Validation of RNA-Seq by qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Data Deposition
3. Results
3.1. Growth, Feed Intake and Somatic Indices
3.2. Histological Evaluation of the Distal Intestine
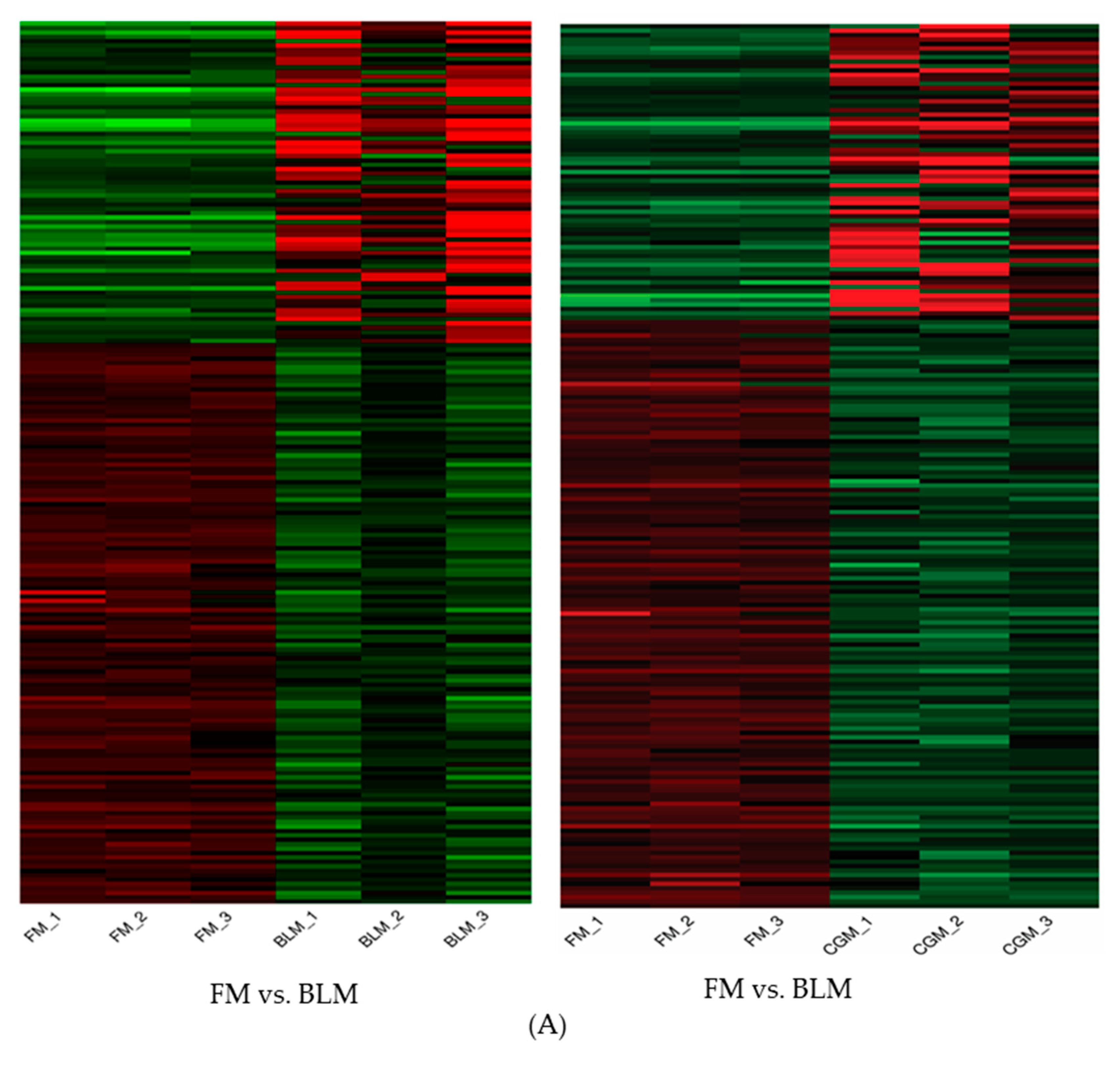
3.3. Transcriptomic Analysis Overview
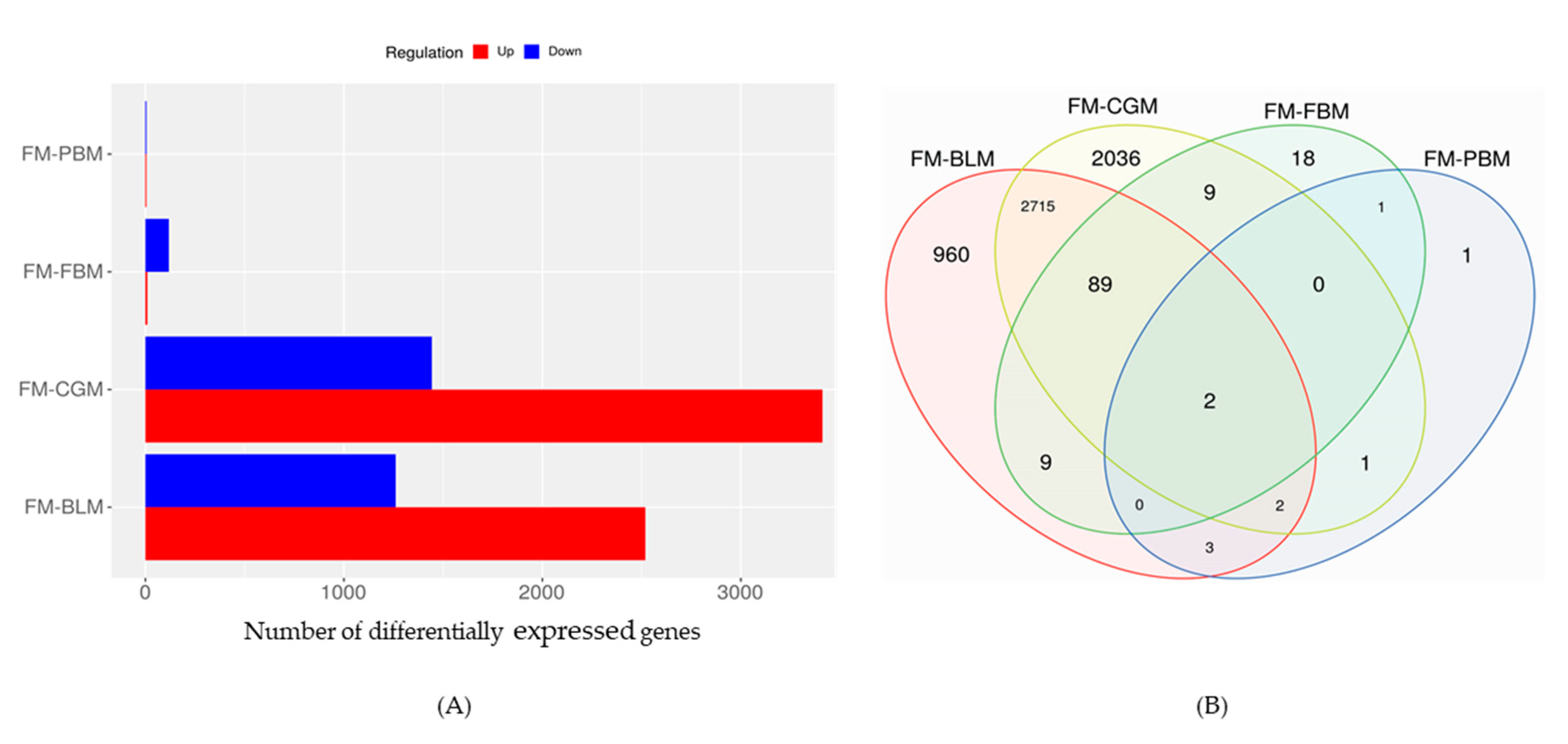
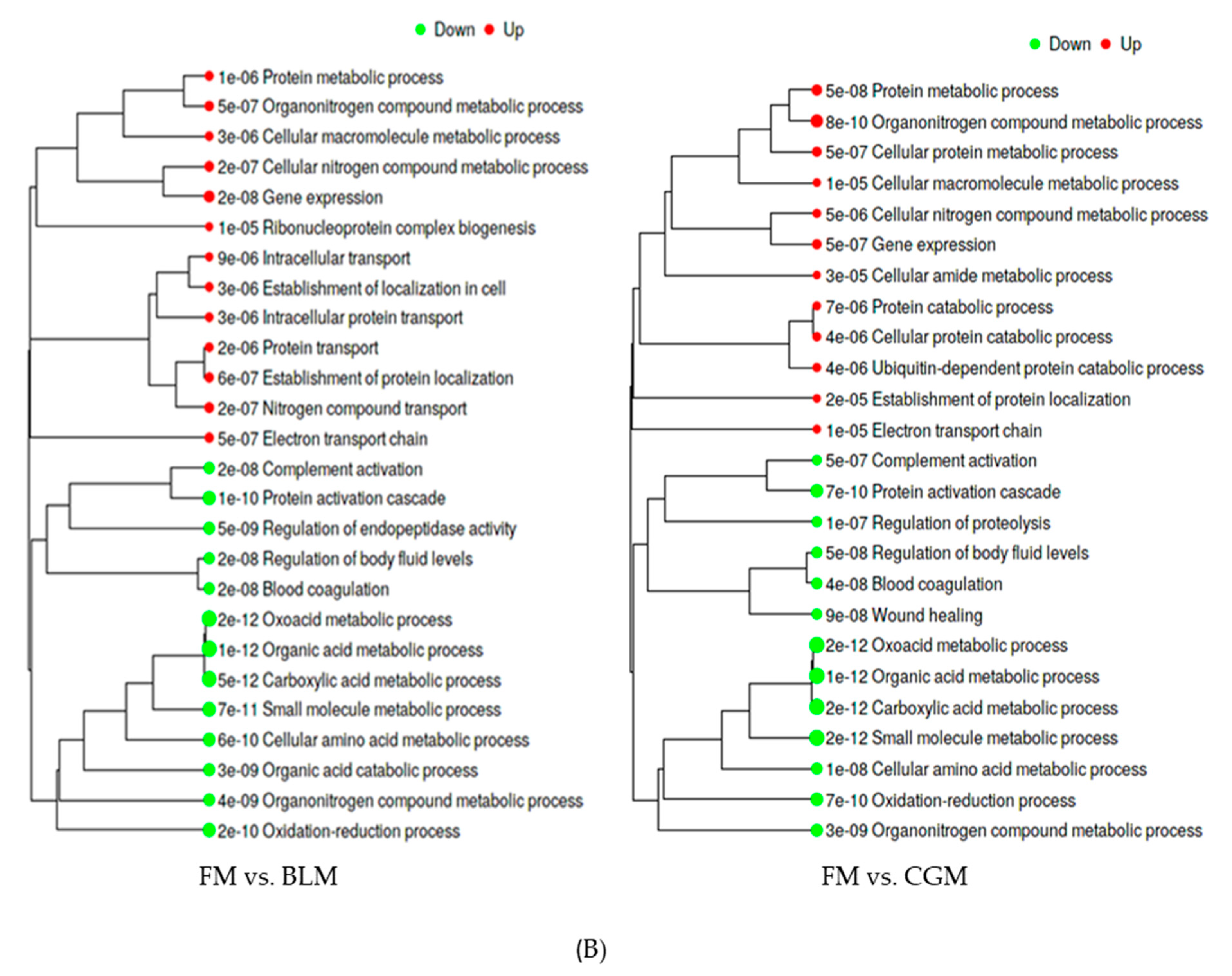
3.4. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in the Distal Intestine
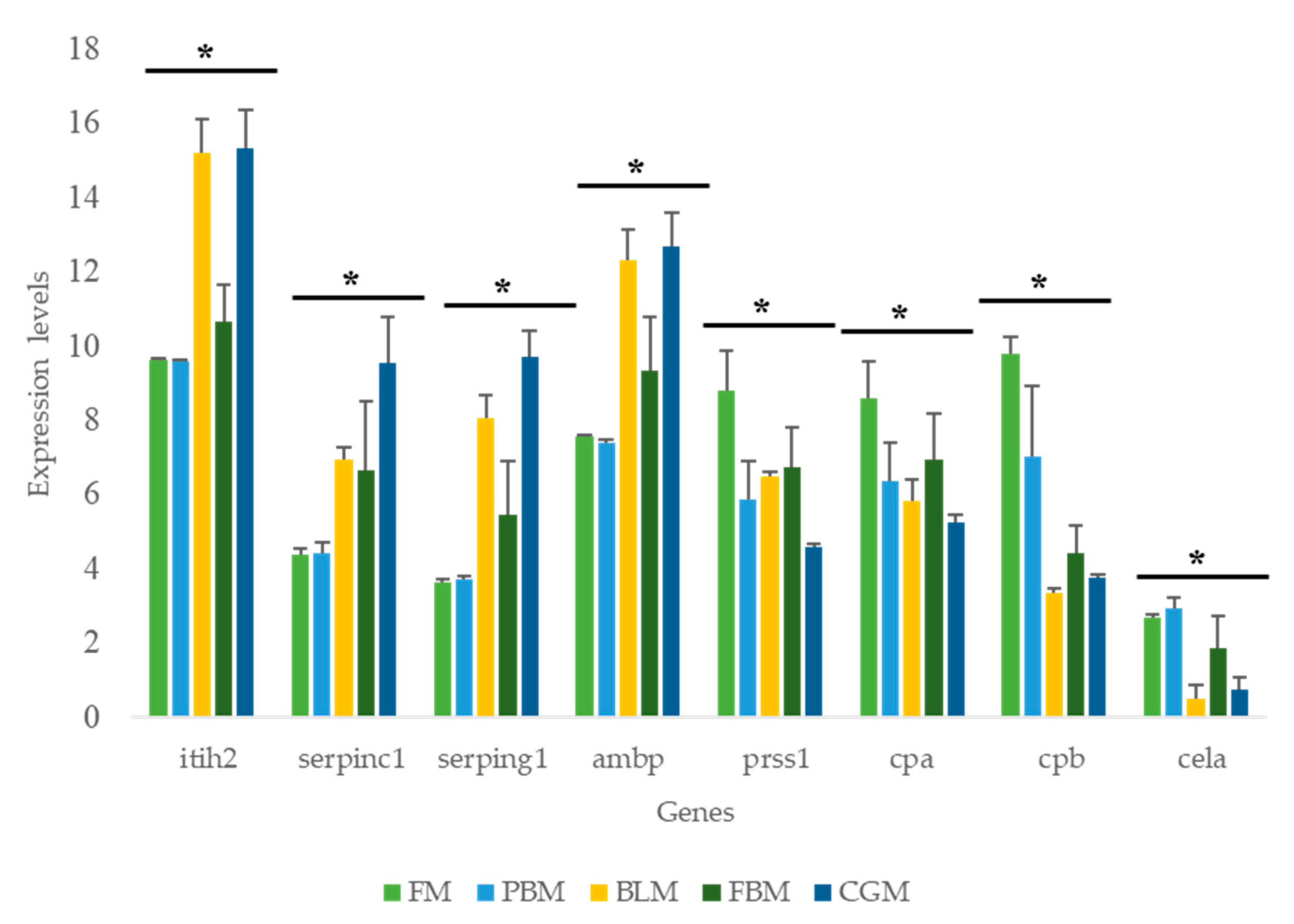
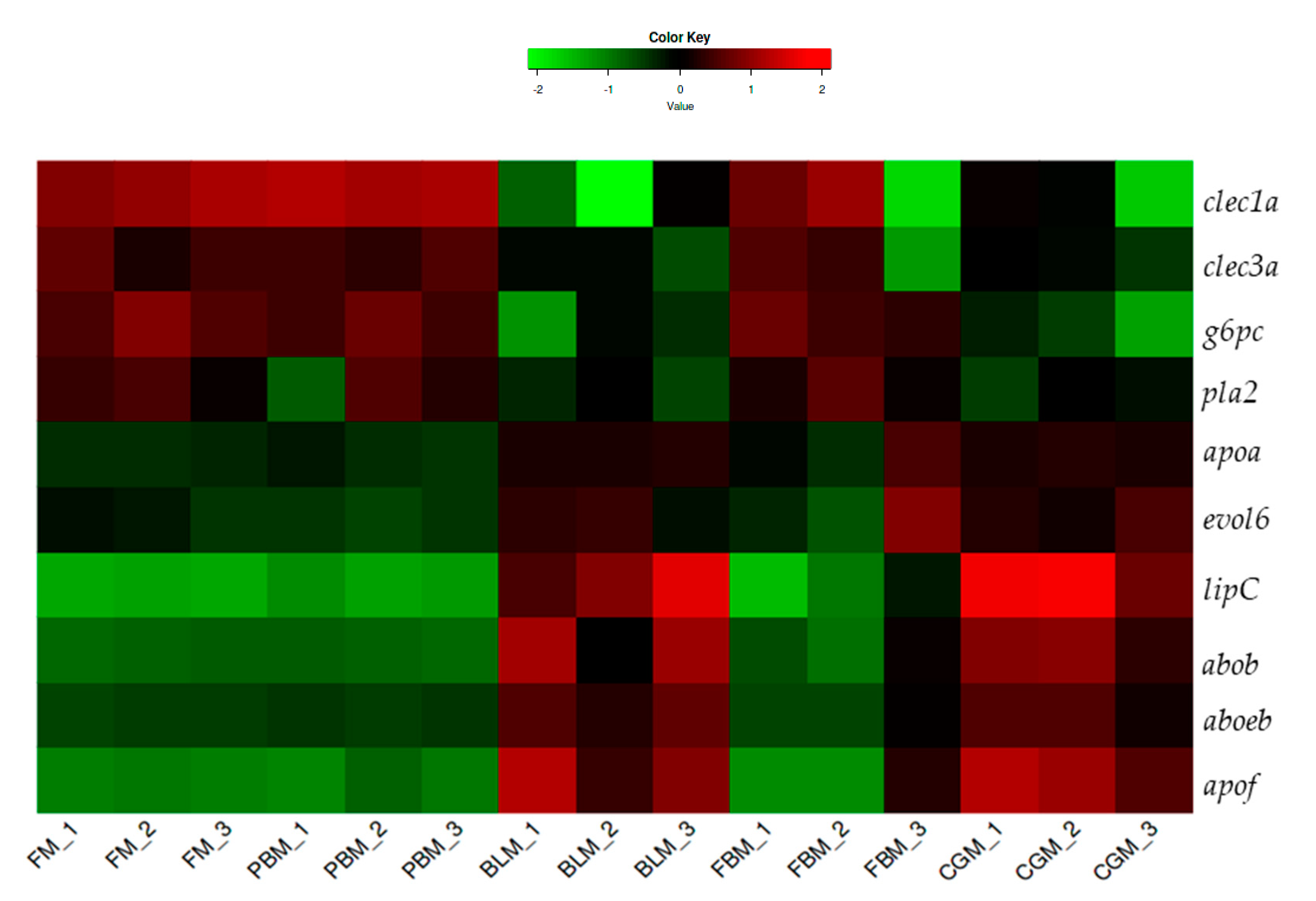
3.5. Expression of Key Nutrient Metabolism and Digestibility Related Genes
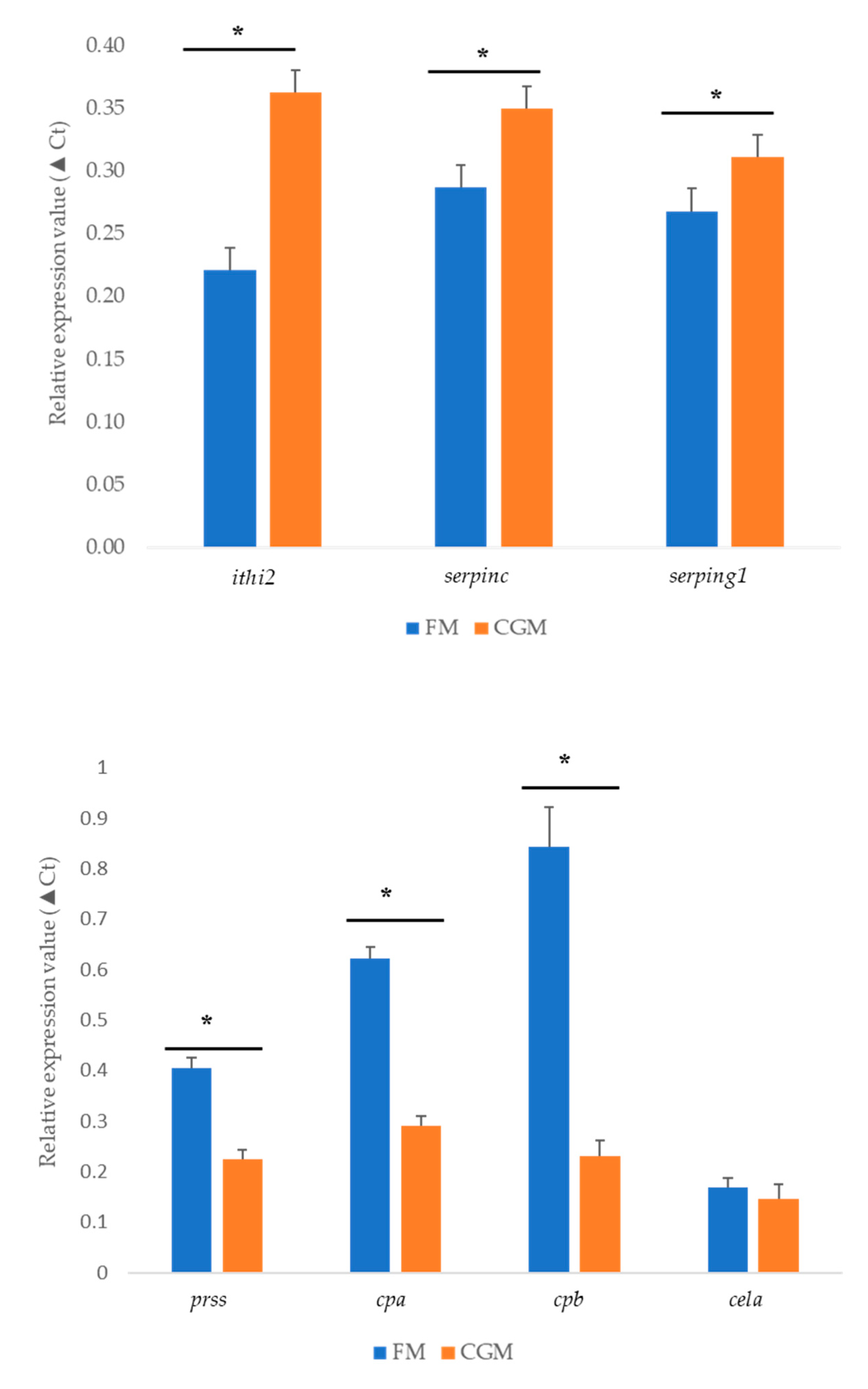
3.6. qPCR Validation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booth, M.; Moses, M.; Allan, G. Utilisation of carbohydrate by yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. Aquaculture 2013, 376, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.; Pirozzi, I. Making sense of nonsense: Using regression analysis to deal with highly variable data collected from a yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) digestibility experiment. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, P.; Nguyen, N.; Miller, A.; Lamont, R.; Powell, D.; D’Antignana, T.; Bubner, E.; Elizur, A.; Knibb, W. Genetic parameters for economically important traits in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. Aquaculture 2013, 400, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, K.; Ernst, I.; Whittington, I. Risk assessment for metazoan parasites of yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi (Perciformes: Carangidae) in South Australian sea-cage aquaculture. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.; Pirozzi, I.; Allan, G.; Fielder, D.S. Aquafin CRC Project 1B5: Feed Technology for Temperate Fish Species. Volume 2: Diet Development; Final Report to FRDC project No.2004/220; Port Stephens Fisheries Institute: New South Wales, Australia, 2010.
- Le, K.; Fotedar, R. Dietary selenium requirement of yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, D.; Bellgrove, E. A literature review: The current status of knowledge of the nutritional requirements of yellowtail kingfish. In Sustainable Feeds and Feed Management for Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi), ASCRC Project, No. 2009/728; Stone, D., Bowyer, J., Eds.; Vol. SARDI Publication No. F2013/000200-1; SARDI Research Report Series No. 751; South Australian Research and Development Institute (Aquatic Sciences): Adelaide, Australia, 2013; pp. 92–121. [Google Scholar]
- Rotman, F.; Stuart, K.; Drawbridge, M. Effects of taurine supplementation in live feeds on larval rearing performance of California yellowtail Seriola lalandi and white seabass Atractoscion nobilis. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Pirozzi, I.; Codabaccus, B.; Hines, B.; Simon, C.; Sammut, J.; Booth, M. Digestible choline requirement of juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Aquaculture 2019, 509, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candebat, C.L.; Booth, M.; Codabaccus, M.B.; Pirozzi, I. Dietary methionine spares the requirement for taurine in juvenile Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, I.; Benito, M.R.; Booth, M. Protein, amino acid and energy utilisation of juvenile Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi): Quantifying abiotic influences. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatlen, B.; Jakobsen, J.; Crampton, V.; Alm, M.; Langmyhr, E.; Espe, M.; Hevrøy, E.; Torstensen, B.; Liland, N.; Waagbø, R. Growth, feed utilization and endocrine responses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed diets added poultry by-product meal and blood meal in combination with poultry oil. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.; Sanchez-Gutierrez, Y.; Hardy, R.; Benitez-Hernández, A.; Domínguez-Jimenez, P.; González-Rodríguez, B.; Osuna-Osuna, L.; Tortoledo, O. The potential of pet-grade poultry by-product meal to replace fish meal in the diet of the juvenile spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus (Steindachner, 1869). Aquac. Nutr. 2014, 20, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, C. The effects of partial replacement of white fish meal by poultry by-product meal and addition of bile acid in feed on growth, digestibility, and serum enzyme activities of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle. Fish Sci. 2017, 83, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, M.; Schiavone, R.; Brizzi, G.; Sicuro, B.; Zilli, L.; Vilella, S. Poultry by-product meal as an alternative to fish meal in the juvenile gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) diet. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, G.; Parkinson, S.; Booth, M.; Stone, D.; Rowland, S.; Frances, J.; Warner-Smith, R. Replacement of fish meal in diets for Australian silver perch, Bidyanus bidyanus: I. Digestibility of alternative ingredients. Aquaculture 2000, 186, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abery, N.; Gunasekera, R.; De Silva, S. Growth and nutrient utilization of Murray cod Maccullochella peelii peelii (Mitchell) fingerlings fed diets with varying levels of soybean meal and blood meal. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, B.; Carter, C.; Duijster, N.; Evans, D.; Dods, K.; McCafferty, P.; Hawkins, W.; Maas, R.; Sipsas, S. A comparison of the digestibility of a range of lupin and soybean protein products when fed to either Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) or rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2004, 237, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Coves, D.; Dutto, G.; Blanc, D. Almost total replacement of fish meal by plant protein sources in the diet of a marine teleost, the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2004, 230, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W. Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: Effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin III, D.; Barrows, F.; Brown, P.; Dabrowski, K.; Gaylord, T.; Hardy, R.; Herman, E.; Hu, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Nelson, R. Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: A review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashita, K.; Matsunari, H.; Fukada, H.; Suzuki, N.; Furuita, H.; Oku, H.; Rønnestad, I.; Yoshinaga, H.; Yamamoto, T. Effect of a plant-based low-fishmeal diet on digestive physiology in yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Rombenso, A.; Del Rio-Zaragoza, O.; Nomura, M.; Díaz-Argüello, R.; Mata-Sotres, J. Intestinal impairment of the California yellowtail, Seriola dorsalis, using soybean meal in the diet. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Song, K. Effects of substituting fishmeal with soybean meal on growth performance and intestinal morphology in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Aquac. Rep. 2017, 5, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calduch-Giner, J.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Gene expression profiling reveals functional specialization along the intestinal tract of a carnivorous teleostean fish (Dicentrarchus labrax). Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, S.; Dehler, C.; Król, E. Transcriptomic responses in the fish intestine. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacchi, L.; Secombes, C.J.; Bickerdike, R.; Adler, M.A.; Venegas, C.; Takle, H.; Martin, S.A. Transcriptomic and physiological responses to fishmeal substitution with plant proteins in formulated feed in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Król, E.; Douglas, A.; Tocher, D.R.; Crampton, V.O.; Speakman, J.R.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A. Differential responses of the gut transcriptome to plant protein diets in farmed Atlantic salmon. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, S.; Cravedi, J.; Lalles, J.; Sumpter, J.; Fauconneau, B.; Laroche, M. Partial or total replacement of fish meal by soybean protein on growth, protein utilization, potential estrogenic or antigenic effects, cholesterolemia and flesh quality in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 1995, 133, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, G.; Teague, M.; Barrows, F. Taurine supplementation of all-plant protein diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2006, 37, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, R.; Machado, M.; Kreuz, E.; Wuertz, S.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Costas, B. The European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) innate immunity and gut health are modulated by dietary plant-protein inclusion and prebiotic supplementation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, C.; Elizur, A.; Ventura, T.; Salini, M.; Smullen, R.; Pirozzi, I.; Booth, M. Apparent digestibility of raw materials by yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.-J.; Li, C.; Bureau, D.P. Effect of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth, feed utilization and carcass composition of cuneate drum (Nibea miichthioides). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urán, P.; Schrama, J.; Rombout, J.; Taverne-Thiele, J.; Obach, A.; Koppe, W.; Verreth, J. Time-related changes of the intestinal morphology of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., at two different soybean meal inclusion levels. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seriola Genomic Resource Website. Available online: https://www.serioladb.org/downloads (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Premachandra, H.; Lafarga-De la Cruz, F.; Takeuchi, Y.; Miller, A.; Fielder, S.; O’Connor, W.; Frère, C.H.; Nguyen, N.H.; Bar, I.; Knibb, W. Genomic DNA variation confirmed Seriola lalandi comprises three different populations in the Pacific, but with recent divergence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Universal ProbeLibrary System Assay Design. Available online: https://lifescience.roche.com/en_au/articles/Universal-ProbeLibrary-System-Assay-Design.html (accessed on 13 February 2020).
- Bowyer, J.; Qin, J.; Smullen, R.; Adams, L.; Thomson, M.; Stone, D. The use of a soy product in juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) feeds at different water temperatures: 2. Soy protein concentrate. Aquaculture 2013, 410, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Bellgrove, E.; Forder, R.; Howarth, G.; Bansemer, M. Inducing subacute enteritis in Yellowtail Kingfish Seriola lalandi: The effect of dietary inclusion of soybean meal and grape seed extract on hindgut morphology and inflammation. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2018, 80, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, J.; Qin, J.; Smullen, R.; Adams, L.; Thomson, M.; Stone, D. The use of a soy product in juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) feeds at different water temperatures: 1. Solvent extracted soybean meal. Aquaculture 2013, 384, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansemer, M.; Forder, R.; Howarth, G.; Suitor, G.; Bowyer, J.; Stone, D. The effect of dietary soybean meal and soy protein concentrate on the intestinal mucus layer and development of subacute enteritis in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) at suboptimal water temperature. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Parr, T.; Lim, Y. The impact of four processing methods on trypsin-, chymotrypsin-and alpha-amylase inhibitors present in underutilised legumes. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.; Becker, K. Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 2001, 199, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cheng, M. Effects of dietary organic acid supplementation on the growth, nutrient digestibility and intestinal histology of the giant grouper Epinephelus lanceolatus fed a diet with soybean meal. Aquaculture 2017, 469, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, T.; Ruchimat, T.; Ito, Y.; Hosokawa, H.; Shimeno, S. Amino acid availability values for several protein sources for yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata). Aquaculture 1996, 146, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, C.; Bartie, K.; Olsen, R.; Taggart, J.; Tocher, D. Nutrigenomic profiling of transcriptional processes affected in liver and distal intestine in response to a soybean meal-induced nutritional stress in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. D Genom. Proteom. 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Gu, M.; Liu, M.; Jia, Q.; Pan, S.; Zhang, Z. Corn gluten meal induces enteritis and decreases intestinal immunity and antioxidant capacity in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) at high supplementation levels. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geay, F.; Ferraresso, S.; Zambonino-Infante, J.; Bargelloni, L.; Quentel, C.; Vandeputte, M.; Kaushik, S.; Cahu, C.; Mazurais, D. Effects of the total replacement of fish-based diet with plant-based diet on the hepatic transcriptome of two European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) half-sibfamilies showing different growth rates with the plant-based diet. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veron, V.; Panserat, S.; Le Boucher, R.; Labbé, L.; Quillet, E.; Dupont-Nivet, M.; Médale, F. Long-term feeding a plant-based diet devoid of marine ingredients strongly affects certain key metabolic enzymes in the rainbow trout liver. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarotto, V.; Médale, F.; Larroquet, L.; Corraze, G. Long-term dietary replacement of fishmeal and fish oil in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Effects on growth, whole body fatty acids and intestinal and hepatic gene expression. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, K.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Lu, M.-W.; Bar, I.; Elizur, A. A transcriptomic investigation of digestive processes in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, before, during, and after metamorphic development. Gene 2018, 661, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuike, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Nishiki, I.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuura, A.; Yoshida, K.; Noda, T.; Andoh, T.; Fujiwara, A. The yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) genome and transcriptome atlas of the digestive tract. DNA. Res. 2018, 25, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Chi, H. Cathepsin S of Sciaenops ocellatus: Identification, transcriptional expression and enzymatic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, K.; Dunkhorst, A.; Mayer, K.; Jordans, S. Cysteine cathepsins: Cellular roadmap to different functions. Biochimie 2008, 90, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, D.; Carter, C.; McCarthy, I. Protein Turnover in Animals, Nitrogen Metabolism and Excretion; Walsh, P., Wright, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero-Solares, A.; Xue, X.; Parrish, C.; Foroutani, M.; Taylor, R.; Rise, M. Changes in the liver transcriptome of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed experimental diets based on terrestrial alternatives to fish meal and fish oil. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leduc, A.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C.; Robert, M.; Corre, E.; Le Corguille, G.; Castel, H.; Lefevre-Scelles, A.; Fournier, V.; Gisbert, E.; Andree, K.B. Dietary aquaculture by-product hydrolysates: Impact on the transcriptomic response of the intestinal mucosa of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed low fish meal diets. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gelder, S.; Sæle, Ø.; de Veen, B.; Vos, J.; Flik, G.; Berntssen, M.; Klaren, P. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons benzo [a] pyrene and phenanthrene inhibit intestinal lipase activity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol 2017, 198, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Infante, J.; Cahu, C. Dietary modulation of some digestive enzymes and metabolic processes in developing marine fish: Applications to diet formulation. Aquaculture 2007, 268, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rønnestad, I.; Yúfera, M.; Ueberschär, B.; Ribeiro, L.; Sæle, Ø.; Boglione, C. Feeding behaviour and digestive physiology in larval fish: Current knowledge, and gaps and bottlenecks in research. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S59–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enes, P.; Panserat, S.; Kaushik, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Nutritional regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caseras, A.; Metón, I.; Fernández, F.; Baanante, I.V. Glucokinase gene expression is nutritionally regulated in liver of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Biochim. et Biophys. Acta -Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1493, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou, M.; Todorčević, M.; Fontanillas, R.; Capilla, E.; Gutiérrez, J.; Navarro, I. Adipose tissue and liver metabolic responses to different levels of dietary carbohydrates in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Int. Physiol. 2014, 175, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FM | PBM | BLM | FBM | CGM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial weight (g) | 586.33 ± 20.55 | 568 ± 12.52 | 517 ± 25.16 | 580.33 ± 8.62 | 561.67 ± 30.24 |
| Harvest weight (g) | 939.33 ± 83.16 | 789 ± 11.27 | 722.33 ± 49.94 | 856.33 ± 61.43 | 780.67 ± 85.70 |
| SGR (%/day) | 1.56 ± 0.29 | 1.10 ± 0.09 | 1.11 ± 0.33 | 1.29 ± 0.24 | 1.09 ± 0.22 |
| Feed intake (g/day) | 79.93 ± 3.73 | 80.07 ± 3.06 | 81.03 ± 2.85 | 79.23 ± 4.77 | 82.87 ± 6.63 |
| FCR | 1.65 ± 0.07 a | 1.83 ± 0.19 a | 2.53 ± 0.30 b | 2.25 ± 0.18 ab | 2.49 ± 0.40 b |
| VSI (%) | 3.94 ± 0. 15 | 4.03 ± 0.23 | 3.94 ± 0.06 | 3.94 ± 0.12 | 4.05 ± 0.13 |
| HSI (%) | 0.79 ± 0.11 | 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.84 ± 0.07 | 0.86 ± 0.15 | 0.83 ± 0.13 |
| Histological score | |||||
| Lamina propria | 1.33 ± 0.57 | 1 ± 0.57 | 1.33 ± 0.57 | 1.33 ± 0. 57 | 1.67 ± 1.15 |
| Mucosal folds | 1.67 ± 0.57 | 1.67 ± 0.57 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 0.57 | 2.00 ± 0.00 |
| Supranuclear vacuoles | 1.33 ± 0.57 | 1.67 ± 1.15 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.33 ± 0.57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dam, C.T.M.; Ventura, T.; Booth, M.; Pirozzi, I.; Salini, M.; Smullen, R.; Elizur, A. Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Highlights Key Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Nutrient Metabolism and Digestion in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) Fed Terrestrial Animal and Plant Proteins. Genes 2020, 11, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060621
Dam CTM, Ventura T, Booth M, Pirozzi I, Salini M, Smullen R, Elizur A. Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Highlights Key Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Nutrient Metabolism and Digestion in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) Fed Terrestrial Animal and Plant Proteins. Genes. 2020; 11(6):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060621
Chicago/Turabian StyleDam, Chinh Thi My, Tomer Ventura, Mark Booth, Igor Pirozzi, Michael Salini, Richard Smullen, and Abigail Elizur. 2020. "Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Highlights Key Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Nutrient Metabolism and Digestion in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) Fed Terrestrial Animal and Plant Proteins" Genes 11, no. 6: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060621
APA StyleDam, C. T. M., Ventura, T., Booth, M., Pirozzi, I., Salini, M., Smullen, R., & Elizur, A. (2020). Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Highlights Key Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Nutrient Metabolism and Digestion in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) Fed Terrestrial Animal and Plant Proteins. Genes, 11(6), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060621







