Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Function of Wild-Type NPM1
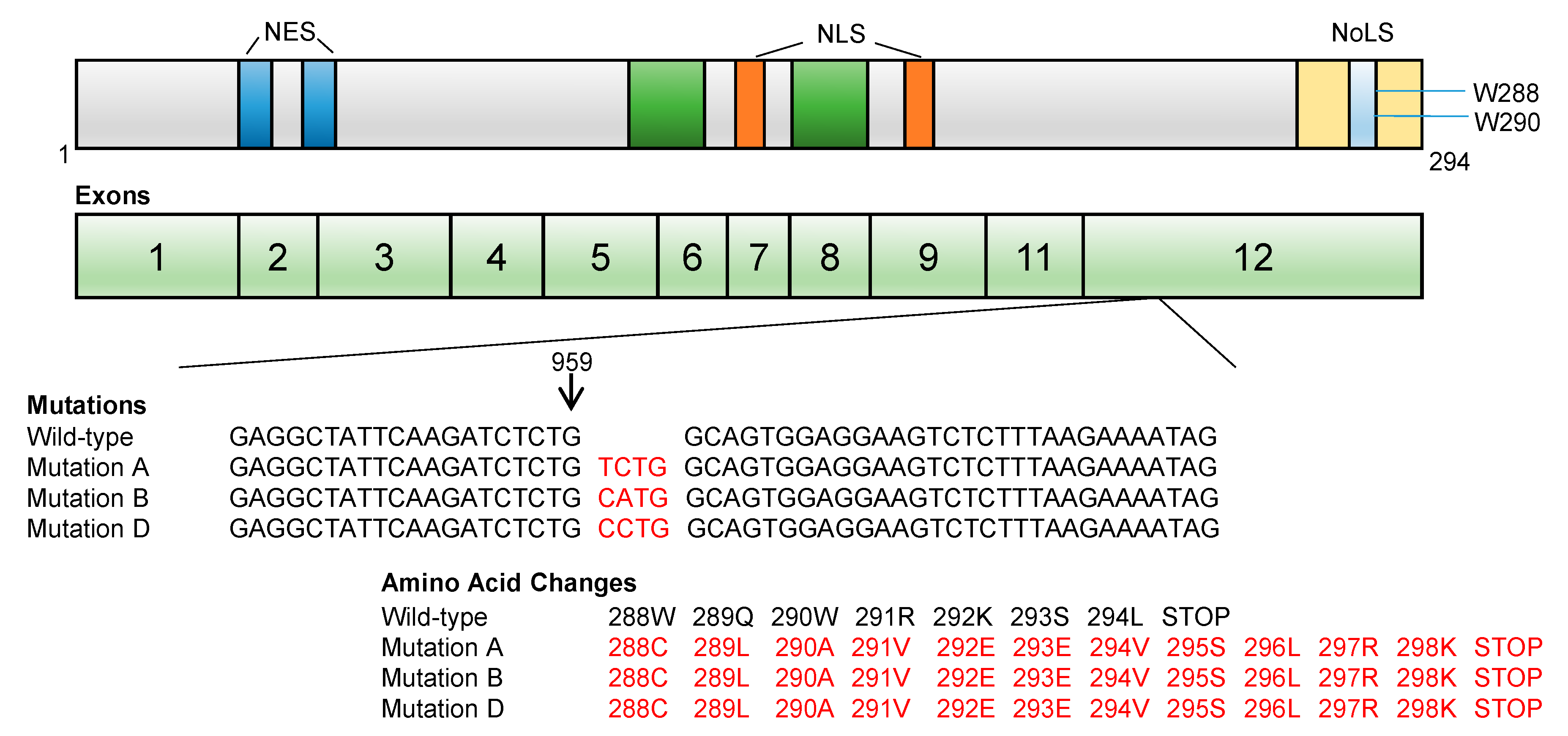
2.1. NPM1 Protein Structure
2.2. Physiologic NPM1 Functions
2.2.1. Ribosome Synthesis
2.2.2. Genomic Stability and DNA Repair
2.2.3. Cellular Growth and Stress Response
2.3. NPM1 Gene Structure
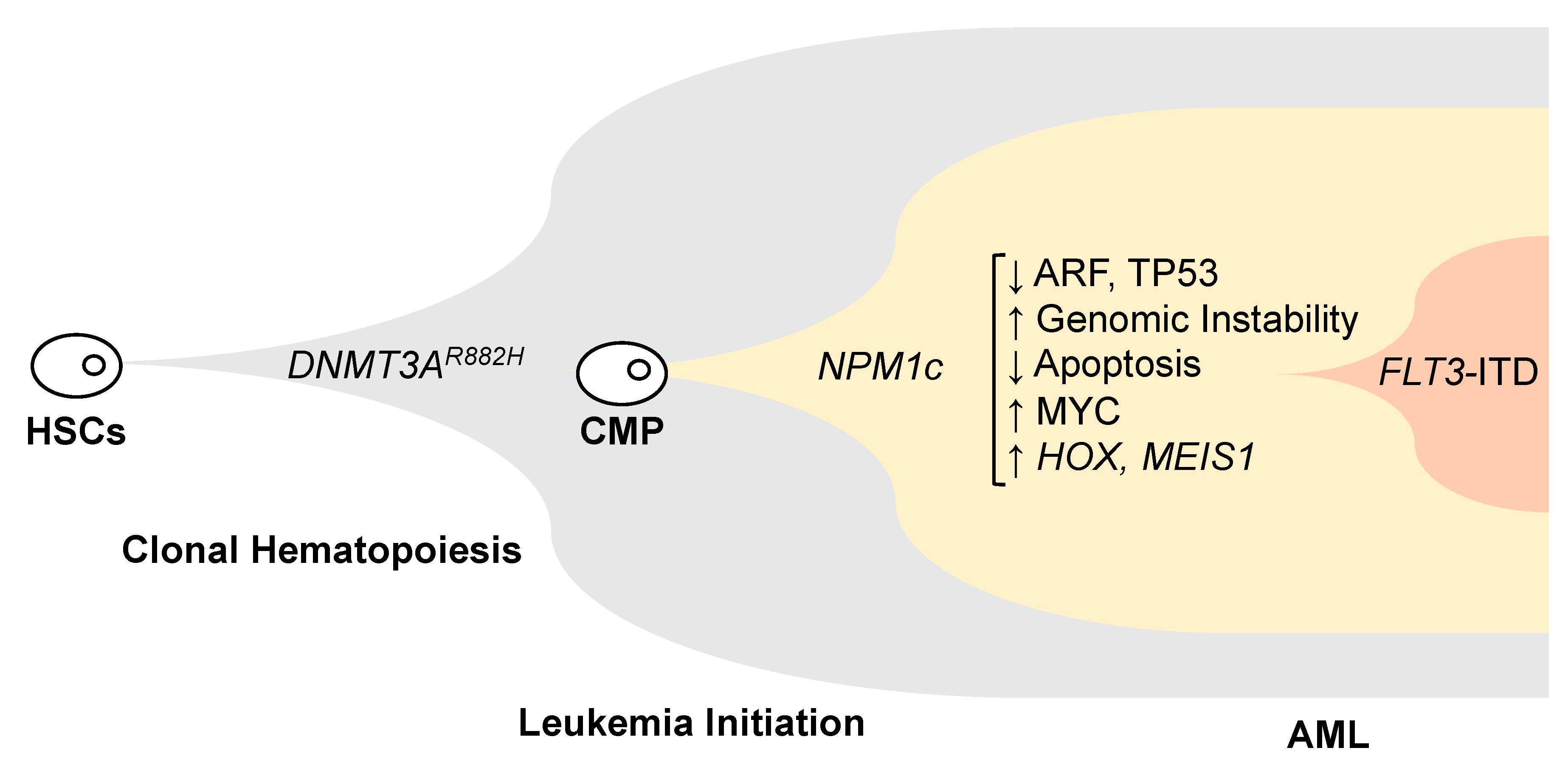
3. NPM1 and Leukemia
3.1. NPM1 Mutations
3.2. Potential Leukemogenic Mechanisms of NPM1 Mutations
3.2.1. Genomic Instability
3.2.2. Loss of ARF and/or p53 Functions
3.2.3. Effect on Apoptosis
3.2.4. Increased MYC
3.2.5. HOX Genes Expression
3.3. Phenotype and Clinical Implications of NPM1 Mutations
3.4. Therapeutic Strategies for Targeting AML with Mutated NPM1 Gene
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Disclosures
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.J.R.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Børresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombret, H.; Gardin, C. An update of current treatments for adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.J.; Rytting, M.E.; Cortes, J.E. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 392, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomic and Epigenomic Landscapes of Adult De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 98. [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Gönen, M.; Figueroa, M.E.; Fernandez, H.; Sun, Z.; Racevskis, J.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Dolgalev, I.; Thomas, S.; Aminova, O.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Integrated Genetic Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Wang, X.W. Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Maggi, L.B., Jr.; Brady, S.N.; Apicelli, A.J.; Dai, M.S.; Lu, H.; Weber, J.D. Nucleophosmin is essential for ribosomal protein L5 nuclear export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3798–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, A.; Olson, M.O. Nucleolar protein B23 has molecular chaperone activities. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, L.; Falini, B. Nucleophosmin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: A tale of protein unfolding and mislocalization. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, N.; De Marco, M.F.; Martelli, M.P.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Rossi, R.; Mannucci, R.; Manes, N.; Pettirossi, V.; Pileri, S.A.; et al. A dose-dependent tug of war involving the NPM1 leukaemic mutant, nucleophosmin, and ARF. Leukemia 2009, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J.; Shen, Q.; Feng, F.; Jing, Y.; Yang, C. RNA aptamers interfering with nucleophosmin oligomerization induce apoptosis of cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 4201–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Akey, I.V.; Dingwall, C.; Hartman, K.L.; Laue, T.; Nolte, R.T.; Head, J.F.; Akey, C.W. The crystal structure of nucleoplasmin-core: Implications for histone binding and nucleosome assembly. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwall, C.; Dilworth, S.M.; Black, S.J.; Kearsey, S.E.; Cox, L.S.; Laskey, R.A. Nucleoplasmin cDNA sequence reveals polyglutamic acid tracts and a cluster of sequences homologous to putative nuclear localization signals. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Furuichi, Y.; Umekawa, H. Tryptophans 286 and 288 in the C-terminal region of protein B23.1 are important for its nucleolar localization. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Grace, C.R.; Buljan, M.; Yun, M.K.; Pytel, N.J.; Satumba, J.; Nourse, A.; Park, C.G.; Madan Babu, M.; White, S.W.; et al. Structural polymorphism in the N-terminal oligomerization domain of NPM1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4466–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, M.; Horn, H.F.; Tarapore, P.; Tokuyama, Y.; Smulian, A.G.; Chan, P.K.; Knudsen, E.S.; Hofmann, I.A.; Snyder, J.D.; Bove, K.E.; et al. Nucleophosmin/B23 is a target of CDK2/cyclin E in centrosome duplication. Cell 2000, 103, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwaki, M. The structure and functions of NPM1/Nucleophsmin/B23, a multifunctional nucleolar acidic protein. J. Biochem. 2008, 143, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwaki, M.; Tsujimoto, M.; Nagata, K. The RNA binding activity of a ribosome biogenesis factor, nucleophosmin/B23, is modulated by phosphorylation with a cell cycle-dependent kinase and by association with its subtype. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2016–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, V.; Kishore, A.H.; Febitha, K.K.; Kundu, T.K. Human histone chaperone nucleophosmin enhances acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7534–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, J.; Swaminathan, V.; Gadad, S.S.; Choudhari, R.; Kodaganur, G.S.; Kundu, T.K. Acetylated NPM1 localizes in the nucleoplasm and regulates transcriptional activation of genes implicated in oral cancer manifestation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 5115–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, E.M.; Chan, S.M.; Minden, M.D.; Murphy, T.; Shlush, L.I.; Schimmer, A.D. Biological and clinical consequences of NPM1 mutations in AML. Leukemia 2017, 31, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Verdun, D.; Junera, H.R. Chapter 4 The nucleolus. In Principles of Medical Biology; Bittar, E.E., Bittar, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani, K.; Szebeni, A.; Olson, M.O. Mapping the functional domains of nucleolar protein B23. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24451–24457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, S.; Bacher, U.; Haferlach, C.; Alpermann, T.; Dicker, F.; Sundermann, J.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T. Characterization of NPM1-mutated AML with a history of myelodysplastic syndromes or myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 2011, 25, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Itahana, K.; Bhat, K.P.; Jin, A.; Itahana, Y.; Hawke, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, Y. Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Chang, J.H.; Chou, C.C.; Yung, B.Y. Involvement of nucleophosmin/B23 in the response of HeLa cells to UV irradiation. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, E.J.; Yun, Y.; Kwon, J. A proteomics approach for the identification of nucleophosmin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1/C2 as chromatin-binding proteins in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Biochem J. 2005, 388, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Chang, J.H.; Yung, B.Y. Resistance to UV-induced cell-killing in nucleophosmin/B23 over-expressed NIH 3T3 fibroblasts: Enhancement of DNA repair and up-regulation of PCNA in association with nucleophosmin/B23 over-expression. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Bonetti, P.; Lazzerini Denchi, E.; Martinelli, P.; Zamponi, R.; Marine, J.C.; Helin, K.; Falini, B.; Pelicci, P.G. Nucleophosmin is required for DNA integrity and p19Arf protein stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8874–8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Bernardi, R.; Rossi, M.; Cheng, K.; Khandker, L.; Manova, K.; Pandolfi, P.P. Role of nucleophosmin in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 437, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportoletti, P.; Grisendi, S.; Majid, S.M.; Cheng, K.; Clohessy, J.G.; Viale, A.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. Npm1 is a haploinsufficient suppressor of myeloid and lymphoid malignancies in the mouse. Blood 2008, 111, 3859–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.H.; Cheng, A.J.; Chang, P.; Pan, T.L.; Yung, B.Y. Association of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA expression with clinical outcome in patients with bladder carcinoma. Urology 2004, 64, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisendi, S.; Mecucci, C.; Falini, B.; Pandolfi, P.P. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Marine, J.C.; Danovi, D.; Falini, B.; Pelicci, P.G. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurki, S.; Peltonen, K.; Latonen, L.; Kiviharju, T.M.; Ojala, P.M.; Meek, D.; Laiho, M. Nucleolar protein NPM interacts with HDM2 and protects tumor suppressor protein p53 from HDM2-mediated degradation. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.L.; den Besten, W.; Bertwistle, D.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J. N-terminal polyubiquitination and degradation of the Arf tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertwistle, D.; Sugimoto, M.; Sherr, C.J. Physical and Functional Interactions of the Arf Tumor Suppressor Protein with Nucleophosmin/B23. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.I.; Haggerty, T.J.; Barrett, J.F.; Guo, Q.; Wonsey, D.R.; Dang, C.V. Characterization of nucleophosmin (B23) as a Myc target by scanning chromatin immunoprecipitation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48285–48291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, K.; Caron, H.N.; van Asperen, R.; Valentijn, L.; Hermus, M.C.; van Sluis, P.; Roobeek, I.; Weis, I.; Voûte, P.A.; Schwab, M.; et al. N-myc enhances the expression of a large set of genes functioning in ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Boone, D.; Hann, S.R. Nucleophosmin interacts directly with c-Myc and controls c-Myc-induced hyperproliferation and transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18794–18799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.J.; Wang, X.W. Nucleophosmin and human cancer. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2006, 30, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, Y.; Van Belzen, N.; Van der Made, A.C.; Dinjens, W.N.; Bosman, F.T. Expression of nucleophosmin/B23 in normal and neoplastic colorectal mucosa. J. Pathol. 1996, 178, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, L.B.; Gercel-Taylor, C.; Yashar, C.M.; Wan, T.C.; Katsanis, W.A.; Spinnato, J.A.; Taylor, D.D. Induction of immune responses to ovarian tumor antigens by multiparity. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 1997, 4, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subong, E.N.; Shue, M.J.; Epstein, J.I.; Briggman, J.V.; Chan, P.K.; Partin, A.W. Monoclonal antibody to prostate cancer nuclear matrix protein (PRO:4-216) recognizes nucleophosmin/B23. Prostate 1999, 39, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaar, T.C.; Prasad, S.C.; Sharareh, S.; Lippman, M.E.; Brunner, N.; Clarke, R. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analyses identify nucleophosmin as an estrogen regulated protein associated with acquired estrogen-independence in human breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 67, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redner, R.L.; Rush, E.A.; Faas, S.; Rudert, W.A.; Corey, S.J. The t(5;17) variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia expresses a nucleophosmin-retinoic acid receptor fusion. Blood 1996, 87, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, S.C.; Dube, I.D.; Valentine, M.B.; Mirro, J., Jr.; Watt, H.J.; Larson, R.A.; Bitter, M.A.; Le Beau, M.M.; Rowley, J.D. Clinicopathologic manifestations and breakpoints of the t(3;5) in patients with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 1989, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kiyoi, H.; Ozeki, K.; Tomita, A.; Yamaji, S.; Suzuki, R.; Kodera, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Asou, N.; Kuriyama, K.; et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic implications of NPM1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohner, K.; Schlenk, R.F.; Habdank, M.; Scholl, C.; Rucker, F.G.; Corbacioglu, A.; Bullinger, L.; Frohling, S.; Dohner, H. Mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) predicts favorable prognosis in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: Interaction with other gene mutations. Blood 2005, 106, 3740–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittger, S.; Schoch, C.; Kern, W.; Mecucci, C.; Tschulik, C.; Martelli, M.F.; Haferlach, T.; Hiddemann, W.; Falini, B. Nucleophosmin gene mutations are predictors of favorable prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. Blood 2005, 106, 3733–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiede, C.; Koch, S.; Creutzig, E.; Steudel, C.; Illmer, T.; Schaich, M.; Ehninger, G.; Leukämie, F.T.D.S. Prevalence and prognostic impact of NPM1 mutations in 1485 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2006, 107, 4011–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Goudswaard, C.S.; van Putten, W.; Bijl, M.A.; Sanders, M.A.; Hugens, W.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Erpelinck, C.A.J.; Delwel, R.; Löwenberg, B.; et al. Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and their favorable prognostic significance. Blood 2005, 106, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrow, J.; Dyer, S.A.; Akiki, S.; Griffiths, M.J. Molecular roulette: Nucleophosmin mutations in AML are orchestrated through N-nucleotide addition by TdT. Blood 2019, 134, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, G.S. The curious incident of TdT-mediated mutations in AML. Blood 2019, 134, 2229–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrow, J.; Dyer, S.A.; Akiki, S.; Griffiths, M.J. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase promotes acute myeloid leukemia by priming FLT3-ITD replication slippage. Blood 2019, 134, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.C.; Tang, J.L.; Lin, L.I.; Yao, M.; Tsay, W.; Chen, C.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Huang, C.F.; Chiou, R.J.; Tseng, M.H.; et al. Nucleophosmin Mutations in De novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Age-Dependent Incidences and the Stability during Disease Evolution. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3310–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, G.S.; Cooper, J.L.; Rad, R.; Li, J.; Rice, S.; Uren, A.; Rad, L.; Ellis, P.; Andrews, R.; Banerjee, R.; et al. Mutant nucleophosmin and cooperating pathways drive leukemia initiation and progression in mice. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovey, O.M.; Cooper, J.L.; Mupo, A.; Grove, C.S.; Lynn, C.; Conte, N.; Andrews, R.M.; Pacharne, S.; Tzelepis, K.; Vijayabaskar, M.S.; et al. Molecular synergy underlies the co-occurrence patterns and phenotype of NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlush, L.I.; Zandi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Chen, W.C.; Brandwein, J.M.; Gupta, V.; Kennedy, J.A.; Schimmer, A.D.; Schuh, A.C.; Yee, K.W.; et al. Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature 2014, 506, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces-Zimmerman, M.R.; Hong, W.J.; Weissman, I.L.; Medeiros, B.C.; Majeti, R. Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, G.; Kahler, A.K.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lindberg, J.; Rose, S.A.; Bakhoum, S.F.; Chambert, K.; Mick, E.; Neale, B.M.; Fromer, M.; et al. Clonal hematopoiesis and blood-cancer risk inferred from blood DNA sequence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; McLellan, M.D.; Johnson, K.J.; Wendl, M.C.; McMichael, J.F.; Schmidt, H.K.; Yellapantula, V.; Miller, C.A.; et al. Age-related mutations associated with clonal hematopoietic expansion and malignancies. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKerrell, T.; Park, N.; Moreno, T.; Grove, C.S.; Ponstingl, H.; Stephens, J.; Crawley, C.; Craig, J.; Scott, M.A.; Hodkinson, C.; et al. Leukemia-associated somatic mutations drive distinct patterns of age-related clonal hemopoiesis. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensma, D.P.; Bejar, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Lindsley, R.C.; Sekeres, M.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ebert, B.L. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2015, 126, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, S.; Fontanillas, P.; Flannick, J.; Manning, A.; Grauman, P.V.; Mar, B.G.; Lindsley, R.C.; Mermel, C.H.; Burtt, N.; Chavez, A.; et al. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2488–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.P.; Manes, N.; Pettirossi, V.; Liso, A.; Pacini, R.; Mannucci, R.; Zei, T.; Bolli, N.; di Raimondo, F.; Specchia, G.; et al. Absence of nucleophosmin leukaemic mutants in B and T cells from AML with NPM1 mutations: Implications for the cell of origin of NPMc+ AML. Leukemia 2008, 22, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzeler, K.H.; Herold, T.; Rothenberg-Thurley, M.; Amler, S.; Sauerland, M.C.; Görlich, D.; Schneider, S.; Konstandin, N.P.; Dufour, A.; Bräundl, K.; et al. Spectrum and prognostic relevance of driver gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haferlach, C.; Mecucci, C.; Schnittger, S.; Kohlmann, A.; Mancini, M.; Cuneo, A.; Testoni, N.; Rege-Cambrin, G.; Santucci, A.; Vignetti, M.; et al. AML with mutated NPM1 carrying a normal or aberrant karyotype show overlapping biologic, pathologic, immunophenotypic, and prognostic features. Blood 2009, 114, 3024–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micol, J.B.; Boissel, N.; Renneville, A.; Castaigne, S.; Gardin, C.; Preudhomme, C.; Dombret, H. The role of cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutations and no FLT3 internal tandem duplication. Blood 2009, 114, 4601–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, L.; Röllig, C.; Montesinos, P.; Martínez-Cuadrón, D.; Barragan, E.; García, R.; Botella, C.; Martínez, P.; Ravandi, F.; Kadia, T.; et al. Chromosomal Abnormalities and Prognosis in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Nine International Cohorts. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2632–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Martinelli, P.; Zamponi, R.; Shing, D.C.; Bonetti, P.; Luzi, L.; Volorio, S.; Bernard, L.; Pruneri, G.; Alcalay, M.; et al. Delocalization and Destabilization of the Arf Tumor Suppressor by the Leukemia-Associated NPM Mutant. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3044–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besten, W.D.; Kuo, M.L.; Williams, R.T.; Sherr, C.J. Myeloid Leukemia-Associated Nucleophosmin Mutants Perturb p53-Dependent and Independent Activities of the Arf Tumor Suppressor Protein. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.M.; Tan, B.X.; Bte Ahmad, B.; Yan, T.; Chee, L.Y.; Ang, S.T.; Tay, K.G.; Koh, L.P.; Yeoh, A.E.J.; Koay, E.S.C.; et al. Mutant nucleophosmin deregulates cell death and myeloid differentiation through excessive caspase-6 and -8 inhibition. Blood 2010, 116, 3286–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Jin, S.; Song, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhan, Q. B23 regulates GADD45a nuclear translocation and contributes to GADD45a-induced cell cycle G2-M arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10988–10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhan, Q.; Coursen, J.D.; Khan, M.A.; Kontny, H.U.; Yu, L.; Hollander, M.C.; O’Connor, P.M.; Fornace, A.J.; Harris, C.C. GADD45 induction of a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3706–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, P.; Davoli, T.; Sironi, C.; Amati, B.; Pelicci, P.G.; Colombo, E. Nucleophosmin and its AML-associated mutant regulate c-Myc turnover through Fbw7γ. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohanian, M.; Rozovski, U.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Loghavi, S.; Kadia, T.; Futreal, A.; Bhalla, K.; Zuo, Z.; Huh, Y.O.; et al. MYC protein expression is an important prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalay, M.; Tiacci, E.; Bergomas, R.; Bigerna, B.; Venturini, E.; Minardi, S.P.; Meani, N.; Diverio, D.; Bernard, L.; Tizzoni, L.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML) shows a distinct gene expression profile characterized by up-regulation of genes involved in stem-cell maintenance. Blood 2005, 106, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, L.; Gundry, M.C.; Sorcini, D.; Guzman, A.G.; Huang, Y.H.; Ramabadran, R.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Nabet, B.; et al. Mutant NPM1 Maintains the Leukemic State through HOX Expression. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Staunton, J.E.; Silverman, L.B.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L.; Minden, M.D.; Sallan, S.E.; Lander, E.S.; Golub, T.R.; Korsmeyer, S.J. MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile that distinguishes a unique leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, A.; Somervaille, T.C.; Smith, K.S.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Meyerson, M.; Cleary, M.L. The menin tumor suppressor protein is an essential oncogenic cofactor for MLL-associated leukemogenesis. Cell 2005, 123, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.W.; Song, E.; Feng, Z.; Sinha, A.; Chen, C.W.; Deshpande, A.J.; Cusan, M.; Farnoud, N.; Mupo, A.; Grove, C.; et al. Targeting Chromatin Regulators Inhibits Leukemogenic Gene Expression in NPM1 Mutant Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1166–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckelmann, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Wong, E.M.; Hatton, C.; Giovinazzo, H.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Rucker, F.G.; Dohner, K.; McGeehan, G.M.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of preleukemia cells in a mouse model of NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Science 2020, 367, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, R.E.; Green, C.; Allen, C.; Mead, A.J.; Burnett, A.K.; Hills, R.K.; Linch, D.C. The impact of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutant level, number, size, and interaction with NPM1 mutations in a large cohort of young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissel, N.; Renneville, A.; Biggio, V.; Philippe, N.; Thomas, X.; Cayuela, J.M.; Terre, C.; Tigaud, I.; Castaigne, S.; Raffoux, E.; et al. Prevalence, clinical profile, and prognosis of NPM mutations in AML with normal karyotype. Blood 2005, 106, 3618–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Dohner, K.; Krauter, J.; Frohling, S.; Corbacioglu, A.; Bullinger, L.; Habdank, M.; Spath, D.; Morgan, M.; Benner, A.; et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.; Grimwade, D.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 2017, 129, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleveedu, K.S.; Sidiqi, M.H.; Nadiminti, K.; Hefazi, M.; Alkhateeb, H.B.; Shah, M.V.; Phelps, A.; He, R.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Dingli, D.; et al. Impact of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant on Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on NPM1 and FLT3 Mutational Status. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, S113–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, P.; Terwey, T.H.; Vuong, L.G.; le Coutre, P.D.; Dörken, B.; Arnold, R. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation For Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Impact Of FLT3 and NPM1 Mutational Status. Blood 2013, 122, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Ravandi, F. How close are we to incorporating measurable residual disease into clinical practice for acute myeloid leukemia? Haematologica 2019, 104, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, A.; Hills, R.K.; Simpson, M.A.; Jovanovic, J.V.; Gilkes, A.; Grech, A.; Patel, Y.; Bhudia, N.; Farah, H.; Mason, J.; et al. Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Standard-Risk AML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwade, D.; Freeman, S.D. Defining minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia: Which platforms are ready for “prime time”? Blood 2014, 124, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.P.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Pierangeli, S.; Mulas, F.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Pettirossi, V.; Rossi, R.; et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, H.; Dassouki, Z.; Berthier, C.; Raffoux, E.; Ades, L.; Legrand, O.; Hleihel, R.; Sahin, U.; Tawil, N.; Salameh, A.; et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide trigger degradation of mutated NPM1, resulting in apoptosis of AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Lambert, J.; Nibourel, O.; Pautas, C.; Hayette, S.; Cayuela, J.M.; Terre, C.; Rousselot, P.; Dombret, H.; Chevret, S.; et al. MRD assessed by WT1 and NPM1 transcript levels identifies distinct outcomes in AML patients and is influenced by gemtuzumab ozogamicin. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6280–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olombel, G.; Guerin, E.; Guy, J.; Perrot, J.Y.; Dumezy, F.; de Labarthe, A.; Bastie, J.N.; Legrand, O.; Raffoux, E.; Plesa, A.; et al. The level of blast CD33 expression positively impacts the effect of gemtuzumab ozogamicin in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2157–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Arellano, M.; Becker, P.S.; Frankfurt, O.; Konopleva, M.; Wei, A.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.H.; Strickland, S.A.; Hou, J.Z.; Fiedler, W.; Lin, T.L.; Walter, R.B.; Enjeti, A.; Tiong, I.S.; Savona, M.; Lee, S.; et al. Venetoclax Combined With Low-Dose Cytarabine for Previously Untreated Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results From a Phase Ib/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachowiez, C.A.; Loghavi, S.; Kadia, T.M.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Naqvi, K.; Alvarado, Y.; Yilmaz, M.; Short, N.; et al. Outcomes of older patients with NPM1-mutated AML: Current treatments and the promise of venetoclax-based regimens. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Martelli, M.P. Dactinomycin in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1180–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Savona, M.; Baz, R.; Andreeff, M.; Gabrail, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Savoie, L.; Mau-Sorensen, P.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Yee, K.; et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of single-agent selinexor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkin, D.; He, S.; Miao, H.; Kempinska, K.; Pollock, J.; Chase, J.; Purohit, T.; Malik, B.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; et al. Pharmacologic Inhibition of the Menin-MLL Interaction Blocks Progression of MLL Leukemia In Vivo. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grembecka, J.; He, S.; Shi, A.; Purohit, T.; Muntean, A.G.; Sorenson, R.J.; Showalter, H.D.; Murai, M.J.; Belcher, A.M.; Hartley, T.; et al. Menin-MLL inhibitors reverse oncogenic activity of MLL fusion proteins in leukemia. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Evans, K.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Eschle, B.K.; Hatton, C.; Uckelmann, H.J.; Ross, K.N.; Perner, F.; Olsen, S.N.; Pritchard, T.; et al. A Menin-MLL Inhibitor Induces Specific Chromatin Changes and Eradicates Disease in Models of MLL-Rearranged Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klossowski, S.; Miao, H.; Kempinska, K.; Wu, T.; Purohit, T.; Kim, E.; Linhares, B.M.; Chen, D.; Jih, G.; Perkey, E.; et al. Menin inhibitor MI-3454 induces remission in MLL1-rearranged and NPM1-mutated models of leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenstein, T.; Leisegang, M.; Uckert, W.; Schreiber, H. Targeting cancer-specific mutations by T cell receptor gene therapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 33, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Robbins, P.F.; Rosenberg, S.A. ‘Final common pathway’ of human cancer immunotherapy: Targeting random somatic mutations. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Lee, D.I.; Reijmers, R.M.; Honders, M.W.; Hagedoorn, R.S.; de Jong, R.C.; Kester, M.G.; van der Steen, D.M.; de Ru, A.H.; Kweekel, C.; Bijen, H.M.; et al. Mutated nucleophosmin 1 as immunotherapy target in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbouh, A.I.; Hleihel, R.S.; Saliba, J.L.; Karam, M.M.; Hamie, M.H.; Wu, H.J.M.; Berthier, C.P.; Tawil, N.M.; Bonnet, P.A.; Deleuze-Masquefa, C.; et al. Imidazoquinoxaline derivative EAPB0503: A promising drug targeting mutant nucleophosmin 1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2017, 123, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balusu, R.; Fiskus, W.; Rao, R.; Chong, D.G.; Nalluri, S.; Mudunuru, U.; Ma, H.; Chen, L.; Venkannagari, S.; Ha, K.; et al. Targeting levels or oligomerization of nucleophosmin 1 induces differentiation and loss of survival of human AML cells with mutant NPM1. Blood 2011, 118, 3096–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Wen, L.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, Y. Deguelin, a selective silencer of the NPM1 mutant, potentiates apoptosis and induces differentiation in AML cells carrying the NPM1 mutation. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Drug Class | Target | Mechanism | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRA + ATO | Antineoplastic agents | ? | Proteasomal degradation of NPM1 | Martelli et al., 2015; El Hajj et al., 2015 |
| Dactinomycin | Chemotherapy | RNA-Pol 1 | Unclear in this setting | Falini et al., 2015 |
| GO | ADC | CD33 | Induces DSBs in DNA, cell cycle Arrest and apoptosis | Lambert et al., 2014; Olombel et al., 2016 |
| Venetoclax | Small molecule | Bcl-2 | Induces apoptosis | Lachowiez et al., 2020 |
| Selinexor | Small molecule | XPO1 | Inhibits translocation of NPM1 to the cytoplasm | Brunetti et al., 2019 |
| EAPB0503 | Small molecule | ? | Proteasomal degradation of NPM1 | Nabbouh et al., 2017 |
| Modified T cells | Immunotherapy | Neoantigen | T-cell activation | Van der Lee et al., 2019 |
| VTP-50469 | Small molecule | Menin | Disrupts MLL chromatin complex Preferential effect on MEIS1 (not HOX) | Uckelman et al., 2020 |
| MI-2, MI-503, MI-463, MI-3454 | Small molecule | Menin | Inhibits HOX genes and MEIS1 | Borkin et al., 2015; Grembecka et al., 2012; Krivtsov et al. 2019 |
| Deguelin | Rotenoid | ? | Induces apoptosis in NPM1c cell lines | Yi et al., 2015 |
| NSC348884 | Small molecule | NPM1 Oligomerization domain | Inhibits oligomerization, leading to apoptosis | Balusa et al., 2011 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarka, J.; Short, N.J.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Issa, G.C. Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes 2020, 11, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060649
Zarka J, Short NJ, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Issa GC. Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes. 2020; 11(6):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060649
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarka, Jabra, Nicholas J. Short, Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, and Ghayas C. Issa. 2020. "Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Genes 11, no. 6: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060649
APA StyleZarka, J., Short, N. J., Kanagal-Shamanna, R., & Issa, G. C. (2020). Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes, 11(6), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060649







