Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.—Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anisakis Simplex
2.2. In Vitro Culture with Ivermectin
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Protein Precipitation and Trypsin Digestion
2.5. TMT Labeling and Reversed-Phase Fractionation
2.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.7. Processing of the MS/MS Data
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Functional Analysis
2.10. Network Analysis
2.11. Transcription Level Determination by Real-Time PCR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Functional Enrichment Analysis
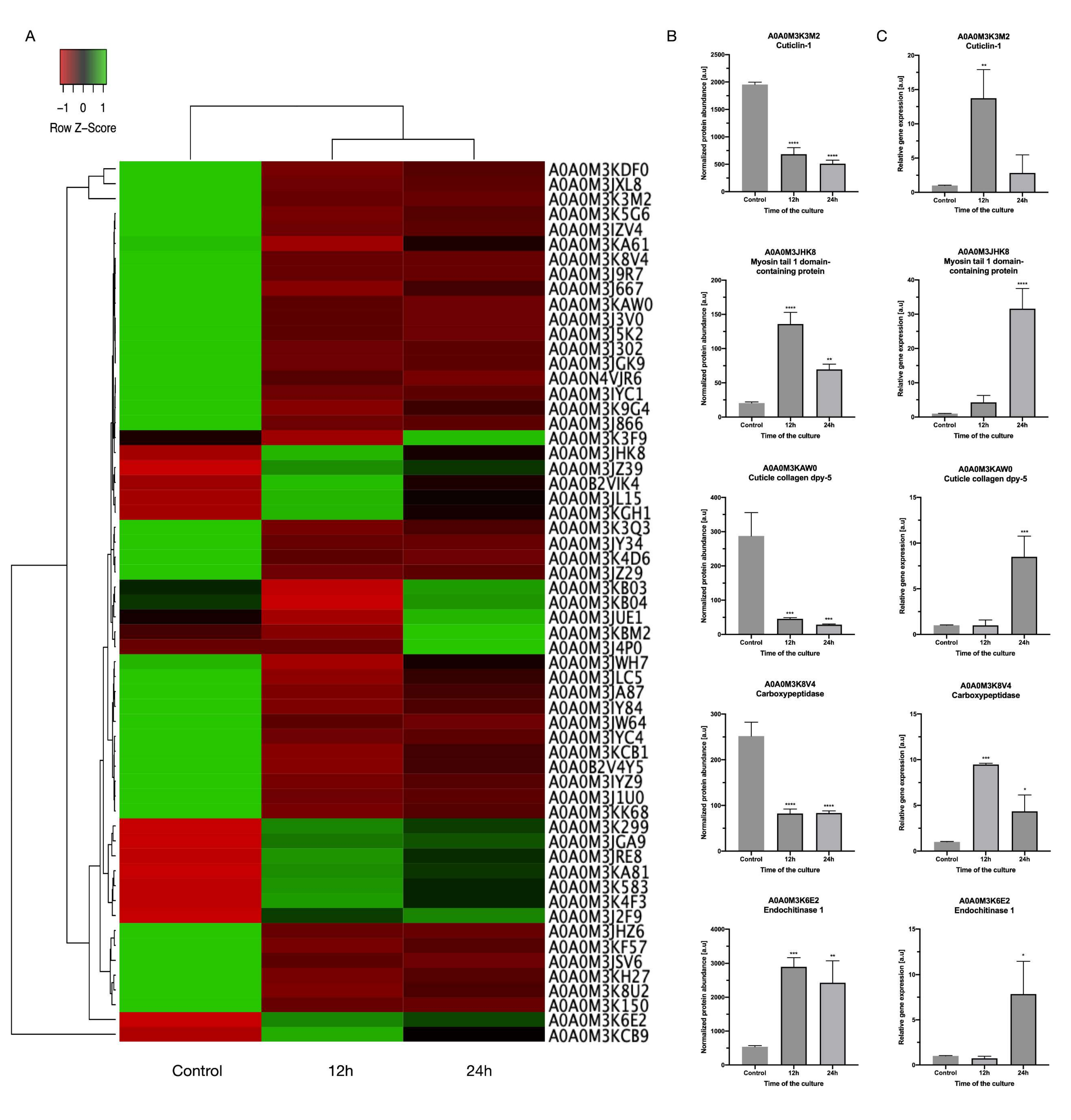
3.2. Differentially Regulated Proteins
3.3. Protein—Protein Interactions
3.4. The Transcription Levels of Selected DRPs
3.5. Detailed Description of Selected DRPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis—A food-borne parasite that triggers allergic host defences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanović, J.; Baltić, M.Ž.; Boskovic, M.; Kilibarda, N.; Dokmanović, M.; Marković, R.; Janjić, J.; Baltić, B. Anisakis allergy in human. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Pierce, G.J.; Pascual, S.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, M.; Mattiucci, S.; Mladineo, I.; Cipriani, P.; Buselic, I.; Strachan, N.J.C. Assessing the risk of an emerging zoonosis of worldwide concern: Anisakiasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pravettoni, V.; Primavesi, L.; Piantanida, M. Anisakis simplex: Current knowledge. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 44, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, L.; Sprong, H.; Ortega, Y.R.; Van Der Giessen, J.W.; Fayer, R. Impacts of globalisation on foodborne parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovic, J.; Baltic, M.Z.; Boskovic, M.; Kilibarda, N.; Dokmanovic, M.; Marković, R.; Janjic, J.; Baltic, B. Anisakis Infection and Allergy in Humans. Procedia Food Sci. 2015, 5, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, M.; Pierce, G.; Strachan, N.; Pascual, S.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, M.; Levsen, A. Human health, legislative and socioeconomic issues caused by the fish-borne zoonotic parasite Anisakis: Challenges in risk assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczyk, L.; Szostakowska, B.; Sobecka, E.; Szczucki, K.; Stankiewicz, K.; Lidia, K.; Beata, S.; Ewa, S.; Krzysztof, S.; Kamil, S. First case of human anisakiasis in Poland. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 76, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramello, P.; Vitali, A.; Canta, F.; Caldana, A.; Santi, F.; Caputo, A.; Lipani, F.; Balbiano, R. Intestinal localization of anisakiasis manifested as acute abdomen. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.-J.; Lee, J.-C.; Kim, M.-J.; Hur, G.-Y.; Shin, S.-Y.; Park, H. The Clinical Characteristics of Anisakis Allergy in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2009, 24, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibinu, I.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis Nematodes in Fish and Shellfish- from infection to allergies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audicana, M.T.; Kennedy, M.W. Anisakis simplex: From Obscure Infectious Worm to Inducer of Immune Hypersensitivity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crump, A. The advent of ivermectin: People, partnerships, and principles. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynagh, T.; Lynch, J.W. Ivermectin binding sites in human and invertebrate Cys-loop receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hibbs, R.E.; Gouaux, E. Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor. Nature 2011, 474, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.; Andersen, E.; Shapiro, J.; Gerke, J.P.; Kruglyak, L. Natural Variation in a Chloride Channel Subunit Confers Avermectin Resistance in C. elegans. Science 2012, 335, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laing, R.; Kikuchi, T.; Martinelli, A.; Tsai, I.J.; Beech, R.; Redman, E.M.; Holroyd, N.E.; Bartley, D.J.; Beasley, H.; Britton, C.; et al. The genome and transcriptome of Haemonchus contortus, a key model parasite for drug and vaccine discovery. Genome Boil. 2013, 14, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shan, Q.; Haddrill, J.L.; Lynch, J.W. Ivermectin, an Unconventional Agonist of the Glycine Receptor Chloride Channel. J. Boil. Chem. 2001, 276, 12556–12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adelsberger, H.; Lepier, A.; Dudel, J. Activation of rat recombinant α1β2γ2S GABAA receptor by the insecticide ivermectin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 394, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, D.F.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Liu, K.K.; Paress, P.S.; Van Der Ploeg, L.H.T.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Arena, J.P. Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1994, 371, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCavera, S.; Rogers, A.T.; Yates, D.; Woods, D.J.; Wolstenholme, A.J. An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laing, R.; Gillan, V.; Devaney, E. Ivermectin–Old Drug, New Tricks? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzik, J.M. Molecules released by helminth parasites involved in host colonization. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2006, 53, 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwarteng, A.; Ahuno, S.; Akoto, F.O. Killing filarial nematode parasites: Role of treatment options and host immune response. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crump, A. Ivermectin: Enigmatic multifaceted ‘wonder’ drug continues to surprise and exceed expectations. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, Q.; Chen, H.N.; Wang, K.; Yuan, K.; Lei, Y.; Li, K.; Zheng, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Ivermectin induces cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/Akt axis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4457–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caly, L.; Druce, J.D.; Catton, M.G.; Jans, D.A.; Wagstaff, K.M. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, S.; Botros, S.; Ismail, M.; Farghally, A.; Day, T.; Bennett, J.L. Praziquantel-induced tegumental damage in vitro is diminished in schistosomes derived from praziquantel-resistant infections. Parasitology 2001, 122, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melman, S.D.; Steinauer, M.L.; Cunningham, C.; Kubatko, L.S.; Mwangi, I.N.; Wynn, N.B.; Mutuku, M.W.; Karanja, D.M.S.; Colley, D.G.; Black, C.L.; et al. Reduced Susceptibility to Praziquantel among Naturally Occurring Kenyan Isolates of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemale, G.; Perally, S.; LaCourse, E.J.; Prescott, M.C.; Jones, L.M.; Ward, D.; Meaney, M.; Hoey, E.; Brennan, G.P.; Fairweather, I.; et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Triclabendazole Response in the Liver FlukeFasciola hepatica. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4940–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, A.J.; Rogers, A.T. Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology 2006, 131, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Ree, A.M.; Mutapi, F. The helminth parasite proteome at the host–parasite interface–Informing diagnosis and control. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 157, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stryiński, R.; Mateos, J.; Pascual, S.; González, Á.F.; Gallardo, J.M.; Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Medina, I.; Carrera, M. Proteome profiling of L3 and L4 Anisakis simplex development stages by TMT-based quantitative proteomics. J. Proteom. 2019, 201, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, L.; Valero, A.; Benítez, R.; Adroher, F.J.; Auroux, F.J.A. In vitrocultivation ofAnisakis simplex:pepsin increases survival and moulting from fourth larval to adult stage. Parasitology 2001, 123, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Ellis, B.L.; Yiu, Y.Y.; Miller, M.M.; Urban, J.F.; Shi, L.Z.; Aroian, R.V. An Extensive Comparison of the Effect of Anthelmintic Classes on Diverse Nematodes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; López-Ferrer, D.; Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Fast Monitoring of Species-Specific Peptide Biomarkers Using High-Intensity-Focused-Ultrasound-Assisted Tryptic Digestion and Selected MS/MS Ion Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5688–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kall, L.; Canterbury, J.D.; Weston, J.; Noble, W.S.; Mac Coss, M.J. Semi-supervised ma-chine learning technique for peptide identification from shotgun proteomics datasets. Nature Met. 2007, 4, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Stryiński, R.; Paukszto, Ł.; Jastrzębski, J.P.; Makowczenko, K. The Selection of Reliable Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Analysis of Anisakis simplex Sensu Stricto Gene Expression from Different Developmental Stages. Acta Parasitol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, P.M.; Mackintosh, N.; Morphew, R. Anthelmintic metabolism in parasitic helminths: Proteomic insights. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça-Previato, L.; Penha, L.; Garcez, T.C.; Jones, C.; Mendonça-Previato, L. Addition of α-O-GlcNAc to threonine residues define the post-translational modification of mucin-like molecules in Trypanosoma cruzi. Glycoconj. J. 2013, 30, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krendel, M.; Mooseker, M.S. Myosins: Tails (and Heads) of Functional Diversity. Physiology 2005, 20, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, X.; Tan, X.; Qi, X.; Huang, A.; Ling, F.; Wang, G. Proteome interrogation using gold nanoprobes to identify targets of arctigenin in fish parasites. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, R.; Holmes, K. Actin structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Dalton, J.P. Advances in Fasciola hepatica research using ‘omics’ technologies. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallero, S.; Lombardo, F.; Salvemini, M.; Pizzarelli, A.; Cantacessi, C.; D’Amelio, S. Comparative Transcriptomics Reveals Clues for Differences in Pathogenicity between Hysterothylacium aduncum, Anisakis simplex sensu stricto and Anisakis pegreffii. Genes 2020, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, J.W.; Shim, J. A novel zinc-carboxypeptidase SURO-1 regulates cuticle formation and body morphogenesis inCaenorhabditis elegans. FEBS Lett. 2010, 585, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torralbo-Ramírez, V.; Molina-Fernández, D.; Malagón, D.; Benítez, R.; Adroher, F.J. Differential Cleaving of Specific Substrates for Cathepsin-Like Activity Shows Cysteine and Serine Protease Activities and a Differential Profile Between Anisakis simplex s.s. and Anisakis pegreffii, Sibling Species Major Etiologic Agents of Anisakiasis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Fernández, D.; Benítez, R.; Adroher, F.J.; Malagón, D. Differential proteolytic activity in Anisakis simplex s.s. and Anisakis pegreffii, two sibling species from the complex Anisakis simplex s.l., major etiological agents of anisakiasis. Acta Trop. 2019, 195, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimakura, K.; Miura, H.; Ikeda, K.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Shirai, T.; Kasuya, S.; Shiomi, K. Purification and molecular cloning of a major allergen from Anisakis simplex. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004, 135, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, A.; Brattig, N.W. Identification, isolation, and cloning of the full-length sequence of a gene encoding trypsin inhibitor-like protein (TIL) secreted by the intestinal parasitic nematode Strongyloides ratti. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2018, 79, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, R.Y.; Ren, H.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Lv, P.; Wei, G.H.; Ming, L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Comparative proteomics analysis of Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae exposed to albendazole sulfoxide stress. Acta Trop. 2018, 185, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młocicki, D.; Sulima, A.; Bień-Kalinowska, J.; Näreaho, A.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Basałaj, K.; Sałamatin, R.; Conn, D.B.; Savijoki, K. Immunoproteomics and Surfaceomics of the Adult Tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Ani s 1, the major allergen of Anisakis simplex: Purification by affinity chromatography and functional expression in Escherichia coli. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, M.; Paoletti, M.; Colantoni, A.; Rughetti, A.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. Gene expression profiles of antigenic proteins of third stage larvae of the zoonotic nematode Anisakis pegreffii in response to temperature conditions. Parasite 2019, 26, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doedens, A.; Loukas, A.; Maizels, R.M. A cDNA encoding Tc-MUC-5, a mucin from Toxocara canis larvae identified by expression screening. Acta Trop. 2001, 79, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, G.M.; Scanlon, M.J.; Swarbrick, J.; Curtis, S.; Gallant, E.; Dulhunty, A.F.; O’Bryan, M.K. The Cysteine-rich Secretory Protein Domain of Tpx-1 Is Related to Ion Channel Toxins and Regulates Ryanodine Receptor Ca2+ Signaling. J. Boil. Chem. 2006, 281, 4156–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Möhrlen, F.; Hutter, H.; Zwilling, R. The astacin protein family in Caenorhabditis elegans. JBIC J. Boil. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 270, 4909–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoušková, P.; Vokral, I.; Lamka, J.; Skálová, L. The Role of Xenobiotic-Metabolizing Enzymes in Anthelmintic Deactivation and Resistance in Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polak, I.; Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Stryiński, R.; Mateos, J.; Carrera, M. Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.—Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin. Genes 2020, 11, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060710
Polak I, Łopieńska-Biernat E, Stryiński R, Mateos J, Carrera M. Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.—Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin. Genes. 2020; 11(6):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060710
Chicago/Turabian StylePolak, Iwona, Elżbieta Łopieńska-Biernat, Robert Stryiński, Jesús Mateos, and Mónica Carrera. 2020. "Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.—Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin" Genes 11, no. 6: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060710
APA StylePolak, I., Łopieńska-Biernat, E., Stryiński, R., Mateos, J., & Carrera, M. (2020). Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.—Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin. Genes, 11(6), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060710