Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P–GI.1d Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction, Genome Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Recombination Analysis
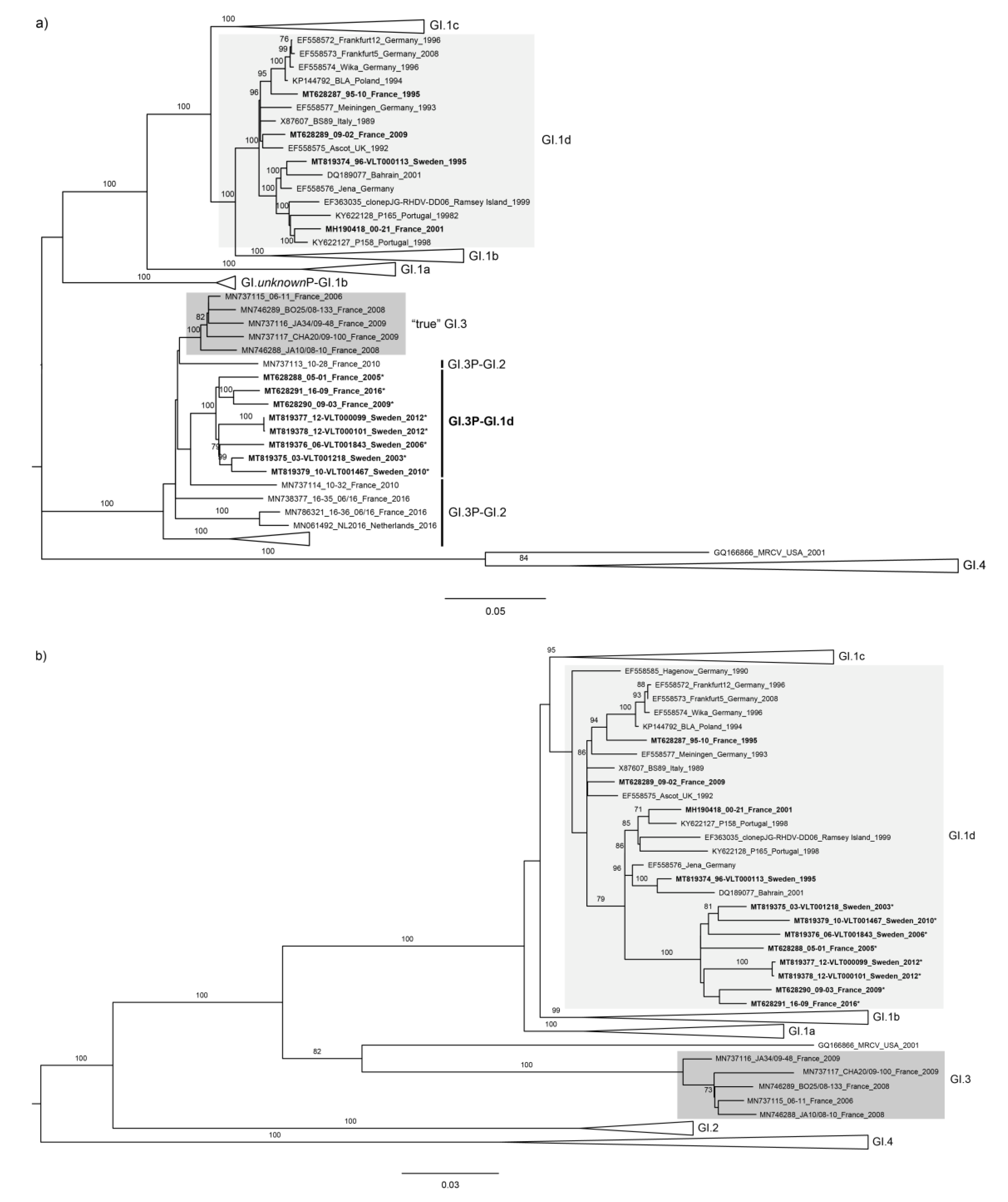
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arenas, M.; Araujo, N.M.; Branco, C.; Castelhano, N.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Pérez-Losada, M. Mutation and recombination in pathogen evolution: Relevance, methods and controversies. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rest, J.S.; Mindell, D.P. SARS associated coronavirus has a recombinant polymerase and coronaviruses have a history of host-shifting. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2003, 3, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Weiller, G.F. Evidence that a plant virus switched hosts to infect a vertebrate and then recombined with a vertebrate-infecting virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8022–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malim, M.H.; Emerman, M. HIV-1 sequence variation: Drift, shift, and attenuation. Cell 2001, 104, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Holmes, E.C. Why do RNA viruses recombine? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Xie, Y. Evidence for inter- and intra-clade recombinations in rabies virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xue, H.; Pu, B.; Qian, N. A new viral disease in rabbit. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 1984, 16, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, J.; van der Loo, W.; Le Pendu, J.; Esteves, P.J. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): A review. Vet. Res. 2012, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.-S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.M.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, L.; Fallacara, F.; Grazioli, S.; Lavazza, A.; Pacciarini, M.L.; Brocchi, E. A further step in the evolution of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: The appearance of the first consistent antigenic variant. Virus Res. 1998, 58, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Lopes, A.M.; Dalton, K.P.; Parra, F.; Esteves, P.J. Detection of RHDVa on the Iberian Peninsula: Isolation of an RHDVa strain from a Spanish rabbitry. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alda, F.; Gaitero, T.; Suárez, M.; Merchán, T.; Rocha, G.; Doadrio, I. Evolutionary history and molecular epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in the Iberian Peninsula and Western Europe. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Freitas, J.; Silva, E.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Alves, P.C.; van der Loo, W.; Kolodziejek, J.; et al. Evolution of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) in the European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) from the Iberian Peninsula. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Laurent, S.; de Boisséson, C.; Portejoie, Y.; Rasschaert, D. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France between 1993 and 2000, and the characterisation of RHDV antigenic variants. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzner, A.; Niedbalski, W. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) strains isolated in Poland. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3197–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bergin, I.L.; Wise, A.G.; Bolin, S.R.; Mullaney, T.P.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K. Novel calicivirus identified in rabbits, Michigan, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, L.; Fusi, P.; Lavazza, A.; Pacciarini, M.L.; Rossi, C. Detection and preliminary characterization of a new rabbit calicivirus related to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus but nonpathogenic. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8614–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Fages, M.-P.; Bertagnoli, S.; Gelfi, J.; Aubineau, J.; Roobrouck, A.; Botti, G.; Lavazza, A.; Marchandeau, S. Characterisation of a non-pathogenic and non-protective infectious rabbit lagovirus related to RHDV. Virology 2011, 410, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strive, T.; Wright, J.D.; Robinson, A.J. Identification and partial characterisation of a new lagovirus in Australian wild rabbits. Virology 2009, 384, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Boucher, S.; Le Normand, B.; Plassiart, G.; Portejoie, Y.; Decors, A.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guérin, J.L.; Marchandeau, S. Detection of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.N.; Mahar, J.E.; Haboury, S.; Stevens, V.; Holmes, E.C.; Strive, T. Emerging rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDVb), Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2276–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Alonso, A.; Martin-Carrillo, N.; Garcia-Livia, K.; Valladares, B.; Foronda, P. Emerging rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2) at the gates of the African continent. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 44, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease, United States of America. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?reportid=28028 (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Eden, J.-S.; Read, A.J.; Duckworth, J.A.; Strive, T.; Holmes, E.C. Resolving the origin of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): Insights from an investigation of the viral stocks released in Australia. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12217–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, P.J.; Kitchen, A.; Holmes, E.C. Origin and phylodynamics of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12129–12138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsworth, P.; Cooke, B.D.; Kovaliski, J.; Sinclair, R.; Holmes, E.C.; Strive, T. Increased virulence of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus associated with genetic resistance in wild Australian rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Virology 2014, 464–465, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.M.; Capucci, L.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Brocchi, E.; Barbieri, I.; Quéménér, A.; Le Pendu, J.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Holmes, E.C.; et al. Molecular evolution and antigenic variation of European brown hare syndrome virus (EBHSV). Virology 2014, 468–470, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, P.J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Cavadini, P.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Guitton, J.-S.; Lavazza, A.; Lemaitre, E.; Letty, J.; Lopes, A.M.; et al. Emergence of pathogenicity in lagoviruses: Evolution from pre-existing nonpathogenic strains or through a species jump? PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.-J.; Thumfart, J.O. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: Genome organization and polyprotein processing of a calicivirus studied after transient expression of cDNA constructs. Virology 2000, 276, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.J.; Meyers, G. Genetic map of the calicivirus rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus as deduced from in vitro translation studies. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7974–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, F.; Boga, J.A.; Marín, M.S.; Casais, R. The amino acid terminal sequence of VP60 from rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus supports its putative subgenomic origin. Virus Res. 1993, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.J. Genomic and subgenomic RNAs of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus are both protein-linked and packaged into particles. Virology 1991, 184, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, R.A.; Hansman, G.S.; Clancy, L.E.; Tanaka, M.M.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Norovirus recombination in ORF1/ORF2 overlap. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansman, G.S.; Oka, T.; Katayama, K.; Takeda, N. Human sapoviruses: Genetic diversity, recombination, and classification. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.P.; Reed, F.C.; Porter, C.J.; Dawson, S.; Gaskell, R.M.; Radford, A.D. Recombination of Feline calicivirus within an endemically infected cat colony. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.N.; Mahar, J.E.; Read, A.J.; Mourant, R.; Piper, M.; Huang, N.; Strive, T. A strain-specific multiplex RT-PCR for Australian rabbit haemorrhagic disease viruses uncovers a new recombinant virus variant in rabbits and hares. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e444–e456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.M.; Dalton, K.P.; Magalhães, M.J.; Parra, F.; Esteves, P.J.; Holmes, E.C.; Abrantes, J. Full genomic analysis of new variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus revealed multiple recombination events. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, J.E.; Read, A.J.; Gu, X.; Urakova, N.; Mourant, R.; Piper, M.; Haboury, S.; Holmes, E.C.; Strive, T.; Hall, R.N. Detection and Circulation of a Novel Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus in Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.M.; Silvério, D.; Magalhães, M.J.; Areal, H.; Alves, P.C.; Esteves, P.J.; Abrantes, J. Characterization of old RHDV strains by complete genome sequencing identifies a novel genetic group. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Droillard, C.; Lopes, A.M.; Lemaitre, E.; Lucas, P.; Blanchard, Y.; Marchandeau, S.; Esteves, P.J.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. Recombination at the emergence of the pathogenic rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2. Sci. Rep. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, N.L.; Moss, S.R.; Turner, S.L.; Scirrmeier, H.; Gould, E.A. Recombination in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus: Possible impact on evolution and epidemiology. Virology 2008, 376, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, J.E.; Nicholson, L.; Eden, J.-S.; Duchêne, S.; Kerr, P.J.; Duckworth, J.; Ward, V.K.; Holmes, E.C.; Strive, T. Benign rabbit caliciviruses exhibit similar evolutionary dynamics to their virulent relatives. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9317–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvério, D.; Lopes, A.M.; Melo-Ferreira, J.; Magalhães, M.J.; Monterroso, P.; Serronha, A.; Maio, E.; Alves, P.C.; Esteves, P.J.; Abrantes, J. Insights into the evolution of the new variant rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (GI.2) and the identification of novel recombinant strains. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; van der Loo, W. Evidence for recombination in the major capsid gene VP60 of the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV). Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Wang, F.; Fan, Z.; Song, Y.; Abrantes, J.; Zuo, Y.; Esteves, P.J. Recombination between G2 and G6 strains of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) in China. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, F.; Decors, A.; Mastain, O.; Quintaine, T.; Berny, P.; Vey, D.; Lasseur, R.; Bro, E. Field evidence of bird poisonings by imidacloprid-treated seeds: A review of incidents reported by the French SAGIR network from 1995 to 2014. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5469–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Portejoie, Y.; Le Gall, G. Immunocapture-RT-PCR assay for detection and molecular epidemiology studies of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease and European Brown Hare Syndrome viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2001, 97, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimanis, A.S.; Ahola, H.; Zohari, S.; Larsson Pettersson, U.; Bröjer, C.; Capucci, L.; Gavier-Widén, D. Arrival of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 to northern Europe: Emergence and outbreaks in wild and domestic rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Sweden. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G.; Arnauld, C.; Boilletot, E.; Morisse, J.P.; Rasschaert, D. Molecular epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus outbreaks in France during 1988 to 1995. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lavazza, A.; Marchandeau, S.; Bertagnoli, S.; Zwingelstein, F.; Cavadini, P.; Martinelli, N.; Lombardi, G.; Guerin, J.-L.; Lemaitre, E.; et al. Emergence of a new lagovirus related to Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, E.; Zwingelstein, F.; Marchandeau, S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. First complete genome sequence of a European non-pathogenic rabbit calicivirus (lagovirus GI.3). Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2921–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lemaitre, E.; Bertagnoli, S.; Hubert, C.; Top, S.; Decors, A.; Marchandeau, S.; Guitton, J.-S. Large-scale lagovirus disease outbreaks in European brown hares (Lepus europaeus) in France caused by RHDV2 strains spatially shared with rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisse, J.P. Hemorrhagic septicemia syndrome in rabbits: First observations in France. Point Vétérinaire 1988, 20, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gavier-Widén, D. Viral hepatitis of rabbits and hares in scandinavia. In Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine, Current Therapy 3; Fowler, M.E., Ed.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny, N.; Bascuñana, C.R.; Ballagi-Pordány, A.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Uhlén, M.; Belák, S. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease and European brown hare syndrome viruses by comparison of sequences from the capsid protein gene. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Balseiro, A.; Muguerza, M.A.; Rosell, J.M.; Casais, R.; Álvarez, Á.L.; Parra, F. Variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in young rabbits, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Parra, F. Spread of new variant RHDV in domestic rabbits on the Iberian Peninsula. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig-Begall, L.F.; Mauroy, A.; Thiry, E. Norovirus recombinants: Recurrent in the field, recalcitrant in the lab—A scoping review of recombination and recombinant types of noroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, W.J. Viral Genetics. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8439/ (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Mahar, J.E.; Hall, R.N.; Shi, M.; Mourant, R.; Huang, N.; Strive, T.; Holmes, E.C. The discovery of three new hare lagoviruses reveals unexplored viral diversity in this genus. Virus Evol. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Uchino, K.; Oka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Takeda, N.; Hansman, G.S. Novel recombinant sapovirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1874–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Code | Location (Department or Municipality, Country) | Collection Date (Month-Year) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 95-10 | Marne, France | 05-1995 | MT628287 |
| 00-21 | Aude, France | 08-2000 | MH190418 |
| 05-01 | Manche, France | 01-2005 | MT628288 |
| 09-02 | Aveyron, France | 01-2009 | MT628289 |
| 09-03 | Bouches du Rhône, France | 02-2009 | MT628290 |
| 16-09 | Loire, France | 01-2016 | MT628291 |
| 96-VLT000113 | Gotland, Sweden | 12-1995 | MT819374 |
| 03-VLT001218 | Rönneby, Sweden | 11-2003 | MT819375 |
| 06-VLT001843 | Kävlinge, Sweden | 09-2006 | MT819376 |
| 10-VLT001467 | Gotland, Sweden | 08-2010 | MT819379 |
| 12-VLT000099 | Tomelilla, Sweden | 01-2012 | MT819377 |
| 12-VLT000101 | Tomelilla, Sweden | 01-2012 | MT819378 |
| Most Likely Donor Strain | Methods and Average p-Values | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strains | Recombination Breakpoint (Nucleotide Positions) 1 | Nonstructural Proteins | Structural Proteins | RDP | BootScan | MaxChi | Chimaera | SiScan | 3Seq |
| 05-01 | 5426 (5384–5444) | 06-11 (GI.3) | 00-21 (GI.1d) | 2.024 × 10−12 | 6.164 × 10−11 | 6.146 × 10−19 | 2.023 × 10−19 | 7.051 × 10−38 | 3.270 × 10−62 |
| 09-03 | |||||||||
| 16-09 | |||||||||
| 03-VLT001218 | |||||||||
| 06-VLT001843 | |||||||||
| 12-VLT000099 | |||||||||
| 12-VLT000101 | |||||||||
| 10-VLT001467 | |||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abrantes, J.; Lopes, A.M.; Lemaitre, E.; Ahola, H.; Banihashem, F.; Droillard, C.; Marchandeau, S.; Esteves, P.J.; Neimanis, A.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P–GI.1d Strains. Genes 2020, 11, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080910
Abrantes J, Lopes AM, Lemaitre E, Ahola H, Banihashem F, Droillard C, Marchandeau S, Esteves PJ, Neimanis A, Le Gall-Reculé G. Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P–GI.1d Strains. Genes. 2020; 11(8):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080910
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbrantes, Joana, Ana M. Lopes, Evelyne Lemaitre, Harri Ahola, Fereshteh Banihashem, Clément Droillard, Stéphane Marchandeau, Pedro J. Esteves, Aleksija Neimanis, and Ghislaine Le Gall-Reculé. 2020. "Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P–GI.1d Strains" Genes 11, no. 8: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080910
APA StyleAbrantes, J., Lopes, A. M., Lemaitre, E., Ahola, H., Banihashem, F., Droillard, C., Marchandeau, S., Esteves, P. J., Neimanis, A., & Le Gall-Reculé, G. (2020). Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P–GI.1d Strains. Genes, 11(8), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080910







