Genetic Evidence for a Mixed Composition of the Genus Myoxocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae) Necessitates Generic Realignment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Specimens and Sequencing
2.2. DNA Sequence Analysis
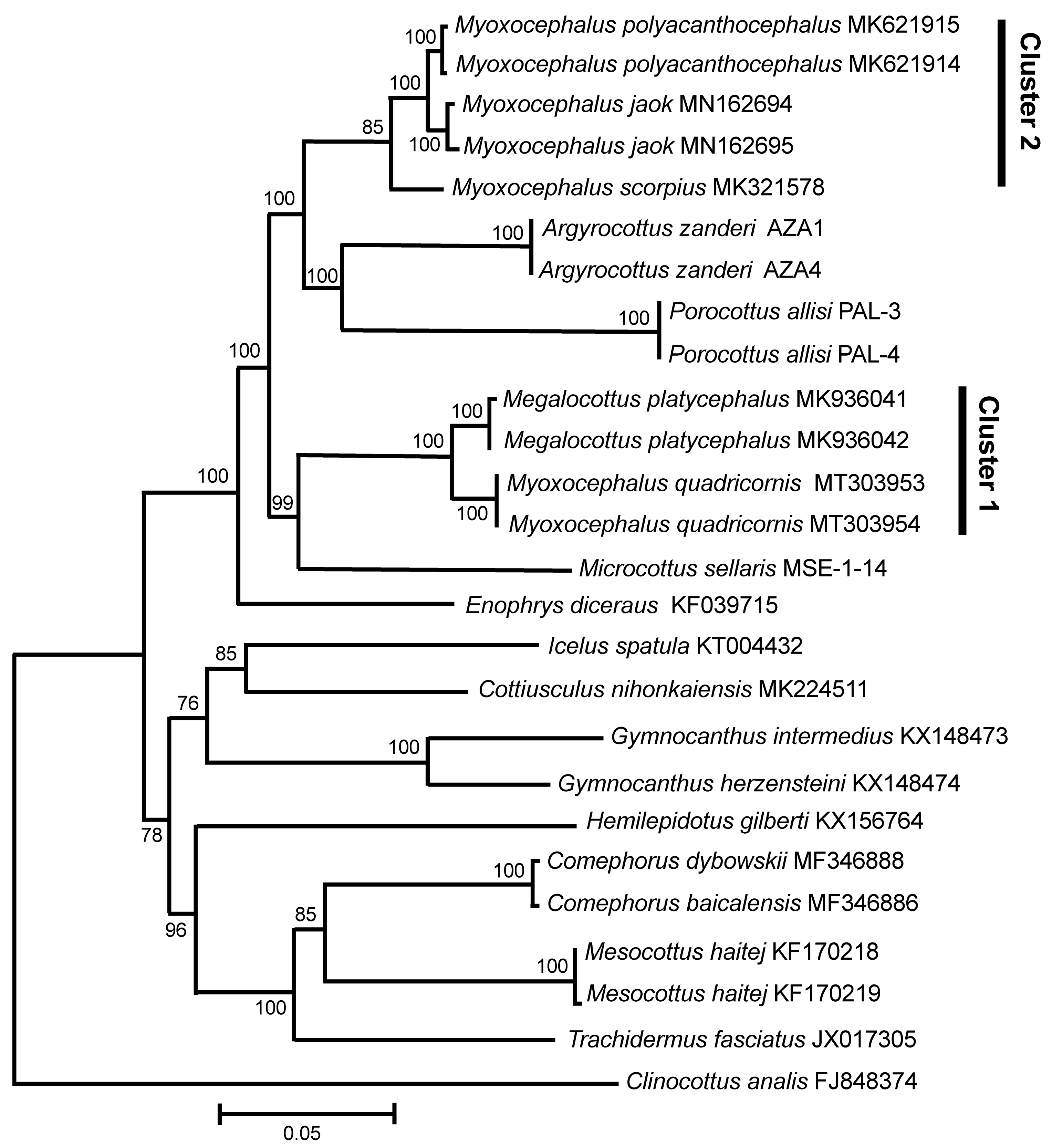
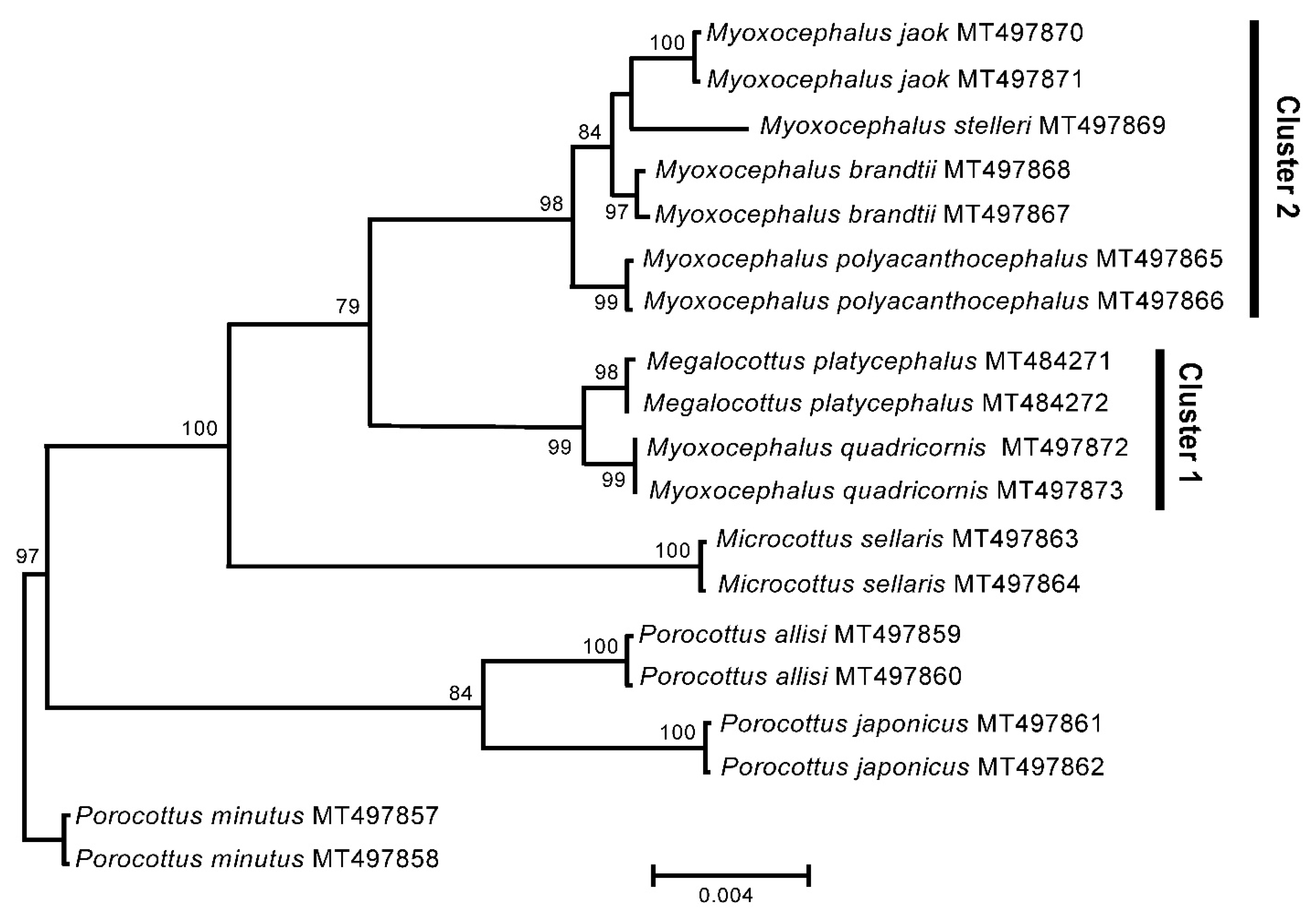
3. Results
3.1. Complete Mitochondrial Genomes
3.2. Nuclear Ribosomal Genes
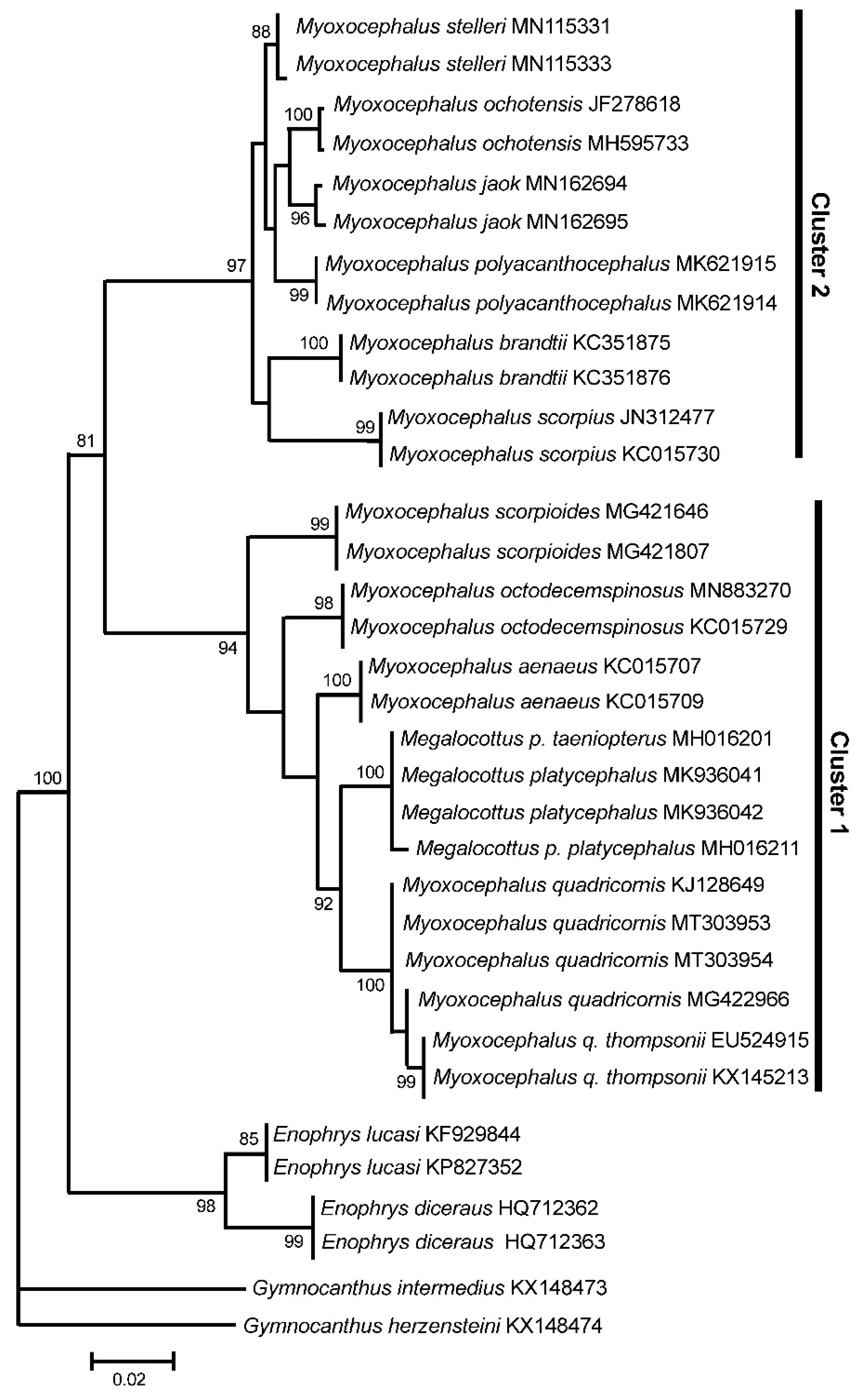
3.3. GenBank COI Gene Dataset
3.4. Alternative Hypotheses: Recombination and Species Misidentification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: http://www.fishbase.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Van der Laan, R. (Eds.) The Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- The Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Available online: https://www.itis.gov/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS). Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/index.php (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Andriashev, A.P. Fishes of the Northern Seas of the USSR; Publishing house of the Academy of Sciences of USSR: Moscow/Leningrad, Russia, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Neyelov, A.V. Seismosensory System and Classification of Sculpins (Cottidae: Myoxocephalinae, Artedellinae); Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, V.V. Cottidae. In Fishes of the North Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean; Whitehead, P.J.P., Bauchot, M.-L., Hureau, J.-C., Nielsen, J.G., Tortonese, E., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1986; Volume 3, pp. 1243–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Mecklenburg, C.W.; Mecklenburg, T.A.; Thorsteinson, L.K. Fishes of Alaska; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; p. 1116. [Google Scholar]
- Mecklenburg, C.W.; Møller, P.R.; Steinke, D. Biodiversity of Arctic marine fishes – taxonomy and zoogeography. Mar. Biodivers. 2011, 41, 109–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranetz, A.Y. On the origin and taxonomy of the Cottoid fishes. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Biol. Sci. Dept. (Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Otdel. Biol. Nauk) 1941, 3, 427–447. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, L.S. Freshwater Fish of the USSR and Adjacent Countries, 4th ed.; Publishing house of the Academy of Sciences of USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1949; pp. 929–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, G.I.M. Comparative morphology of the cottid genus Myoxocephalus based on meristic, morphometric, and another anatomical characters. Can. J. Zool. 1971, 49, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, M. Comparative osteology and myology of the superfamily Cottoidea (Pisces: Scorpaeniformes), and its phylogenetic classification. Mem. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1985, 32, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, P.Y. Fishes of the Sea of Okhotsk. Transact. Pac. Commit. Acad. Sci. USSR 1950, 6, 1–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, G.U.; Krasyukova, Z.V. Fishes of the Sea of Japan and the Adjacent Areas of the Sea of Okhotsk and Yellow Sea; Part 5; Akad. Nauk. SSSR: Leningrad, Russia, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Sharina, S.N.; Goto, T.; Balanov, A.A.; Hanzawa, N. Sequence diversity at cytochrome oxidase 1 (Co1) gene among Sculpins (Scorpaeniformes, Cottidae) and some other scorpionfish of Russia Far East with phylogenetic and taxonomic insights. Genes Genom. 2009, 31, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Rozhkovan, K.V.; Masalkova, N.A. Phylogeny based on two mtDNA genes (Co-1, Cyt-B) among sculpins (Scorpaeniformes, Cottidae) and some other scorpionfish in the Russian Far East. Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 2225–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlesnykh, A.V.; Moreva, I.N. Variability and relationships of the Far Eastern species of sculpins Myoxocephalus and Megalocottus (Cottidae) based on mtDNA markers and karyological data. Russ. J. Genet. 2014, 50, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knope, M.L. Phylogenetics of the marine sculpins (Teleostei: Cottidae) of the North American Pacific Coast. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchenko, O.A.; Petrovskaya, A.V. Molecular-genetic differentiation of the belligerent sculpin Megalocottus platycephalus (Pallas, 1814) (Scorpaeniformes: Cottidae). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2019, 45, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; Busby, M.S. Phylogeny and taxonomy of sculpins, sandfishes, and snailfishes (Perciformes: Cottoidei) with comments on the phylogenetic significance of their early-life-history specializations. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 79, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreva, I.N. The karyotype of the brightbelly sculpin Microcottus sellaris (Gilbert, 1896) (Cottidae: Myoxocephalinae). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2020, 46, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, L.; Westin, L. On the problem of sibling species and possible intraspecific variation in Fourhorn sculpin, Myoxocephalus quadricornis (L.). Rep. Inst. Freshwater Res. 1968, 48, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten, U.; Ryman, N. Biochemical genetic variation and population structure of fourhorn sculpin (Myoxocephalus quadricornis; Cottidae) in Scandinavia. Hereditas 1988, 108, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontula, T.; Väinölä, R. Relationships of Palearctic and Nearctic ‘glacial relict’ Myoxocephalus sculpins from mitochondrial DNA data. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 12, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontula, T.; Kirilchik, S.V.; Väinöä, R. Endemic diversification of the monophyletic cottoid fish species flock in Lake Baikal explored with mtDNA sequencing. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2003, 27, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, N.; Hanner, R.; Holm, E.; Mandrak, N.E.; Taylor, E. Identifying Canadian freshwater fishes through DNA Barcodes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mecklenburg, C.W.; Steinke, D. Ichthyofaunal baselines in the Pacific Arctic region and RUSALCA study area. Oceanography 2015, 28, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, M.R.; Denti, D.; Van Guelpen, L.; Kenchington, E.; Bentzen, P. Barcoding Atlantic Canada’s commonly encountered marine fishes. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2012, 13, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Saveliev, P.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Amur sculpin Cottus szanaga (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2016, 1, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Saveliev, P.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Volk’s sculpin Cottus volki (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2017, 2, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Saveliev, P.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Sakhalin sculpin Cottus amblystomopsis (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2017, 2, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Saveliev, P.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genomes of the Cherskii’s sculpin Cottus czerskii and Siberian taimen Hucho taimen reveal GenBank entry errors: Incorrect species identification and recombinant mitochondrial genome. Evolut. Bioinform. 2017, 13, 1176934317726783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Kravchenko, A.Y.; Saveliev, P.A.; Semenchenko, A.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the great sculpin Myoxocephalus polyacanthocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2019, 4, 2361–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Kravchenko, A.Y.; Cherepkova, E.V.; Saveliev, P.A.; Semenchenko, A.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the belligerent sculpin Megalocottus platycephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2019, 4, 2980–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Kravchenko, A.Y.; Cherepkova, E.V.; Saveliev, P.A.; Semenchenko, A.A.; Ayala, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the plain sculpin Myoxocephalus jaok (Cottoidei: Cottidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Res. 2020, 5, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an accurate and automatic annotation pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelsky, A.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling genomes and mini-metagenomes from highly chimeric reads. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2013, 7821, 158–170. [Google Scholar]
- The National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filatov, D.A. PROSEQ: A software for preparation and evolutionary analysis of DNA sequence data sets. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavaré, S. Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. Lect. Math. Life Sci. 1986, 17, 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Taka-aki, Y. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G.E. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.; Guindon, S. Partitionfinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douady, C.J.; Delsuc, F.; Boucher, Y.; Doolittle, W.F.; Douzery, E.J. Comparison of Bayesian and maximum likelihood bootstrap measures of phylogenetic reliability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, P.; Wallis, G.P.; Cameron-Christie, S.R.; Kennedy, H.L.; Palmer, G.; Tessa, R.; Sanders, T.R.; Winter, D.J. Interspecific hybridization causes long-term phylogenetic discordance between nuclear and mitochondrial genomes in freshwater fishes. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3116–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Toews, D.; Brelsford, A. The biogeography of mitochondrial and nuclear discordance in animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3907–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.M.; Dixon, M.T. Ribosomal DNA: Molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q. Rev. Biol. 1991, 66, 411–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A. Molecular phylogenetic studies of fish. In Genetics and Evolution of Aquatic Organisms; Beaumont, A.R., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1994; pp. 219–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, D.M.; Dixon, M.T. Vertebrate phylogeny: Evidence from 28S ribosomal DNA sequences. In Hierarchy of Life: Molecules and Morphology in Phylogenetic Analysis; Fernholm, B., Bremer, K., Brudin, L., Jornvall, H., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 355–367. [Google Scholar]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Krupnova, T.N.; Ayala, F.J. DNA variation in the phenotypically diverse brown alga Saccharina japonica. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Romanov, N.S.; Mikheev, P.B.; Ayala, F.J. Mitochondrial DNA variation and introgression in Siberian taimen Hucho taimen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreva, I.N.; Borisenko, S.A. The karyotype of the flathead sculpin Megalocottus platycephalus (Pallas, 1814) (Pisces: Cottidae) from Odyan Bay, Sea of Okhotsk. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 40, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranetz, A.Y. Handbook for identification of fishes of Soviet Far East and adjacent waters. Izv. TINRO 1937, 11, 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Taranetz, A.Y. Material to the knowledge of the ichthyofauna of Soviet Sakhalin. Izv. TINRO 1937, 12, 5–50. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, V. Fishes of western arctic America and eastern arctic Siberia: Taxonomy and zoogeography. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1955, 10, 255–368. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, G.I.M. Relationships within the genus Myoxocephalus (Pisces: Cottidae) based on morphological and biochemical data using numerical and conventional method of analyses. Ibid 1972, 50, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wägele, J.-W. Foundations of Phylogenetic Systematics; Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil: München, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mecklenburg, C.W.; Lynghammar, A.; Johannesen, E.; Byrkjedal, I.; Christiansen, J.S.; Dolgov, A.V.; Karamushko, O.V.; Møller, P.R.; Steinke, D.; Wienerroither, R.M. Marine Fishes of the Arctic Region; Monitoring Series Report 28; Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna: Akureyri, Iceland, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 1–454. [Google Scholar]
- Togashi, K.; Yamazaki, A.; Awata, S.; Koya, Y.; Abe, T.; Tsuruoka, S.; Takeshima, H.; Malkevich, A.; Munehara, H. Molecular phylogeny and Adaptive radiation of Cottoidei. Unpublished. Uploaded to GenBank on 14/02/2019.
- Naciri, Y.; Linder, P. Species delimitation and relationships: The dance of the seven veils. Taxon 2015, 64, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakirev, E.S. Conservation genetics of marine biological resources: Methodological aspects with the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius as an example. In Studies of Marine Organisms in the Far East: Biodiversity, Monitoring, and Rational Management of Resources; Malakhov, V.V., Chernyshev, A.V., Eds.; Far Eastern Federal University Press: Vladivostok, Russia, 2020; pp. 36–103. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, 4th ed.; The International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dadswell, M.J. Distribution, ecology, and postglacial dispersal of certain crustaceans and fishes in eastern North America. Nat. Mus. Nat. Sci. Publ. Zool. 1974, 11, 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, D.E. The origin and status of the deepwater sculpin, Myoxocephalus thompsonii, a Nearctic glacial relict. Bull. Nat. Mus. Can. Contrib. Zool. 1961, 172, 44–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, A.; Nishimiya, Y.; Tsuda, S.; Togashi, K.; Munehara, H. Gene expression of antifreeze protein in relation to historical distributions of Myoxocephalus fish species. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjanova, E.F. The peculiar properties of the Arctic Ocean fauna and their value for the understanding the history of its developments. In The Arctic Ocean and Its Coast in Cainozoe; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1970; pp. 126–161. [Google Scholar]
- De Queiroz, K.; Gauthier, J. Toward a phylogenetic system of biological nomenclature. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, E.O.; Lieberman, B.S. Phylogenetics: Theory and Practice of Phylogenetic Systematic, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, C.S.; Stange, M.; Berner, D.; Roesti, M.; Quintella, B.R.; Alves, M.J.; Almeida, P.R.; Salzburger, W. Strong genome-wide divergence between sympatric European river and brook lampreys. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R649–R650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardi, G.; Nelson, P.; Paddack, M.; Rulmal, J., Jr.; Crane, N. Genomic islands of divergence in the Yellow Tang and the Brushtail Tang Surgeonfishes. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 8676–8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitney, J.L.; Bowen, B.W.; Karl, S.A. Flickers of speciation: Sympatric colour morphs of the arc-eye hawkfish, Paracirrhites arcatus, reveal key elements of divergence with gene flow. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, K.; Vargas, M.; Höppner, M.P.; McMillan, W.O.; Puebla, O. Inter-chromosomal coupling between vision and pigmentation genes during genomic divergence. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balakirev, E.S.; Kravchenko, A.Y.; Semenchenko, A.A. Genetic Evidence for a Mixed Composition of the Genus Myoxocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae) Necessitates Generic Realignment. Genes 2020, 11, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091071
Balakirev ES, Kravchenko AY, Semenchenko AA. Genetic Evidence for a Mixed Composition of the Genus Myoxocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae) Necessitates Generic Realignment. Genes. 2020; 11(9):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091071
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalakirev, Evgeniy S., Alexandra Yu. Kravchenko, and Alexander A. Semenchenko. 2020. "Genetic Evidence for a Mixed Composition of the Genus Myoxocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae) Necessitates Generic Realignment" Genes 11, no. 9: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091071
APA StyleBalakirev, E. S., Kravchenko, A. Y., & Semenchenko, A. A. (2020). Genetic Evidence for a Mixed Composition of the Genus Myoxocephalus (Cottoidei: Cottidae) Necessitates Generic Realignment. Genes, 11(9), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091071



