Expression Levels of the Immune-Related p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Transcript in Response to Environmental Pollutants on Macrophthalmus japonicus Crab
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organisms and Pollutants Exposure
2.2. Exposure Experiments
2.3. M. japonicus p38 MAPK Gene Identification and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Tissue Distribution and Expression Analysis of p38 MAPK
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Characterization of the M. japonicus p38 MAPK Gene
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationship of M. japonicus p38 MAPK with Other p38 MAPK Genes
3.3. Tissue Distribution Levels of M. japonicus p38 MAPK
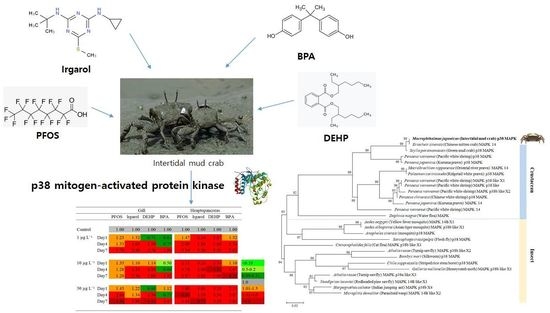
3.4. Expression Profiles of p38 MAPK after PFOS or Irgarol Exposures
3.5. Expression Profiles of p38 MAPK after DEHP or BPA Exposures
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W. Transcriptomic Changes in Liver of Juvenile Cynoglossus Semilaevis Following Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.E.; Son, Y.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K.; Zoh, K.D. Concentration and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Asan Lake area of South Korea. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 381, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, A.; Wagner, M.; Ternes, T.A. Transformation of biocides irgarol and terbutryn in the biological wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.W.U.; Wang, H.; Yao, W.; Deantes-Espinosa, V.M.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Ozonation of the algaecide irgarol: Kinetics, transformation products, and toxicity. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. Worldwide occurrence and effects of antifouling paint booster biocides in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.R.; Arifin, M.M.; Sheikh, M.A.; Mohamed Shazili, N.A.; Bachok, Z. Occurrence and distribution of antifouling biocide Irgarol-1051 in coastal waters of Peninsular Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, J.L.M.; Dos Santos, S.R.V.; Dos Santos Franco, T.C.R.; Almeida, M.A.P. Occurrence and partitioning of antifouling booster biocides in sediments and porewaters from Brazilian Northeast. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Z. DEHP induces immunosuppression through disturbing inflammatory factors and CYPs system homeostasis in common carp neutrophils. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, G.; Hilgert, S.; Fuchs, S.; Azevedo, J.C.R. Emerging contaminants and antibiotic resistance in the different environmental matrices of Latin America. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, G.H. Distribution of PAEs in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 124, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Ríos, D.F.; Lara-Borrero, J.A.; Duque-Pardo, V.; Madera-Parra, C.A.; Jimenez, E.M.; Toro, A.F. Study of the occurrence and ecosystem danger of selected endocrine disruptors in the urban water cycle of the city of Bogot_a, Colombia. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 53, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, V.G.O.; Carneiro, D.C.; Pereira, S.A.; da Silva, M.R.D.; Candé, A.A.; da Cunha Lima, S.T. Analyzing the toxicity of bisphenol-A to microalgae for ecotoxicological applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.M.; Brito, N.M. Analysis and occurrence of endocrine disruptors in Brazilian water by HPLC-fluorescence detection. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 225, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, S.S.; Rombaldi, C.; Lucas, J.; Arias, D.O.; Marube, L.C.; Gilberto, E. Multiresidue method for determination of 58 pesticides, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water using solvent demulsification dispersive liquid e liquid microextraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 146, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Huang, A.; Wang, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; Ou, Y.; Wang, J. Molecular characterization of a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase gene from Scylla paramamosain and its expression profiles during pathogenic challenge. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 144, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wen, H.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Identification of mapk gene family in Lateolabrax maculatus and their expression profiles in response to hypoxia and salinity challenges. Gene 2019, 684, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, P.C.; Bhaskaran, M.; Patel, J.; Patel, K.; Kasinath, B.S.; Duraisamy, S.; Franki, N.; Reddy, K.; Kapasi, A.A. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and Fas-Fas ligand interaction in morphine-induced macrophage apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, A.S.; Paulson, E.K.; McDevitt, M.A.; Rieger-Christ, K.; Summerhayes, I.; Berasi, S.P.; Kim, J.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, X. The HBP1 transcriptional repressor and the p38 MAP kinase: Unlikely partners in G1 regulation and tumor suppression. Gene 2004, 336, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuder, L.E.; Keener, J.M.; Eckert, R.E.; Trujillo, J.C.; Jones, S.L. Role of p38 MAPK in LPS induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in equine leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 129, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, C.; Ma, X.; Wu, R.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Deng, F.; Wu, J.; Geng, S.; et al. Phthalates promote prostate cancer cell proliferation through activation of ERK5 and p38. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 63, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, A.D.; Cohen, R.D.; Whittaker, G.R. Activation of p38 MAPK by feline infectious peritonitis virus regulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in primary blood-derived feline mononuclear cells. Virology 2009, 384, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Qian, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Mi, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X. Molecular characterization of a p38 MAPK from Litopenaeus vannamei and its expression during the molt cycle and following pathogen infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Jin, P.; Ma, F. Identification and characterization of a p38-like gene from amphioxus (Branchiostoma belcheri): An insight into amphioxus innate immunity and evolution. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Qian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) disrupts blood-testis barrier by down-regulating junction proteins via p38 MAPK/ATF2/MMP9 signaling pathway. Toxicology 2016, 373, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, J.; Nishida, M.; Wada, K. Genetic and behavioral diversity in the Macrophthalmus japonicus species complex (Crustacea: Brachyura: Ocypodidae). Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Aoki, S.; Okamoto, K. Effects of the bioturbating crab Macrophthalmus japonicus on abiotic and biotic tidal mudflat characteristics in the Tama River, Tokyo Bay, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2017, 12, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S.; Kozuki, Y.; Yamanaka, R.; Sasaoka, H.; Ishiyama, T.; Okitsu, Y.; Sakai, H.; Fujiki, Y. The role of crabs (Macrophthalmus japonicus) burrows on organic carbon cycle in estuarine tidal flat, Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kwak, T.S.; Kim, W.S.; Kwak, I.S. Changes in exoskeleton surface roughness and expression of chitinase genes in mud crab Macrophthalmus japonicus following heavy metal differences of estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Chung, W.H.; Bae, C.H.; Hwang, K.W.; Kim, H.H. Isolation and carbohydrate binding specificity of a lectin from the hemolymph of coastal crab Macrophthalmus japonicus. Yakhak Hoeji. 2006, 50, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yao, W.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Expression profiles of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway from Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis in response to viral and bacterial infections. Gene 2018, 642, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yin, B.; Li, H.; Xiao, B.; Lv, K.; Feng, C.; He, J.; Li, C. MKK4 from Litopenaeus vannamei is a regulator of p38 MAPK kinase and involved in anti-bacterial response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kwak, T.S.; Kwak, I.S. Antioxidative-related genes expression following perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure in the intertidal mud crab, Macrophthalmus japonicus. Ocean Sci. J. 2015, 50, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kim, W.S.; Kwak, T.S.; Kwak, I.S. Changes of exoskeleton surface roughness and expression of crucial participation genes for chitin formation and digestion in the mud crab (Macrophthalmus japonicus) following the antifouling biocide irgarol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kwak, I.S. Salinity and bisphenol A alter cellular homeostasis and immune defense by heat shock proteins in the intertidal crab Macrophthalmus japonicus. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 229, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, W.S.; Kwak, I.S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals impair the innate immune prophenoloxidase system in the intertidal mud crab, Macrophthalamus japonicus. Fish Shell. Immun. 2019, 87, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kwak, I.S. Identification and expression of proteolysis response genes for Macrophthalmus japonicus exposure to irgarol toxicity. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2016, 52, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔ CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressurreição, M.; Rollinson, D.; Emery, A.M.; Walker, A.J. A role for p38 MAPK in the regulation of ciliary motion in a eukaryote. BMC Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akella, R.; Moon, T.M.; Goldsmith, E.J. Unique MAP Kinase binding sites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roskoski, R. MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umasuthan, N.; Bathige, S.D.; Noh, J.K.; Lee, J. Gene structure, molecular characterization and transcriptional expression of two p38 isoforms (MAPK11 and MAPK14) from rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röszer, T. The invertebrate midintestinal gland (‘‘hepatopancreas”) is an evolutionary forerunner in the integration of immunity and metabolism. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Wang, B.J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K.Y.; Wang, L. A comparative study on oxidative stress response in the hepatopancreas and midgut of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei under gradual changes to low or high pH environment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikerd, J.L.; Burnett, K.G.; Burnett, L.E. Effects of salinity on the accumulation of hemocyte aggregates and bacteria in the gills of Callinectes sapidus, the Atlantic blue crab, injected with Vibrio campbellii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 183, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Qian, Y.; Yang, J. Impairments of cadmium on vitellogenin accumulation in the hepatopancreas of freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 18160–18167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.A.; Dutra, B.K.; Mosele, F.; Araujo, A.S.R.; Ferreira, G.D.; Belló-Klein, A.; Kucharski, L.C.; Vinagre, A.S.; Da Silva, R.S.M. Redox and metabolic strategies developed by anterior and posterior gills of the crab Neohelice granulata after short periods of hypo- or hyper-osmotic stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L. C-type lectin response to bacterial infection and ammonia nitrogen stress in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.G.; Yang, J.H. Perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells is mediated by ERK 1/2 pathway. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B.; Nandi, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Raha, S.; Sen, P.C.; Jana, K. Resveratrol ameliorates benzo(a)pyrene-induced testicular dysfunction and apoptosis: Involvement of p38 MAPK/ATF2/iNOS signaling. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 34, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, I.; Miled, W.; Slama, R.B.; Ladhari, N. Antifouling processes and toxicity effects of antifouling paints on marine environment. A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, H.; Minamide, S.; Takeuchi, I. Identification and characterization of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) in the hard coral Acropora tenuis in response to Irgarol 1051. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Jo, H.; Kim, D.K.; Kwak, I.S. Environmental pollutants impair transcriptional regulation of the vitellogenin gene in the burrowing mud crab (Macrophthalmus japonicus). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.; Ha, M.; Yang, M.; Yue, P.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C. Di2-ethylhexyl phthalate disrupts thyroid hormone homeostasis through activating the Ras/Akt/TRHr pathway and inducing hepatic enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ha, M.; Wei, L.; Guan, X.; Li, L.; Liu, C. p53-dependent apoptosis contributes to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced hepatotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.K.; Chiang, L.F.; Tan, S.W.; Chen, P.J. Environmentally relevant concentrations of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate exposure alter larval growth and locomotion in medaka fish via multiple pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Asai, D.; Katayama, Y. Bisphenol A in the aquatic environment and its endocrine-disruptive effects on aquatic organisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Fu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Quan, C.; Kourouma, A.; Yan, M.; Yu, T.; Duan, P.; Yang, K. BPA-induced apoptosis of rat Sertoli cells through Fas/FasL and JNKs/p38 MAPK pathways. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 50, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Kang, J.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Chen, Z. Bisphenol A suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in colonic epithelial cells through mitochondrial and MAPK/AKT pathways. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, Y.; Wei, S.; Huang, X.; Ye, F.; Fu, J.; Qin, Q. Characterization of p38 MAPKs from orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides involved in SGIV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gill | Hepatopancreas | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOS | Irgarol | DEHP | BPA | PFOS | Irgarol | DEHP | BPA | |||
| Control | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| 1 µg L−1 | Day1 | 1.23 | 1.32 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 1.47 | 2.34 | 1.87 | 1.32 | |
| Day4 | 1.33 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 0.75 | 2.80 | 1.88 | 1.88 | 1.54 | ||
| Day7 | 1.76 | 3.30 | 2.78 | 1.98 | 3.54 | 3.30 | 3.30 | 2.61 | ||
| 10 µg L−1 | Day1 | 1.35 | 1.10 | 1.14 | 0.50 | 2.11 | 3.23 | 2.54 | 1.10 | |
| Day4 | 1.28 | 1.54 | 2.05 | 0.60 | 3.78 | 2.00 | 4.32 | 2.67 | 0.2–0.5 | |
| Day7 | 1.20 | 2.56 | 2.00 | 1.52 | 2.87 | 3.80 | 3.80 | 4.21 | 0.51–0.99 | |
| 1.0 | ||||||||||
| 30 µg L−1 | Day1 | 1.43 | 1.22 | 0.86 | 1.12 | 1.80 | 3.01 | 3.23 | 2.73 | 1.01–1.5 |
| Day4 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 2.30 | 0.72 | 4.60 | 1.59 | 3.54 | 3.67 | 1.51–4.0 | |
| Day7 | 4.30 | 3.88 | 4.10 | 3.47 | 3.42 | 4.73 | 3.22 | 3.82 | >4.0 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.; Kim, W.-S.; Choi, B.; Kwak, I.-S. Expression Levels of the Immune-Related p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Transcript in Response to Environmental Pollutants on Macrophthalmus japonicus Crab. Genes 2020, 11, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090958
Park K, Kim W-S, Choi B, Kwak I-S. Expression Levels of the Immune-Related p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Transcript in Response to Environmental Pollutants on Macrophthalmus japonicus Crab. Genes. 2020; 11(9):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090958
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kiyun, Won-Seok Kim, Bohyung Choi, and Ihn-Sil Kwak. 2020. "Expression Levels of the Immune-Related p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Transcript in Response to Environmental Pollutants on Macrophthalmus japonicus Crab" Genes 11, no. 9: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090958
APA StylePark, K., Kim, W.-S., Choi, B., & Kwak, I.-S. (2020). Expression Levels of the Immune-Related p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Transcript in Response to Environmental Pollutants on Macrophthalmus japonicus Crab. Genes, 11(9), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090958