An 8.22 Mb Assembly and Annotation of the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) Y Chromosome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Samples and DNA Isolation
2.3. Cell Cultures and Cytogenetics
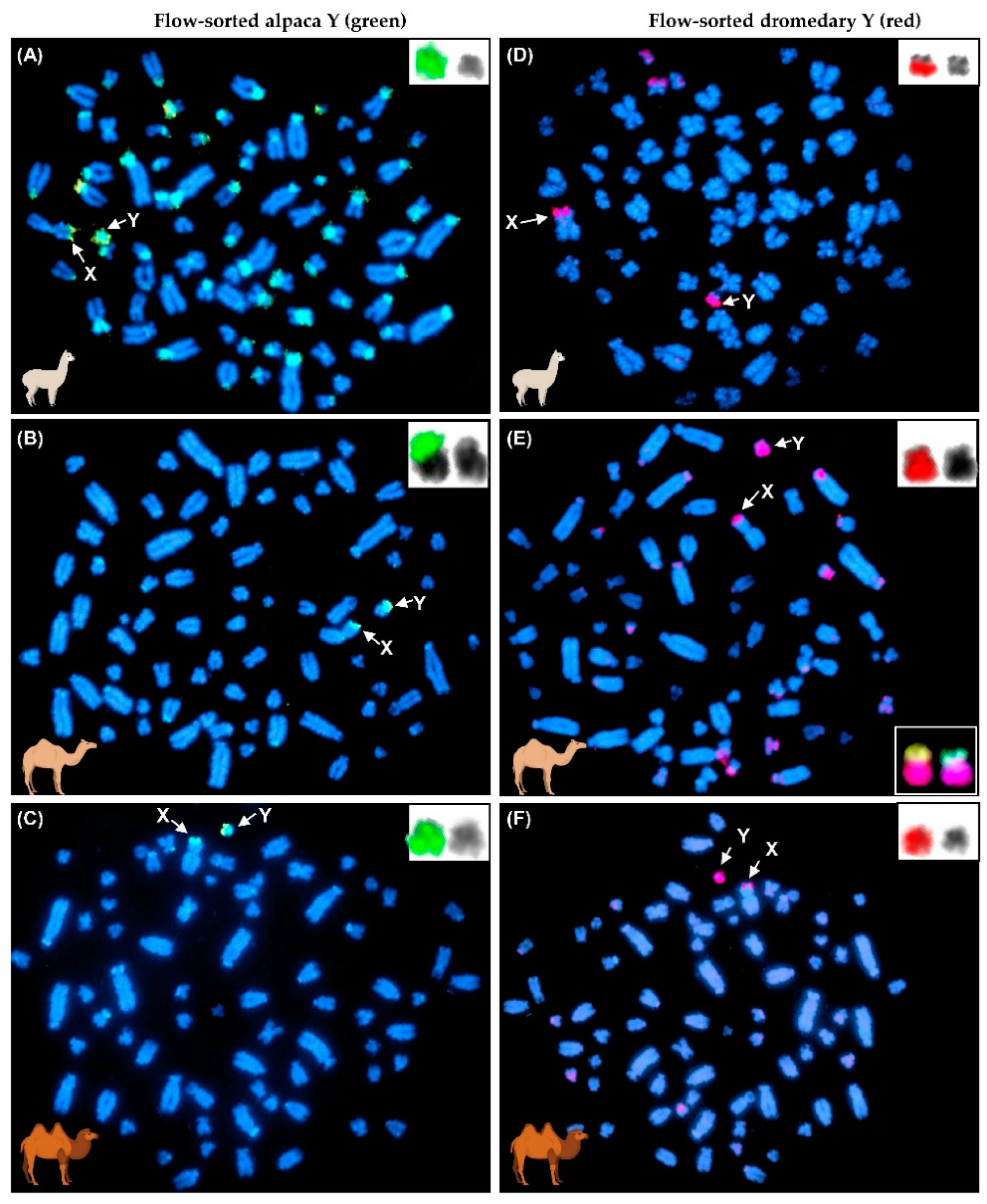
2.4. Flow-Sorting Alpaca and Dromedary Y Chromosomes, Y DNA Amplification and Validation by FISH
2.5. Sequencing and Assembly of the Flow-Sorted Alpaca Y Chromosome
2.6. Testis RNA Isolation, cDNA Library Preparation and Hybridization Capture of Y-Specific Transcripts
2.7. Sequencing and de Novo Assembly of Y-Enriched Cdna Libraries
2.8. Y-Enriched Testis Transcriptome Annotation
2.9. Validation of the Alpaca Y Assembly and Putative Y Transcripts
2.10. Quantitative Pcr (Qpcr) Analysis of Putative Multi-Copy Sequences
2.11. Construction of Neighbor-Joining Trees for Alpaca Y Genes
3. Results
3.1. Y Chromosome Cytogenetics and Flow-Sorting
3.2. Alpaca Y Genomic Assembly and Analysis
3.3. Transcriptome Assembly and Msy Annotation
3.4. Demarcation of PAR-Y and Putative Pseudoautosomal Boundary (PAB)
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Alpaca Y Transcripts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Approaches
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Data Access
References
- Lahn, B.T.; Page, D.C. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 1999, 286, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, J.A.M. Weird Animal Genomes and the Evolution of Vertebrate Sex and Sex Chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, D.; Marin, R.; Toledo-Flores, D.; Froidevaux, L.; Liechti, A.; Waters, P.D.; Grützner, F.; Kaessmann, H. Origins and functional evolution of Y chromosomes across mammals. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 508, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D. Y-chromosome evolution: Emerging insights into processes of Y-chromosome degeneration. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.D.; Wallis, M.C.; Graves, J.A.M. Mammalian sex—Origin and evolution of the Y chromosome and SRY. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 18, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.D.; Ruiz-Herrera, A. Meiotic Executioner Genes Protect the Y from Extinction. Trends Genet. 2020, 36, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp, T.; Chowdhary, B.P. The Eutherian Pseudoautosomal Region. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 147, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, L.; Barchi, M.; Baudat, F.; Romanienko, P.; Keeney, S.; Jasin, M. Distinct Properties of the XY Pseudoautosomal Region Crucial for Male Meiosis. Science 2011, 331, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.A.M. Evolution of vertebrate sex chromosomes and dosage compensation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.F.; Page, D.C. The Biology and Evolution of Mammalian Y Chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.L.; Kopania, E.E.K.; Good, J.M. Spermatogenesis and the Evolution of Mammalian Sex Chromosomes. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.F.; Rozen, S. Genomics and Genetics of Human and Primate Y Chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2012, 13, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paria, N.; Raudsepp, T.; Wilkerson, A.J.P.; O’Brien, P.C.M.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Love, C.C.; Arnold, C.; Rakestraw, P.; Murphy, W.J.; Chowdhary, B.P. A Gene Catalogue of the Euchromatic Male-Specific Region of the Horse Y Chromosome: Comparison with Human and Other Mammals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, W.J.; Wilkerson, A.J.P.; Raudsepp, T.; Agarwala, R.; Schaffer, A.A.; Stanyon, R.; Chowdhary, B.P. Novel gene acquisition on carnivore Y chromosomes. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brashear, W.A.; Raudsepp, T.; Murphy, W.J. Evolutionary conservation of Y Chromosome ampliconic gene families despite extensive structural variation. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaletsky, H.; Kuroda-Kawaguchi, T.; Minx, P.J.; Cordum, H.S.; Hillier, L.; Brown, L.G.; Repping, S.; Pyntikova, T.; Ali, J.; Bieri, T.; et al. The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 2003, 423, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, Y.S.; Alföldi, J.; Pyntikova, T.; Brown, L.G.; Graves, T.; Minx, P.J.; Fulton, R.S.; Kremitzki, C.; Koutseva, N.; Mueller, J.L.; et al. Sequencing the Mouse Y Chromosome Reveals Convergent Gene Acquisition and Amplification on Both Sex Chromosomes. Cell 2014, 159, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janečka, J.E.; Davis, B.W.; Ghosh, S.; Paria, N.; Das, P.J.; Orlando, L.; Schubert, M.; Nielsen, M.K.; Stout, T.A.E.; Brashear, W.; et al. Horse Y chromosome assembly displays unique evolutionary features and putative stallion fertility genes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellott, D.W.; Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Brown, L.G.; Pyntikova, T.; Cho, T.-J.; Koutseva, N.; Zaghlul, S.; Graves, T.; Rock, S.; et al. Mammalian Y chromosomes retain widely expressed dosage-sensitive regulators. Nature 2014, 508, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Bachtrog, D. The Y chromosome may contribute to sex-specific ageing in Drosophila. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, C.; Toot, J.; Terwilliger, M.; Payne, R.; Turner, M.; Ely, D. The SHR Y chromosome increases cardiovascular, endocrine, and behavioral responses to stress compared to the WKY Y chromosome. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, L.K.; Wall, E.H.; E Osmanski, E.E.; Dragon, J.A.; Saligrama, N.; Zachary, J.F.; Lemos, B.; Blankenhorn, E.P.; Teuscher, C. Copy number variation in Y chromosome multicopy genes is linked to a paternal parent-of-origin effect on CNS autoimmune disease in female offspring. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, T.; Lau, Y.-F.C. Roles of the Y chromosome genes in human cancers. Asian J. Androl. 2015, 17, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calafell, F.; Larmuseau, M.H.D. The Y chromosome as the most popular marker in genetic genealogy benefits interdisciplinary research. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinotti, T.; Bergström, A.; Geppert, M.; Bawn, M.; Ohasi, D.; Shi, W.; Lacerda, D.R.; Solli, A.; Norstedt, J.; Reed, K.; et al. Y Chromosome Sequences Reveal a Short Beringian Standstill, Rapid Expansion, and early Population structure of Native American Founders. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 149–157.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, M.A.; Tyler-Smith, C. Human Y-chromosome variation in the genome-sequencing era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-J.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.-L.; Lv, F.-H.; Cao, Y.-H.; Li, W.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Q.; Liu, Y.-G.; et al. The Genome Landscape of Tibetan Sheep Reveals Adaptive Introgression from Argali and the History of Early Human Settlements on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felkel, S.; Wallner, B.; Chuluunbat, B.; Yadamsuren, A.; Faye, B.; Brem, G.; Walzer, C.; Burger, P.A. A First Y-Chromosomal Haplotype Network to Investigate Male-Driven Population Dynamics in Domestic and Wild Bactrian Camels. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yan, W.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Luo, Y. Y chromosomal haplotype characteristics of domestic sheep (Ovis aries) in China. Gene 2015, 565, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgason, A.; Einarsson, A.W.; Guðmundsdóttir, V.B.; Sigurðsson, Á.; Gunnarsdóttir, E.D.; Jagadeesan, A.; Ebenesersdóttir, S.S.; Kong, A.; Schreiber, S. The Y-chromosome point mutation rate in humans. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachtrog, D. The Y Chromosome as a Battleground for Intragenomic Conflict. Trends Genet. 2020, 36, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Davis, B.W.; Raudsepp, T.; Wilkerson, A.J.P.; Mason, V.C.; Ferguson-Smith, M.; O’Brien, P.C.; Waters, P.D.; Murphy, W.J. Comparative analysis of mammalian Y chromosomes illuminates ancestral structure and lineage-specific evolution. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Pyntikova, T.; Graves, T.A.; van Daalen, S.K.M.; Minx, P.J.; Fulton, R.S.; McGrath, S.D.; Locke, D.P.; Friedman, C.; et al. Chimpanzee and human Y chromosomes are remarkably divergent in structure and gene content. Nature 2010, 463, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Brown, L.G.; Pyntikova, T.; Graves, T.; Fulton, R.S.; Dugan, S.; Ding, Y.; Buhay, C.J.; Kremitzki, C.; et al. Strict evolutionary conservation followed rapid gene loss on human and rhesus Y chromosomes. Nature 2012, 483, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszkiewicz, M.; Rangavittal, S.; Cechova, M.; Sanchez, R.C.; Fescemyer, H.W.; Harris, R.; Ye, D.; O’Brien, P.C.M.; Chikhi, R.; Ryder, O.A.; et al. A time- and cost-effective strategy to sequence mammalian Y Chromosomes: An application to the de novo assembly of gorilla Y. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Retzel, E.F.; Liu, W.-S. Male-specific region of the bovine Y chromosome is gene rich with a high transcriptomic activity in testis development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12373–12378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Pyntikova, T.; Koutseva, N.; Raudsepp, T.; Brown, L.G.; Bellott, D.W.; Cho, T.-J.; Dugan-Rocha, S.; Khan, Z.; et al. Sequence analysis in Bos taurus reveals pervasiveness of X–Y arms races in mammalian lineages. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, O.; Drögemüller, C.; Obexer-Ruff, G.; Reber, I.; Jordana, J.; Martínez, A.; Bâlteanu, V.A.; Delgado, J.V.; Eghbalsaied, S.; Landi, V.; et al. Differential distribution of Y-chromosome haplotypes in Swiss and Southern European goat breeds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, H.M.; Wadlington, W.H.; Johnson, J.L.; Stutchman, J.T.; Trut, L.; Farré, M.; Kukekova, A.V. The Red Fox Y-Chromosome in Comparative Context. Genes 2019, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidon, T.; Janke, A.; Fain, S.R.; Eiken, H.G.; Hagen, S.B.; Saarma, U.; Hallström, B.M.; LeComte, N.; Hailer, F. Brown and Polar Bear Y Chromosomes Reveal Extensive Male-Biased Gene Flow within Brother Lineages. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidon, T.; Schreck, N.; Hailer, F.; Nilsson, M.A.; Janke, A. Genome-Wide Search Identifies 1.9 Mb from the Polar Bear Y Chromosome for Evolutionary Analyses. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2010–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, S.; Goto, M.; Pastene, L.A.; Kanda, N.; Koike, H. Phylogenetic Relationships Among Cetaceans Revealed by Y-Chromosome Sequences. Zoolog. Sci. 2007, 24, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Guang, X.; Al-Fageeh, M.B.; Cao, J.; Pan, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; AbuTarboush, M.H.; Xing, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. Camelid genomes reveal evolution and adaptation to desert environments. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.F.; Munyard, K.; Croft, L.J.; Allnutt, T.R.; Jackling, F.; Alshanbari, F.; Jevit, M.; Wright, G.A.; Cransberg, R.; Tibary, A.; et al. Chromosome-Level Alpaca Reference Genome VicPac3.1 Improves Genomic Insight Into the Biology of New World Camelids. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, S.; Burger, P.A.; Ciani, E.; Castelli, V.; Linguiti, G.; Plasil, M.; Massari, S.; Horin, P.; Antonacci, R. The Camel Adaptive Immune Receptors Repertoire as a Singular Example of Structural and Functional Genomics. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Yang, G. Phylogenomic analyses and improved resolution of Cetartiodactyla. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2011, 61, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.A. The history of Old World camelids in the light of molecular genetics. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.N.; Raudsepp, T.; More, M.J.; Gutiérrez, G.; De León, F.A.P. Cytogenetic Mapping of 35 New Markers in the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos). Genes 2020, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, J.P.; Rogers, M.F.; Perelman, P.L.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Serdyukova, N.A.; Johnson, W.E.; Horin, P.; Corander, J.; Murphy, D.; Burger, P.A. Improving Illumina assemblies with Hi-C and long reads: An example with the North African dromedary. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, J.C.; Romero, K.; Rivera, R.; Johnson, W.E.; González, B.A. Y-chromosome and mtDNA variation confirms independent domestications and directional hybridization in South American camelids. Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirimutu, Z.W.; Ding, G.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Hasi, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; et al. Genome sequences of wild and domestic bactrian camels. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1202. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, P.A.; Palmieri, N. Estimating the population mutation rate from a de novo assembled Bactrian camel genome and cross-species comparison with dromedary ESTs. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X. Y-chromosome polymorphisms of the domestic Bactrian camel in China. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp, T.; Chowdhary, B.P. FISH for Mapping Single Copy Genes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 422, 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Seabright, M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 1971, 2, 971–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, F.; Baily, M.P.; Perelman, P.; Das, P.J.; Pontius, J.; Chowdhary, R.; Owens, E.; Johnson, W.E.; Merriwether, D.A.; Raudsepp, T. A Comprehensive Whole-Genome Integrated Cytogenetic Map for the Alpaca (Lama pacos). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 144, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmus, G.; Trifonov, V.A.; Biltueva, L.S.; O’Brien, P.C.M.; Alkalaeva, E.S.; Fu, B.; Skidmore, J.A.; Allen, T.; Graphodatsky, A.S.; Yang, F.; et al. Cross-species chromosome painting among camel, cattle, pig and human: Further insights into the putative Cetartiodactyla ancestral karyotype. Chromosom. Res. 2007, 15, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Yang, F.; O’Brien, P.C.M. Comparative Mapping Using Chromosome Sorting and Painting. ILAR J. 1998, 39, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, V.C.; Li, G.; Helgen, K.M.; Murphy, W.J. Efficient cross-species capture hybridization and next-generation sequencing of mitochondrial genomes from noninvasively sampled museum specimens. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, D.M.; Johnson, K.; DiTommaso, T.; Tickle, T.; Couger, M.B.; Payzin-Dogru, D.; Lee, T.J.; Leigh, N.D.; Kuo, T.-H.; Davis, F.G.; et al. A Tissue-Mapped Axolotl De Novo Transcriptome Enables Identification of Limb Regeneration Factors. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes11Edited by F. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H.A. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.-H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Wang, Z.; Yi, L.; Batmunkh, M.; Liu, T.; Siren, D.; He, J.; Juramt, N.; Jambl, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Chromosome-level assembly of wild Bactrian camel genome reveals organization of immune gene loci. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Yuan, L.; Yi, L.; Ding, G.; Hasi, S.; Chen, G.; Jambl, T.; Hedayat-Evright, N.; Batmunkh, M.; Badmaevna, G.K.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of 128 camels across Asia reveals origin and migration of domestic Bactrian camels. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.M.; Sargent, C.A.; Churcher, C.; Hunt, T.; Herrero, J.; Loveland, J.E.; Dunn, M.; Louzada, S.; Fu, B.; Chow, W.; et al. The pig X and Y Chromosomes: Structure, sequence, and evolution. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudsepp, T.; Chowdhary, B.P. Construction of chromosome-specific paints for meta- and submetacentric autosomes and the sex chromosomes in the horse and their use to detect homologous chromosomal segments in the donkey. Chromosom. Res. 1999, 7, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumillon, M.; Necsulea, A.; Weier, M.; Brawand, D.; Zhang, X.; Gu, H.; Barthès, P.; Kokkinaki, M.; Nef, S.; Gnirke, A.; et al. Cellular Source and Mechanisms of High Transcriptome Complexity in the Mammalian Testis. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Korf, I.; Robb, S.M.; Parra, G.; Ross, E.; Moore, B.; Holt, C.; Alvarado, A.S.; Yandell, M. MAKER: An easy-to-use annotation pipeline designed for emerging model organism genomes. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Koutseva, N.; Pyntikova, T.; Page, D.C. Sex chromosome-to-autosome transposition events counter Y-chromosome gene loss in mammals. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gvozdev, V.A.; Kogan, G.L.; Usakin, L.A. The Y chromosome as a target for acquired and amplified genetic material in evolution. BioEssays 2005, 27, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Cai, Q.; Li, H.; Hu, P. Comparison of droplet digital PCR to real-time PCR for quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.M.; Lachani, K.; Sargent, C.A.; Yang, F.; Ellis, P.; Hunt, T.; Fu, B.; Louzada, S.; Churcher, C.; Tyler-Smith, C.; et al. Expansion of the HSFY gene family in pig lineages: HSFY expansion in suids. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, A.J.P.; Raudsepp, T.; Graves, T.; Albracht, D.; Warren, W.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Skow, L.; Murphy, W.J. Gene discovery and comparative analysis of X-degenerate genes from the domestic cat Y chromosome. Genomics 2008, 92, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raudsepp, T.; Das, P.; Avila, F.; Chowdhary, B. The Pseudoautosomal Region and Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies in Domestic Species. Sex. Dev. 2012, 6, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.O.; Larramendy, M.L.; Bianchi, M.S.; Cortes, L. Karyological conservatism in South American camelids. Experientia 1986, 42, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miga, K.H. Centromere studies in the era of ’telomere-to-telomere’ genomics. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Total Assembly | 20,060,146 bp |
|---|---|
| Contig N50 | 288,719 bp |
| Contig L50 | 21 |
| Number of Contigs | 652 |
| Largest Contig | 1,433,950 bp |
| Smallest Contig | 1142 bp |
| Mean Contig Length | 30,767 bp |
| Contig ID | Size, bp | GC, % | LINE, % | SINE, % | Simple Repeats, % | LTR, % | Total Repetitive, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tig1 | 1,120,224 | 35.8 | 43.43 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 9.77 | 54.2 |
| Tig467 | 400,437 | 35.6 | 26.79 | 0.69 | 0.81 | 4.73 | 37.1 |
| Tig251 | 381,152 | 44.6 | 18.14 | 1.90 | 1.1 | 6.17 | 32.8 |
| Tig3291 | 348,639 | 36.5 | 41.52 | 0.71 | 0.92 | 4.64 | 50.4 |
| Tig3262 | 337,762 | 36.5 | 38.74 | 0.37 | 1.63 | 24.03 | 65.2 |
| Tig419 * | 307,557 | 43.6 | 21.81 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 3.31 | 29.5 |
| Tig223 | 297,467 | 33.3 | 67.38 | 0.16 | 1.48 | 2.76 | 72.0 |
| Tig352 | 290,908 | 37.9 | 36.0 | 1 | 0.8 | 10.3 | 49.1 |
| Tig667 | 169,226 | 37.1 | 35.47 | 0.19 | 1.43 | 7.32 | 46.3 |
| Tig292 | 139,608 | 40.0 | 15.1 | 2.30 | 0.7 | 4.0 | 23.4 |
| Tig469 | 136,307 | 36.60 | 58.56 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 2.28 | 62.76 |
| Tig313 | 132,018 | 34.5 | 44.44 | 0.38 | 0.77 | 5.13 | 53.3 |
| Tig5 | 124,853 | 34.9 | 31.4 | 0 | 1.3 | 13.4 | 46.4 |
| Tig538 | 107,714 | 34.87 | 51.3 | 0.42 | 1.06 | 3.07 | 57.08 |
| Tig3300 | 65,384 | 43.2 | 19.77 | 0.49 | 0.94 | 3.98 | 25.4 |
| Tig723 | 64,517 | 33.85 | 30.60 | 1.07 | 0.55 | 2.97 | 40.02 |
| Tig713 | 32,281 | 40.1 | 12.39 | 0 | 0 | 6.27 | 18.9 |
| Tig3301 | 29,614 | 43.5 | 20.13 | 0 | 0.73 | 7.27 | 29.3 |
| Total/Average | 4,485,668 | 37.4 | 37.2 | 0.6 | 1 | 7.9 | 48.3 |
| Gene/Transcript Symbol | MSY Contig | Gene Category | No of Exons | Copy Number | Transcript Size, bp | ORF, aa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMELY | tig3291 | X-degenerate | n/a | 1 | n/a | n/a |
| CUL4BY | tig469, tig538 | X-degenerate | 8 | 2 | 1123 | 303 |
| DDX3Y | tig467 | X-degenerate | 16 | 1 | 4873 | 474 |
| EIF1AY | tig419 | X-degenerate | 7 | 2 | 2795 | 145 |
| EIF2S3Y | tig313 | X-degenerate | 15 | 1 | 4588 | 472 |
| HSFY | tig1, tig223, tig419 | X-degenerate | 2 | 26 | 1082 | 356 |
| KDM5D | tig667 | X-degenerate | 26 | 1 | 10,322 | 1219 |
| OFD1Y | tig467 | X-degenerate | 7 | 1 | 2182 | 450 |
| RBMY | tig713, tig3300, tig3301 | X-degenerate | 4 | 3 | 3831 | 116 |
| SRY | tig3262 | X-degenerate | 1 | 1 | 723 | 240 |
| TSPY | tig251, tig3300, tig3301 | X-degenerate | 7 | 3 | 4880 | 140 |
| UKN_1123 | tig667 | novel | 1 | 1 | 994 | 104 |
| UKN_9026 | tig467 | novel | 1 | 1 | 773 | 143 |
| USP9Y | tig467 | X-degenerate | 42 | 1 | 9928 | 2,489 |
| UTY | tig467, tig723 | X-degenerate | 28 | 1 | 6366 | 913 |
| WWC3Y | tig3291 | X-degenerate | 21 | 1 | 2109 | 246 |
| ZFY | tig3291 | X-degenerate | 5 | 1 | 9574 | 509 |
| Alpaca Gene | Presence in Other Mammals |
|---|---|
| AMELY | horse, pig, cattle, cat, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus |
| CUL4BYMC? | horse MC, pig MC, cat MC, dog MC |
| DDX3Y | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse, rat |
| EIF1AYMC? | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset |
| EIF2S3Y | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, mouse, rat |
| HSFYMC | horse MC, pig MC, cattle MC, dog, cat MC, human MC, gorilla MC, macaque |
| KDM5D | horse, pig, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse, rat |
| OFD1Y | horse, pig, cattle, dog human PS, chimp PS, gorilla, macaque PS |
| RBMYMC | horse MC, pig MC, cattle, dog, human MC, chimp MC, gorilla MC, rhesus, marmoset, mouse MC, rat MC |
| SRY | horse, pig MC, cattle, cat, dog MC, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse, rat MC, opossum |
| TSPYMC? | horse MC, pig MC, cattle MC, cat MC, dog MC, human MC, chimp MC, gorilla MC, rhesus MC, marmoset, mouse PS, rat MC |
| USP9Y | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse, rat |
| UTY | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse, rat |
| WWC3Y | horse |
| ZFY | horse, pig, cattle, cat, dog, human, chimp, gorilla, rhesus, marmoset, mouse MC, rat |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jevit, M.J.; Davis, B.W.; Castaneda, C.; Hillhouse, A.; Juras, R.; Trifonov, V.A.; Tibary, A.; Pereira, J.C.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Raudsepp, T. An 8.22 Mb Assembly and Annotation of the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) Y Chromosome. Genes 2021, 12, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010105
Jevit MJ, Davis BW, Castaneda C, Hillhouse A, Juras R, Trifonov VA, Tibary A, Pereira JC, Ferguson-Smith MA, Raudsepp T. An 8.22 Mb Assembly and Annotation of the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) Y Chromosome. Genes. 2021; 12(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleJevit, Matthew J., Brian W. Davis, Caitlin Castaneda, Andrew Hillhouse, Rytis Juras, Vladimir A. Trifonov, Ahmed Tibary, Jorge C. Pereira, Malcolm A. Ferguson-Smith, and Terje Raudsepp. 2021. "An 8.22 Mb Assembly and Annotation of the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) Y Chromosome" Genes 12, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010105
APA StyleJevit, M. J., Davis, B. W., Castaneda, C., Hillhouse, A., Juras, R., Trifonov, V. A., Tibary, A., Pereira, J. C., Ferguson-Smith, M. A., & Raudsepp, T. (2021). An 8.22 Mb Assembly and Annotation of the Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) Y Chromosome. Genes, 12(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010105








