Identification and Expression Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs in Serum of Cysticercus pisiformis-Infected Rabbits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Parasites and Animals
2.3. Blood Samples Collection and RNA Isolation
2.4. Small RNA Library Generation and Sequencing
2.5. Reads Analysis and MiRNA Prediction
2.6. Verification of Differential Expression MiRNAs by Using qRT-PCR
2.7. Function Prediction of Dysregulated MiRNAs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
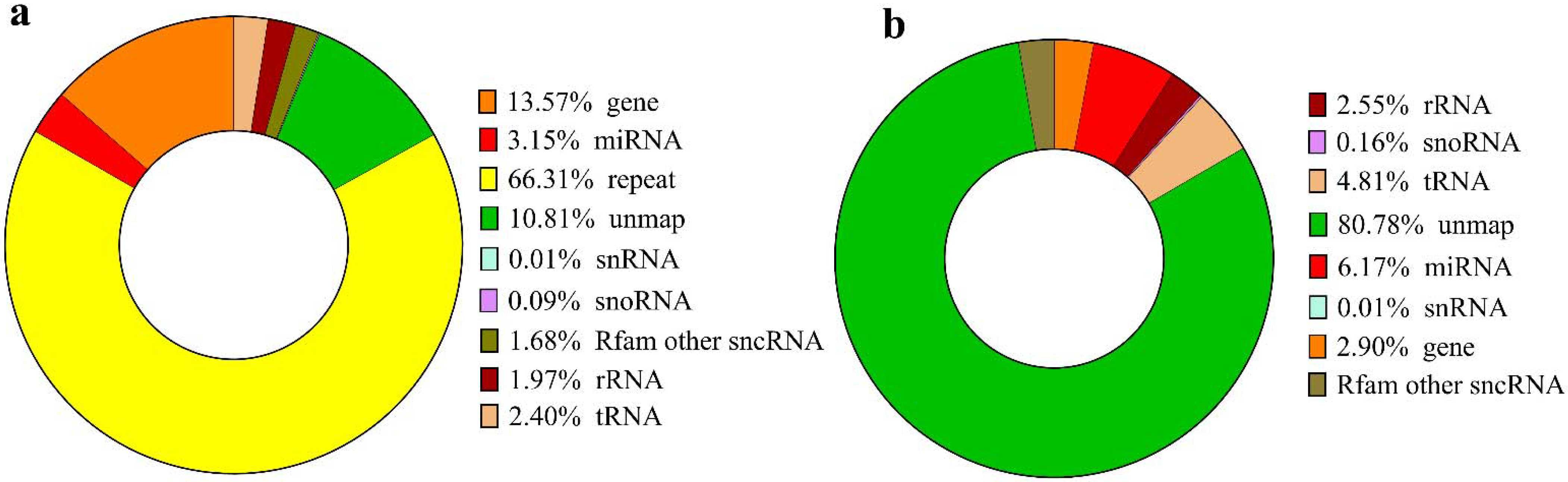
3.1. Characterization of the sRNAs Libraries
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
3.3. qRT-PCR Verification of miRNA Expression
3.4. Prediction of miRNA Target Genes
3.5. Functional Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of the Larval and Adult Stages of Taenia pisiformis. Genes 2019, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stancampiano, L.; Ravagnan, S.; Capelli, G.; Militerno, G. Cysticercosis by Taenia pisiformis in Brown Hare (Lepus europaeus) in Northern Italy: Epidemiologic and pathologic features. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, A.; Hou, J.; Wu, R. Molecular cloning and characterization of leucine aminopeptidase gene from Taenia pisiformis. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, R.M.; Whitfield, P.J.; Lewis, J.W. The epidemiology of Taenia pisiformis infections in domestic dogs in Cairo. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 597–610. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Roldan, R.; Perez-Martinez, M.; Rosetti, M.F.; Arias-Hernandez, D.; Bernal-Fernandez, G.; Flores-Perez, F.I.; Hallal-Calleros, C. High frequency of Taenia pisiformis metacestodes and high sex-associated susceptibility to cysticercosis in naturally infected wild rabbits. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2201–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Ren, Y.J.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Nong, X.; Gu, X.B.; Wang, S.X.; Peng, X.R.; Yang, G.Y. Genetic characteristics of Chinese isolates of the tapeworm Taenia pisiformis based on two mitochondrial genes. J. Helminthol. 2015, 89, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal-Calleros, C.; Morales-Montor, J.; Orihuela-Trujillo, A.; Togno-Peirce, C.; Murcia-Mejia, C.; Bielli, A.; Hoffman, K.L.; Flores-Perez, F.I. Taenia pisiformis cysticercosis induces decreased prolificacy and increased progesterone levels in rabbits. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 229, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Hernandez, D.; Garcia-Jimenez, S.; Dominguez-Roldan, R.; Murcia-Mejia, C.; Baez-Saldana, A.; Hallal-Calleros, C.; Flores-Perez, I. Effects of Taenia Pisiformis Infection and Obesity on Clinical Parameters, Organometry and Fat Distribution in Male Rabbits. Pathogens 2020, 9, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, D.; Gu, X.; Peng, X.; Yang, G. Evaluation of a novel Dot-ELISA assay utilizing a recombinant protein for the effective diagnosis of Taenia pisiformis larval infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 204, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Q.; Li, L.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Wu, Y.T.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, N.Z.; Fu, B.Q.; Yan, H.B.; Jia, W.Z. A multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection of Taenia hydatigena, T. multiceps, T. pisiformis, and Dipylidium caninum infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabekkodu, S.; Shukla, V.; Varghese, V.K.; Souza, J.D.; Chakrabarty, S.; Satyamoorthy, K. Clustered miRNAs and their role in biological functions and diseases. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1955–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lai, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Ye, X. MicroRNA-33a disturbs influenza A virus replication by targeting ARCN1 and inhibiting viral ribonucleoprotein activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Ren, G.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; He, X. The upregulation of miRNA-146a inhibited biological behaviors of ESCC through inhibition of IRS2. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 4641–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muxel, S.M.; Acuna, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Zampieri, R.A.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Toll-Like Receptor and miRNA-let-7e Expression Alter the Inflammatory Response in Leishmania amazonensis-Infected Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, F.; Roy, S.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.L.; Zhou, N.K.; Luo, C.H. MiRNA-155 and miRNA-132 as potential diagnostic biomarkers for pulmonary tuberculosis: A preliminary study. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Gong, A.Y.; Eischeid, A.N.; Chen, X.M. miR-27b targets KSRP to coordinate TLR4-mediated epithelial defense against Cryptosporidium parvum infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menard, K.L.; Haskins, B.E.; Colombo, A.P.; Denkers, E.Y. Toxoplasma gondii Manipulates Expression of Host Long Noncoding RNA during Intracellular Infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Liu, C.; Du, X.; Nawaratna, S.; Rivera, V.; Harvie, M.; Jones, M.; McManus, D.P. Suppression of Schistosoma japonicum Acetylcholinesterase Affects Parasite Growth and Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, D.; Luo, S.; Xu, L.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z. Regulatory effect of host miR-101b-3p on parasitism of nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis via superoxide dismutase 3. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liao, Q.; Zeng, X.; Lv, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, Z. MicroRNA expressions associated with eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection in a mouse model. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zheng, Y. Expression profiling of circulating miRNAs in mouse serum in response to Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Cai, P.; Olveda, R.M.; Ross, A.G.; Olveda, D.U.; McManus, D.P. Parasite-derived circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for the detection of human Schistosoma japonicum infection. Parasitology 2020, 147, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, Z.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Spotin, A.; Kazemi, T.; Ahmadpour, E.; Cai, P.; Shanehbandi, D.; Shekari, N. Parasite-derived microRNAs in plasma as novel promising biomarkers for the early detection of hydatid cyst infection and post-surgery follow-up. Acta Trop. 2020, 202, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, K.; Bert, A.G.; Dredge, B.K.; Toubia, J.; Gregory, P.A.; Pillman, K.A.; Goodall, G.J.; Bracken, C.P. Insufficiently complex unique-molecular identifiers (UMIs) distort small RNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Chen, W.; Adamidi, C.; Maaskola, J.; Einspanier, R.; Knespel, S.; Rajewsky, N. Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soemedi, R.; Cygan, K.J.; Rhine, C.L.; Glidden, D.T.; Taggart, A.J.; Lin, C.L.; Fredericks, A.M.; Fairbrother, W.G. The effects of structure on pre-mRNA processing and stability. Methods 2017, 125, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, A. WEGO 2.0: A web tool for analyzing and plotting GO annotations, 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W71–W75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Huang, Q. Interactions Among Host-Parasite MicroRNAs During Nosema ceranae Proliferation in Apis mellifera. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Shi, W.; Wang, T.; Ruan, Q. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of T helper type 17/regulatory T-cell balance in autoimmune disease. Immunology 2018, 155, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.Q.; Liu, T.L.; Liang, P.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, T.S.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, G.X.; Mao, L.; Luo, X.N. Characterization of exosome-like vesicles derived from Taenia pisiformis cysticercus and their immunoregulatory role on macrophages. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchiaroli, N.; Cucher, M.; Kamenetzky, L.; Yones, C.; Bugnon, L.; Berriman, M.; Olson, P.D.; Rosenzvit, M.C. Identification and expression profiling of microRNAs in Hymenolepis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa, A.; Navarro, L.; Ochoa-Sanchez, A.; Jimenez, L. Taenia solium and Taenia crassiceps: miRNomes of the larvae and effects of miR-10-5p and let-7-5p on murine peritoneal macrophages. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Mao, L.; Liang, P.; Fasihi, H.M.; Li, T.; Luo, X. Exosomal microRNA let-7-5p from Taenia pisiformis Cysticercus Prompted Macrophage to M2 Polarization through Inhibiting the Expression of C/EBP delta. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Colon, L.; Deep, G.; Kumar, D. Emerging role of microRNA 628-5p as a novel biomarker for cancer and other diseases. Tumour Biol. 2019, 41, 1391208320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.; Wu, Q.; Williams, V.; Clark, G.; Guruli, G.; Zehner, Z. A Panel of MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Identification of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoy, A.M.; Lundie, R.J.; Ivens, A.; Quintana, J.F.; Nausch, N.; Forster, T.; Jones, F.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Dunne, D.W.; Mutapi, F.; et al. Parasite-derived microRNAs in host serum as novel biomarkers of helminth infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, P.; Gobert, G.N.; You, H.; Duke, M.; McManus, D.P. Circulating miRNAs: Potential Novel Biomarkers for Hepatopathology Progression and Diagnosis of Schistosomiasis Japonica in Two Murine Models. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deping, C.; Bofan, J.; Yaogang, Z.; Mingquan, P. microRNA-125b-5p is a promising novel plasma biomarker for alveolar echinococcosis in patients from the southern province of Qinghai. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z.Y.; Maleewong, W.; Maleewong, P.; Liang, J.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Z.D.; Sun, X. Serum aca-mir-146a is a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample Name | Number of Infected C. pisiformis | Raw Tag Count | Clean Tag Count | Percentage of Clean Tag(%) | Mapped Tag of Oryctolagus cuniculus Genome | Percentage of Mapped Tag of Oryctolagus cuniculus Genome(%) | Mapped Tag of T. pisiformis Genome | Percentage of Mapped Tag of T. pisiformis Genome(%) | Known miRNA Count | Novel miRNA Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC-1 | 0 | 28,101,107 | 25,647,172 | 91.27 | 22,472,334 | 87.62 | 1,329,791 | 5.18 | 23 | 491 |
| NC-2 | 0 | 28,011,580 | 25,355,821 | 90.52 | 23,862,803 | 94.11 | 1,337,063 | 5.27 | 40 | 186 |
| NC-3 | 0 | 28,343,925 | 26,650,162 | 94.02 | 22,681,061 | 85.11 | 1,267,343 | 4.76 | 17 | 453 |
| Cpi-1 | 180 | 27,813,172 | 25,843,308 | 92.92 | 22,232,314 | 86.03 | 671,980 | 2.60 | 39 | 216 |
| Cpi-2 | 206 | 28,839,799 | 27,578,609 | 95.63 | 25,076,910 | 90.93 | 1,250,296 | 4.53 | 28 | 121 |
| Cpi-3 | 194 | 28,139,567 | 26,404,625 | 93.83 | 23,154,753 | 87.69 | 788,071 | 2.98 | 27 | 112 |
| miRNAs | Primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| U6 | F: GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| R: CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | |
| novel-miR1 | TATACGCAGGTGCGAAAGCAGG |
| novel-miR857 | AGAGAGCGGTCGGACACC |
| novel-miR476 | TGATTGGTGAGCGTAGAGGTCG |
| novel-miR318 | TATATAGTGGCGCGAAGCGGG |
| novel-miR307 | TATATACCCGCGAGGGGGC |
| novel-miR303 | TATATACCGGGGCGGGGTG |
| novel-miR128 | TATATATAGCGCGCGTGCGCC |
| novel-miR150 | TATATAGGCGGGGTGCGGG |
| novel-miR57 | CGCAATTGCACGGTATCCATCTGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Luo, X. Identification and Expression Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs in Serum of Cysticercus pisiformis-Infected Rabbits. Genes 2021, 12, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101591
Chen G, Wang L, Liu T, Li Y, Zhang S, Li H, Luo X. Identification and Expression Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs in Serum of Cysticercus pisiformis-Infected Rabbits. Genes. 2021; 12(10):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101591
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guoliang, Liqun Wang, Tingli Liu, Yanping Li, Shaohua Zhang, Hong Li, and Xuenong Luo. 2021. "Identification and Expression Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs in Serum of Cysticercus pisiformis-Infected Rabbits" Genes 12, no. 10: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101591
APA StyleChen, G., Wang, L., Liu, T., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Li, H., & Luo, X. (2021). Identification and Expression Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs in Serum of Cysticercus pisiformis-Infected Rabbits. Genes, 12(10), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101591






