The Origin of Plasma-Derived Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
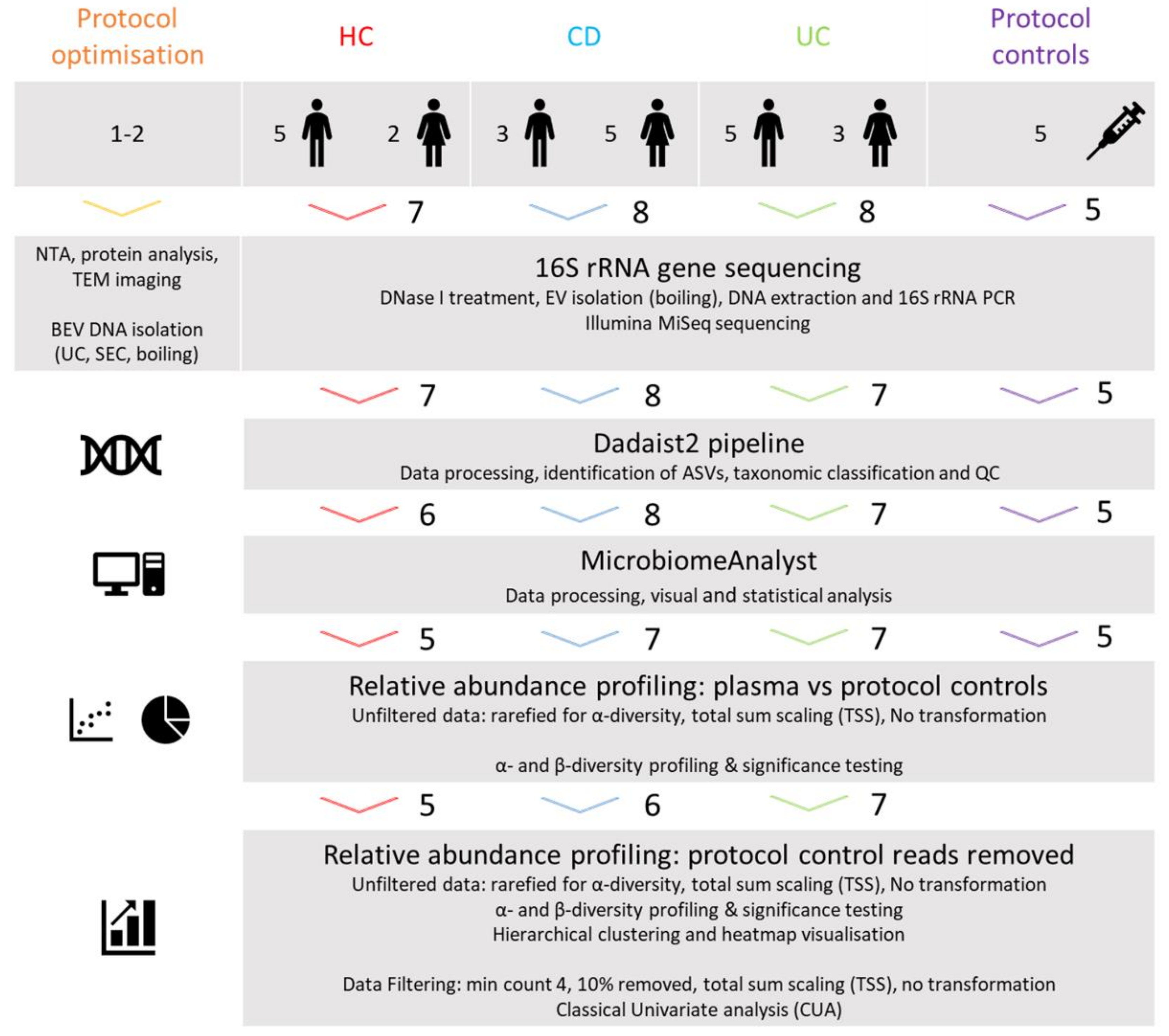
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.3. Protein Concentration Measurement
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation from Plasma
2.5.1. Ultracentrifugation
2.5.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.5.3. Boiling
2.6. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.7. PCR and Gel Densitometry
2.8. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.9. Data Analysis
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
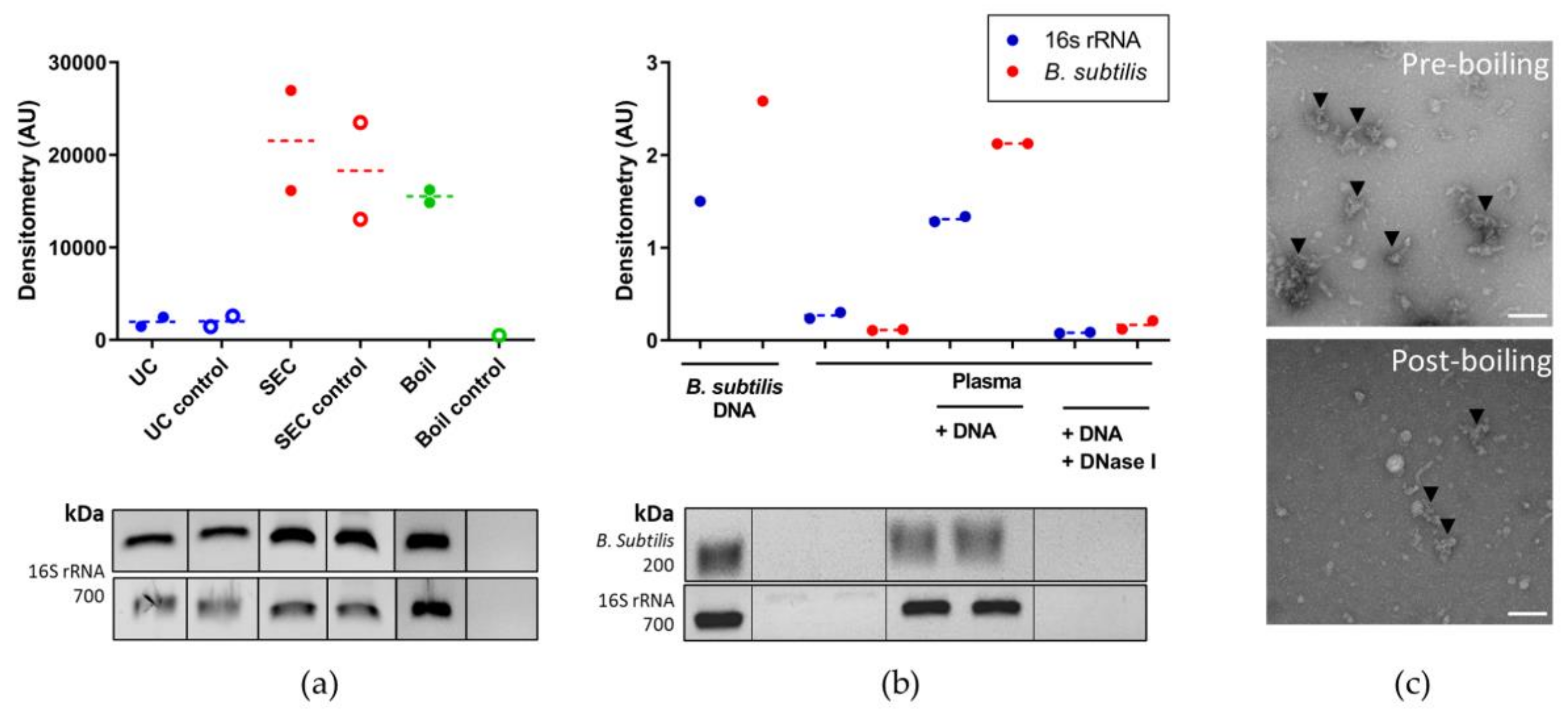
3.2. Features of Plasma Nanoparticles
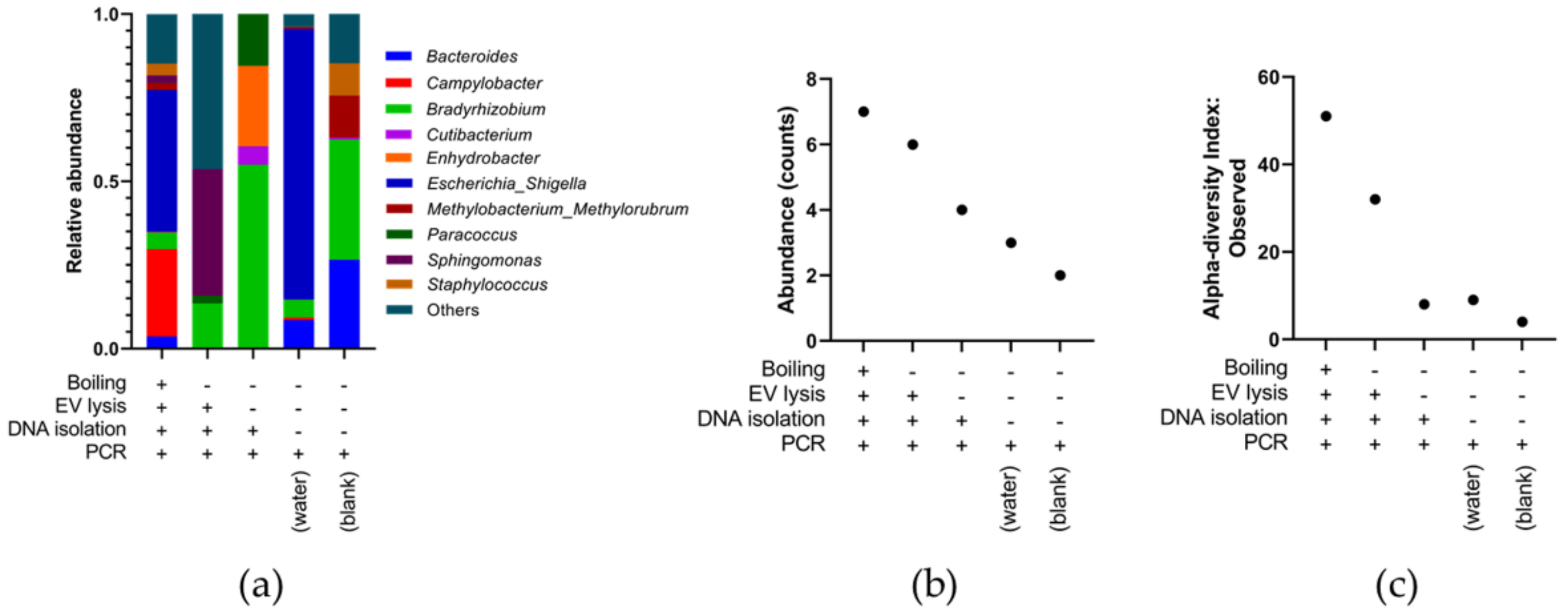
3.3. Optimising Bacterial Extracellular DNA Isolation from Plasma
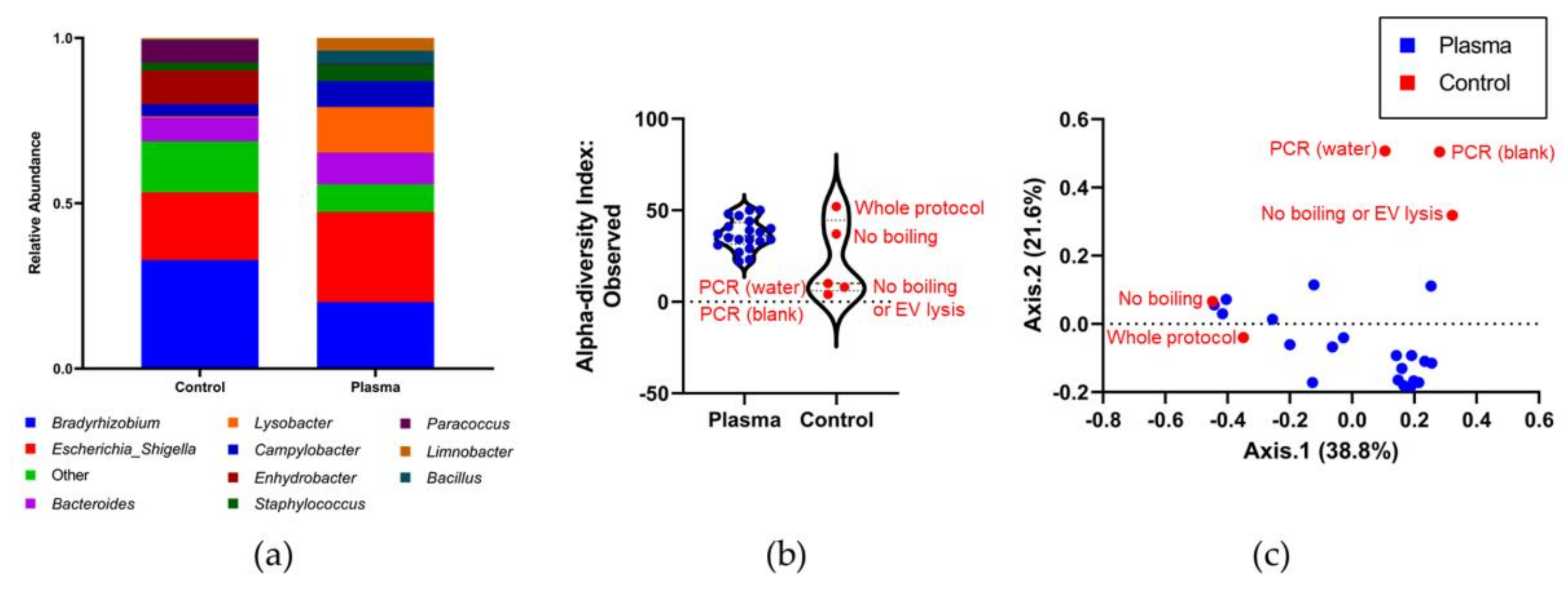
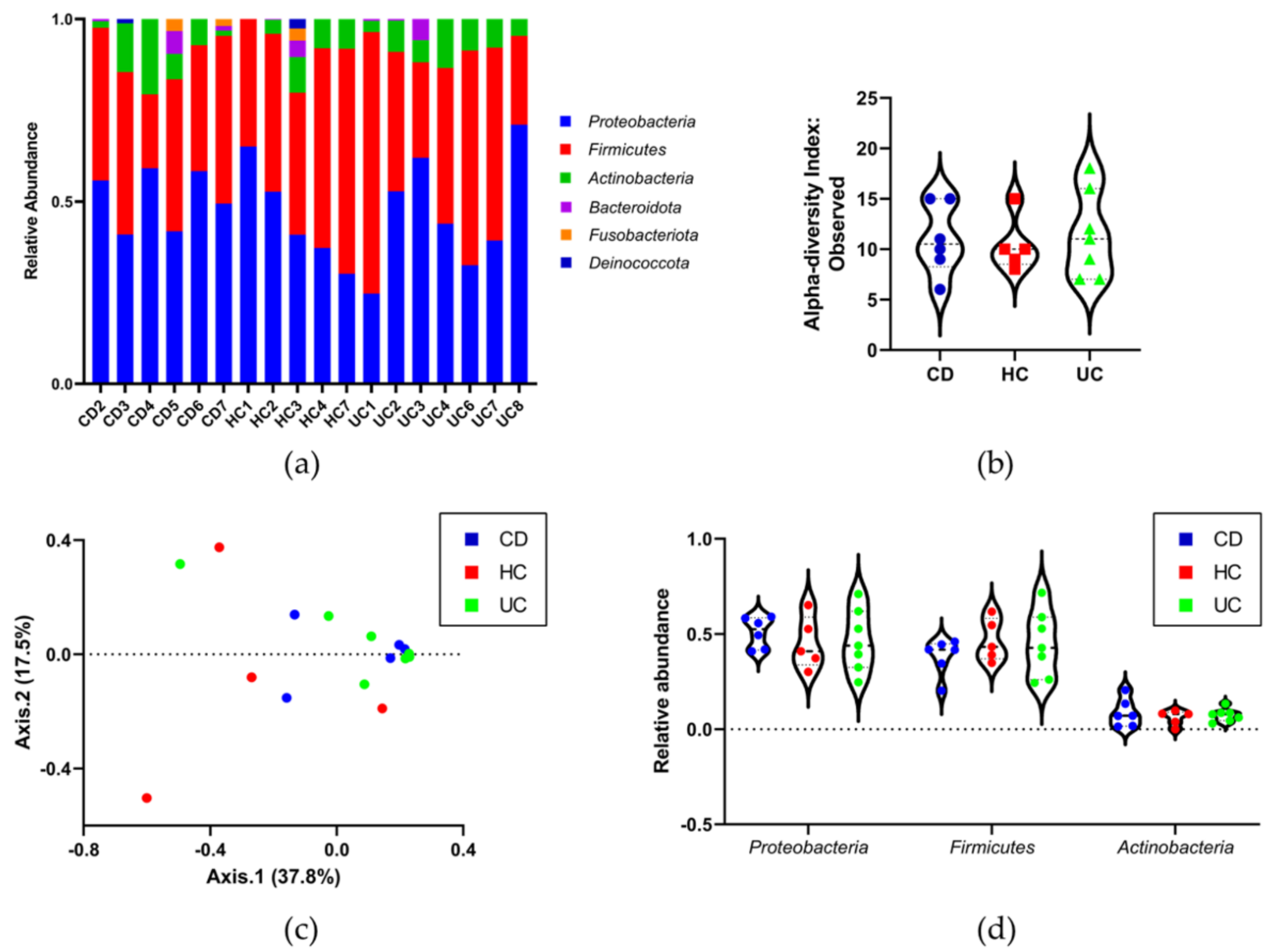
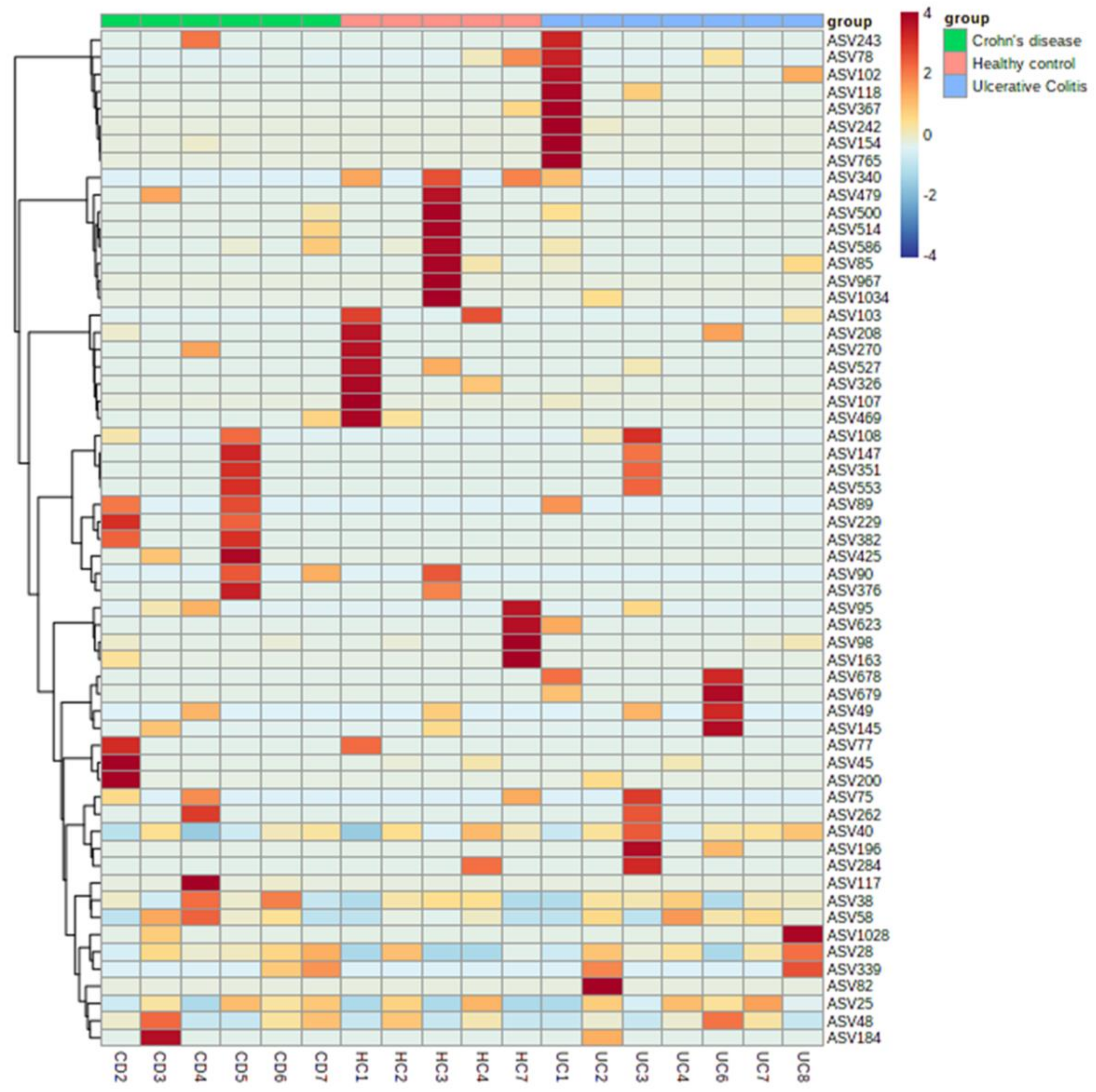
3.4. Identifying the Origin of Plasma Derived Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carding, S.; Verbeke, K.; Vipond, D.T.; Corfe, B.M.; Owen, L.J. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.A.; Xu, Z.; Knight, R. Meta-analyses of human gut microbes associated with obesity and IBD. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kanai, T. The gut microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G.D.; Albenberg, L.; Tomov, V.T. Gut microbiota and IBD: Causation or correlation? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stentz, R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Jones, E.J.; Carding, S.R. Fantastic voyage: The journey of intestinal microbiota-derived microvesicles through the body. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sina, C.; Kemper, C.; Derer, S. The intestinal complement system in inflammatory bowel disease: Shaping intestinal barrier function. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 37, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbull, L.; Toyofuku, M.; Hynen, A.L.; Kurosawa, M.; Pessi, G.; Petty, N.K.; Osvath, S.R.; Cárcamo-Oyarce, G.; Gloag, E.S.; Shimoni, R.; et al. Explosive cell lysis as a mechanism for the biogenesis of bacterial membrane vesicles and biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauros-Singorenko, P.; Blenkiron, C.; Phillips, A.; Swift, S. The functional RNA cargo of bacterial membrane vesicles. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 3, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitto, N.J.; Chapman, R.; Pidot, S.; Costin, A.; Lo, C.; Choi, J.; D’Cruze, T.; Reynolds, E.C.; Dashper, S.G.; Turnbull, L.; et al. Bacterial membrane vesicles transport their DNA cargo into host cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitto, N.J.; Cheng, L.; Johnston, E.L.; Pathirana, R.; Phan, T.K.; Poon, I.K.H.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Hill, A.F.; Stinear, T.P.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles contain immunostimulatory DNA, RNA and peptidoglycan that activate innate immune receptors and induce autophagy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, W.A.; Stentz, R.; Le Gall, G.; Sternberg, M.J.E.; Carding, S.R.; Wilhelm, T. In Silico Analysis of the Small Molecule Content of Outer Membrane Vesicles Produced by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Indicates an Extensive Metabolic Link between Microbe and Host. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.L.; Fonseca, S.; Miquel-Clopés, A.; Cross, K.; Kok, K.S.; Wegmann, U.; Gil-Cordoso, K.; Bentley, E.G.; Al Katy, S.H.M.; Coombes, J.L.; et al. Bioengineering commensal bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles for delivery of biologics to the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1632100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Coyne, M.J.; Comstock, L.E. An ecological network of polysaccharide utilization among human intestinal symbionts. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stentz, R.; Horn, N.; Cross, K.; Salt, L.; Brearley, C.; Livermore, D.M.; Carding, S.R. Cephalosporinases associated with outer membrane vesicles released by Bacteroides spp. protect gut pathogens and commensals against β-lactam antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durant, L.; Stentz, R.; Noble, A.; Brooks, J.; Gicheva, N.; Reddi, D.; O’Connor, M.J.; Hoyles, L.; McCartney, A.L.; Man, R.; et al. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron-derived outer membrane vesicles promote regulatory dendritic cell responses in health but not in inflammatory bowel disease. Microbiome 2020, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.J.; Booth, C.; Fonseca, S.; Parker, A.; Cross, K.; Miquel-Clopés, A.; Hautefort, I.; Mayer, U.; Wileman, T.; Stentz, R.; et al. The Uptake, Trafficking, and Biodistribution of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Generated Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irvine, E.J.; Marshall, J.K. Increased intestinal permeability precedes the onset of Crohn’s disease in a subject with familial risk. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosli, M.H.; Zou, G.; Garg, S.K.; Feagan, S.G.; MacDonald, J.K.; Chande, N.; Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G. C-Reactive Protein, Fecal Calprotectin, and Stool Lactoferrin for Detection of Endoscopic Activity in Symptomatic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2015, 110, 802–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, D.J.; Rifkin, R.F.; Cowan, D.A.; Potgieter, M. The Healthy Human Blood Microbiome: Fact or Fiction? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, E.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R.; Kim, Y.K.; Han, P.L. Metagenome Analysis of Bodily Microbiota in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease Using Bacteria-derived Membrane Vesicles in Blood. Exp. Neurobiol. 2017, 26, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Qin, N.; Chen, S.D.; Xiao, Q. Detection of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene in the Blood of Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; McDowell, A.; Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Min, T.K.; Jee, Y.K.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.S.; Pyun, B.Y.; Kim, Y.K. Diagnostic Models for Atopic Dermatitis Based on Serum Microbial Extracellular Vesicle Metagenomic Analysis: A Pilot Study. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.P.; Yang, J.; Won, H.K.; Park, C.S.; Song, W.J.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, T.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, H.S.; et al. Metagenome analysis using serum extracellular vesicles identified distinct microbiota in asthmatics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakaran, V.; Rathinavel, A.; Pushpanathan, M.; Sivakumar, R.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rajendhran, J. Elevated levels of circulating DNA in cardiovascular disease patients: Metagenomic profiling of microbiome in the circulation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Chen, B.; Pan, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Zou, M.; Yang, J.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, R.; et al. Detection of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene in the Serum of Patients with Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.K.; Min, S.K.; Lee, W.H. 16S rDNA microbiome composition pattern analysis as a diagnostic biomarker for biliary tract cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Patton, M.J.; Floyd, J.L.; Vieira, C.P.; Fortmann, S.; DuPont, M.; Harbour, A.; Jeremy, C.S.; Wright, J.; Lamendella, R.; et al. Plasma microbiome in COVID-19 subjects: An indicator of gut barrier defects and dysbiosis. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkens, J.; Vergauwen, G.; Van Deun, J.; Geeurickx, E.; Dhondt, B.; Lippens, L.; De Scheerder, M.A.; Miinalainen, I.; Rappu, P.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. Increased levels of systemic LPS-positive bacterial extracellular vesicles in patients with intestinal barrier dysfunction. Gut 2020, 69, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noble, A.; Durant, L.; Hoyles, L.; McCartney, A.L.; Man, R.; Segal, J.; Costello, S.P.; Hendy, P.; Reddi, D.; Bouri, S.; et al. Deficient Resident Memory T Cell and CD8 T Cell Response to Commensals in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Mortazavi, S.; Bahrami, A.; Sadeghi, B.; Matin, M. Designing a SYBR Green Absolute Real time PCR Assay for Specific Detection and Quantification of Bacillus subtilis in Dough Used for Bread Making. J. Cell Mol. Res. 2014, 6, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorge, R.; Birolo, G.; James, S.A.; Telatin, A. Dadaist2: A Toolkit to Automate and Simplify Statistical Analysis and Plotting of Metabarcoding Experiments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telatin, A.; Fariselli, P.; Birolo, G. SeqFu: A Suite of Utilities for the Robust and Reproducible Manipulation of Sequence Files. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E. Using DECIPHER v2.0 to Analyze Big Biological Sequence Data in R. R J. 2016, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arraud, N.; Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Pasquet, J.M.; Mornet, S.; Brisson, A.R. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: Determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Catchpole, R.; Forterre, P. Extracellular membrane vesicles in the three domains of life and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cruz, C.; Delgado, L.; López-Iglesias, C.; Mercade, E. Outer-inner membrane vesicles naturally secreted by gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, L.; Baeza, N.; Pérez-Cruz, C.; López-Iglesias, C.; Mercadé, E. Cryo-transmission Electron Microscopy of Outer-inner Membrane Vesicles Naturally Secreted by Gram-negative Pathogenic Bacteria. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanov, A.; Shtam, T.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Garaeva, L.; Verlov, N.; Miliukhina, I.; Kudrevatykh, A.; Gavrilov, G.; Zabrodskaya, Y.; Pchelina, S.; et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles from cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuana, Y.; Koning, R.I.; Kuil, M.E.; Rensen, P.C.; Koster, A.J.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergauwen, G.; Dhondt, B.; Van Deun, J.; De Smedt, E.; Berx, G.; Timmerman, E.; Gevaert, K.; Miinalainen, I.; Cocquyt, V.; Braems, G.; et al. Confounding factors of ultrafiltration and protein analysis in extracellular vesicle research. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tulkens, J.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. Analyzing bacterial extracellular vesicles in human body fluids by orthogonal biophysical separation and biochemical characterization. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 40–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.; Coumans, F.A.; Maltesen, R.G.; Böing, A.N.; Bonnington, K.E.; Broekman, M.L.; Broom, M.F.; Buzás, E.I.; Christiansen, G.; Hajji, N.; et al. A standardized method to determine the concentration of extracellular vesicles using tunable resistive pulse sensing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauros Singorenko, P.; Chang, V.; Whitcombe, A.; Simonov, D.; Hong, J.; Phillips, A.; Swift, S.; Blenkiron, C. Isolation of membrane vesicles from prokaryotes: A technical and biological comparison reveals heterogeneity. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1324731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, C.H.K.; Yang, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kym, S.; Ahn, Y.M. Comparison of serum microbiome composition in bipolar and major depressive disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 123, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Kang, N.; Leem, S.; Yang, J.; Jo, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.S.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, T.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Serum Microbe-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Diagnostic Models to Differentiate Ovarian Cancer and Benign Ovarian Tumor. Cancers 2020, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, G.; Park, S.C.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Won, S. Type-2 Diabetics Reduces Spatial Variation of Microbiome Based on Extracellur Vesicles from Gut Microbes across Human Body. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liangsupree, T.; Multia, E.; Riekkola, M.L. Modern isolation and separation techniques for extracellular vesicles. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1636, 461773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrich, L.S.; Farrer, A.G.; Eisenhofer, R.; Arriola, L.A.; Young, J.; Selway, C.A.; Handsley-Davis, M.; Adler, C.J.; Breen, J.; Cooper, A. Laboratory contamination over time during low-biomass sample analysis. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salter, S.J.; Cox, M.J.; Turek, E.M.; Calus, S.T.; Cookson, W.O.; Moffatt, M.F.; Turner, P.; Parkhill, J.; Loman, N.J.; Walker, A.W. Reagent and laboratory contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenhofer, R.; Minich, J.J.; Marotz, C.; Cooper, A.; Knight, R.; Weyrich, L.S. Contamination in Low Microbial Biomass Microbiome Studies: Issues and Recommendations. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olomu, I.N.; Pena-Cortes, L.C.; Long, R.A.; Vyas, A.; Krichevskiy, O.; Luellwitz, R.; Singh, P.; Mulks, M.H. Elimination of “kitome” and “splashome” contamination results in lack of detection of a unique placental microbiome. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, A.P.; Roche, A.M.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Bailey, A.; Laughlin, A.L.; Bittinger, K.; Leite, R.; Elovitz, M.A.; Parry, S.; Bushman, F.D. Comparison of placenta samples with contamination controls does not provide evidence for a distinct placenta microbiota. Microbiome 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glassing, A.; Dowd, S.E.; Galandiuk, S.; Davis, B.; Chiodini, R.J. Inherent bacterial DNA contamination of extraction and sequencing reagents may affect interpretation of microbiota in low bacterial biomass samples. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grahn, N.; Olofsson, M.; Ellnebo-Svedlund, K.; Monstein, H.J.; Jonasson, J. Identification of mixed bacterial DNA contamination in broad-range PCR amplification of 16S rDNA V1 and V3 variable regions by pyrosequencing of cloned amplicons. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 219, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, K.; Martin, K.; FitzGerald, S.P.; O’Sullivan, J.; Wu, Y.; Blanco, A.; Richardson, C.; Mc Gee, M.M. A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Brisson, A.R.; Buzas, E.I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.E.E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.F.; et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, L.; Nanan, R.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Grau, G.E. Host- and Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles, Immune Function, and Disease Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stentz, R.; Osborne, S.; Horn, N.; Li, A.W.; Hautefort, I.; Bongaerts, R.; Rouyer, M.; Bailey, P.; Shears, S.B.; Hemmings, A.M.; et al. A bacterial homolog of a eukaryotic inositol phosphate signaling enzyme mediates cross-kingdom dialog in the mammalian gut. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, C.H.; Desai, H.; Sylvetsky, A.C.; LoTempio, J.; Ayanyan, S.; Carrie, J.; Crandall, K.A.; Fochtman, B.C.; Gasparyan, L.; Gulzar, N.; et al. Baseline human gut microbiota profile in healthy people and standard reporting template. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0206484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Carcione, D.; Messina, S.; Colombo, G.I.; D’Alessandra, Y. Circulating 16S RNA in Biofluids: Extracellular Vesicles as Mirrors of Human Microbiome? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | HC 1 | CD 2 | UC 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| Male/female | 5/2 | 3/5 | 5/3 |
| Mean age at sampling | 44 (28–57) * | 49 (24–73) * | 56 (41–71) * |
| Mean age at diagnosis | 37 (19–61) * | 40 (24–53) * | |
| Symptoms at sampling: | |||
| Diarrhea/loose stools | 3 | 2 | |
| Abdominal pain/bloating/flatulence | 0 | 1 | |
| Peri-anal pain/itch/disease | 1 | 1 | |
| Anal fissure/bleed/proctitis | 1 | 2 | |
| None | 5 | 3 | |
| Medications at sampling: | |||
| IBD 4 medications | 6 | 6 | |
| Non-IBD medications | 1 | 3 | |
| None | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, E.; Stentz, R.; Telatin, A.; Savva, G.M.; Booth, C.; Baker, D.; Rudder, S.; Knight, S.C.; Noble, A.; Carding, S.R. The Origin of Plasma-Derived Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study. Genes 2021, 12, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101636
Jones E, Stentz R, Telatin A, Savva GM, Booth C, Baker D, Rudder S, Knight SC, Noble A, Carding SR. The Origin of Plasma-Derived Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study. Genes. 2021; 12(10):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101636
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Emily, Régis Stentz, Andrea Telatin, George M. Savva, Catherine Booth, David Baker, Steven Rudder, Stella C. Knight, Alistair Noble, and Simon R. Carding. 2021. "The Origin of Plasma-Derived Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study" Genes 12, no. 10: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101636







