4mCPred-CNN—Prediction of DNA N4-Methylcytosine in the Mouse Genome Using a Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
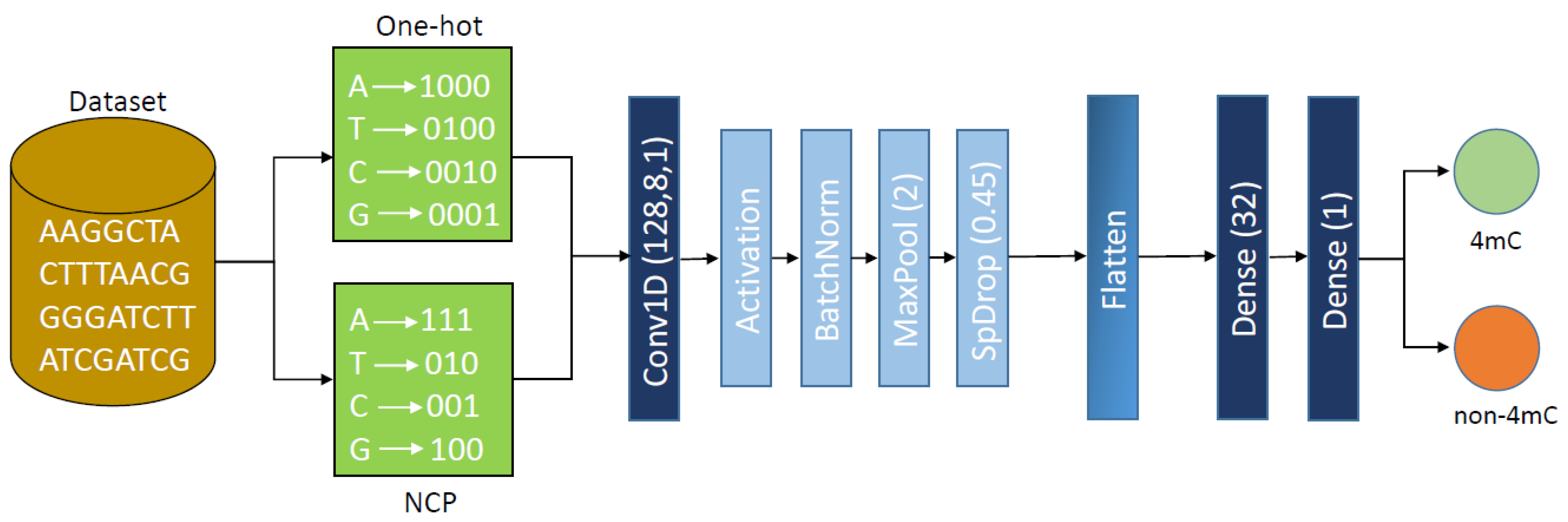
2. Datasets
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. One-Hot Encoding
3.2. Nucleotide Chemical Properties
4. Evaluation Metrics
5. Results
5.1. One-Hot vs. NCPs
5.2. Comparison of 4mCPred-CNN with Previous Models on the Benchmark Dataset
5.3. Comparison of 4mCPred-CNN with Previous Models on the Independent Dataset
6. Web Server
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathi, P.; Maurer, S.; Summerer, D. Selective recognition of N 4-methylcytosine in DNA by engineered transcription-activator-like effectors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeltsch, A.; Jurkowska, R.Z. New concepts in DNA methylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, W.; Ali, S.D.; Tayara, H.; to Chong, K. A CNN-based RNA n6-methyladenosine site predictor for multiple species using heterogeneous features representation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 138203–138209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.P.; Wang, T.; Seetin, M.G.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lin, K.; Liu, Y.; Byrum, S.D.; Mackintosh, S.G.; Zhong, M.; et al. DNA methylation on N 6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Nature 2016, 532, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Niu, R.; Huang, T.; Shao, L.W.; Peng, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G.; He, C.; Li, C.Y.; et al. N6-methyldeoxyadenine is a transgenerational epigenetic signal for mitochondrial stress adaptation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, G.Z.; Wang, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Zong, X.; Chen, K.; Yin, H.; Fu, Y.; et al. Abundant DNA 6mA methylation during early embryogenesis of zebrafish and pig. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Tayara, H.; to Chong, K. SpineNet-6mA: A Novel Deep Learning Tool for Predicting DNA N6-Methyladenine Sites in Genomes. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 201450–201457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Chong, K.T. DNA6mA-MINT: DNA-6mA modification identification neural tool. Genes 2020, 11, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Hong, K.J.; Tayara, H.; to Chong, K. m6A-NeuralTool: Convolution Neural Tool for RNA N6-Methyladenosine Site Identification in Different Species. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 17779–17786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Groop, L. Epigenetics: A molecular link between environmental factors and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, B.; Jin, P. Cytosine modifications in neurodevelopment and diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X. DNA modification by methyltransferases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1995, 5, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, B.S.; He, C. Nucleic acid modifications in regulation of gene expression. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ku, J.L.; Jeon, Y.K.; Park, J.G. Methylation-specific PCR. In Epigenetics Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Domon, B.; Aebersold, R. Mass spectrometry and protein analysis. Science 2006, 312, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, R.; Couldrey, C. Exploring genome wide bisulfite sequencing for DNA methylation analysis in livestock: A technical assessment. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ardui, S.; Ameur, A.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Hestand, M.S. Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: Applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brown, Z.K.; Boulias, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.Y.; O’Brown, N.M.; Hao, Z.; Shibuya, H.; Fady, P.E.; Shi, Y.; He, C.; et al. Sources of artifact in measurements of 6mA and 4mC abundance in eukaryotic genomic DNA. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, P.; Luan, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Xie, Z. MethSMRT: An integrative database for DNA N6-methyladenine and N4-methylcytosine generated by single-molecular real-time sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D85–D89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. 4mCpred-EL: An ensemble learning framework for identification of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in the mouse genome. Cells 2019, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Jia, C.; Zou, Q. 4mCPred: Machine learning methods for DNA N4-methylcytosine sites prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Luan, S.; Nagai, L.A.E.; Su, R.; Zou, Q. Exploring sequence-based features for the improved prediction of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in multiple species. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Manavalan, B.; Khatun, M.S.; Kurata, H. i4mC-ROSE, a bioinformatics tool for the identification of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in the Rosaceae genome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Manavalan, B.; Shoombuatong, W.; Khatun, M.S.; Kurata, H. i4mC-Mouse: Improved identification of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in the mouse genome using multiple encoding schemes. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espada, J.; Esteller, M. Mouse models in epigenetics: Insights in development and disease. Briefings Funct. Genom. 2013, 12, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uhl, E.W.; Warner, N.J. Mouse models as predictors of human responses: Evolutionary medicine. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; Han, D.; Zhu, H. From machine learning to deep learning: Progress in machine intelligence for rational drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, D.; Ding, X.; Hou, T. From machine learning to deep learning: Advances in scoring functions for protein–ligand docking. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1429. [Google Scholar]
- Ongsulee, P. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 15th International Conference on ICT and Knowledge Engineering (ICT&KE), Bangkok, Thailand, 22–24 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Huss, M.; Abid, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Torkamani, A.; Telenti, A. A primer on deep learning in genomics. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Dao, F.Y.; Guan, Z.X.; Zhang, D.; Tan, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, H. iDNA6mA-Rice: A computational tool for detecting N6-methyladenine sites in rice. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 793. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Leier, A.; Revote, J.; Zhu, Y.; Powell, D.R.; Akutsu, T.; Webb, G.I.; et al. iLearn: An integrated platform and meta-learner for feature engineering, machine-learning analysis and modeling of DNA, RNA and protein sequence data. Briefings Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.X.; Lv, H.; Wang, F.; Dao, F.Y.; Chen, W.; Ding, H. A survey for predicting enzyme family classes using machine learning methods. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, P.; Zheng, G.; Chen, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhu, F. What contributes to serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors’ dual-targeting mechanism? The key role of transmembrane domain 6 in human serotonin and norepinephrine transporters revealed by molecular dynamics simulation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, R.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. 6mA-DNA-binding factor Jumu controls maternal-to-zygotic transition upstream of Zelda. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahab, A.; Mahmoudi, O.; Kim, J.; Chong, K.T. DNC4mC-Deep: Identification and analysis of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites based on different encoding schemes by using deep learning. Cells 2020, 9, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lang, K.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y.; Pian, C. SOMM4mC: A second-order Markov model for DNA N4-methylcytosine site prediction in six species. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4103–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. Deep4mC: Systematic assessment and computational prediction for DNA N4-methylcytosine sites by deep learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, bbaa099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Encoding Technique | Acc (%) | Sn (%) | Sp (%) | MCC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-hot | 87.50 | 88.75 | 86.25 | 0.75 | 0.95 |
| NCPs | 83.71 | 81.72 | 85.68 | 0.73 | 0.93 |
| Methods | Acc (%) | Sn (%) | Sp (%) | MCC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4mCpred-EL | 79.50 | 80.40 | 78.70 | 0.591 | 0.874 |
| i4mC-Mouse | 79.30 | 68.31 | 90.20 | 0.651 | 0.904 |
| 4mCPred-CNN | 85.72 | 80.32 | 91.12 | 0.717 | 0.910 |
| Methods | Acc (%) | Sn (%) | Sp (%) | MCC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4mCpred-EL | 79.10 | 75.72 | 82.51 | 0.584 | 0.881 |
| i4mC-Mouse | 81.61 | 80.71 | 82.52 | 0.633 | 0.920 |
| 4mCPred-CNN | 87.50 | 88.75 | 86.25 | 0.750 | 0.950 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, Z.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. 4mCPred-CNN—Prediction of DNA N4-Methylcytosine in the Mouse Genome Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Genes 2021, 12, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020296
Abbas Z, Tayara H, Chong KT. 4mCPred-CNN—Prediction of DNA N4-Methylcytosine in the Mouse Genome Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Genes. 2021; 12(2):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020296
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Zeeshan, Hilal Tayara, and Kil To Chong. 2021. "4mCPred-CNN—Prediction of DNA N4-Methylcytosine in the Mouse Genome Using a Convolutional Neural Network" Genes 12, no. 2: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020296
APA StyleAbbas, Z., Tayara, H., & Chong, K. T. (2021). 4mCPred-CNN—Prediction of DNA N4-Methylcytosine in the Mouse Genome Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Genes, 12(2), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020296








