Analysis of Human Gut Microbiome: Taxonomy and Metabolic Functions in Thai Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Assessment of Taxonomic Profiles of Gut Microbiome from Thai Adults Using 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Data
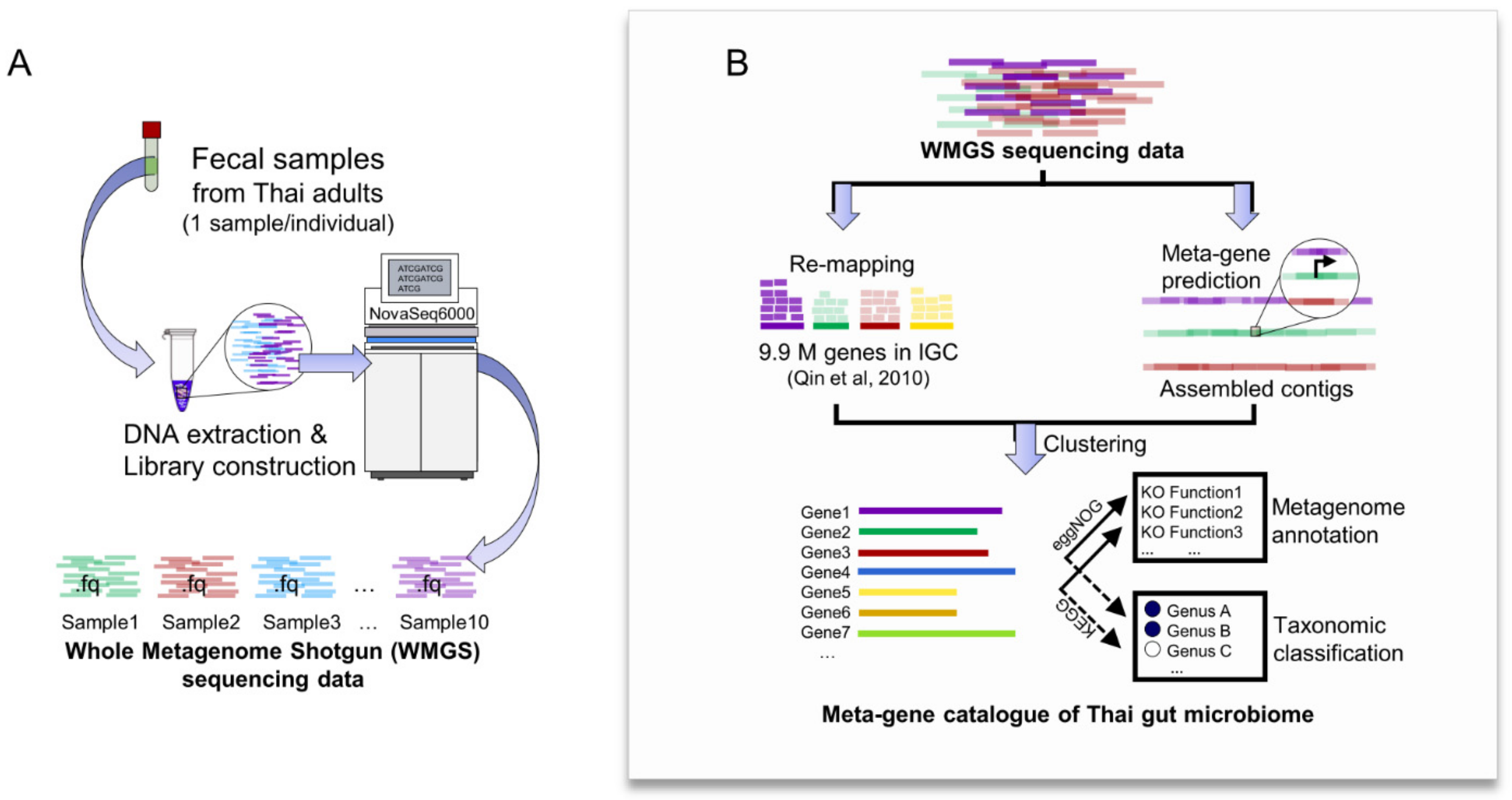
2.2. Construction of Meta-Gene Catalogue of Thai Gut Microbiome from WMGS Sequencing Data
2.3. Annotation of Genes Associated with Metabolic Functions of Thai Gut Microbiome from WMGS Sequencing Data
2.4. Bacterial Community-Wide Metabolic Functional Analysis Involved in Carbohydrate Metabolism
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants and Fecal Sample Collection
4.2. Metagenomic DNA Extraction
4.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing, Reads Processing and Microbial Composition Analysis
4.4. Assessment of Whole Metagenome Shotgun (WMGS) Sequencing Data Obtained from the Gut Microbiome of Thai Adults
4.5. An Integrated Pipeline for Constructing the Meta-Gene Catalogue of Thai Gut Microbiome from WMGS Sequencing Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, J.; Kim, S.; Cabatbat, J.J.T.; Jang, S.; Jin, Y.S.; Jung, G.Y.; Chia, N.; Kim, P.J. Global metabolic interaction network of the human gut microbiota for context-specific community-scale analysis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Chain, F.; Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Courau, S.; Langella, P. Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cianci, R.; Pagliari, D.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Fritz, J.H.; Gambassi, G. The microbiota and immune system crosstalk in health and disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 2912539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benitez-Paez, A.; Kjolbaek, L.; Gomez Del Pulgar, E.M.; Brahe, L.K.; Astrup, A.; Matysik, S.; Schott, H.F.; Krautbauer, S.; Liebisch, G.; Boberska, J.; et al. A multi-omics approach to unraveling the microbiome-mediated effects of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides in overweight humans. mSystems 2019, 4, e00209-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnúsdóttir, S.; Ravcheev, D.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Thiele, I. Systematic genome assessment of B-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumatey, A.P.; Adeyemo, A.; Zhou, J.; Lei, L.; Adebamowo, S.N.; Adebamowo, C.; Rotimi, C.N. Gut microbiome profiles are associated with type 2 diabetes in urban Africans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Arze, C.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Schirmer, M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Poon, T.W.; Andrews, E.; Ajami, N.J.; Bonham, K.S.; Brislawn, C.J.; et al. Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature 2019, 569, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Li, A.Y.L.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chung, A.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N.; et al. Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. The human microbiome project, structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A new genomic blueprint of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vangay, P.; Johnson, A.J.; Ward, T.L.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Hillmann, B.M.; Lucas, S.K.; Beura, L.K.; Thompson, E.A.; Till, L.M.; et al. US immigration westernizes the human gut microbiome. Cell 2018, 175, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruengsomwong, S.; Korenori, Y.; Sakamoto, N.; Wannissorn, B.; Nakayama, J.; Nitisinprasert, S. Senior Thai fecal microbiota comparison between vegetarians and non-vegetarians using PCR-DGGE and real-time PCR. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittipongpattana, P.; Chatchatee, P.; Senavonge, A.; Vongsangnak, W.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Weerapakorn, W.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Roytrakul, S.; Nakphaichit, M.; Suratannon, N. Alteration of gut microbiota and microbial products in distinct allergic phenotypes: Data from an Asian birth cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, AB64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisuse, J.; La-ongkham, O.; Nakphaichit, M.; Therdtatha, P.; Momoda, R.; Tanaka, M.; Fukuda, S.; Popluechai, S.; Kespechara, K.; Sonomoto, K.; et al. Urban diets linked to gut microbiome and metabolome alterations in children: A comparative cross-sectional study in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruengsomwong, S.; La-Ongkham, O.; Jiang, J.; Wannissorn, B.; Nakayama, J.; Nitisinprasert, S. Microbial community of healthy Thai vegetarians and non-vegetarians, their core gut microbiota and pathogen risk. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La-ongkham, O.; Nakphaichit, M.; Nakayama, J.; Keawsompong, S.; Nitisinprasert, S. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota and the core gut microbiome of healthy Thai humans. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmann, B.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Zhu, Q.; Gohl, D.M.; Beckman, K.B.; Knight, R.; Knights, D. Evaluating the information content of shallow shotgun metagenomics. mSystems 2018, 3, e00069-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanovitch, K.; Klaewkla, J.; Chongsuwat, R.; Viwatwongkasem, C.; Kitvorapat, W. The intake of energy and selected nutrients by Thai urban sedentary workers: An evaluation of adherence to dietary recommendations. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 145182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishijima, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Kim, S.W.; Hirose, Y.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M. The gut microbiome of healthy Japanese and its microbial and functional uniqueness. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cao, H.; et al. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, E.S.; Utami, T.; Mariyatun, M.; Hasan, P.N.; Kamil, R.Z.; Setyawan, R.H.; Pamungkaningtyas, F.H.; Harahap, I.A.; Wiryohanjoyo, D.V.; Pramesi, P.C.; et al. Gut microbiota profile in healthy Indonesians. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1478–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, C.; Jackson, M.A.; Pallister, T.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Valdes, A.M. Gut microbiome diversity and high-fibre intake are related to lower long-term weight gain. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, G.K.; Mullin, G.E. The gut microbiome and obesity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patumcharoenpol, P.; Nakphaichit, M.; Panagiotou, G.; Senavonge, A.; Suratannon, N.; Vongsangnak, W. MetGEMs Toolbox: Metagenome-scale models as integrative toolbox for uncovering metabolic functions and routes of human gut microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanca, A.; Abbondio, M.; Palomba, A.; Fraumene, C.; Manghina, V.; Cucca, F.; Fiorillo, E.; Uzzau, S. Potential and active functions in the gut microbiota of a healthy human cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verberkmoes, N.C.; Russell, A.L.; Shah, M.; Godzik, A.; Rosenquist, M.; Halfvarson, J.; Lefsrud, M.G.; Apajalahti, J.; Tysk, C.; Hettich, R.L.; et al. Shotgun metaproteomics of the human distal gut microbiota. ISME J. 2009, 3, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarborough, M.J.; Lawson, C.E.; Hamilton, J.J.; Donohue, T.J.; Noguera, D.R. Metatranscriptomic and thermodynamic insights into medium-chain fatty acid production using an anaerobic microbiome. mSystems 2018, 3, e00221-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillman, E.T.; Kozik, A.J.; Hooker, C.A.; Burnett, J.L.; Heo, Y.; Kiesel, V.A.; Nevins, C.J.; Oshiro, J.M.K.I.; Robins, M.M.; Thakkar, R.D.; et al. Comparative genomics of the genus Roseburia reveals divergent biosynthetic pathways that may influence colonic competition among species. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotou, G.; Andersen, M.R.; Grotkjaer, T.; Regueira, T.B.; Hofmann, G.; Nielsen, J.; Olsson, L. Systems analysis unfolds the relationship between the phosphoketolase pathway and growth in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, S.H.; Holtrop, G.; Lobley, G.E.; Calder, A.G.; Stewart, C.S.; Flint, H.J. Contribution of acetate to butyrate formation by human faecal bacteria. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 91, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakphaichit, M.; Thanomwongwattana, S.; Phraephaisarn, C.; Sakamoto, N.; Keawsompong, S.; Nakayama, J.; Nitisinprasert, S. The effect of including Lactobacillus reuteri KUB-AC5 during post-hatch feeding on the growth and ileum microbiota of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arummugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyatt, D.; LoCascio, P.F.; Hauser, L.J.; Uberbacher, E.C. Gene and translation initiation site prediction in metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Forslund, K.; Coelho, L.P.; Szklarczyk, D.; Jensen, L.J.; von Mering, C.; Bork, P. Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Heller, D.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Forslund, S.K.; Cook, H.; Mende, D.R.; Letunic, I.; Rattei, T.; Jensen, L.J.; et al. eggNOG 5.0: A hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D309–D314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG tools for functional characterization of genome and metagenome sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raethong, N.; Nakphaichit, M.; Suratannon, N.; Sathitkowitchai, W.; Weerapakorn, W.; Keawsompong, S.; Vongsangnak, W. Analysis of Human Gut Microbiome: Taxonomy and Metabolic Functions in Thai Adults. Genes 2021, 12, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030331
Raethong N, Nakphaichit M, Suratannon N, Sathitkowitchai W, Weerapakorn W, Keawsompong S, Vongsangnak W. Analysis of Human Gut Microbiome: Taxonomy and Metabolic Functions in Thai Adults. Genes. 2021; 12(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaethong, Nachon, Massalin Nakphaichit, Narissara Suratannon, Witida Sathitkowitchai, Wanlapa Weerapakorn, Suttipun Keawsompong, and Wanwipa Vongsangnak. 2021. "Analysis of Human Gut Microbiome: Taxonomy and Metabolic Functions in Thai Adults" Genes 12, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030331
APA StyleRaethong, N., Nakphaichit, M., Suratannon, N., Sathitkowitchai, W., Weerapakorn, W., Keawsompong, S., & Vongsangnak, W. (2021). Analysis of Human Gut Microbiome: Taxonomy and Metabolic Functions in Thai Adults. Genes, 12(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030331






