Genetic Causes of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Clinical Examination
2.3. Sanger Sequencing of Known OCA Genes
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Manifestation
3.2. Identification of Pathogenic Variants in OCA-Affected Families
3.3. Protein Modeling of TYR and OCA2 Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasmeier, C.; Hume, A.N.; Bolasco, G.; Seabra, M. Melanosomes at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhill, E.R.; Rocco, A.; Vibert, L.; Nikaido, M.; Kelsh, R.N. An iterative genetic and dynamical modelling approach identifies novel features of the gene regulatory network underlying melanocyte development. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiaffino, M.V. Signaling pathways in melanosome biogenesis and pathology. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, S.A.N.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The protective role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubasch, A.S.; Meurer, M. Okulokutaner und okulärer Albinismus. Hautarzt 2017, 68, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.V. Oculocutaneous albinism. Cutis 2013, 91, E1–E4. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, J.R.; Krishnamurthy, K. Albinism; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Montoliu, L.; Grønskov, K.; Wei, A.-H.; Martínez-García, M.; Fernández, A.; Arveiler, B.; Morice-Picard, F.; Riazuddin, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ahmed, Z.M.; et al. Increasing the complexity: New genes and new types of albinism. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Lloyd, I.C. Oculocutaneous albinism. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 80, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lasseaux, E.; Plaisant, C.; Michaud, V.; Pennamen, P.; Trimouille, A.; Gaston, L.; Monfermé, S.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C.; Morice-Picard, F.; et al. Molecular characterization of a series of 990 index patients with albinism. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, L.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in OCA2 gene associated with non-syndromic oculocutaneous albinism in a Chinese Han patient: A case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yi, S.; Li, M.; Xie, B.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Rong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Hang, L.; et al. Genetic analyses of oculocutaneous albinism types 1 and 2 with four novel mutations. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ii, K.L.Y.; Kassouf, C.; Dolinska, M.B.; Anderson, D.E.; Sergeev, Y.V. Human tyrosinase: Temperature-dependent kinetics of oxidase activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellono, N.W.; Escobar, I.E.; Lefkovith, A.J.; Marks, M.S.; Oancea, E. An intracellular anion channel critical for pigmentation. eLife 2014, 3, e04543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, L.; Escobar, I.E.; Ho, T.; Lefkovith, A.J.; Latteri, E.; Haltaufderhyde, K.D.; Dennis, M.K.; Plowright, L.; Sviderskaya, E.V.; Bennett, D.C.; et al. SLC45A2 protein stability and regulation of melanosome pH determine melanocyte pigmentation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2020, 31, 2687–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, S.M.; Spritz, R.A. A comprehensive genetic study of autosomal recessive ocular albinism in Caucasian patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.-H.; Yang, X.-M.; Lian, S.; Li, W. Genetic analyses of Chinese patients with digenic oculocutaneous albinism. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.-C.; Lv, J.-N.; Yang, H.; Yang, F.-M.; Lin, R.; Lin, Q.; Shen, R.-J.; Wang, J.-B.; Duan, W.-H.; Hu, M.; et al. Nonhuman primate model of oculocutaneous albinism with TYR and OCA2 mutations. Research 2020, 2020, 1658678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, S.; Gazzo, A.; Versbraegen, N.; Nachtegael, C.; Aerts, J.; Moreau, Y.; Van Dooren, S.; Nowé, A.; Smits, G.; Lenaerts, T. Predicting disease-causing variant combinations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11878–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerinckx, S.; Jacquemin, V.; Drunat, S.; Vial, Y.; Passemard, S.; Perazzolo, C.; Massart, A.; Soblet, J.; Racapé, J.; Desmyter, L.; et al. Digenic inheritance of human primary microcephaly delineates centrosomal and non-centrosomal pathways. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 41, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, T.J.; Kausar, T.; Bell, S.M.; Tariq, N.; Maqsood, M.I.; Sohail, A.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, F.; Rasool, S.; Riazuddin, S.; et al. Molecular genetic studies and delineation of the oculocutaneous albinism phenotype in the Pakistani population. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, M.; Yousaf, S.; Waryah, Y.M.; Gul, H.; Kausar, T.; Tariq, N.; Mahmood, U.; Ali, M.; Khan, M.A.; Waryah, A.M.; et al. Molecular outcomes, clinical consequences, and genetic diagnosis of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Aguilera, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. DANN: A deep learning approach for annotating the pathogenicity of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jhong, J.H.; Lee, J.; Koo, J.Y. Meta-analytic support vector machine for integrating multiple omics data. BioData Min. 2017, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, D.; Tanyalcin, I.; Ferté, J.; Gazzo, A.; Orlando, G.; Lenaerts, T.; Rooman, M.; Vranken, W. DEOGEN2: Prediction and interactive visualization of single amino acid variant deleteriousness in human proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W201–W206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, H.; Ali, M.Z.; Khan, E.; Zubair, M.; Badar, M.; Khan, S.; Shah, A.H.; Khan, M.A. Ophthalmo-genetic analysis of Pakistani patients with nonsyndromic oculocutaneous albinism through whole exome sequencing. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mondal, M.; Sengupta, M.; Ray, K. Functional assessment of tyrosinase variants identified in individuals with albinism is essential for unequivocal determination of genotype-to-phenotype correlation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskarides, K.; Papagregoriou, G.; Hadjipanagi, D.; Petrou, I.; Savva, I.; Elia, A.; Athanasiou, Y.; Pastelli, A.; Kkolou, M.; Hadjigavriel, M.; et al. COL4A5 and LAMA5 variants co-inherited in familial hematuria: Digenic inheritance or genetic modifier effect? BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Fei, P.; She, K.; Zhao, P. The characteristics of digenic familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beales, P.L.; Badano, J.L.; Ross, A.J.; Ansley, S.J.; Hoskins, B.E.; Kirsten, B.; Mein, C.A.; Froguel, P.; Scambler, P.J.; Lewis, R.A.; et al. Genetic interaction of BBS1 mutations with alleles at other BBS loci can result in non-mendelian Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanis, N. The oligogenic properties of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, R65–R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
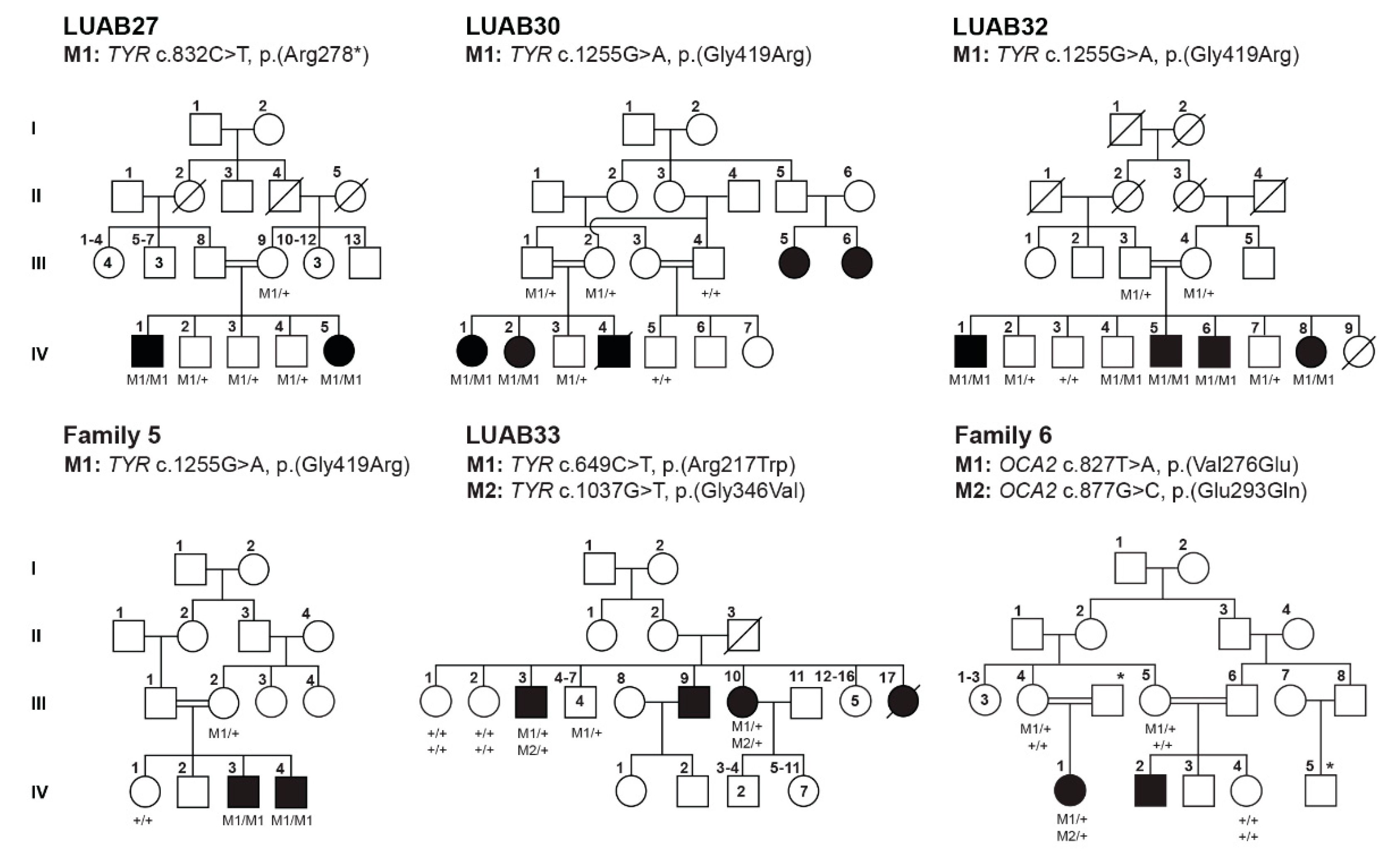
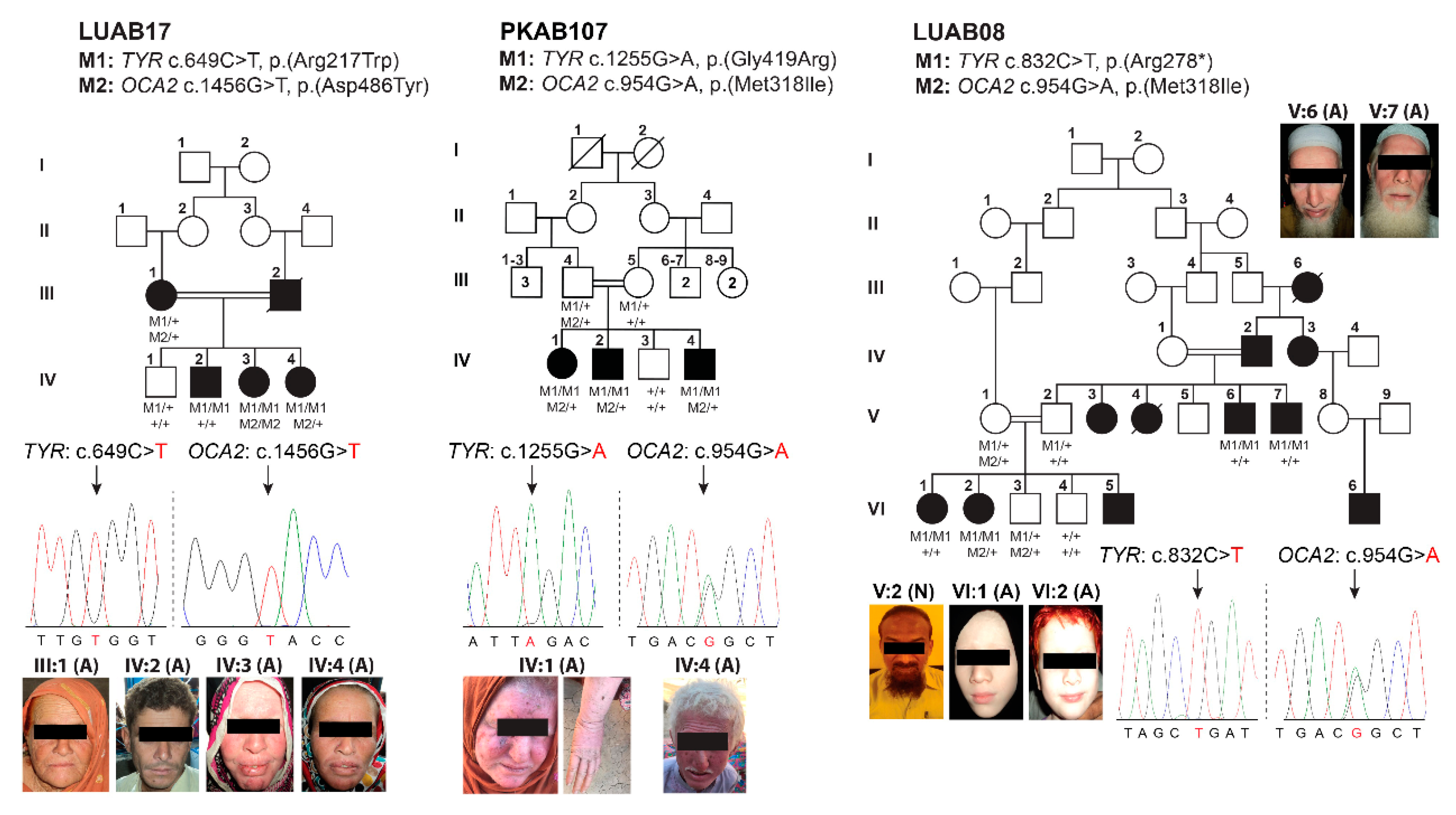


| Family | Subject ID | Sex | Age (Years) | Status | Ethnicity | Hair Color | Skin Tone | Iris Color | Visual Acuity | Refractive Error | Photophobia | Nystagmus | Fundus | Foveal Hypoplasia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | ||||||||||||||
| LUAB27 | IV:2 | M | 16 | Normal | Sindh | Black | Wheat | Black | 6/6 | 6/6 | Normal | No | No | Normal | Formed |
| IV:1 | M | 19 | Affected | White | Pinkish white | Brown | 6/40 | 6/40 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Poorly formed | ||
| IV:5 | F | 8 | White | White | Brown | 6/20 | 6/20 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Poorly formed | |||
| LUAB30 | IV:3 | M | 4 | Normal | Sindh | Black | Wheat | Black | NA | NA | NA | No | No | NA | NA |
| IV:1 | F | 5 | Affected | White | White | Brown | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | ||
| LUAB32 | IV:3 | M | 24 | Normal | Sindh | Black | Wheat | Brown | 6/6 | 6/6 | Normal | No | No | Normal | Normal |
| IV:1 | M | 35 | Affected | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | C.F | C.F | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Small pigmented | Poorly formed | ||
| IV:5 | M | 26 | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | 6/60 | 6/60 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | |||
| IV:6 | M | 23 | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | 6/20 | 6/40 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Absent | |||
| IV:8 | F | 28 | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | |||
| Family 5 | IV:1 | F | 17 | Normal | Kashmir | Black | White | Brown | NA | NA | NA | No | No | Normal | No |
| IV:3 | M | 23 | Affected | White | White | Blue | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | ||
| IV:4 | M | 26 | White | White | Blue | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | |||
| Family 6 | III:4 | F | 40 | Normal | Kashmir | Black | Brown | Brown | NA | NA | NA | No | No | Normal | No |
| IV:1 | F | 5 | Affected | White | White | Gray blue | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | ||
| LUAB08 | V:2 | M | 45 | Normal | Sindh | Black | Wheat | Brown | 6/6 | 6/7 | Normal | No | No | Normal | Formed |
| V:6 | M | 47 | Affected | White | White | Gray blue | C.F | C.F | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Poorly formed | ||
| V:7 | M | 41 | White | White | Gray blue | 4/60 | 4/60 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Albinotic | Yes | |||
| VI:1 | F | 26 | White | Pinkish white | Brown | C.F | C.F | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Absent | |||
| VI:2 | F | 24 | White | White | Brown | C.F | C.F | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | Pigmented | Absent | |||
| LUAB17 | III:1 | F | 68 | Affected | Sindh | White | White | Brown | 6/60 | 6/40 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | NA | NA |
| IV:2 | M | 31 | Affected | Brown | Pale white | Brown | 6/20 | 6/20 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | ||
| IV:3 | F | 36 | Yellow white | Pinkish white | Gray | 6/10 | 6/10 | Hypermetropia | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | |||
| IV:4 | F | 46 | Brown | Pale white | Gray blue | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | ||||
| PKAB107 | IV:1 | F | 25 | Affected | Punjab | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | 6/60 | 6/60 | Hyperopic | Yes | Yes | Albinotic | Yes |
| IV:2 | M | 30 | Affected | White | Pinkish white | Gray blue | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | Albinotic | Yes | ||
| Family | Gene | cDNA Change | AA Change | gnomAD | CADD | DANN | REVEL | MetaSVM | DEOGEN2 | ACMG Classification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUAB27 | TYR | c.832C > T | p.(Arg278*) | 0.000169 | 39 | 0.99 | NA | NA | NA | Pathogenic (PM2, PVS1, PP3, PP5) | [18] |
| LUAB30 | c.1255G > A | p.(Gly419Arg) | 0.000060 | 29 | 0.99 | Pathogenic | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PS1, PM1, PM2, PP2, PP3, PP5) | [30] | |
| LUAB32 | |||||||||||
| Family 5 | |||||||||||
| LUAB33 | c.649C > T | p.(Arg217Trp) | 0.000191 | 23 | 0.99 | Benign | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM5, PP2, PP5, BP4) | [23] | |
| c.1037G > T | p.(Gly346Val) | Not found | 33 | 0.99 | Pathogenic | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PM2, PM5, PP2, PP3, PP5) | [31] | ||
| Family 6 | OCA2 | c.827T > A | p.(Val276Glu) | Not found | 19 | 0.97 | Benign | Damaging | Damaging | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP2, PP3) | This study |
| c.877G > C | p.(Glu293Gln) | Not found | 22 | 0.98 | Benign | Damaging | Tolerated | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP2, PP3) | This study | ||
| LUAB08 | TYR | c.832C > T | p.(Arg278*) | 0.000169 | 39 | 0.99 | NA | NA | NA | Pathogenic (PM2, PVS1, PP3, PP5) | [18] |
| OCA2 | c.954G > A | p.(Met318Ile) | 0.000428 | 22 | 0.98 | Benign | Damaging | Tolerated | Uncertain significance (PP2, PM2) | This study | |
| LUAB17 | TYR | c.649C > T | p.(Arg217Trp) | 0.000191 | 23 | 0.99 | Benign | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM5, PP2, PP5, BP4) | [23] |
| OCA2 | c.1456G > T | p.(Asp486Tyr) | 0.000023 | 30 | 0.99 | Pathogenic | Damaging | Damaging | Uncertain significancePM2, PP2, PP3 | [11] | |
| PKAB107 | TYR | c.1255G > A | p.(Gly419Arg) | 0.000060 | 29 | 0.99 | Pathogenic | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PS1, PM1, PM2, PP2, PP3, PP5) | [30] |
| OCA2 | c.954G > A | p.(Met318Ile) | 0.000428 | 22 | 0.98 | Benign | Damaging | Tolerated | Uncertain significance (PP2, PM2) | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajid, Z.; Yousaf, S.; Waryah, Y.M.; Mughal, T.A.; Kausar, T.; Shahzad, M.; Rao, A.R.; Abbasi, A.A.; Shaikh, R.S.; Waryah, A.M.; et al. Genetic Causes of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani Population. Genes 2021, 12, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040492
Sajid Z, Yousaf S, Waryah YM, Mughal TA, Kausar T, Shahzad M, Rao AR, Abbasi AA, Shaikh RS, Waryah AM, et al. Genetic Causes of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani Population. Genes. 2021; 12(4):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajid, Zureesha, Sairah Yousaf, Yar M. Waryah, Tauqeer A. Mughal, Tasleem Kausar, Mohsin Shahzad, Ali R. Rao, Ansar A. Abbasi, Rehan S. Shaikh, Ali M. Waryah, and et al. 2021. "Genetic Causes of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani Population" Genes 12, no. 4: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040492
APA StyleSajid, Z., Yousaf, S., Waryah, Y. M., Mughal, T. A., Kausar, T., Shahzad, M., Rao, A. R., Abbasi, A. A., Shaikh, R. S., Waryah, A. M., Riazuddin, S., & Ahmed, Z. M. (2021). Genetic Causes of Oculocutaneous Albinism in Pakistani Population. Genes, 12(4), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040492






