Identification and Validation of Marketing Weight-Related SNP Markers Using SLAF Sequencing in Male Yangzhou Geese
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Samples and Phenotypic Measurements
2.3. Preparation and Construction of SLAF Library
2.4. Sequencing Analysis and Detection of MW-Related SNPs
2.5. Quality Control of SLAF Tags
2.6. Replication Association Study
2.7. Genotyping of Female Goslings of First and Second Populations
2.8. Verification of MW-Related SNP Genotypes
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Statistical, Bioinformatics, and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Goslings’ Marketing Weight
3.2. SLAF Sequencing
3.3. Discovering of Goslings MW-Related SNPs
3.4. Verification of MW-Related SNPs in Male Goslings
3.5. Replication Association Analysis for Male Goslings
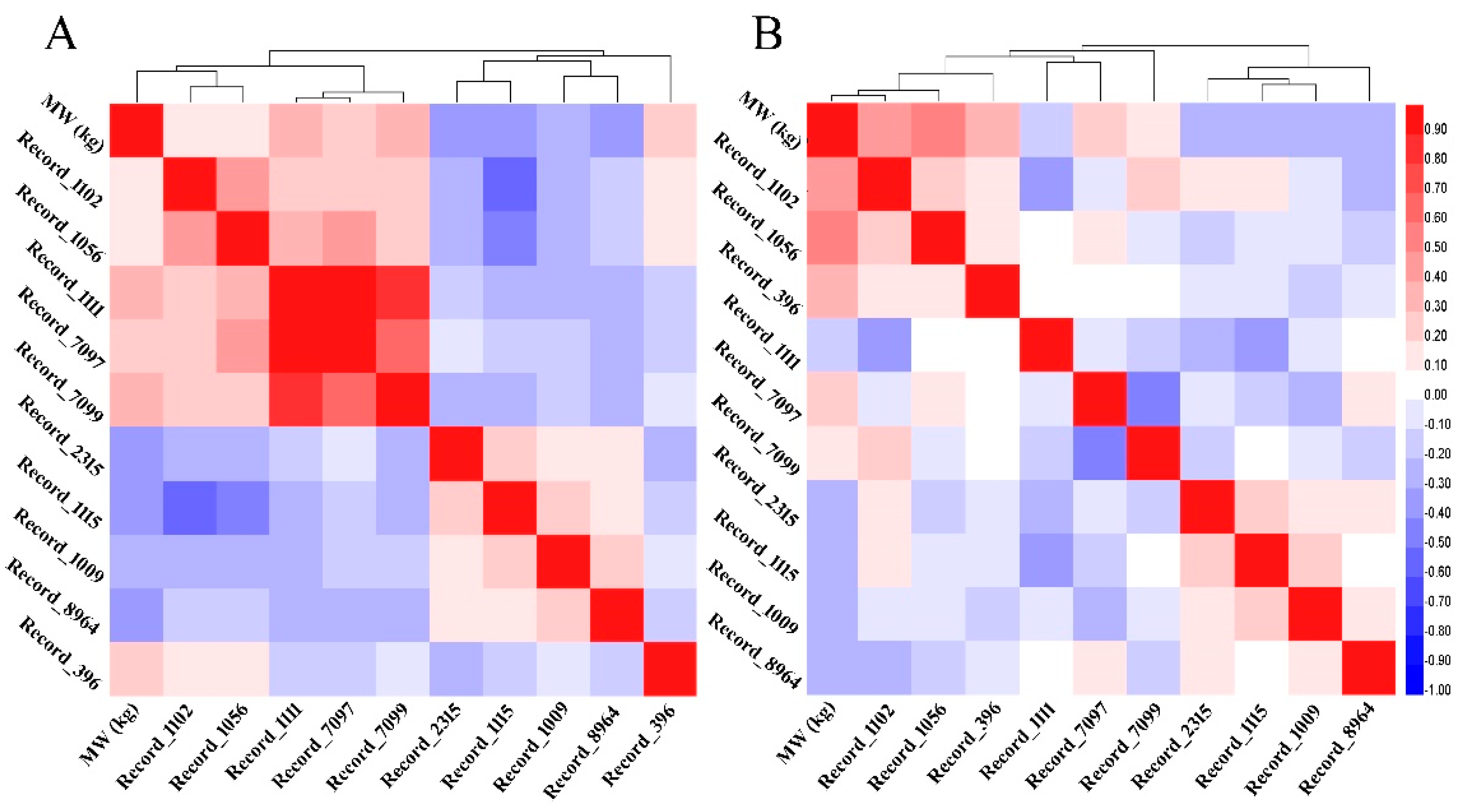
3.6. Linear Regression Model and SNP Networks Analysis of Male Goslings Marketing Weight
3.7. Additive, Dominance, and Recessive Effects of Significant SNPs
3.8. Correlations between MW and SNPs’ Genotypes
3.9. Verification of MW-Related SNPs in Female Goslings
3.10. Annotation of Genes Harboring SNPs Associated with Goslings MW
3.11. Relative Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike’s Information Criterion |
| AS-PCR | Allele-specific polymerase chain reaction |
| BSA | Bulked segregant analysis |
| EBV | Estimated breeding value |
| ED | Euclidean distance |
| ELFN1 | Extracellular leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1 gene |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GATK | Genome analysis toolkit |
| GC (%) | The percentage of G and C bases in the total bases in the sequencing results |
| GWASs | Genome-wide association studies |
| HMX1 | H6 family homeobox 1 gene |
| LRRFIP1 | LRR binding FLII interacting protein 1 gene |
| MW | Marketing weight (body weight at nine weeks of age) |
| P1 | First population |
| P2 | Second population |
| PDGFD | Platelet-derived growth factor D gene |
| PPP2R2C | Protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B γ gene |
| Q30 (%) | The percentage of bases with a sequencing quality value greater than or equal to 30 |
| SAMtools | Sequence alignment/map format |
| SLAF-seq | Specific locus amplified fragment sequencing |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| SOAP | Short oligonucleotide alignment program |
| SSCP | Single-strand conformation polymorphism |
| ti/tv | Transition/transversion ratio |
| UCHL1 | Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 gene |
References
- Rodenburg, T.; Turner, S. The role of breeding and genetics in the welfare of farm animals. Anim. Front. 2012, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CALU. CALU Factsheet: Meat Geese Seasonal Production (PDF). 2014. Available online: http://www.calu.bangor.ac.uk/Technical%20leaflets/040803seasonalgeese.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Jiang, N. Effects of dietary threonine on growth performance and carcass traits of Yangzhou geese. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 55, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Nitrogen requirement for maintenance in Yangzhou goslings. Br. Poult. Sci. 2007, 48, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Dai, W.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chang, G.; Xu, Q.; Chen, G. Effects of forage feeding versus grain feeding on the growth performance and meat quality of Yangzhou geese. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, M.; Mukesh, M.; Prakash, B.; Mishra, B.P.; Sobti, R.C.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, S.; Ahlawat, S.P.S. MspI Allelic Pattern of Bovine Growth Hormone Gene in Indian Zebu Cattle (Bos indicus) Breeds. Biochem. Genet. 2007, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, M.; Russell, J.; Squirrell, J.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; MacKenzie, K.; Gibby, M.; Powell, W. Comparative analysis of population genetic structure in Athyrium distentifolium (Pteridophyta) using AFLPs and SSRs from anonymous and transcribed gene regions. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 1681–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hua, W. An improved allele-specific PCR primer design method for SNP marker analysis and its application. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Lightfoot, D.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; et al. Domestication footprints anchor genomic regions of agronomic importance in soybeans. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, C.; Guan, N.; Ma, C.; Zeng, H.; et al. SLAF-seq: An Efficient Method of Large-Scale De Novo SNP Discovery and Genotyping Using High-Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, D.; Liu, J.-F.; Chen, S.; Qu, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, N. A Genome-Wide SNP Scan Reveals Novel Loci for Egg Production and Quality Traits in White Leghorn and Brown-Egg Dwarf Layers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolc, A.; Arango, J.; Settar, P.; Fulton, J.E.; O’Sullivan, N.P.; Preisinger, R.; Habier, D.; Fernando, R.; Garrick, D.J.; Hill, W.G.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis and genetic architecture of egg weight and egg uniformity in layer chickens. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43 (Suppl. S1), 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Feng, C.; Ma, L.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Da, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Ye, S.; Ge, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Body Weight in Chicken F2 Resource Population. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Luo, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Nie, Q.; Ma, L.; Hu, X.; Li, N.; Da, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identified a Narrow Chromosome 1 Region Associated with Chicken Growth Traits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Loci and Candidate Genes for Body Composition and Meat Quality Traits in Beijing-You Chickens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chu, W.; Zhang, L.; Han, H.; Zhao, R.; Wu, W.; Zhu, J.; Dodson, M.V.; Wei, W.; Liu, H.; et al. Identification of Laying-Related SNP Markers in Geese Using RAD Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xin, H.; Li, D.; Ma, C.; Ding, X.; Hong, W.; Zhang, X. Construction of a high-density genetic map for sesame based on large scale marker development by specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michelmore, R.W.; Paran, I.; Kesseli, R.V. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9828–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneeberger, K.; Ossowski, S.; Lanz, C.; Juul, T.; Petersen, A.H.; Nielsen, K.L.; Jørgensen, J.-E.; Weigel, D.; Andersen, S.U. SHOREmap: Simultaneous mapping and mutation identification by deep sequencing. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, K.; Chen, C. A genome-wide association study of growth trait-related single nucleotide polymorphisms in Chinese Yancheng chickens. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 15783–15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Han, H.; Lei, Q.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, D. Genome-wide association study of body weight in Wenshang Barred chicken based on the SLAF-seq technology. J. Appl. Genet. 2018, 59, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, K. Genome-wide association study of growth traits in Jinghai Yellow chicken hens using SLAF-seq technology. Anim. Genet. 2015, 50, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, G.R.; Acosta, J.J. An Algorithm for Genetic Analysis of Full-Sib Datasets with Mixed-Model Software Lacking a Numerator Relationship Matrix Function, and a Comparison with Results from a Dedicated Genetic Software Package. Forests 2020, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.-W.; Yiu, S.-M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 genome project data processing subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, J.; Demarest, B.L.; Bisgrove, B.W.; Gorsi, B.; Su, Y.-C.; Yost, H.J. MMAPPR: Mutation Mapping Analysis Pipeline for Pooled RNA-seq. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ashikawa, I. Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics notes: Multiple significance tests: The Bonferroni method. BMJ 1995, 310, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple Range and Multiple F Tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, R.N.; Stokes, M. SAS/STAT 13.1: Round-Up. In Proceedings of the SAS Global Forum 2014 Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 March 2014; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2014. Available online: http//support.sas.com/resources/papers/proceedings14/SAS181-2014.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Jiang, Z.; Michal, J.J.; Chen, J.; Daniels, T.F.; Kunej, T.; Garcia, M.D.; Gaskins, C.T.; Busboom, J.R.; Alexander, L.J.; Wright, R.W., Jr.; et al. Discovery of novel genetic networks associated with 19 economically important traits in beef cattle. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Jacquie, J.; Pescatore, T. Selecting Geese. Agriculture and Natural Resources Family and Consumer Sciences. 4-H Youth Development Community and Economic Development. 2013. Available online: www.ca.uky.edu (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, X.-C. Observation on Dabble Habits of Yangzhou Goose in Primrose Season. Poult. Sci. 2013, 05, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hrnčár, C.; Bujko, J.; Bandík, S.; Weis, J. An evaluation of growth ability in domestic geese. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2016, 19, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakeley, J. The excess of transitions among nucleotide substitutions: New methods of estimating transition bias underscore its significance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begun, D.J.; Holloway, A.K.; Stevens, K.; Hillier, L.W.; Poh, Y.-P.; Hahn, M.; Nista, P.M.; Jones, C.D.; Kern, A.D.; Dewey, C.N.; et al. Population Genomics: Whole-Genome Analysis of Polymorphism and Divergence in Drosophila simulans. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, A.; Eyre-Walker, A. Human Triallelic Sites: Evidence for a New Mutational Mechanism? Genetics 2010, 184, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonker, R.M.; Zhang, Q.; Van Hooft, P.; Loonen, M.J.; Van Der Jeugd, H.P.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Groenen, M.A.M.; Prins, H.H.T.; Kraus, R.H.S. The Development of a Genome Wide SNP Set for the Barnacle Goose Branta leucopsis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, G. Association of Polymorphisms of Exon 2 of the Growth Hormone Gene with Production Performance in Huoyan Goose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Huang, P.; Cheng, J.; Gan, L.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y. A novel SMAD family protein, SMAD9 is involved in follicular initiation and changes egg yield of geese via synonymous mutations in exon1 and intron2. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 42, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; Farquharson, K.A.; McLennan, E.A.; Belov, K.; Hogg, C.J.; Grueber, C.E. From reference genomes to population genomics: Comparing three reference-aligned reduced-representation sequencing pipelines in two wildlife species. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smołucha, G.; Kozubska-Sobocińska, A.; Koseniuk, A.; Żukowski, K.; Lisowski, M.; Grajewski, B. Polymorphism of the Myostatin (MSTN) Gene in Landes and Kielecka Geese Breeds. Animal 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Gao, D.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, R.; Yin, C.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Hu, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study-Based Identification of SNPs and Haplotypes Associated With Goose Reproductive Performance and Egg Quality. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrwasser, A.; Lott, P.; Weiss, R.B.; Lalouel, J. From Genetics to Mechanism of Disease Liability. Adv Genet. 2008, 60, 701–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, R.J.; Prabhu, V.; Acland, G.M.; Johnson, K.R.; Harris, B.S.; O’Brien, T.P.; Welsh, I.C.; Noden, D.M.; Schimenti, J.C. Mouse H6 Homeobox 1 (Hmx1) mutations cause cranial abnormalities and reduced body mass. BMC Dev. Biol. 2009, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plourde, M.; Vohl, M.-C.; Bellis, C.; Carless, M.; Dyer, T.; Dolley, G.; Marette, A.; Després, J.-P.; Bouchard, C.; Blangero, J.; et al. A variant in theLRRFIP1gene is associated with adiposity and inflammation. Obesity 2013, 21, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, N.; Kwon, J.-S.; Kim, J.-R.; Eom, G.H.; Kim, Y.; Nam, K.I.; Ahn, Y.; Kee, H.J.; Kook, H. The microRNA miR-132 targets Lrrfip1 to block vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Atherosclerosis 2013, 229, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-P.; Cao, N.-X.; Jiang, R.-T.; He, S.-J.; Huang, T.-M.; Wu, B.; Chen, D.-F.; Ma, P.; Chen, L.; Zhou, S.-F.; et al. Knockdown of GCF2/LRRFIP1 by RNAi Causes Cell Growth Inhibition and Increased Apoptosis in Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fan, E.; Yu, J.W.; Strack, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structure of the Protein Phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme. Cell 2006, 127, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Backx, L.; Vermeesch, J.; Pijkels, E.; De Ravel, T.; Seuntjens, E.; Van Esch, H. PPP2R2C, a gene disrupted in autosomal dominant intellectual disability. Eur. J. Med Genet. 2010, 53, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mei, C.; Su, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Zan, L. MEF2A Regulates the MEG3-DIO3 miRNA Mega Cluster-Targeted PP2A Signaling in Bovine Skeletal Myoblast Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajna, A.; Gibling, H.; Sarr, O.; Matravadia, S.; Holloway, G.P.; Mutch, D.M. α-linolenic acid and linoleic acid differentially regulate the skeletal muscle secretome of obese Zucker rats. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittoli, V.; Fortunato, A.E.; Fasano, G.; Coppola, U.; Gentile, A.; Maiella, S.; Langellotto, F.; Porreca, I.; De Paolo, R.; Marino, R.; et al. Characterization of paralogous uncx transcription factor encoding genes in zebrafish. Gene X 2019, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Marrades, M.P.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Differential Proinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Response and Vulnerability to Metabolic Syndrome in Habitual High-Fat Young Male Consumers Putatively Predisposed by Their Genetic Background. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17238–17255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bollepalli, S.; Kaye, S.; Heinonen, S.; Kaprio, J.; Rissanen, A.; A Virtanen, K.; Pietiläinen, K.; Ollikainen, M. Subcutaneous adipose tissue gene expression and DNA methylation respond to both short- and long-term weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; Fuentes, L.D.L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Subsequent Progressive Weight Loss on Metabolic Function and Adipose Tissue Biology in Humans with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piórkowska, K.; Żukowski, K.; Ropka-Molik, K.; Tyra, M.; Gurgul, A. A comprehensive transcriptome analysis of skeletal muscles in two Polish pig breeds differing in fat and meat quality traits. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sherif, M.; Lin, X.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. A novel c.-652C> T mutation in UCHL1 gene is associ-ated with the growth performance in Yangzhou goose. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample ID * | Clean Reads | Total Reads | GC (%) | Q30 (%) | Total SNP | Heter. Ratio (%) | SLAF Number | Total Depth | Average Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEBV | 2.66 Gb | 10,310,004 | 42.90 | 93.32 | 149.05 | 35.92 | 383.53 | 9,480,575 | 24.72 |
| LEBV | 2.73 Gb | 10,571,785 | 42.86 | 93.21 | 149.05 | 37.72 | 384.63 | 9,726,388 | 25.29 |
| Control | Rice | 1,291,422 | 41.60 | 93.28 |
| SNP ID | SNP Type | Chr.* | Pos. | ED | Adjusted p-Value | Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDR | Bonferroni | p | AIC | p | AIC | |||||
| Record_1102 | C/T | KZ155846.1 | 6778745 | 0.81 | 9.22 × 10−33 | 2.77 × 10−32 | 7.87 × 10−5 | 39.2 | 0.021 | 65.7 |
| Record_1111 | G/A | KZ155846.1 | 7205384 | 0.87 | 1.65 × 10−18 | 8.253 × 10−18 | 3.64 × 10−4 | 43.5 | 0.033 | 71.8 |
| Record_2315 | G/A | KZ155852.1 | 9238683 | 1.04 | 5.45 × 10−16 | 4.358 × 10−15 | 1.06 × 10−2 | 44.0 | 0.393 | 50.3 |
| Record_1009 | T/C | KZ155846.1 | 3215955 | 0.75 | 7.22 × 10−16 | 7.70 × 10−15 | 3.93 × 10−4 | 38.2 | 0.247 | 66.0 |
| Record_1056 | G/C | KZ155846.1 | 4966566 | 0.75 | 4.82 × 10−15 | 6.18 × 10−14 | 2.34 × 10−6 | 33.3 | 0.027 | 69.4 |
| Record_7086 | G/T | KZ155908.1 | 2312525 | 0.72 | 2.98 × 10−8 | 6.265 × 10−7 | 4.45 × 10−3 | 43.7 | 0.782 | 71.8 |
| Record_1115 | T/C | KZ155846.1 | 7261356 | 0.78 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 2.40 × 10−6 | 3.98 × 10−5 | 39.1 | 0.006 | 64.8 |
| Record_7099 | C/T | KZ155908.1 | 2482155 | 0.79 | 4.20 × 10−7 | 1.091 × 10−5 | 8.44 × 10−7 | 9.4 | 0.311 | 77.3 |
| Record_7097 | C/G | KZ155908.1 | 2481905 | 0.77 | 4.93 × 10−7 | 1.331 × 10−5 | 8.79 × 10−5 | 35.3 | 0.705 | 76.6 |
| Record_8964 | G/C | KZ155945.1 | 1664422 | 0.76 | 2.97 × 10−6 | 8.313 × 10−5 | 3.22 × 10−5 | 20.6 | 0.009 | 73.2 |
| Record_1057 | A/G | KZ155846.1 | 4997778 | 0.82 | 4.85 × 10−6 | 0.0001406 | 3.59 × 10−2 | 52.4 | 0.728 | 73.1 |
| Record_396 | T/C | KZ155843.1 | 11357652 | 0.71 | 6.74 × 10−6 | 0.0002155 | 1.13 × 10−6 | -6.2 | 0.328 | 68.2 |
| Record_11546 | C/T | KZ156052.1 | 690770 | 1.07 | 2.26 × 10−6 | 0.0008542 | 9.36 × 10−3 | 41.7 | 0.093 | 71.4 |
| SNP Id * | Index | P1 Males | P2 Males | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | SE | p | AIC | Values | SE | p | AIC | ||
| Record_1102 | Additive | 0.027 | 0.03 | 0.377 | 45.83 | −0.114 | 0.05 | 0.026 | 21.87 |
| Dominance | −0.058 | 0.06 | 0.358 | 45.76 | −0.211 | 0.08 | 0.007 | 19.46 | |
| Recessive | −0.134 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 38.53 | −0.062 | 0.08 | 0.450 | 26.38 | |
| Record_1111 | Additive | −0.076 | 0.03 | 0.007 | 40.80 | −0.124 | 0.05 | 0.006 | 17.10 |
| Dominance | −0.170 | 0.04 | 0.000 | 33.81 | −0.198 | 0.10 | 0.051 | 20.85 | |
| Recessive | −0.187 | 0.05 | 0.000 | 35.07 | −0.148 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 18.62 | |
| Record_2315 | Additive | 0.265 | 0.10 | 0.008 | 51.18 | −0.198 | 0.05 | 0.000 | 10.10 |
| Dominance | −0.185 | 0.16 | 0.258 | 57.04 | −0.430 | 0.10 | 0.000 | 8.94 | |
| Recessive | −0.453 | 0.10 | 0.000 | 38.18 | −0.247 | 0.08 | 0.002 | 16.72 | |
| Record_1009 | Additive | −0.067 | 0.03 | 0.007 | 38.64 | −0.078 | 0.04 | 0.045 | 22.55 |
| Dominance | −0.151 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 34.33 | −0.232 | 0.06 | 0.000 | 13.30 | |
| Recessive | −0.120 | 0.05 | 0.025 | 40.90 | 0.006 | 0.07 | 0.930 | 26.71 | |
| Record_1056 | Additive | −0.063 | 0.02 | 0.010 | 43.68 | −0.166 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 7.77 |
| Dominance | −0.121 | 0.04 | 0.005 | 42.55 | −0.258 | 0.10 | 0.015 | 13.35 | |
| Recessive | −0.073 | 0.06 | 0.197 | 48.76 | −0.187 | 0.06 | 0.004 | 11.04 | |
| Record_1115 | Additive | 0.003 | 0.03 | 0.928 | 47.53 | −0.120 | 0.05 | 0.011 | 10.87 |
| Dominance | −0.212 | 0.07 | 0.002 | 38.14 | −0.169 | 0.10 | 0.106 | 14.87 | |
| Recessive | −0.167 | 0.04 | 0.000 | 32.02 | −0.143 | 0.06 | 0.021 | 12.02 | |
| Record_7099 | Additive | −0.118 | 0.02 | 0.000 | −12.14 | 0.030 | 0.05 | 0.575 | 25.00 |
| Dominance | −0.214 | 0.04 | 0.000 | −20.52 | 0.104 | 0.06 | 0.100 | 22.54 | |
| Recessive | −0.139 | 0.04 | 0.001 | −2.47 | −0.245 | 0.12 | 0.053 | 21.47 | |
| Record_7097 | Additive | −0.057 | 0.03 | 0.014 | 36.10 | −0.091 | 0.05 | 0.042 | 18.62 |
| Dominance | −0.144 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 30.92 | −0.154 | 0.06 | 0.020 | 17.26 | |
| Recessive | −0.284 | 0.08 | 0.000 | 28.50 | −0.070 | 0.08 | 0.404 | 22.17 | |
| Record_8964 | Additive | −0.024 | 0.03 | 0.397 | 22.05 | −0.096 | 0.04 | 0.028 | 22.53 |
| Dominance | −0.159 | 0.05 | 0.002 | 13.32 | −0.076 | 0.08 | 0.317 | 26.48 | |
| Recessive | −0.160 | 0.04 | 0.000 | 8.39 | −0.176 | 0.07 | 0.011 | 20.76 | |
| Record_396 | Additive | −0.056 | 0.04 | 0.138 | −2.06 | −0.131 | 0.04 | 0.005 | 1.98 |
| Dominance | −0.132 | 0.05 | 0.010 | −6.63 | −0.259 | 0.08 | 0.001 | −0.52 | |
| Recessive | −0.148 | 0.05 | 0.002 | −9.21 | −0.099 | 0.07 | 0.153 | 8.08 | |
| SNP ID * | SNP | Acc. No. | Chr. | Pos. (bp) | Nearest Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record_1102 | C/T | NW_013185655.1 | KZ155846.1 | 5835696 | intron 4 HMX1 |
| Record_1111 | G/A | NW_013185655.1 | KZ155846.1 | 5409310 | 29.5 Kb upstream LOC106034756 |
| Record_2315 | G/A | NW_013185684.1 | KZ155852.1 | 2233138 | 10 Kb upstream LRRFIP1 |
| Record_1009 | T/C | NW_013185655.1 | KZ155846.1 | 9373018 | 14.5 Kb upstream LOC106035299 |
| Record_1056 | G/C | NW_013185655.1 | KZ155846.1 | 7629761 | intron 1 PPP2R2C |
| Record_1115 | T/C | NW_013185655.1 | KZ155846.1 | 5353256 | intron 1 LOC106034755 |
| Record_7099 | C/T | NW_013185939.1 | KZ155908.1 | 659136 | 3.3 Kb downstream UCHL1 |
| Record_7097 | C/G | NW_013185939.1 | KZ155908.1 | 659384 | 3 Kb downstream UCHL1 |
| Record_8964 | G/C | NW_013185681.1 | KZ155945.1 | 769175 | 28.3 Kb downstream LOC106034143 |
| 769175 | 41.2 Kb upstream PDGFD | ||||
| Record_396 | T/C | NW_013185677.1 | KZ155843.1 | 7668615 | 24.6 Kb upstream ELFN1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melak, S.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Elbeltagy, A.; Chen, J. Identification and Validation of Marketing Weight-Related SNP Markers Using SLAF Sequencing in Male Yangzhou Geese. Genes 2021, 12, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081203
Melak S, Wang Q, Tian Y, Wei W, Zhang L, Elbeltagy A, Chen J. Identification and Validation of Marketing Weight-Related SNP Markers Using SLAF Sequencing in Male Yangzhou Geese. Genes. 2021; 12(8):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081203
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelak, Sherif, Qin Wang, Ye Tian, Wei Wei, Lifan Zhang, Ahmed Elbeltagy, and Jie Chen. 2021. "Identification and Validation of Marketing Weight-Related SNP Markers Using SLAF Sequencing in Male Yangzhou Geese" Genes 12, no. 8: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081203
APA StyleMelak, S., Wang, Q., Tian, Y., Wei, W., Zhang, L., Elbeltagy, A., & Chen, J. (2021). Identification and Validation of Marketing Weight-Related SNP Markers Using SLAF Sequencing in Male Yangzhou Geese. Genes, 12(8), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081203






