Genetic Rescue of the Highly Inbred Norwegian Lundehund
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Genetic Rescue in Domestic and Wild Populations
1.2. Breed History and Typical Traits
1.3. The Outbreeding Project
1.4. Aim of the Investigation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Statistical Analyses
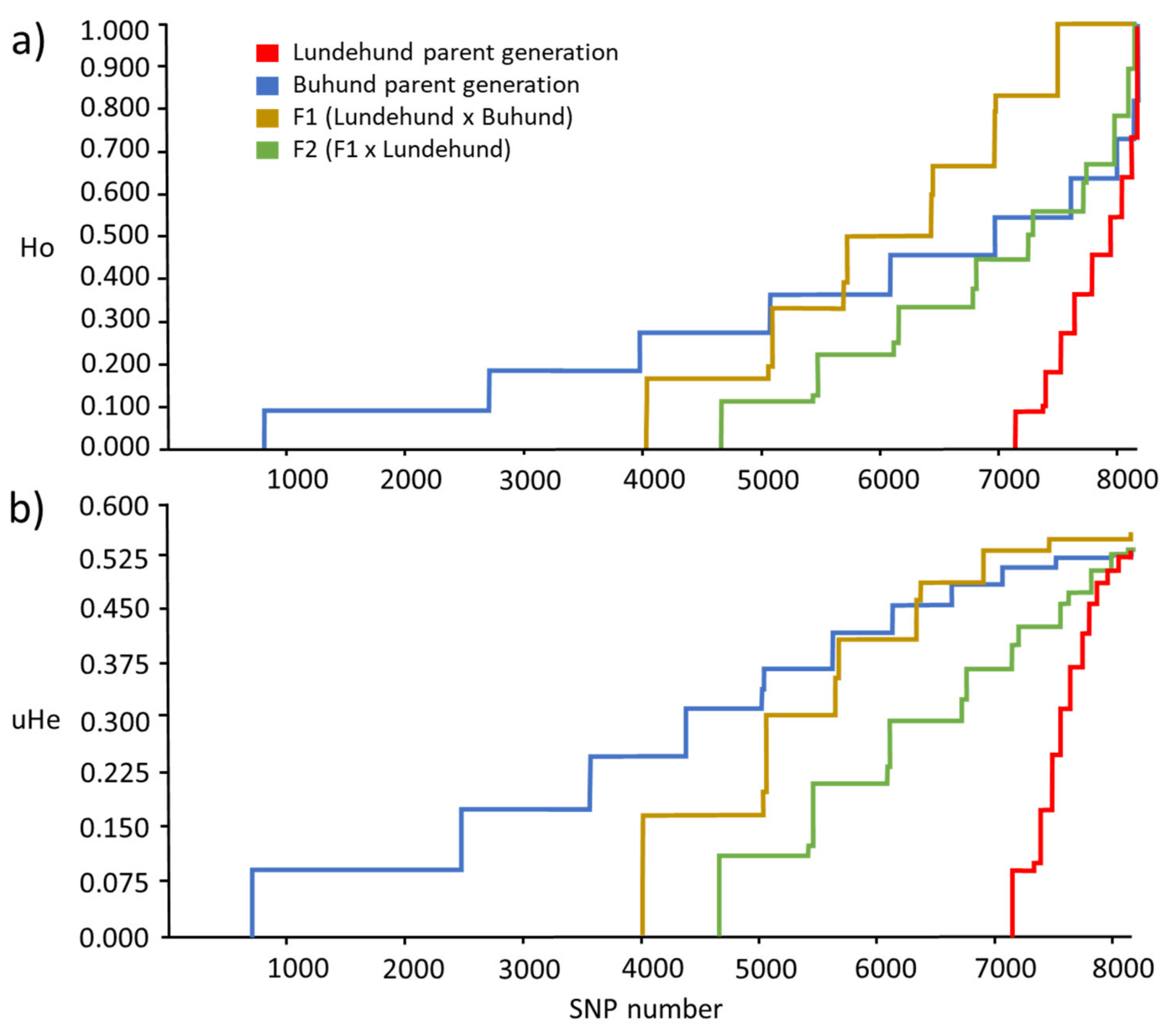
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Frankham, R. Genetic rescue of small inbred populations: Meta-analysis reveals large and consistent benefits of gene flow. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2610–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.E.; Onorato, D.P.; Roelke, M.E.; Land, E.D.; Cunningham, M.; Belden, R.C.; McBride, R.; Jansen, D.; Lotz, M.; Shindle, D.; et al. Genetic Restoration of the Florida Panther. Science 2010, 329, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, J.T.; Forbes, S.H.; Steele, B.M.; Luikart, G. Genetic rescue of an insular population of large mammals. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Åkesson, M.; Liberg, O.; Sand, H.; Wabakken, P.; Bensch, S.; Flagstad, Ø. Genetic rescue in a severely inbred wolf population. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4745–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, Z.L.; Bell, D.A.; Dhendup, T.; Luikart, G.; Whiteley, A.R.; Kardos, M. Evaluating the outcomes of genetic rescue attempts. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmands, S. Between a rock and a hard place: Evaluating the relative risks of inbreeding and outbreeding for conservation and management. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windig, J.J.; Doekes, H.P. Limits to genetic rescue by outcross in pedigree dogs. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2018, 135, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralls, K.; Sunnucks, P.; Lacy, R.C.; Frankham, R. Genetic rescue: A critique of the evidence supports maximizing genetic diversity rather than minimizing the introduction of putatively harmful genetic variation. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 251, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D. The Dalmatian/Pointer Backcross Project: Overcoming 20th Century Attitude about Crossbreeding. Available online: https://www.vin.com/apputil/content/defaultadv1.aspx?pId=11340&catId=34514&id=5101841 (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Cattanach, B.M. Genetics Can Be Fun. Available online: http://www.steynmere.co.uk/ARTICLES1.html (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Irish Kennel Club. International Outcross Programme Irish Red and White Setters and Irish Red Setters. Available online: http://www.ikc.ie/international-outcross-programme-irish-red-and-white-setters-and-irish-red-setters (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Melis, C.; Borg, A.A.; Espelien, I.S.; Jensen, H. Low neutral genetic variability in a specialist puffin hunter: The Norwegian Lundehund. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espelien, I.S. Lundehundboka [The Lundehund Book]; Espelien, I.S., Ed.; Forlaget Vigmostad & Bjørke AS: Bergen, Norway, 2012. (In Norwegian) [Google Scholar]
- Pfahler, S.; Distl, O. A massive reduction of the genetic diversity in the Lundehund. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropatsch, R.; Melis, C.; Stronen, A.V.; Jensen, H.; Epplen, J.T. Molecular Genetics of Sex Identification, Breed Ancestry and Polydactyly in the Norwegian Lundehund Breed. J. Hered. 2015, 106, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kettunen, A.; Daverdin, M.; Helfjord, T.; Berg, P. Cross-Breeding Is Inevitable to Conserve the Highly Inbred Population of Puffin Hunter: The Norwegian Lundehund. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170039. [Google Scholar]
- Pfahler, S.; Distl, O. Effective Population Size, Extended Linkage Disequilibrium and Signatures of Selection in the Rare Dog Breed Lundehund. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qvigstad, G.; Kolbjørnsen, O.; Skancke, E.; Waldum, H.L. Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Associated with Atrophic Gastritis in the Norwegian Lundehund. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 139, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbjørnsen, O.; Press, C.M.; Landsverk, T. Gastropathies in the Lundehund 1. Gastritis and Gastric Neoplasia Associated with Intestinal Lymphangiectasia. Apmis 1994, 102, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbjørnsen, O.; Press, C.M.; Landsverk, T. Gastropathies in the Lundehund 2. A Study of Mucin Profiles. Apmis 1994, 102, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, J.; Pfahler, S.; Distl, O. Variant detection and runs of homozygosity in next generation sequencing data elucidate the genetic background of Lundehund syndrome. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norwegian Lundehund Club. Rasespesifikk Avlsstrategi (RAS) for Norsk Lundehund [Breed Specific Breeding Strategy for Norwegian Lundehund]; Norwegian Lundehund Club: Oslo, Norway, 2014; p. 28. (In Norwegian) [Google Scholar]
- Stronen, A.V.; Salmela, E.; Baldursdottir, B.K.; Berg, P.; Espelien, I.S.; Jarvi, K.; Jensen, H.; Kristensen, T.N.; Melis, C.; Manenti, T.; et al. Genetic rescue of an endangered domestic animal through outcrossing with closely related breeds: A case study of the Norwegian Lundehund. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espelien, I.S.; Gautun, H.; Helfjord, T. The new breeding strategy of the Norwegian Lundehund Club. Lundehund-Nytt 2013, 2, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Norwegian Lundehund Club. Database of the Norwegian Lundehund. Available online: https://natron.vm.ntnu.no/nlk/ (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Chang, M.L.; Terrill, R.L.; Bautista, M.M.; Carlson, E.J.; Dyer, D.J.; Overall, K.L.; Hamilton, S.P. Large-Scale SNP Genotyping with Canine Buccal Swab DNA. J. Hered. 2007, 98, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joanes, D.N.; Gill, C.A. Comparing measures of sample skewness and kurtosis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D 1998, 47, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rousset, F. GENEPOP’ 007: A complete re-implementation of the GENEPOP software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervey, S.D.; Rutledge, L.Y.; Patterson, B.R.; Romanski, M.C.; Vucetich, J.A.; Belant, J.L.; Beyer, D.E.; Moore, S.A.; Brzeski, K.E. A first genetic assessment of the newly introduced Isle Royale gray wolves (Canis lupus). Conserv. Genet. 2021, 22, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| LUN Ho | BUH Ho | F1 Ho | F2 Ho | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 12 | 12 | 7 | 10 |
| Mean | 0.043 | 0.269 | 0.272 | 0.153 |
| S.E. | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| Median | 0 | 0.273 | 0.167 | 0 |
| 25% | 0 | 0.091 | 0 | 0 |
| 75% | 0 | 0.455 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| Skewness | 3.456 | 0.534 | 0.956 | 1.402 |
| Kurtosis | −4009.148 | −659.838 | −680.202 | −1108.418 |
| Group | uHE ± SE | FIS ± SE | HWE Test | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUN | 0.041 ± 0.001 | −0.083 ± 0.003 | *** | 12.74% |
| BUH | 0.267 ± 0.002 | −0.051 ± 0.003 | * | 90.96% |
| F1 | 0.195 ± 0.002 | −0.420 ± 0.004 | *** | 50.89% |
| F2 | 0.127 ± 0.002 | −0.216 ± 0.002 | *** | 42.93% |
| BUH | F1 | F2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LUN | 0.424 | 0.319 | 0.134 |
| BUH | 0.1241 | 0.252 | |
| F1 | 0.319 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melis, C.; Pertoldi, C.; Ludington, W.B.; Beuchat, C.; Qvigstad, G.; Stronen, A.V. Genetic Rescue of the Highly Inbred Norwegian Lundehund. Genes 2022, 13, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13010163
Melis C, Pertoldi C, Ludington WB, Beuchat C, Qvigstad G, Stronen AV. Genetic Rescue of the Highly Inbred Norwegian Lundehund. Genes. 2022; 13(1):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13010163
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelis, Claudia, Cino Pertoldi, William Basil Ludington, Carol Beuchat, Gunnar Qvigstad, and Astrid Vik Stronen. 2022. "Genetic Rescue of the Highly Inbred Norwegian Lundehund" Genes 13, no. 1: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13010163
APA StyleMelis, C., Pertoldi, C., Ludington, W. B., Beuchat, C., Qvigstad, G., & Stronen, A. V. (2022). Genetic Rescue of the Highly Inbred Norwegian Lundehund. Genes, 13(1), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13010163









