Sex-Biased Expression of Olfaction-Related Genes in the Antennae of Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and RNA-Seq Library Sequencing
2.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Identification of Olfaction-Related Genes
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing Data
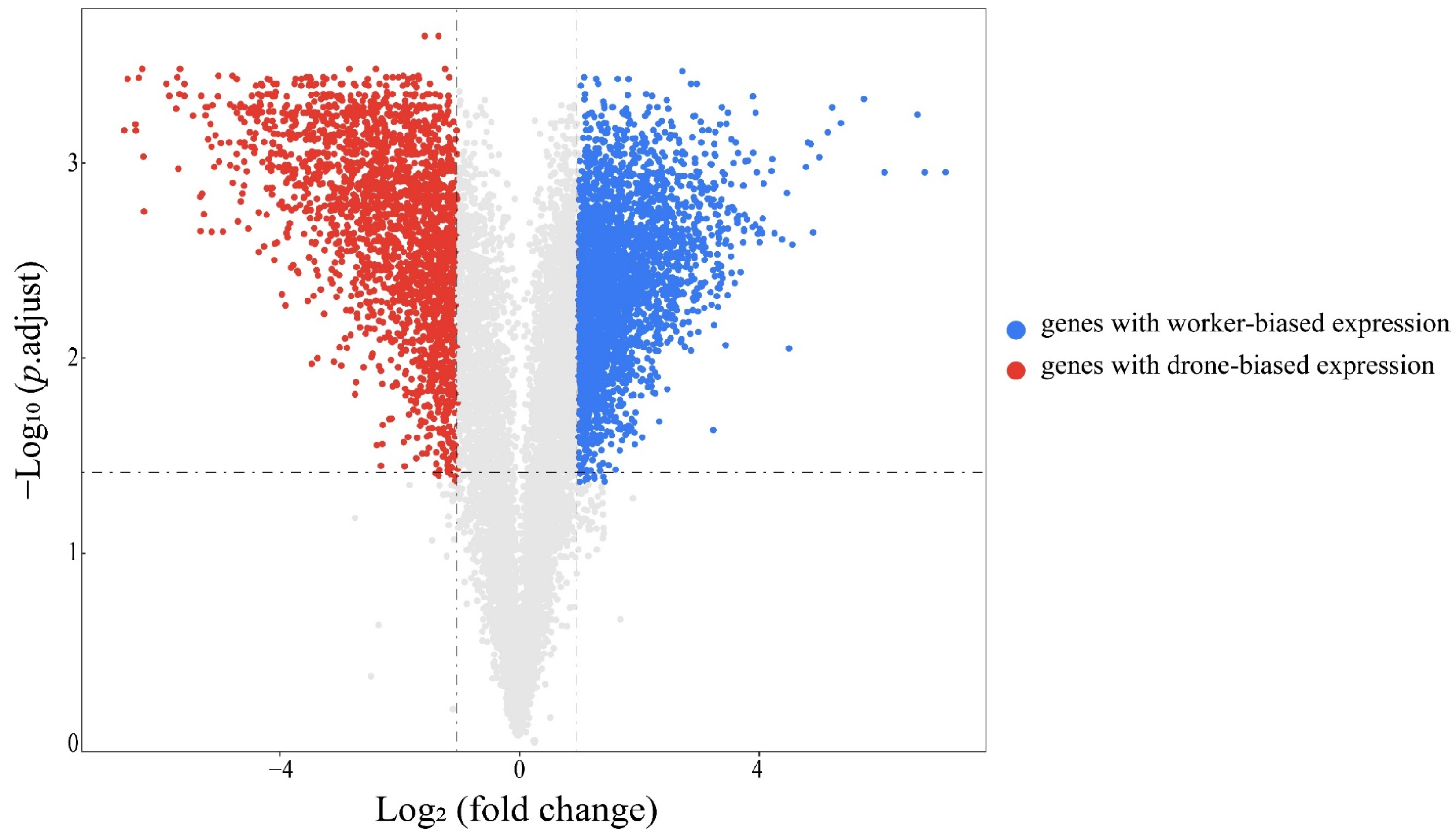
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes between Workers and Drones
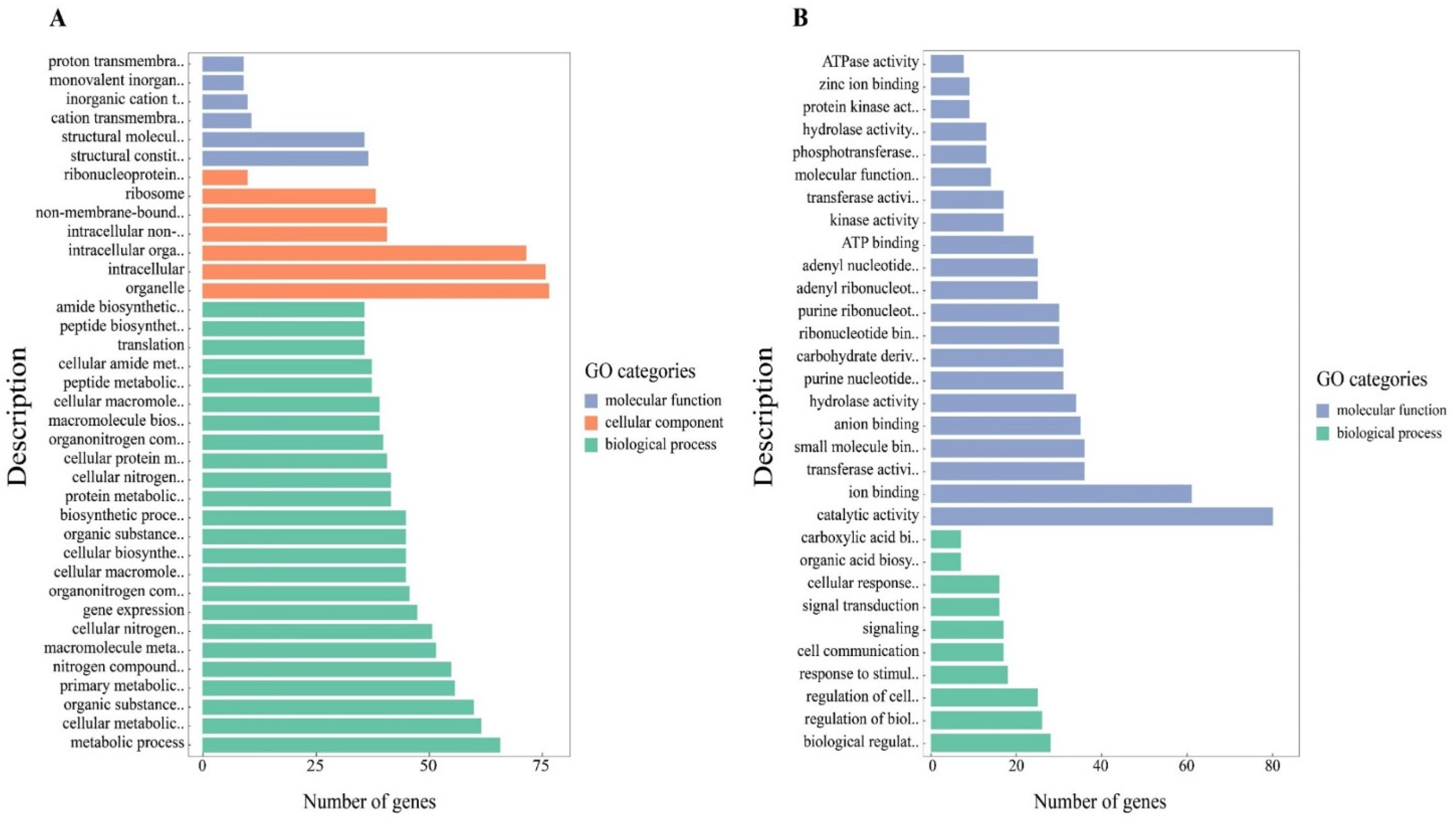
3.3. GO Analysis and Pathway Analysis
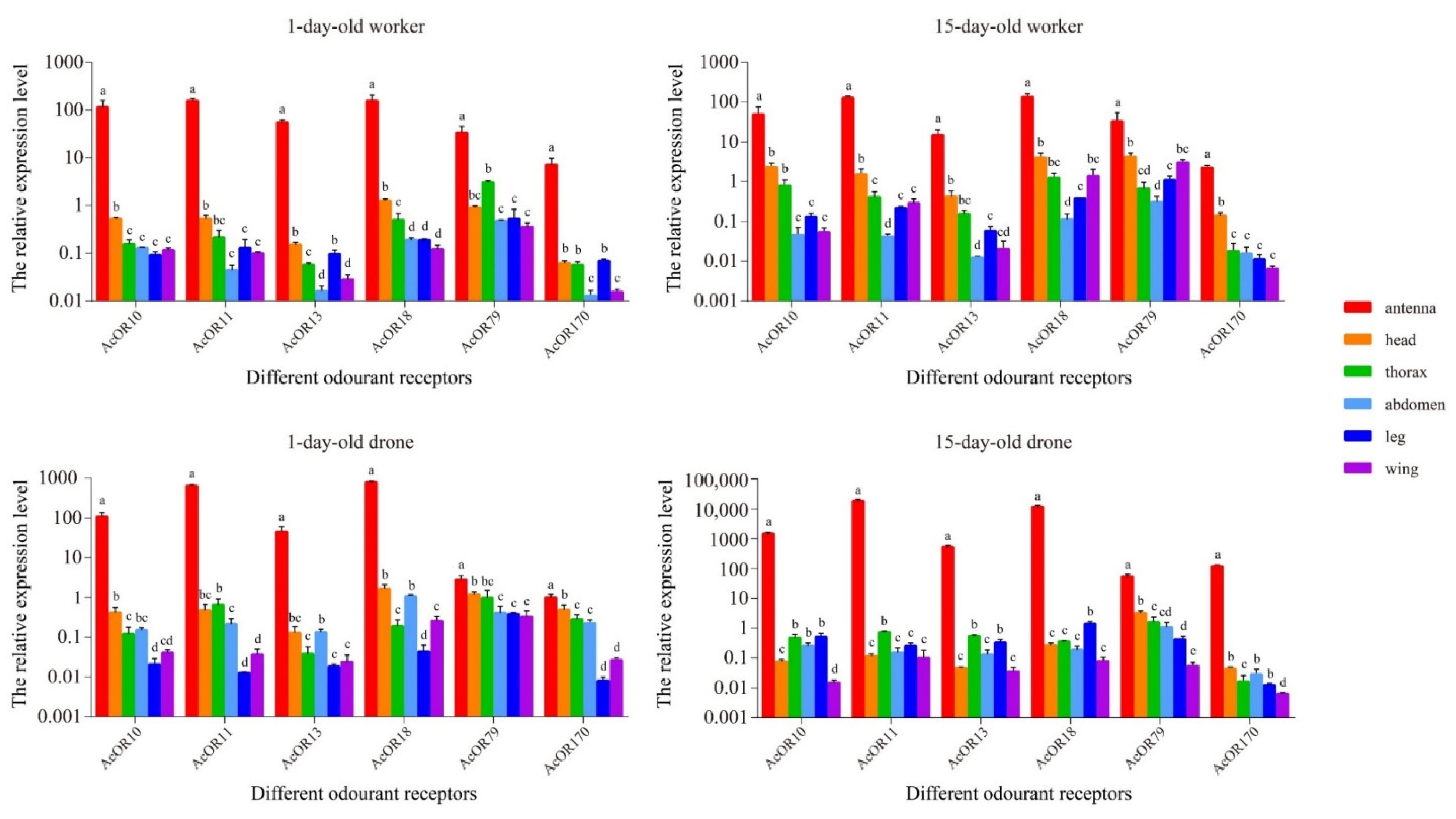
3.4. Candidate Olfaction-Related Genes and Their Expression Profiles
3.5. Validation of DEGs by RT-qPCR
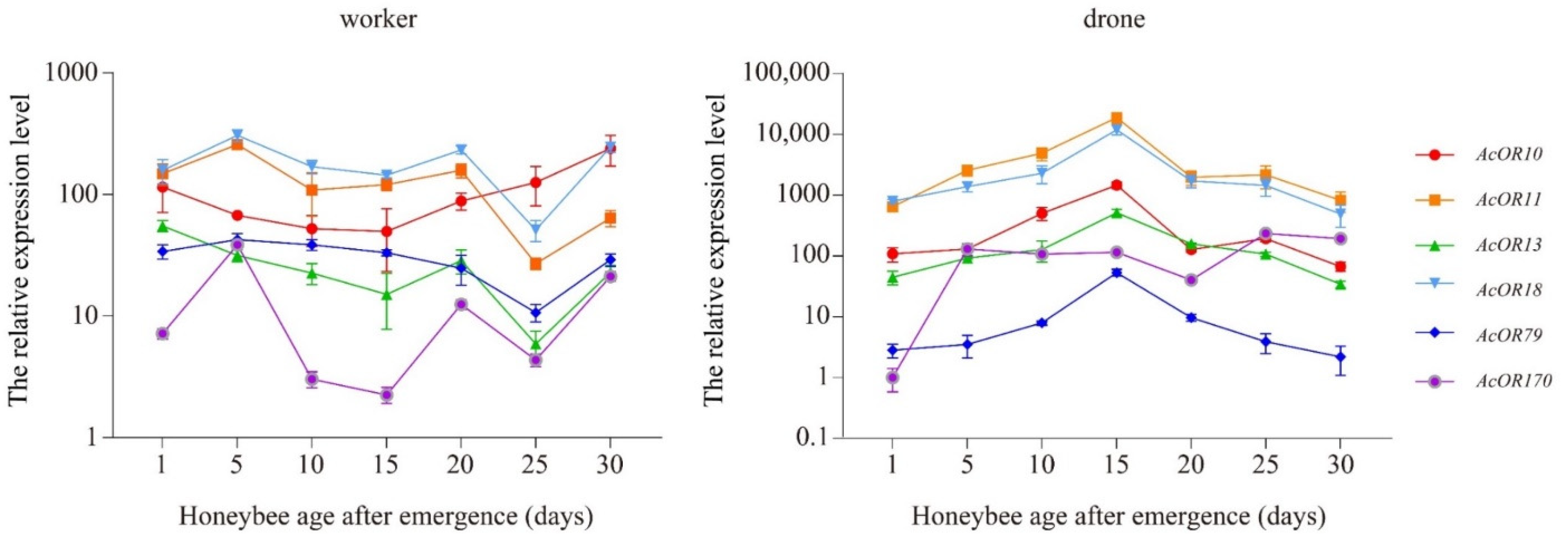
3.6. Expression Patterns of AcOR10, AcOR11, AcOR13, AcOR18, AcOR79 and AcOR170
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renou, M.; Anton, S. Insect olfactory communication in a complex and changing world. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, A.F.; Carlson, J.R. Insect olfaction from model systems to disease control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12987–12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.N.; Löfstedt, C.; Newcomb, R.D. Insect olfaction and the evolution of receptor tuning. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 3, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.-J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Stocker, R.F. Molecular architecture of smell and taste in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 505–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, A.; Brückner, D.; Crewe, R.M. The EAG response spectra of workers and drones to queen honeybee mandibular gland components: The evolution of a social signal. Naturwissenschaften 1998, 85, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltedji, D.; Song, F.; Zhang, L.; Gala, A.; Han, B.; Feng, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, J. Western honeybee drones and workers (Apis mellifera ligustica) have different olfactory mechanisms than eastern honeybees (Apis cerana cerana). J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4526–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghamdi, A.A. Scanning electron microscopic studies on antennal sensilla organs of adult honey bee workers in genus Apis (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bull. Entomol. Soc. Egypt. 2006, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brockmann, A.; Brückner, D. Structural differences in the drone olfactory system of two phylogenetically distant Apis species, A. florea and A. mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 2001, 88, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Radloff, S.E. Honeybees of Asia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Dai, R.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; et al. Managed honeybee colony losses of the Eastern honeybee (Apis cerana) in China (2011–2014). Apidologie 2017, 48, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Ni, C.-X.; Tan, J.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Hu, F.-L. Chemosensory proteins of the eastern honeybee, Apis cerana: Identification, tissue distribution and olfactory related functional characterization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B-Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 194, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, P.; Wang, S.; Pan, J.; Jiang, Y. Antennal transcriptome and differential expression analysis of five chemosensory gene families from the Asian honeybee Apis cerana cerana. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xu, K.; Ma, W.; Su, W.; Tai, M.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X. Contact chemosensory genes identified in leg transcriptome of Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Identification and functional characterization of AcerOBP15 from Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Apidologie 2021, 52, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, H.M.; Wanner, K.W. The chemoreceptor superfamily in the honey bee, Apis mellifera: Expansion of the odorant, but not gustatory, receptor family. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forêt, S.; Maleszka, R. Function and evolution of a gene family encoding odorant binding-like proteins in a social insect, the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forêt, S.; Wanner, K.W.; Maleszka, R. Chemosensory proteins in the honey bee: Insights from the annotated genome, comparative analyses and expressional profiling. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croset, V.; Rytz, R.; Cummins, S.F.; Budd, A.; Brawand, D.; Kaessmann, H.; Gibson, T.J.; Benton, R. Ancient protostome origin of chemosensory ionotropic glutamate receptors and the evolution of insect taste and olfaction. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, Z.; Vogt, R.G. The SNMP/CD36 gene family in Diptera, Hymenoptera and Coleoptera: Drosophila melanogaster, D. pseudoobscura, Anopheles gambiae, Aedes aegypti, Apis mellifera, and Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Jung, J.W.; Choi, B.-S.; Jayakodi, M.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Yu, Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, M.-L.; Park, Y.; et al. Uncovering the novel characteristics of Asian honey bee, Apis cerana, by whole genome sequencing. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, K.W.; Nichols, A.S.; Walden, K.K.O.; Brockmann, A.; Luetje, C.W.; Robertson, H.M. A honey bee odorant receptor for the queen substance 9-oxo-2-decenoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14383–14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plettner, E.; Otis, G.W.; Wimalaratne, P.D.C.; Winston, M.L.; Slessor, K.N.; Pankiw, T.; Punchihewa, P.W.K. Species- and caste-determined mandibular gland signals in honeybees (Apis). J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, W.; Gao, P.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Y. Sequence and expression characterization of an OBP1 gene in the Asian honeybee, Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Appl. Entomol. Zoolog. 2014, 49, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danty, E.; Arnold, G.; Huet, J.-C.; Huet, D.; Masson, C.; Pernollet, J.-C. Separation, characterization and sexual heterogeneity of multiple putative odorant-binding proteins in the honeybee Apis mellifera L.(Hymenoptera: Apidea). Chem. Senses. 1998, 23, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danty, E.; Briand, L.; Michard-Vanhée, C.; Perez, V.; Arnold, G.; Gaudemer, O.; Huet, D.; Huet, J.-C.; Ouali, C.; Masson, C.; et al. Cloning and expression of a queen pheromone-binding protein in the honeybee: An olfactory-specific, developmentally regulated protein. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7468–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Y.; Luo, C.; Li, H. Prokaryotic expression and ligand binding characteristics of pheromone binding protein ASP1 in the Chinese honeybee (Apis cerana cerana). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2013, 56, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-F.; Wu, F.; Tang, M.-Z.; Chen, D.-X.; Tan, J.; Liu, Q.-J.; Li, H.-L. Study on specific Apis cerana honeybee queen pheromone biosensor based on pheromone-binding protein ASP1. IEEE. Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8855–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Yin, L.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Shen, J.; Shen, F. Transcriptional responses in eastern honeybees (Apis cerana) infected with mites, Varroa destructor. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 8888–8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharlaken, B.; de Graaf, D.C.; Goossens, K.; Peelman, L.J.; Jacobs, F.J. Differential gene expression in the honeybee head after a bacterial challenge. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Ma, C.; Han, B.; Meng, L.; Hu, H.; Fang, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhang, X.; Rueppell, O.; Li, J. Behavioural, physiological and molecular changes in alloparental caregivers may be responsible for selection response for female reproductive investment in honey bees. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4212–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Xu, S.; Xie, C.; Geng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, W.-f.; Lin, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Apis mellifera antennae of workers performing different tasks. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Zheng, H.; Corona, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Sohr, A.; Hu, F. Transcriptome comparison between inactivated and activated ovaries of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 23, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.-N.; Nuo, S.-M.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Liu, N.-Y. The ionotropic receptor gene family in Lepidoptera and Trichoptera: Annotation, evolutionary and functional perspectives. Genomics 2021, 113, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample Name | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Mapping to Reference Genome | Q30 | GC Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Mapped Ratio | Uniquely Mapped Ratio | Multiple Mapped Ratio | |||||
| Ac_drone1 | 38,909,258 | 37,006,285 | 88.71 | 87.04 | 1.67 | 93.98% | 39.50% |
| Ac_drone2 | 35,430,933 | 33,495,876 | 82.02 | 80.34 | 1.68 | 93.98% | 40.50% |
| Ac_drone3 | 36,043,980 | 34,451,429 | 88.06 | 86.14 | 1.92 | 94.21% | 38.00% |
| Ac_worker1 | 31,093,034 | 28,795,612 | 91.77 | 89.63 | 2.14 | 94.04% | 37.00% |
| Ac_worker2 | 31,606,090 | 29,115,010 | 91.91 | 89.71 | 2.20 | 94.04% | 36.00% |
| Ac_worker3 | 34,306,996 | 31,213,014 | 90.92 | 88.65 | 2.27 | 93.45% | 36.00% |
| Gene Name | Log2 (Fold Change) Worker vs. Drone | |
|---|---|---|
| RNA-Seq | RT-qPCR | |
| AcOR10 | −1.9696 | −2.3067 |
| AcOR11 | −3.7412 | −3.6056 |
| AcOR13 | −1.5385 | 0.2311 |
| AcOR18 | −2.2875 | −2.4844 |
| AcOR79 | −2.4173 | −2.8022 |
| AcOR170 | −3.4653 | −3.6911 |
| AcOBP1 | 1.3586 | 1.0198 |
| AcOBP2 | 4.213 | 3.4844 |
| AcOBP17 | −1.7026 | −2.9178 |
| AcCSP1 | 3.803 | 2.3789 |
| AcCSP3 | 2.2829 | 2.1622 |
| Ac_venom carboxylesterase-6 | −1.3597 | −2.6311 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, H.; Su, W.; Huang, J.; Ding, G. Sex-Biased Expression of Olfaction-Related Genes in the Antennae of Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Genes 2022, 13, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101771
Du H, Su W, Huang J, Ding G. Sex-Biased Expression of Olfaction-Related Genes in the Antennae of Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Genes. 2022; 13(10):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101771
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Hanchao, Wenting Su, Jiaxing Huang, and Guiling Ding. 2022. "Sex-Biased Expression of Olfaction-Related Genes in the Antennae of Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae)" Genes 13, no. 10: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101771
APA StyleDu, H., Su, W., Huang, J., & Ding, G. (2022). Sex-Biased Expression of Olfaction-Related Genes in the Antennae of Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Genes, 13(10), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101771





