Genetic Overlap Analysis Identifies a Shared Etiology between Migraine and Headache with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Summary Statistics for Migraine, Headache, and T2D
2.3. Summary Statistics for Sex-Stratified Migraine, Headache, and T2D
2.4. Analysis of Sex-Stratified Effects
2.5. Pre-Processing of GWAS Data
2.6. Genetic Overlap between Migraine and Headache with T2D
2.7. SNP-Based Heritability and Genome-Wide Genetic Correlation
2.8. Regional Pleiotropic Genetic Effects
2.9. Cross-Trait Meta-Analysis between Migraine and Headache with T2D
2.10. Identification of Independent Novel Lead SNP or Genomic Loci
2.11. Gene-Based Association Analysis to Examine the Genetic Overlap
2.11.1. Gene-Based Test
2.11.2. Independent Gene-Based Test
2.11.3. Test for Gene-Level Genetic Overlap
2.12. Testing Causal Association
2.12.1. Mendelian Randomisation
2.12.2. Latent Causal Variable Model
2.13. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Cross-Trait-Associated Genes
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Overlap of Migraine and Headache with T2D
3.2. Genetic Correlations of T2D with Migraine and Headache
3.3. Pairwise GWAS of Migraine and Headache with T2D
3.4. Identification of Novel Lead SNPs between Migraine and Headache with T2D
3.5. Utility of the Cross-Trait GWAS Meta-Analysis Approach
3.6. Gene-Based Genetic Overlap between Migraine and Headache with T2D
3.7. Causal Inference between Migraine and Headache with T2D
3.8. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Genes Associated across Migraine and Headache with T2D
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautakangas, H.; Winsvold, B.S.; Ruotsalainen, S.E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Harder, A.V.E.; Kogelman, L.J.A.; Thomas, L.F.; Noordam, R.; Benner, C.; Gormley, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of 102,084 migraine cases identifies 123 risk loci and subtype-specific risk alleles. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormley, P.; Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Palta, P.; Esko, T.; Pers, T.H.; Farh, K.-H.; Cuenca-Leon, E.; Muona, M.; Furlotte, N.A. Meta-analysis of 375,000 individuals identifies 38 susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Rist, P.M.; Daghlas, I.; Giulianini, F.; Gormley, P.; Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Palta, P.; Esko, T.; Pers, T.H.; et al. A genome-wide cross-phenotype meta-analysis of the association of blood pressure with migraine. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghlas, I.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Danning, R.; Gormley, P.; Malik, R.; Amouyel, P.; Metso, T.; Pezzini, A.; Kurth, T.; Debette, S.; et al. Migraine, Stroke, and Cervical Arterial Dissection. Neurol. Genet. 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, T.; Winter, A.C.; Eliassen, A.H.; Dushkes, R.; Mukamal, K.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M. Migraine and risk of cardiovascular disease in women: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2016, 353, i2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Timón, I.; Sevillano-Collantes, C.; Segura-Galindo, A.; Del Cañizo-Gómez, F.J. Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors the same strength? World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 444–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigal, M.E.; Kurth, T.; Hu, H.; Santanello, N.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine and cardiovascular disease: Possible mechanisms of interaction. Neurology 2009, 72, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R.B. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, G.; El Fatouhi, D.; Fournier, A.; Gusto, G.; Mancini, F.R.; Balkau, B.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Kurth, T.; Bonnet, F. Associations Between Migraine and Type 2 Diabetes in Women: Findings From the E3N Cohort Study. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nyholt, D.R. Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine-A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration. Genes 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, K.M.; Klarin, D.; Damrauer, S.M.; Chang, K.-M.; Tsao, P.S.; Assimes, T.L.; Davey Smith, G.; Voight, B.F.; The International Headache Genetics, C. Cross-trait analyses with migraine reveal widespread pleiotropy and suggest a vascular component to migraine headache. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.B.; Groop, L. Genetics of type 2 diabetes-pitfalls and possibilities. Genes 2015, 6, 87–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, I.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Terwindt, G.M. Advance in genetics of migraine. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Adams, M.J.; Hebert, H.L.; Deary, I.J.; McIntosh, A.M.; Smith, B.H. A Genome-Wide Association Study Finds Genetic Associations with Broadly-Defined Headache in UK Biobank (N = 223,773). EBioMedicine 2018, 28, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, N.; Linnman, C.; Brawn, J.; Burstein, R.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Her versus his migraine: Multiple sex differences in brain function and structure. Brain 2012, 135, 2546–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Loder, S.; Loder, E.; Smitherman, T.A.; Pain, F. The prevalence and burden of migraine and severe headache in the U nited S tates: Updated statistics from government health surveillance studies. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2015, 55, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale Lab. Rapid GWAS of Thousands of Phenotypes for 337,000 Samples in the UK Biobank. 2017. Available online: http://www.nealelab.is/blog/2017/7/19/rapid-gwas-of-thousands-of-phenotypes-for-337000-samples-in-the-uk-biobank (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Gormley, P.; Kurth, T.; Bettella, F.; McMahon, G.; Kallela, M.; Malik, R.; De Vries, B.; Terwindt, G. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Loder, E.W.; Gorman, J.A.; Stewart, W.F.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B. Sex Differences in the Prevalence, Symptoms, and Associated Features of Migraine, Probable Migraine and Other Severe Headache: Results of the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2013, 53, 1278–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassany, L.; Haas, J.; Piccininni, M.; Kurth, T.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A.; Rohmann, J.L. Giving Researchers a Headach—Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 549038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholt, D.R. SECA: SNP effect concordance analysis using genome-wide association summary results. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2086–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.-R.; Duncan, L.; Perry, J.R.B.; Patterson, N.; Robinson, E.B.; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. Neurol. 2018, 17, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Berisa, T.; Liu, J.Z.; Ségurel, L.; Tung, J.Y.; Hinds, D.A. Detection and interpretation of shared genetic influences on 42 human traits. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Eskin, E. Random-effects model aimed at discovering associations in meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Eskin, E. Interpreting Meta-Analyses of Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLOS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, J.R.; Blackshaw, J.; Kamat, M.A.; Ellis, S.; Surendran, P.; Sun, B.B.; Paul, D.S.; Freitag, D.; Burgess, S.; Danesh, J.; et al. PhenoScanner: A database of human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3207–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Eising, E.; de Vries, B.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Kurth, T.; Stefansson, H.; Kallela, M.; Malik, R.; et al. Gene-based pleiotropy across migraine with aura and migraine without aura patient groups. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2016, 36, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-X.; Gui, H.-S.; Kwan, J.S.H.; Sham, P.C. GATES: A rapid and powerful gene-based association test using extended Simes procedure. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, P.; Huang, H.; Arking, D.E.; Bader, J.S. Fast association tests for genes with FAST. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Yeung, J.M.; Cherny, S.S.; Sham, P.C. Evaluating the effective numbers of independent tests and significant p-value thresholds in commercial genotyping arrays and public imputation reference datasets. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, E.O.; Sapkota, Y.; Auta, A.; Yoshihara, K.; Nyegaard, M.; Griffiths, L.R.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al.; International Endogene Consortium; 23andMe Research Team; International Headache Genetics Consortium Shared Molecular Genetic Mechanisms Underlie Endometriosis and Migraine Comorbidity. Genes 2020, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Boomsma, D.I.; Ligthart, L.; Belin, A.C.; Smith, G.D.; Esko, T.; Freilinger, T.M.; Hansen, T.F.; Ikram, M.A.; et al. Molecular genetic overlap between migraine and major depressive disorder. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, E.O.; Mehta, D.; Sapkota, Y.; Auta, A.; Yoshihara, K.; Nyegaard, M.; Griffiths, L.R.; Montgomery, G.W.; Chasman, D.I.; Nyholt, D.R. Genetic analysis of endometriosis and depression identifies shared loci and implicates causal links with gastric mucosa abnormality. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Nyholt, D.R. Gene-based analyses reveal novel genetic overlap and allelic heterogeneity across five major psychiatric disorders. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Trzaskowski, M.; Maier, R.; Robinson, M.R.; McGrath, J.J.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; et al. Causal associations between risk factors and common diseases inferred from GWAS summary data. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, L.J.; Price, A.L. Distinguishing genetic correlation from causation across 52 diseases and complex traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimand, J.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Kolberg, L.; Reisberg, S.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler-a web server for functional interpretation of gene lists (2016 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W83–W89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Split, W.; Szydlowska, M. Headaches in non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Funct. Neurol. 1997, 12, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Victor, T.W.; Hu, X.; Campbell, J.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine prevalence by age and sex in the United States: A life-span study. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allais, G.; Chiarle, G.; Sinigaglia, S.; Airola, G.; Schiapparelli, P.; Benedetto, C. Gender-related differences in migraine. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratten, J.; Visscher, P.M. Genetic pleiotropy in complex traits and diseases: Implications for genomic medicine. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic, M.; Keaton, J.M.; Lynch, J.A.; Miller, D.R.; Zhou, J.; Tcheandjieu, C.; Huffman, J.E.; Assimes, T.L.; Lorenz, K.; Zhu, X.; et al. Discovery of 318 new risk loci for type 2 diabetes and related vascular outcomes among 1.4 million participants in a multi-ancestry meta-analysis. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A.; Warfvinge, K. Does inflammation have a role in migraine? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Eleftheriadou, M.; Kelaini, S.; Morrison, T.; González, M.V.; Caines, R.; Edwards, N.; Yacoub, A.; Edgar, K.; Moez, A.; et al. Targeting QKI-7 in vivo restores endothelial cell function in diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, A.; Alberini, C.M. NLGN1 and NLGN2 in the prefrontal cortex: Their role in memory consolidation and strengthening. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, N.H.; Yasuda, H.; Miyamoto, H.; Hatayama, M.; Morimura, N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Odagawa, M.; Odaka, Y.S.; Iwayama, Y. Elfn1 recruits presynaptic mGluR7 in trans and its loss results in seizures. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, J.; Mitchell, K.J. Mutation of Elfn1 in mice causes seizures and hyperactivity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, S.; Hindley, G.; Winsvold, B.S.; O’Connell, K.S.; Frei, O.; Shadrin, A.; Cheng, W.; Bettella, F.; Rødevand, L.; Odegaard, K.J.; et al. Dissecting the shared genetic basis of migraine and mental disorders using novel statistical tools. Brain 2022, 145, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, L.; Lo Buono, V.; De Salvo, S.; Ruvolo, C.; Torre, V.; Bramanti, P.; Marino, S.; Corallo, F. Brain morphologic abnormalities in migraine patients: An observational study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panganiban, R.A.; Park, H.R.; Sun, M.; Shumyatcher, M.; Himes, B.E.; Lu, Q. Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies suppressors of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13384–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.-i.; Gerondopoulos, A.; Linford, A.; Rigden, D.J.; Barr, F.A. Family-wide characterization of the DENN domain Rab GDP-GTP exchange factors. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Oliveira, M.; Akerman, S.; Holland, P.R.; Hoffmann, J.R.; Tavares, I.; Goadsby, P.J. Neuroendocrine signaling modulates specific neural networks relevant to migraine. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 101, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, S.; Altobelli, E.; Ornello, R.; Ripa, P.; Pistoia, F.; Carolei, A. Insulin resistance in migraineurs: Results from a case-control study. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2014, 34, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Borsook, D.; Griffiths, L.R. Migrainomics—Identifying brain and genetic markers of migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamodt, A.H.; Stovner, L.J.; Midthjell, K.; Hagen, K.; Zwart, J.A. Headache prevalence related to diabetes mellitus. The Head-HUNT study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonazzo, I.C.; Riise, T.; Cortese, M.; Berge, L.I.; Engeland, A.; Bernt Fasmer, O.; Lund, A.; Joachim Ødegaard, K.; Poluzzi, E.; Bjornevik, K. Diabetes is associated with decreased migraine risk: A nationwide cohort study. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2018, 38, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, L.I.; Riise, T.; Fasmer, O.B.; Hundal, Ø.; Oedegaard, K.J.; Midthjell, K.; Lund, A. Does diabetes have a protective effect on migraine? J. Epidemiol. 2013, 24, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Zhou, S.X.; Li, R.C.; Zheng, L.R.; Zhu, J.H.; Hu, S.J.; Sun, Y.L. Serum levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P are decreased in patients with diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmine Belin, A.; Ran, C.; Edvinsson, L. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) and Cluster Headache. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.P.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.J.; Sun, T.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X. Association of down-regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P with increase of myocardial vulnerability in diabetic neuropathic rats. Peptides 2017, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, P.L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and migraine. Headache 2006, 46 (Suppl S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.E.; Eaton, S.E.; Cotter, M.A.; Tesfaye, S. Vascular factors and metabolic interactions in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 1973–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.H.; Antevska, A.; Link, B.A.; Bogin, B.; Burke, S.J.; Dupuy, S.D.; Collier, J.J.; Levine, Z.A.; Karlstad, M.D.; Do, T.D. α-CGRP disrupts amylin fibrillization and regulates insulin secretion: Implications on diabetes and migraine. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5853–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Trait 1 | Trait 2 | Rg | SE | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine | T2D | 0.0589 | 0.0135 | 1.37 × 10−5 |
| Migraine (Male) | T2D (Male) | 0.0007 | 0.0759 | 0.9929 |
| Migraine (Female) | T2D (Female) | 0.0743 | 0.0537 | 0.1663 |
| Headache | T2D | 0.0657 | 0.0182 | 3.0 × 10−4 |
| Headache (Male) | T2D (Male) | 0.0922 | 0.0355 | 9.4 × 10−3 |
| Headache (Female) | T2D (Female) | 0.0049 | 0.0396 | 0.9009 |
| Trait 1 | Trait 2 | Region | Chr | Start bp | End bp | Locus | PPA1 | PPA2 | PPA3 | PPA4 | Genome-Wide Significant Genes Overlapping both Traits in the Highlighted Region (Psingle trait FDR < 0.1 and Pmeta FCP < 3.65 × 10−6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine | T2D | 88 | chr1 | 177434054 | 178944161 | 1q25.2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 0.01 | * SEC16B |
| 283 | chr3 | 8648561 | 9541905 | 3p26.1–p25.3 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 0.07 | * SETD5, * LHFPL4 | ||
| 402 | chr4 | 2844097 | 3845571 | 4p16.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | * ADD1, * MFSD10, * NOP14, * HTT, * MSANTD1 | ||
| 564 a | chr5 | 73759326 | 75795407 | 5q13.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.93 | 0.07 | GCNT4, ANKRD31, * HMGCR, * COL4A3BP, * POLK, * ANKDD1B, * POC5 | ||
| 734 | chr6 | 160581374 | 162169452 | 6q25.3–q26 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 0.04 | * SLC22A3 | ||
| 1005 | chr9 | 135298917 | 137040737 | 9q34.13–q34.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.03 | * ABO, BRD3 | ||
| 1123 | chr11 | 47008125 | 49865926 | 11p11.2–p11.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.03 | DDB2, MYBPC3, * SPI1, SLC39A13, PSMC3, * RAPSN, * CELF1, * PTPMT1, * KBTBD4, * NDUFS3, * FAM180B, * C1QTNF4, * MTCH2, * AGBL2, * FNBP4, * NUP160 | ||
| 1348 | chr14 | 57482514 | 59448252 | 14q22.3–q23.1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.04 | * PSMA3, * ACTR10, * ARID4A, TOMM20L, TIMM9 | ||
| 1370 a | chr14 | 94325812 | 95750857 | 14q32.12–q32.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | SERPINA2, * SERPINA1 | ||
| 1400 | chr15 | 53069747 | 54508497 | 15q21.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.95 | 0.04 | * ONECUT1, * LOC101928499 | ||
| 1518 | chr17 | 59312894 | 61545486 | 17q23.2–q23.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | EFCAB3, METTL2A, * TLK2, * MRC2 | ||
| Headache | T2D | 76 | chr1 | 153181186 | 154770139 | 1q21.3 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.94 | 0.02 | * AQP10, * ATP8B2 |
| 324 | chr3 | 70449145 | 72528844 | 3p13 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.93 | 0.05 | - | ||
| 564 a | chr5 | 73759326 | 75797683 | 5q13.3 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.01 | HMGCR, COL4A3BP, POLK, * ANKDD1B, * POC5 | ||
| 745 | chr7 | 1353067 | 2062006 | 7p22.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.03 | * MAD1L1 | ||
| 1370 a | chr14 | 94325596 | 95750857 | 14q32.12–q32.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | SERPINA2, * SERPINA1 |
| Lead SNP | CHR | BP | EA | NEA | FE Meta-Analysis | Migraine | T2D | Variant Annotation | Nearest Coding Gene | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | FDR | OR | p-Value | FDR | |||||||
| rs11590235 | 1 | 2208123 | T | C | 1.05 | 4.33 × 10−9 | 1.05 | 3.59 × 10−6 | 1.77 × 10−3 | 1.05 | 3.00 × 10−4 | 3.22 × 10−2 | Intronic | SKI |
| rs1841499 | 1 | 72836456 | A | T | 0.98 | 2.86 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 2.64 × 10−4 | 3.78 × 10−2 | 0.97 | 1.65 × 10−5 | 4.03 × 10−3 | Intergenic | NEGR1 |
| rs6748072 | 2 | 202980887 | A | G | 0.98 | 3.00 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 7.20 × 10−5 | 1.62 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 9.37 × 10−5 | 1.45 × 10−2 | Non-coding transcript exon | KIAA2012 |
| rs9817547 | 3 | 18753414 | C | A | 0.98 | 1.88 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 5.34 × 10−5 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 0.97 | 8.02 × 10−5 | 1.30 × 10−2 | Intronic | SATB1 |
| rs536445 | 3 | 173120103 | C | T | 0.98 | 1.35 × 10−9 | 0.98 | 2.07 × 10−5 | 6.66 × 10−3 | 0.97 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 2.85 × 10−3 | Intronic | * NLGN1 |
| rs4619890 | 4 | 7853160 | G | A | 1.02 | 2.84 × 10−9 | 1.03 | 7.54 × 10−7 | 5.30 × 10−4 | 1.02 | 8.58 × 10−4 | 4.79 × 10−2 | Intronic | AFAP1 |
| rs6829081 | 4 | 48693247 | T | A | 0.97 | 1.17 × 10−10 | 0.98 | 3.89 × 10−5 | 1.05 × 10−2 | 0.96 | 2.71 × 10−7 | 1.18 × 10−4 | Intronic | FRYL |
| rs171697 | 5 | 103956516 | G | C | 1.03 | 7.73 × 10−10 | 1.03 | 7.93 × 10−7 | 5.52 × 10−4 | 1.03 | 2.36 × 10−4 | 2.74 × 10−2 | Intronic | NUDT12 |
| rs29648 | 5 | 170559580 | A | G | 0.98 | 3.10 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 3.26 × 10−5 | 9.30 × 10−3 | 0.97 | 2.50 × 10−4 | 2.27 × 10−2 | Intronic | TLX3 |
| rs62442924 | 7 | 1989976 | T | C | 0.97 | 1.94 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 3.33 × 10−4 | 4.37 × 10−2 | 0.96 | 6.80 × 10−6 | 1.06 × 10−3 | Intronic | * ELFN1 |
| rs6947337 | 7 | 41854681 | A | G | 0.98 | 3.90 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 7.78 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 1.20 × 10−4 | 1.60 × 10−2 | Intergenic | INHBA |
| rs10101067 | 8 | 72407374 | C | G | 1.05 | 9.71 × 10−10 | 1.04 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 5.00 × 10−3 | 1.05 | 1.47 × 10−5 | 4.15 × 10−3 | Intronic | EYA1 |
| rs11140324 | 9 | 86634309 | T | C | 0.97 | 1.65 × 10−9 | 0.97 | 7.51 × 10−6 | 3.09 × 10−3 | 0.97 | 5.11 × 10−5 | 7.49 × 10−3 | Intergenic | RMI1 |
| rs2670139 | 9 | 126634255 | C | T | 1.03 | 3.11 × 10−12 | 1.03 | 1.43 × 10−6 | 8.71 × 10−4 | 1.04 | 2.82 × 10−7 | 1.24 × 10−4 | Intronic | DENND1A |
| rs72854192 | 11 | 9587144 | T | A | 1.06 | 3.52 × 10−8 | 1.06 | 2.27 × 10−5 | 7.14 × 10−3 | 1.06 | 4.16 × 10−4 | 3.07 × 10−2 | Intergenic | WEE1 |
| rs11233452 | 11 | 82796110 | G | A | 1.03 | 9.52 × 10−9 | 1.02 | 1.32 × 10−4 | 2.45 × 10−2 | 1.03 | 1.08 × 10−5 | 2.15 × 10−3 | Intronic | RAB30 |
| rs10875762 | 12 | 48580759 | G | A | 1.03 | 1.83 × 10−9 | 1.02 | 8.09 × 10−5 | 1.75 × 10−2 | 1.04 | 3.06 × 10−6 | 7.87 × 10−4 | Downstream | CCDC184 |
| rs116862713 | 12 | 120185393 | T | C | 1.07 | 1.01 × 10−8 | 1.06 | 8.87 × 10−5 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 1.08 | 2.42 × 10−5 | 5.46 × 10−3 | Intronic | PRKAB1 |
| rs4902684 | 14 | 69445385 | T | G | 1.03 | 1.56 × 10−10 | 1.02 | 2.81 × 10−5 | 8.37 × 10−3 | 1.04 | 5.73 × 10−7 | 2.55 × 10−4 | 5′ UTR | ACTN1 |
| rs299717 | 18 | 46163555 | T | C | 1.03 | 3.98 × 10−8 | 1.03 | 3.62 × 10−4 | 4.60 × 10−2 | 1.04 | 1.59 × 10−5 | 2.29 × 10−3 | Intronic | CTIF |
| rs1013710 | 20 | 39882781 | A | G | 1.02 | 7.42 × 10−9 | 1.02 | 3.25 × 10−6 | 1.64 × 10−3 | 1.02 | 5.87 × 10−4 | 4.86 × 10−2 | Intronic | ZHX3 |
| rs4809370 | 20 | 62470872 | T | C | 0.98 | 1.06 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 2.47 × 10−2 | 0.97 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 2.85 × 10−3 | Downstream | ZBTB46 |
| rs28457031 | 22 | 41597228 | A | G | 1.07 | 9.99 × 10−9 | 1.07 | 1.10 × 10−5 | 4.17 × 10−3 | 1.07 | 2.29 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−2 | Upstream | L3MBTL2 |
| Lead SNP | CHR | BP | EA | NEA | FE Meta-Analysis | Headache | T2D | Variant Annotation | Nearest Coding Gene | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | FDR | OR | p-Value | FDR | |||||||
| rs546738 | 3 | 173117548 | G | T | 1.03 | 3.38 × 10−10 | 1.03 | 6.48 × 10−6 | 7.69 × 10−3 | 1.03 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 3.26 × 10−3 | Non-coding transcript exon | NLGN1 |
| rs73050128 | 7 | 1961882 | A | C | 0.96 | 1.50 × 10−11 | 0.96 | 3.04 × 10−7 | 5.53 × 10−4 | 0.96 | 1.06 × 10−5 | 2.87 × 10−3 | Intronic | ELFN1 |
| rs12432645 | 14 | 69599483 | T | G | 1.03 | 8.47 × 10−10 | 1.03 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 1.26 × 10−2 | 1.03 | 1.67 × 10−5 | 4.53 × 10−3 | Intronic | DCAF5 |
| Discovery | Target | Number of Overlapping Genes between Migraine and T2D | Proportion of Overlapping Genes between Migraine and T2D | Binomial Test p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Migraine | T2D | Expected | Observed | ||
| Total number of genes | ||||||
| Raw number of genes | 18309 | 18309 | ||||
| Effective number of independent genes | 13757 | 13694 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.1 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.1 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 5965 | 7305 | 2786 | 0.367 | 0.474 | 1.29 × 10−44 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 4102 | 5023 | 1943 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.298 | 0.367 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.05 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.05 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 4421 | 5677 | 1774 | 0.281 | 0.403 | 2.83 × 10−46 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 2959 | 3850 | 1193 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.215 | 0.281 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.01 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.01 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 2236 | 3348 | 662 | 0.159 | 0.295 | 1.24 × 10−37 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 1391 | 2171 | 411 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.101 | 0.159 | ||||
| Discovery | Target | Number of Overlapping Genes between Headache and T2D | Proportion of Overlapping Genes between Headache and T2D | Binomial Test p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Headache | T2D | Expected | Observed | ||
| Total number of genes | ||||||
| Raw number of genes | 18261 | 18261 | ||||
| Effective number of independent genes | 13002 | 13143 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.1 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.1 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 3993 | 7350 | 1844 | 0.380 | 0.477 | 5.99 × 10−25 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 2719 | 4997 | 1297 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.209 | 0.380 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.05 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.05 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 2659 | 5612 | 1050 | 0.287 | 0.412 | 4.08 × 10−29 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 1731 | 3770 | 714 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.133 | 0.287 | ||||
| Genes with p-value ≤ 0.01 | Genes with p-value ≤ 0.01 | |||||
| Raw number of genes | 1163 | 3257 | 353 | 0.161 | 0.325 | 6.36 × 10−25 |
| Effective number of independent genes | 653 | 2119 | 212 | |||
| Proportion of effective number of genes | 0.050 | 0.161 | ||||
| Genes | Chr | Start Position (hg19) | End Position (hg19) | LD Relationship between Top SNPs (r2) | Migraine | T2D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene p-Value | Top SNP | Top SNP p-Value | Gene p-Value | Top SNP | Top SNP p-Value | |||||
| MACF1 | 1 | 39549839 | 39952810 | 0.920 | 2.76 × 10−6 | rs1472662 | 1.75 × 10−8 | 1.25 × 10−22 | rs61779275 | 7.90 × 10−25 |
| KIAA0754 | 1 | 39875176 | 39882154 | 1.000 | 1.04 × 10−6 | rs113214136 | 8.05 × 10−8 | 2.18 × 10−23 | rs113214136 | 2.30 × 10−24 |
| BMP8A | 1 | 39957318 | 39995541 | 0.703 | 2.74 × 10−6 | rs61779314 | 9.60 × 10−8 | 1.51 × 10−23 | rs72663520 | 3.10 × 10−25 |
| THADA | 2 | 43457975 | 43823185 | 0.062 | 6.29 × 10−8 | rs12712881 | 3.50 × 10−10 | 4.13 × 10−28 | rs80147536 | 2.70 × 10−30 |
| SLC9B1 | 4 | 103806205 | 103947552 | 0.520 | 3.47 × 10−6 | rs4645215 | 9.53 × 10−8 | 2.34 × 10−7 | rs13150953 | 6.70 × 10−9 |
| ANKDD1B | 5 | 74907301 | 74967671 | 0.499 | 4.80 × 10−11 | rs42854 | 9.39 × 10−13 | 2.27 × 10−12 | rs34341 | 5.70 × 10−14 |
| POC5 | 5 | 74970023 | 75013313 | 0.650 | 4.20 × 10−11 | rs42854 | 9.39 × 10−13 | 1.48 × 10−14 | rs2307111 | 3.30 × 10−16 |
| NEU1 | 6 | 31826829 | 31830709 | 0.010 | 1.38 × 10−7 | rs41267082 | 5.50 × 10−9 | 6.02 × 10−9 | rs9267653 | 2.40 × 10−10 |
| * SLC44A4 | 6 | 31830969 | 31846823 | 0.005 | 1.72 × 10−7 | rs74434374 | 4.51 × 10−9 | 4.58 × 10−14 | rs9267658 | 1.20 × 10−15 |
| * EHMT2 | 6 | 31847536 | 31865464 | 0.005 | 1.59 × 10−7 | rs74434374 | 4.51 × 10−9 | 4.22 × 10−14 | rs9267658 | 1.20 × 10−15 |
| * PLEKHA1 | 10 | 124134094 | 124191871 | 0.070 | 2.78 × 10−7 | rs76568359 | 6.38 × 10−9 | 8.73 × 10−12 | rs2280141 | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| CALCB | 11 | 15095143 | 15103888 | 0.011 | 4.56 × 10−7 | rs10741662 | 2.16 × 10−8 | 7.82 × 10−7 | rs74643981 | 3.70 × 10−8 |
| CELF1 | 11 | 47487489 | 47574792 | 1.000 | 9.73 × 10−7 | rs7124681 | 2.15 × 10−8 | 2.90 × 10−7 | rs7124681 | 6.40 × 10−9 |
| PTPMT1 | 11 | 47586888 | 47595013 | 1.000 | 3.77 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 2.86 × 10−8 | 1.21 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 9.20 × 10−9 |
| KBTBD4 | 11 | 47593749 | 47600567 | 1.000 | 4.50 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 2.86 × 10−8 | 1.45 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 9.20 × 10−9 |
| NDUFS3 | 11 | 47600562 | 47606115 | 1.000 | 3.06 × 10−7 | rs11039307 | 1.84 × 10−8 | 1.46 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 9.20 × 10−9 |
| FAM180B | 11 | 47608230 | 47610746 | 1.000 | 3.36 × 10−7 | rs11039307 | 1.84 × 10−8 | 1.60 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 9.20 × 10−9 |
| C1QTNF4 | 11 | 47611216 | 47615961 | 1.000 | 3.26 × 10−7 | rs11039307 | 1.84 × 10−8 | 1.55 × 10−7 | rs12798028 | 9.20 × 10−9 |
| MTCH2 | 11 | 47638858 | 47664206 | 1.000 | 1.11 × 10−7 | rs12419507 | 4.53 × 10−9 | 7.36 × 10−7 | rs11039324 | 3.00 × 10−8 |
| PSMA3 | 14 | 58711523 | 58738727 | 0.523 | 2.71 × 10−7 | rs9323331 | 8.89 × 10−9 | 2.59 × 10−6 | rs12892257 | 8.50 × 10−8 |
| * BCAR1 | 16 | 75262928 | 75301951 | 0.084 | 7.91 × 10−8 | rs2865826 | 1.07 × 10−9 | 8.87 × 10−22 | rs72802395 | 1.20 × 10−23 |
| * CFDP1 | 16 | 75327608 | 75467387 | 0.001 | 1.46 × 10−11 | rs34624768 | 1.71 × 10−13 | 8.56 × 10−13 | rs72804157 | 1.00 × 10−14 |
| * TMEM170A | 16 | 75477136 | 75498584 | 0.142 | 5.74 × 10−11 | rs1030261 | 1.38 × 10−12 | 2.20 × 10−9 | rs56258397 | 5.30 × 10−11 |
| * CHST6 | 16 | 75507022 | 75528926 | 0.088 | 2.86 × 10−7 | rs12924333 | 4.95 × 10−9 | 6.94 × 10−8 | rs72789426 | 1.20 × 10−9 |
| SUGP1 | 19 | 19387320 | 19431321 | 0.003 | 5.01 × 10−7 | rs74182632 | 1.43 × 10−8 | 2.94 × 10−13 | rs8107974 | 6.30 × 10−15 |
| MAU2 | 19 | 19431496 | 19469563 | 0.003 | 4.55 × 10−7 | rs34351431 | 1.48 × 10−8 | 1.10 × 10−11 | rs73001065 | 3.00 × 10−13 |
| GATAD2A | 19 | 19496642 | 19619741 | 0.002 | 1.95 × 10−6 | rs113920263 | 3.26 × 10−8 | 2.69 × 10−10 | rs3794991 | 4.50 × 10−12 |
| TSSK6 | 19 | 19625028 | 19626469 | 0.215 | 8.70 × 10−7 | rs34183201 | 5.24 × 10−8 | 1.83 × 10−7 | rs7252888 | 1.10 × 10−8 |
| NDUFA13 | 19 | 19626550 | 19639858 | 0.209 | 5.61 × 10−7 | rs34539063 | 2.70 × 10−8 | 2.29 × 10−7 | rs7252888 | 1.10 × 10−8 |
| CILP2 | 19 | 19649057 | 19657468 | 0.003 | 6.41 × 10−7 | rs34539063 | 2.70× 10−8 | 2.37 × 10−9 | rs17216525 | 1.00 × 10−10 |
| LPAR2 | 19 | 19734464 | 19739039 | 0.003 | 3.03 × 10−6 | rs2304129 | 1.73 × 10−7 | 2.98 × 10−9 | rs73004975 | 1.70 × 10−10 |
| EYA2 | 20 | 45523263 | 45817492 | 0.005 | 1.56 × 10−6 | rs6124969 | 7.81 × 10−9 | 1.67 × 10−8 | rs6063048 | 5.80 × 10−11 |
| L3MBTL2 | 22 | 41601312 | 41627276 | 0.243 | 1.99 × 10−6 | rs5751069 | 6.92 × 10−8 | 2.86 × 10−6 | rs2038209 | 1.20 × 10−7 |
| Gene | Chr | Start Position (hg19) | End Position (hg19) | LD Relationship between Top SNPs (r2) | Headache | T2D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene p-Value | Top SNP | Top SNP p-Value | Gene p-Value | Top SNP | Top SNP p-Value | |||||
| HLA-C | 6 | 31236526 | 31239913 | 0.06 | 3.11 × 10−6 | rs9264490 | 1.66 × 10−7 | 1.73 × 10−9 | rs9264533 | 9.00 × 10−11 |
| SLC44A4 | 6 | 31830969 | 31846823 | 0.03 | 3.77 × 10−6 | rs652888 | 9.05 × 10−8 | 5.00 × 10−14 | rs9267658 | 1.20 × 10−15 |
| EHMT2 | 6 | 31847536 | 31865464 | 0.03 | 3.77 × 10−6 | rs652888 | 9.05 × 10−8 | 4.99 × 10−14 | rs9267658 | 1.20 × 10−15 |
| CYP21A2 | 6 | 32006093 | 32009447 | 0.00 | 2.74 × 10−6 | rs433061 | 1.52 × 10−7 | 1.01 × 10−6 | rs115521560 | 5.60 × 10−8 |
| ATF6B | 6 | 32083045 | 32096017 | 0.01 | 1.71 × 10−6 | rs1269852 | 7.46 × 10−8 | 4.81 × 10−14 | rs3130342 | 2.10 × 10−15 |
| PLEKHA1 | 10 | 124134094 | 124191871 | 0.07 | 2.66 × 10−9 | rs78438709 | 5.37 × 10−11 | 1.04 × 10−11 | rs2280141 | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| BCAR1 | 16 | 75262928 | 75301951 | 0.08 | 4.79 × 10−7 | rs12928974 | 6.04 × 10−9 | 9.52 × 10−22 | rs72802395 | 1.20 × 10−23 |
| CFDP1 | 16 | 75327608 | 75467387 | 0.11 | 2.38 × 10−9 | rs3863442 | 2.48 × 10−11 | 1.05 × 10−12 | rs72804157 | 1.00 × 10−14 |
| TMEM170A | 16 | 75477136 | 75498584 | 0.14 | 5.40 × 10−9 | rs7198873 | 1.28 × 10−10 | 2.68 × 10−9 | rs56258397 | 5.30 × 10−11 |
| CHST6 | 16 | 75507022 | 75528926 | 0.09 | 2.65 × 10−7 | rs12446877 | 3.88 × 10−9 | 8.20 × 10−8 | rs72789426 | 1.20 × 10−9 |
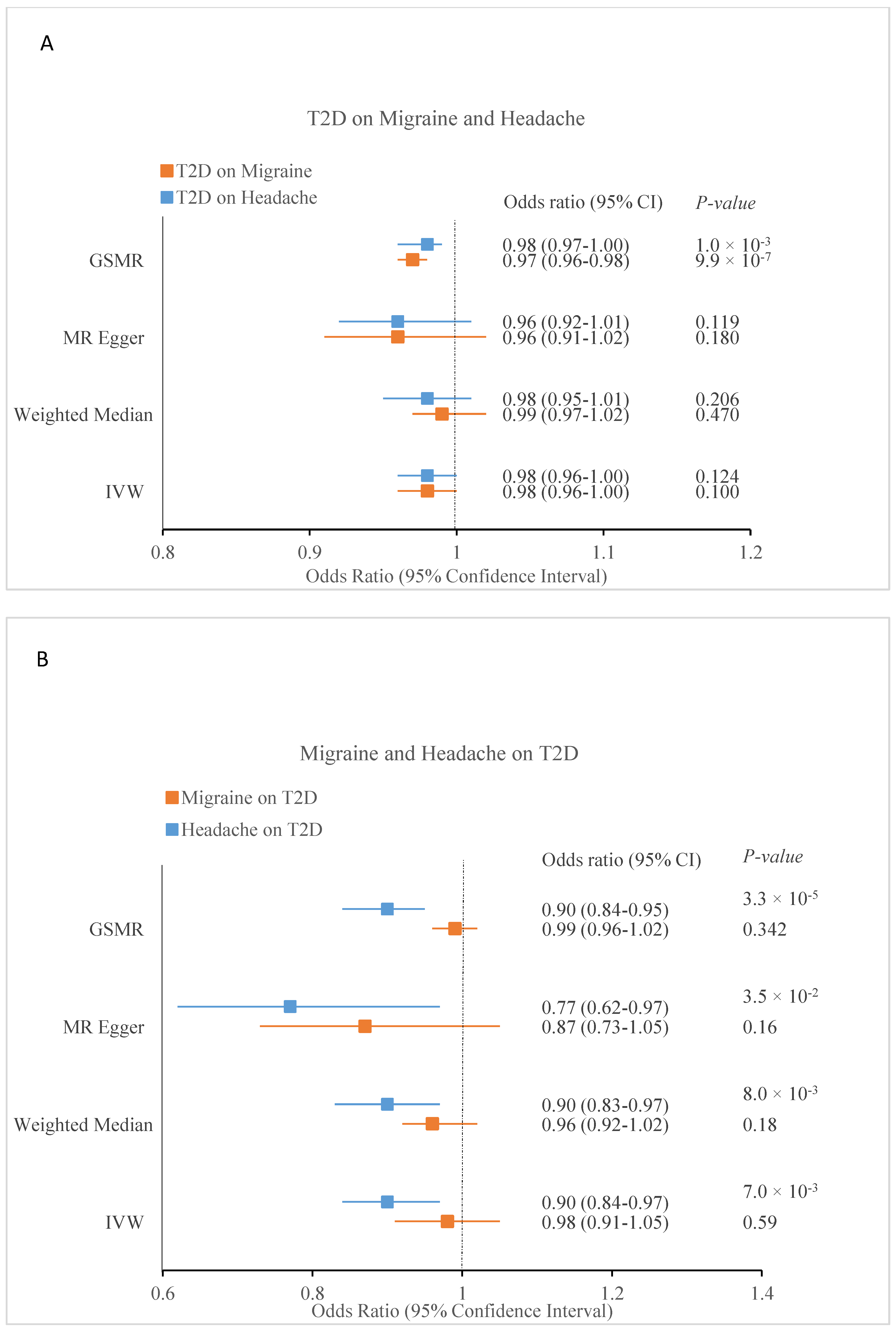
| Exposure | Outcome | nSNPs | IVW | Weighted Median | MR-Egger | MR-PRESSO | nSNPs | GSMR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR | p | Global p | OR (95% CI) | p | ||||
| T2D | Migraine | 195 | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.1 | 0.99 (0.97–1.02) | 0.47 | 0.96 (0.91–1.02) | 0.18 | 0.98 | 0.11 | <2 × 10−5 | 314 | 0.97 (0.96–0.98) | 9.9 × 10−7 |
| T2D | Headache | 195 | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.124 | 0.98 (0.95–1.01) | 0.206 | 0.96 (0.92–1.01) | 0.119 | 0.99 | 0.19 | <2 × 10−5 | 321 | 0.98 (0.97–1.00) | 0.01 |
| Migraine | T2D | 96 | 0.98 (0.91–1.05) | 0.59 | 0.96 (0.92–1.02) | 0.18 | 0.87 (0.73–1.05) | 0.16 | 1 | 0.89 | <2 × 10−5 | 117 | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) | 0.342 |
| Headache | T2D | 30 | 0.90 (0.84–0.97) | 0.007 | 0.90 (0.83–0.97) | 0.008 | 0.77 (0.62–0.97) | 0.035 | 0.9 | 7 × 10−5 | 4.7 × 10−3 | 35 | 0.90 (0.84–0.95) | 3.3 × 10−5 |
| T2D (M) | Migraine (M) | 19 | 1.02 (0.91–1.14) | 0.743 | 0.96 (0.81–1.12) | 0.592 | 0.97 (0.73–1.29) | 0.825 | 1.02 | 0.71 | 0.80 | 29 | 1.02 (0.92–1.12) | 0.69 |
| T2D (M) | Headache (M) | 33 | 0.97 (0.93–1.00) | 0.072 | 0.99 (0.94–1.04) | 0.711 | 0.93 (0.85–1.03) | 0.18 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 50 | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) | 0.43 |
| Migraine (M) | T2D (M) | 6 | 1.04 (0.93–1.15) | 0.499 | 1.01 (0.90–1.14) | 0.809 | 0.98 (0.46–2.07) | 0.958 | 1.04 | 0.53 | 0.19 | na * | - | - |
| Headache (M) | T2D (M) | 6 | 0.84 (0.71–0.99) | 0.049 | 0.83 (0.68–1.01) | 0.062 | 0.64 (0.18–2.21) | 0.519 | 0.84 | 0.007 | 0.96 | 74 * | 0.97 (0.90–1.04) | 0.37 |
| T2D (F) | Migraine (F) | 6 | 0.93 (0.85–1.02) | 0.117 | 0.96 (0.86–1.08) | 0.496 | 1.45 (0.58–3.64) | 0.464 | 0.93 | 0.076 | 0.78 | 16 | 0.93 (0.88–0.98) | 5.0 × 10−3 |
| T2D (F) | Headache (F) | 16 | 0.95 (0.92–0.98) | 0.001 | 0.97 (0.93–1.01) | 0.159 | 0.92 (0.85–1.00) | 0.066 | 0.95 | 0.004 | 0.11 | 27 | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | 4.0 × 10−3 |
| Migraine (F) | T2D (F) | 6 | 0.95 (0.74–1.21) | 0.666 | 0.96 (0.77–1.20) | 0.701 | 0.63 (0.12–3.34) | 0.613 | 0.95 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 27 * | 0.97 (0.97–1.17) | 0.21 |
| Headache (F) | T2D (F) | 21 | 1.04 (0.87–1.24) | 0.701 | 1.11 (0.90–1.37) | 0.343 | 1.15 (0.56–2.37) | 0.7 | 1.04 | 0.705 | 0.14 | 22 | 0.98 (0.83–1.13) | 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.R.; The International Headache Genetics Consortium (IHGC); Nyholt, D.R. Genetic Overlap Analysis Identifies a Shared Etiology between Migraine and Headache with Type 2 Diabetes. Genes 2022, 13, 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101845
Islam MR, The International Headache Genetics Consortium (IHGC), Nyholt DR. Genetic Overlap Analysis Identifies a Shared Etiology between Migraine and Headache with Type 2 Diabetes. Genes. 2022; 13(10):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101845
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Rafiqul, The International Headache Genetics Consortium (IHGC), and Dale R. Nyholt. 2022. "Genetic Overlap Analysis Identifies a Shared Etiology between Migraine and Headache with Type 2 Diabetes" Genes 13, no. 10: 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101845
APA StyleIslam, M. R., The International Headache Genetics Consortium (IHGC), & Nyholt, D. R. (2022). Genetic Overlap Analysis Identifies a Shared Etiology between Migraine and Headache with Type 2 Diabetes. Genes, 13(10), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101845






