Assessment of the Genetic Relationship and Population Structure in Oil-Tea Camellia Species Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. SSR Analysis
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of SSR Marker Diversity Levels
3.2. Genetic Diversity of Oil-Tea Camellia Species Based on SSR Analysis
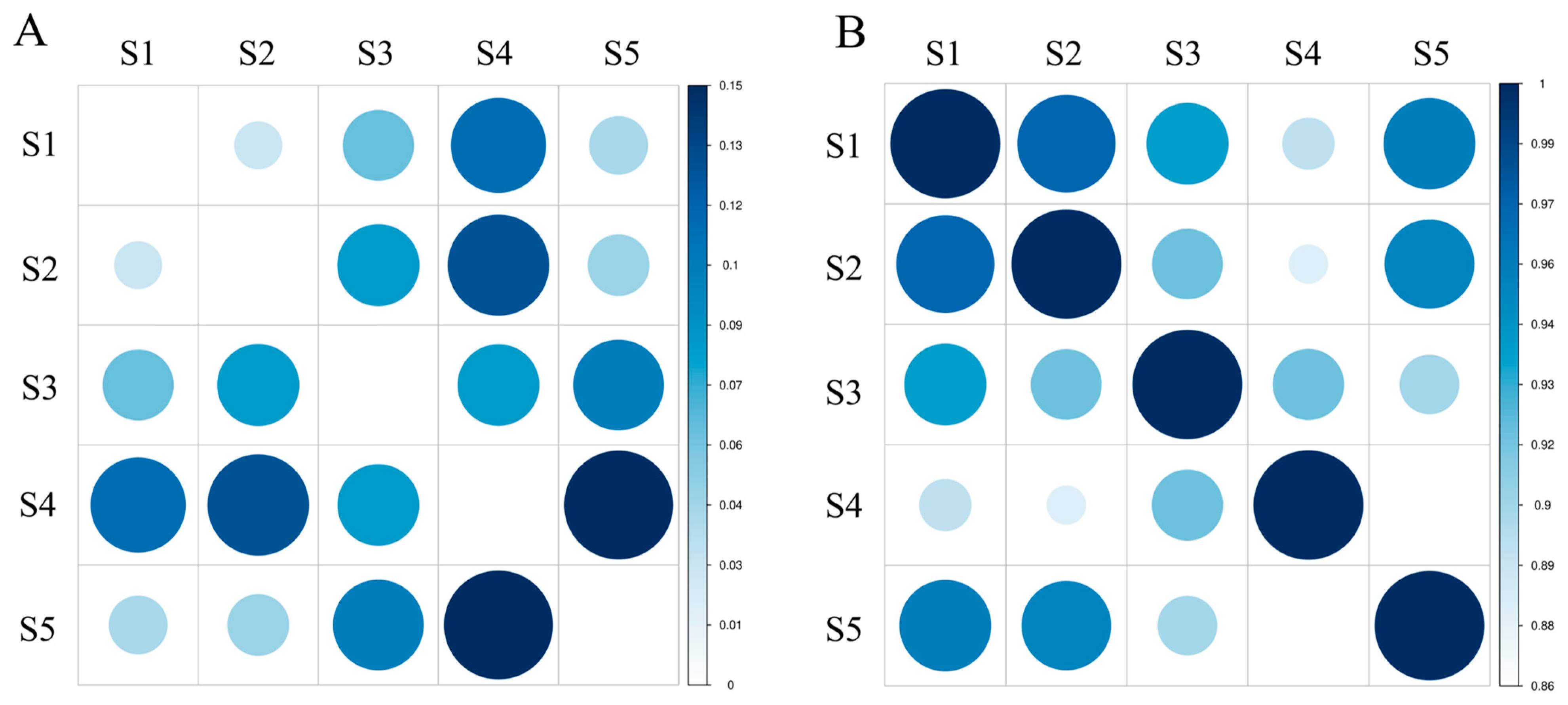
3.3. Analysis of Nei’s Genetic Distance between Species
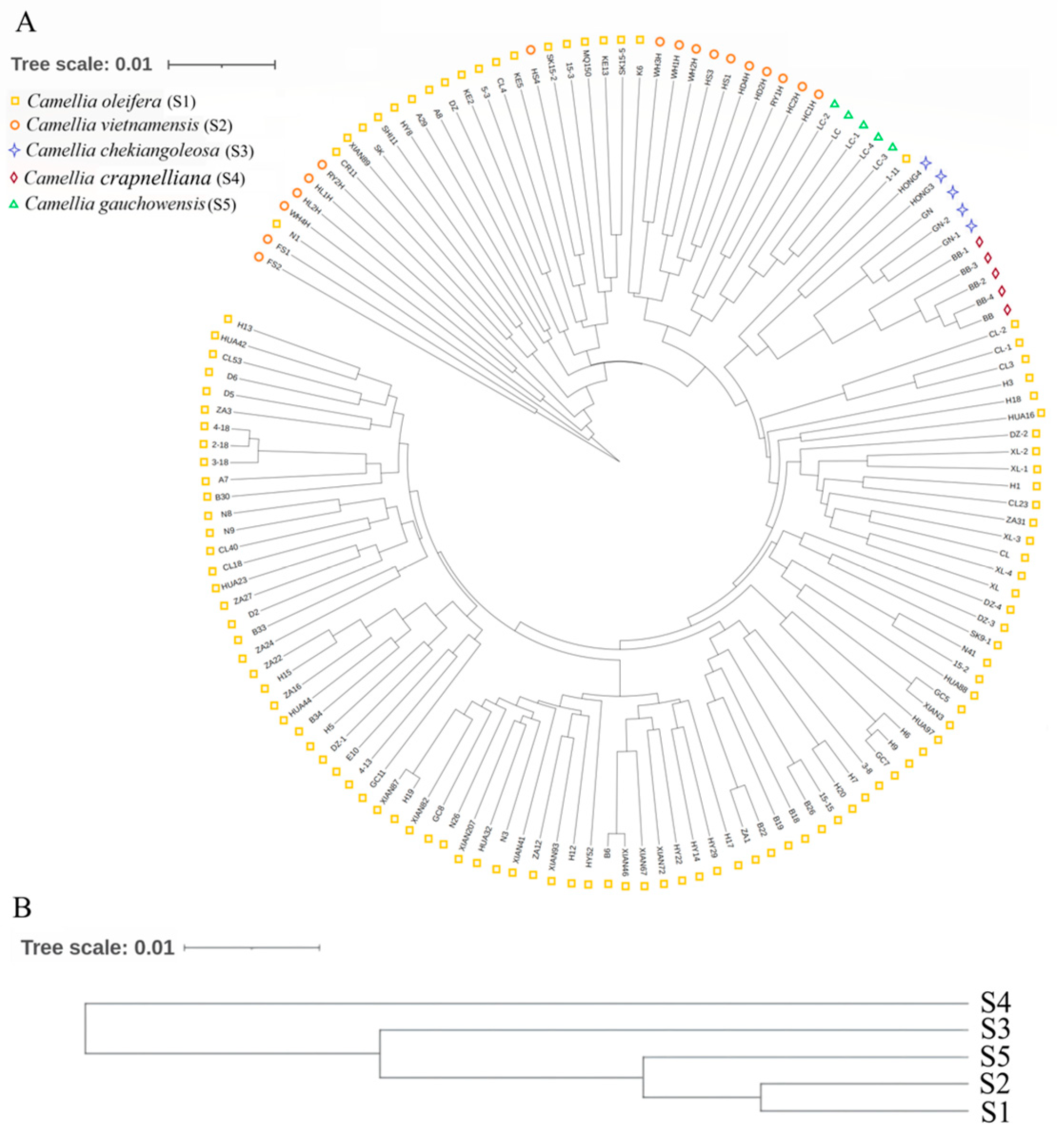
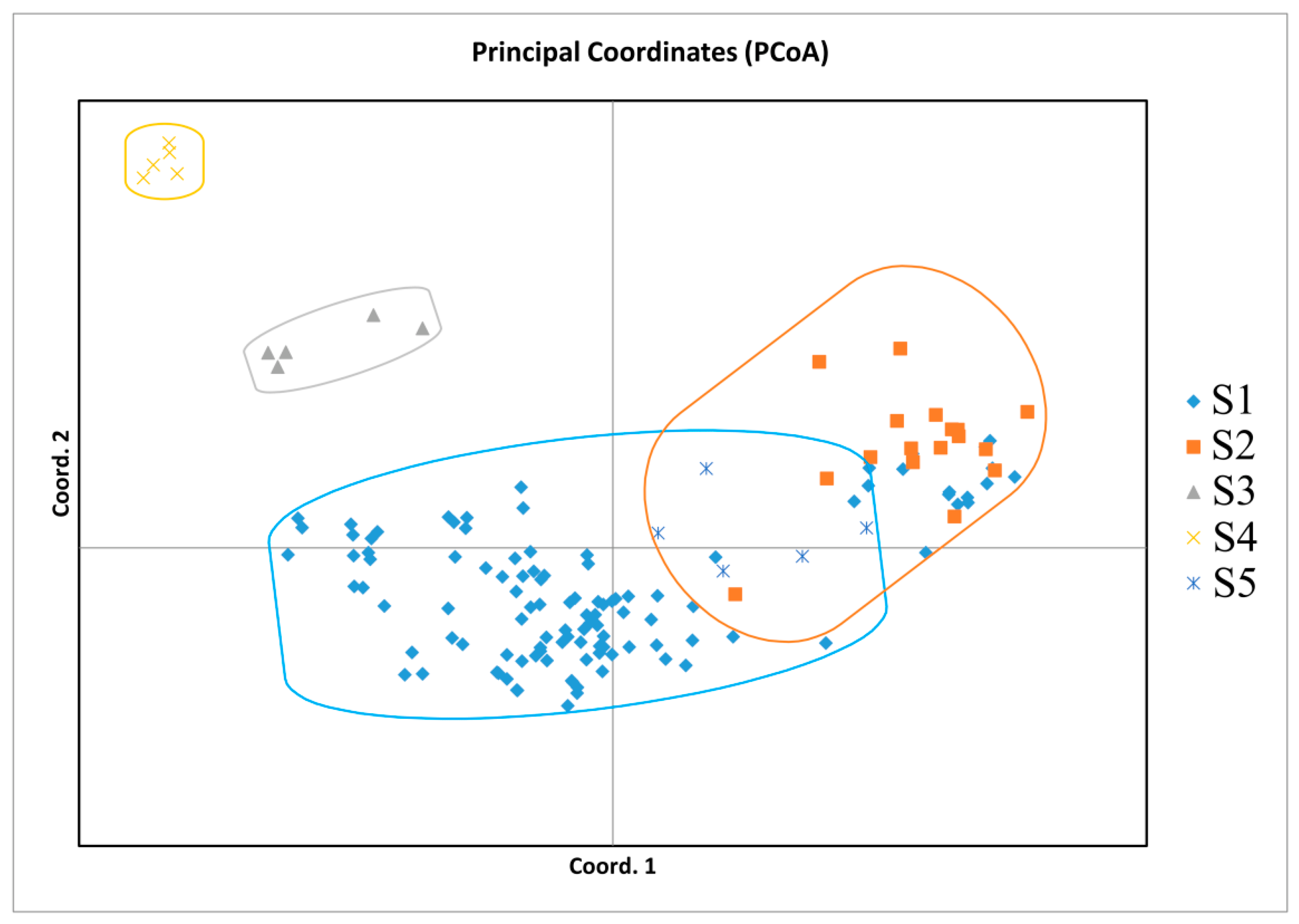
3.4. UPGMA and PCoA Analysis
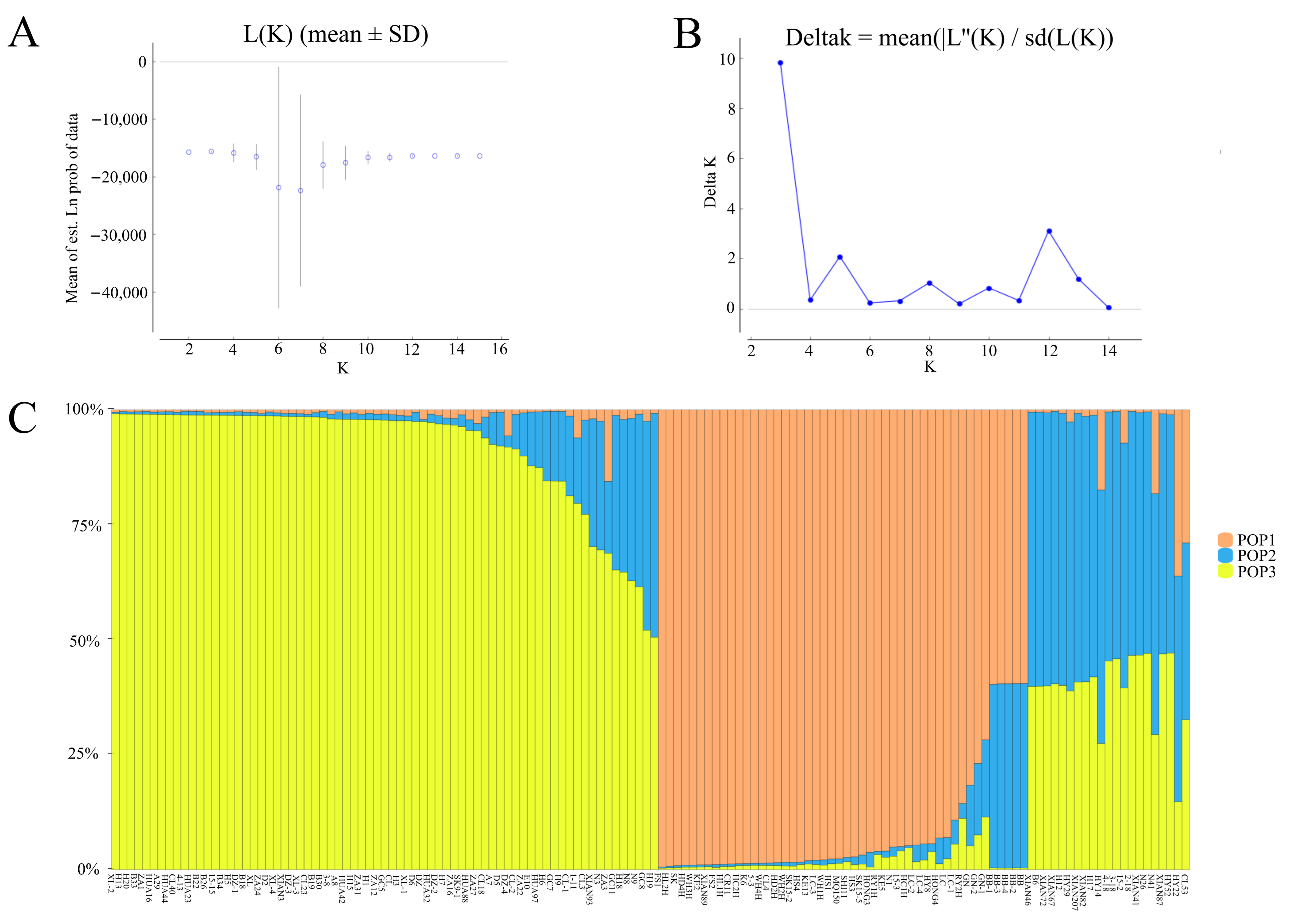
3.5. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis and Population Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.J.; Hu, X.W.; Zhou, K.B. Comparison of the chloroplast genome sequences of 13 oil-tea Camellia samples and identification of an undetermined oil-tea Camellia species from Hainan province. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 798581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.G.; Lin, Q.; Feng, Y.Z.; Hu, X.Y.; Tan, X.F.; Shao, F.G.; Zhang, L. Development and cross-species transferability of unigene-derived microsatellite markers in an edible oil woody plant, Camellia oleifera (Theaceae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 6906–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Deng, Z.; Liu, W.; Rehman, F.; Yang, T.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Gong, H.G. Development of expressed sequence tag simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) markers and genetic resource analysis of tea oil plants (Camellia spp.). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2022, 14, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Yang, Z.J.; Chen, S.P.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Chen, H. High throughput sequencing of small RNAs reveals dynamic microRNAs expression of lipid metabolism during Camellia oleifera and C. meiocarpa seed natural drying. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, P. Quality Evaluation of the Oil of Camellia spp. Foods 2022, 11, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, S.Y. Comparison of Oil Content and Fatty Acid Profifile of Ten New Camellia oleifera Cultivars. J. Lipids 2016, 2016, 3982486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.C.; Wu, Y.G.; Ul Haq Muhammad, Z.; Yan, W.P.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Yao, G.L.; Hu, X.W. Complementary transcriptome and proteome profiling in the mature seeds of Camellia oleifera from Hainan Island. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.N.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Yan, H.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.G.; Hu, X.W.; Lai, H.G. cDNA cloning, prokaryotic expression, and functional analysis of squalene synthase (SQS) in Camellia vietnamensis Huang. Protein Expres. Purif. 2022, 194, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.F.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.C.; Liao, Q.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Xiao, H.W.; Cao, Z.J.; Hu, S.Z. Postharvest Processing and Storage Methods for Camellia oleifera Seeds. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z. Determination of the evolutionary pressure on Camellia oleifera on Hainan Island using the complete chloroplast genome sequence. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Ma, C.L.; Yao, M.Z.; Jin, J.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, L. Microsatellite markers from tea plant expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and their applicability for cross-species/genera amplification and genetic mapping. Sci. Hortic. Amst. 2012, 134, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, R.K.; Rai, M.K.; Kalia, S.; Singh, R.; Dhawan, A.K. Microsatellite markers: An overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica 2010, 177, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, D.; Hu, J.; Jia, H. Analysis of the genetic diversity and population structure of Salix psammophila based on phenotypic traits and simple sequence repeat markers. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, F.; Fukuoka, H.; Tanaka, J. Expressed sequence tags from organ-specific cDNA libraries of tea (Camellia sinensis) and polymorphisms and transferability of EST-SSRs across Camellia species. Breed. Sci. 2012, 62, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Q.Y.; Su, X.J.; Ma, H.H.; Du, K.B.; Yang, M.; Chen, B.L.; Fu, S.; Fu, T.J.; Ciang, C.L.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Development of genic SSR marker resources from RNA-seq data in Camellia japonica and their application in the genus Camellia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dai, X.G.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, J.H.; Shi, J.S.; Yin, T.M. Discovery and experimental analysis of microsatellites in an oil woody plant Camellia chekiangoleosa. Plant Syst. Evol. 2013, 299, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.Z.; Tian, Y. Assessment of genetic diversity in Camellia oleifera Abel. accessions using morphological traits and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Breed. Sci. 2020, 70, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, C.; Tang, J.R.; Xin, Y.X.; Dong, Z.H.; Bai, B.; Xin, P.Y. Genetic diversity analysis of Camellia fascicularis H. T. Chang based on SSR markers. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aroma. 2022, 31, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Population genetic structure and interspecific introgressive hybridization between Camellia meiocarpa and C. oleifera. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Bin, X.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Yellow Camellia (Camellia nitidissima) in China as Revealed by RAPD and AFLP Markers. Biochem. Genet. 2006, 44, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynov, M.; Suleymanova, Z.; Ojaghi, J.; Mammadov, A. Characterization and Phylogeny Analysis of Azerbaijan Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Genotypes by Molecular Markers. Cytol. Genet. 2022, 56, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, L.P.; Chen, Y.Z.; Jiang, X.C. Genetic diversity of oil-tea camellia germplasms revealed by ISSR analysis. Int. J. Biomath. 2015, 08, 1550070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Tang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; He, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; et al. Assessment of genetic diversity in Camellia oleifera Abel. accessions using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphic markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, P. Integrative Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Regulatory Network of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Response to MeJA in Camellia vietnamensis Huang. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.M.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Lai, H.G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, J.; Pang, Z.Z. Development and evaluation of Hainan Camellia SSR molecular marker basrd on transcriptome data. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 1–19. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220316.2203.008.html (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Gu, X.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Ma, X.; Bai, S.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, C.B.; Chen, S.Y.; Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.H.; Huang, L.K.; et al. Population genetic variability and structure of Elymus breviaristatus (Poaceae: Triticeae) endemic to Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau inferred from SSR markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 58, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.D.; Liu, W.H.; Sun, M.; Zhou, J.Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Peng, Y.; Huang, L.K.; Ma, X. Genetic diversity and structure of Elymus tangutorum accessions from Western China as unrevealed by AFLP markers. Hereditas 2019, 156, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. J. Ecol. 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Genetic Distance between Populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Ma, X.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, D. Revelation of genetic diversity and structure of wild Elymus excelsus (Poaceae: Triticeae) collection from western China by SSR markers. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.S.; Regnaut, S.J.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.F.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Zou, R.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, X. Genetic diversity analysis of endangered plant Camellia pubipetala detected by ISSR. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2014, 34, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najaphy, A.; Parchin, R.A.; Farshadfar, E. Evaluation of genetic diversity in wheat cultivars and breeding lines using inter simple sequence repeat markers. Biotechnol. Biotec. Eq. 2011, 25, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.S.; Dai, J.N.; Yang, Y.N.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, L.C.; Wu, Y.G.; Lai, H.G.; Hu, X.W.; Yu, J. Identification of Camellia oleifera seed DNA barcode based on trnH-psbA and matK sequence. Mol. Plant Breed. 2019, 17, 5057–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.N.; Yu, J.; Qi, H.S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.G.; Lai, H.G.; Hu, X.W. DNA Barcoding Identification of Different Species in Camellia Based on trnH-psbA and matK Sequences. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2021, 42, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
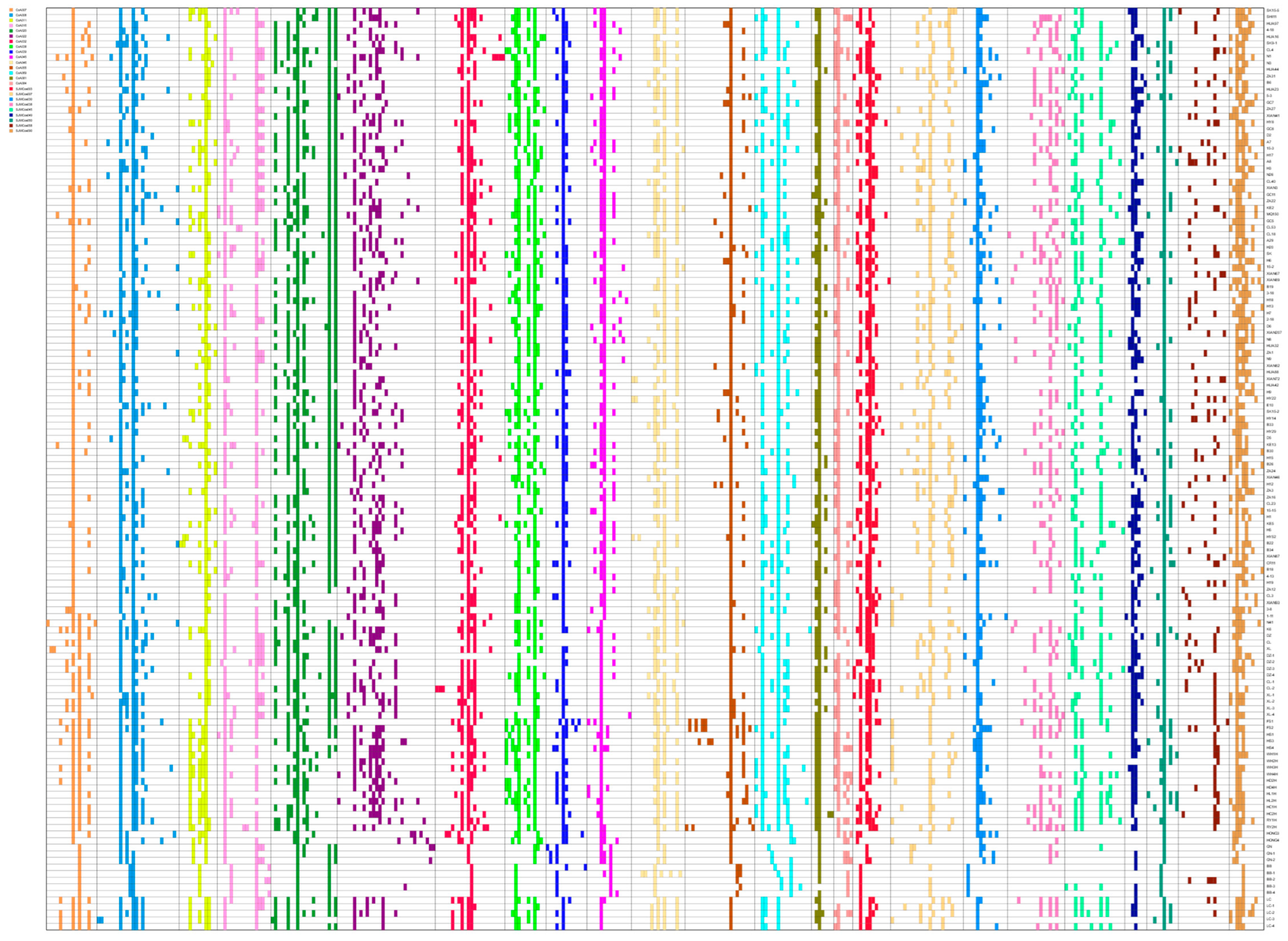

| No. | Name | Tissue | species | Group | Origin | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1_11 | Leaves | C. oleifera | S1 | Nursery of oil-tea camellia germplasm resources, Danzhou campus, Hainan University, China | 109°29′45″ E, 19°30′28″ N |
| 2 | 15_15 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 3 | 15_2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 4 | 15_3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 5 | 2_18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 6 | 3_18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 7 | 3_8 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 8 | 4_13 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 9 | 4_18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 10 | 5_3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 11 | A29 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 12 | A7 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 13 | A8 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 14 | B18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 15 | B19 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 16 | B22 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 17 | B26 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 18 | B30 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 19 | B33 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 20 | B34 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 21 | B6 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 22 | CL18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 23 | CL23 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 24 | CL3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 25 | CL40 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 26 | CL4 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 27 | CL53 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 28 | CR11 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 29 | D2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 30 | D5 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 31 | D6 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 32 | E10 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 33 | GC11 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 34 | GC5 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 35 | GC7 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 36 | GC8 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 37 | H12 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 38 | H13 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 39 | H15 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 40 | H17 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 41 | H18 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 42 | H19 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 43 | H1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 44 | H20 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 45 | H3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 46 | H5 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 47 | H6 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 48 | H7 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 49 | H9 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 50 | HUA16 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 51 | HUA23 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 52 | HUA32 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 53 | HUA42 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 54 | HUA44 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 55 | HUA88 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 56 | HUA97 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 57 | HY14 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 58 | HY22 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 59 | HY29 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 60 | HY52 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 61 | HY8 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 62 | K6 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 63 | KE13 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 64 | KE2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 65 | KE5 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 66 | MQ150 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 67 | N1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 68 | N26 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 69 | N3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 70 | N41 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 71 | N8 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 72 | N9 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 73 | SHI11 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 74 | SK15-2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 75 | SK15-5 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 76 | SK9-1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 77 | SK | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 78 | XIAN207 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 79 | XIAN3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 80 | XIAN41 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 81 | XIAN46 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 82 | XIAN67 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 83 | XIAN72 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 84 | XIAN82 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 85 | XIAN87 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 86 | XIAN89 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 87 | XIAN93 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 88 | ZA12 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 89 | ZA16 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 90 | ZA1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 91 | ZA22 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 92 | ZA24 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 93 | ZA27 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 94 | ZA31 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 95 | ZA3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 96 | FS1 | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Fansai Village, Wuzhishan City, Hainan Province | 109°32′24″ E, 18°50′37″ N | |
| 97 | FS2 | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 98 | HC1H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Fushan Town, Chengmai County, Hainan Province | 109°54′55″ E, 19°52′20″ N | |
| 99 | HC2H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 100 | HD2H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Shangke Town, Qionghai City, Hainan Province | 110°20′39″ E, 19°04′20″ N | |
| 101 | HD4H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 102 | HL1H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Qiongshan Area, Haikou City, Hainan Province | 110°21′54″ E, 19°59′25″ N | |
| 103 | HL2H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 104 | HS1 | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Hongshan Village, Wuzhishan City, Hainan Province | 109°30′56″ E, 18°51′35″ N | |
| 105 | HS3 | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 106 | HS4 | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 107 | RY1H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Wencheng Town, Wenchang City, Hainan Province | 110°47′38″ E, 19°33′13″ N | |
| 108 | RY2H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 109 | WH1H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | Wanling Town, Qiongzhong County, Hainan Province | 109°53′48″ E, 19°08′35″ N | |
| 110 | WH2H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 111 | WH3H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 112 | WH4H | C. vietnamensis | S2 | |||
| 113 | HONG3 | C. chekiangoleosa | S3 | Wuzhishan City, Hainan Province | 109°30′57″ E, 18°46′29″ N | |
| 114 | HONG4 | C. chekiangoleosa | S3 | |||
| 115 | CL | Seeds | C. oleifera | S1 | Xixiangtang Area, Nanning City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region | 108°21′7″ E, 22°55′6″ N |
| 116 | CL-1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 117 | CL-2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 118 | DZ | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 119 | DZ-1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 120 | DZ-2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 121 | DZ-3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 122 | DZ-4 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 123 | XL | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 124 | XL-1 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 125 | XL-2 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 126 | XL-3 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 127 | XL-4 | C. oleifera | S1 | |||
| 128 | GN | C. chekiangoleosa | S3 | |||
| 129 | GN-1 | C. chekiangoleosa | S3 | |||
| 130 | GN-2 | C. chekiangoleosa | S3 | |||
| 131 | BB | C. crapnelliana | S4 | |||
| 132 | BB-1 | C. crapnelliana | S4 | |||
| 133 | BB-2 | C. crapnelliana | S4 | |||
| 134 | BB-3 | C. crapnelliana | S4 | |||
| 135 | BB-4 | C. crapnelliana | S4 | |||
| 136 | LC | C. gauchowensis | S5 | |||
| 137 | LC-1 | C. gauchowensis | S5 | |||
| 138 | LC-2 | C. gauchowensis | S5 | |||
| 139 | LC-3 | C. gauchowensis | S5 | |||
| 140 | LC-4 | C. gauchowensis | S5 |
| No. | Locus | Repeat Unit | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence | Pre Experiment Size (bp) | Fluorescent Dyes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoA007 | (TCT)6 | CCAATCTCCAAACGCAACTT | CAGAGGAAATCGAGAGGCAG | 245 | FAM |
| 2 | CoA008 | (ATAG)6 | CCAGCCAGCTAAGAGGTTTG | CAGGTCATAGCTACCACGGA | 188 | FAM |
| 3 | CoA011 | (CTT)5 | TGGGTGGCTCAATATCATCA | ACCGGCCATTTATATGGGTT | 200 | FAM |
| 4 | CoA016 | (ATC)6 | GTAAGTCTCTGCACCGCCTC | TCGATTTCGTCCAATCCTTC | 211 | FAM |
| 5 | CoA020 | (AGG)6 | AGGGCATAAGAGGGAGTGGT | CGACCTCGACCTTCAAGAAC | 207 | FAM |
| 6 | CoA022 | (GA)12 | TAGCCAATAACATGCCCACA | AGTTGTCCAACCCTTCCTCA | 147 | FAM |
| 7 | CoA032 | (GCG)5 | TTATTCTTCGGGAACAACGG | ACACATGAAACAACGGCAAA | 170 | FAM |
| 8 | CoA038 | (GTG)7 | GAGATCGGCCAGAGTTTGAG | CATCAAAGCCACACTCGCTA | 202 | FAM |
| 9 | CoA039 | (TTA)6 | GCAAGAGGTCTCTTTGGGTG | AACCTCATGAGCTAAAGCCG | 113 | FAM |
| 10 | CoA045 | (ACC)5 | TCCAAACAGGCCAACTAAGC | GCTTGAGAAACCCAAAGCAG | 244 | FAM |
| 11 | CoA046 | (TAAC)4 | AACCAGAGGAACATCCAACG | TATCCTTGCCGCTTTGAATC | 196 | FAM |
| 12 | CoA055 | (CAT)6 | TCTGGTGTGCTTCAAACTGC | GCTCCAGCAAATATTCAGGC | 265 | FAM |
| 13 | CoA069 | (TGC)6 | CATGGCTTGGCTTCAATCTT | CAATGTTCCCAAGCGATTCT | 224 | FAM |
| 14 | CoA081 | (CAA)5 | ATATGAATCGGCCAATCGAC | AGATGACGCCTTTCGAAGAA | 154 | FAM |
| 15 | CoA084 | (GTG)6 | GACGGCTTAAACATGGAGGA | TTCATTTAATGGCAGGAGGC | 110 | FAM |
| 16 | SJMCoa003 | (CAA)7 | ACGAAACATGTCGGACGTGA | GGGAATGGACGAGACTTGGG | 120 | FAM |
| 17 | SJMCoa007 | (TTC)6 | GCAGCAGCGAGAGTAACAGT | GTGGGACGATTGAGCTTCCT | 149 | FAM |
| 18 | SJMCoa030 | (CCT)10 | GGTGTGGTGGTGAAGCAGTA | TTGTCTGGATCCATAGCCGC | 248 | FAM |
| 19 | SJMCoa038 | (TTAT)5 | TGCTTGGTCACTACCCAGTC | TGACACCTTGGTGCCAAAGA | 266 | FAM |
| 20 | SJMCoa045 | (AAT)5 | TTTGGGCGGGCAAAGATTTG | ACTCAAGCATGGACATCGGG | 276 | FAM |
| 21 | SJMCoa049 | (AAT)5 | AAGACCCAAACTGGACTGCA | ACCTTGCACCATAATGGGTT | 254 | FAM |
| 22 | SJMCoa050 | (AAT)7 | TGGAGCGTTAGTCTGGAGTC | GGCCTCTCATCCATGTCAGG | 249 | FAM |
| 23 | SJMCoa058 | (CCA)9 | GTGCCCTGTGACACCAAGTA | CGACGGTGGAGATTTGGTGA | 245 | FAM |
| 24 | SJMCoa090 | (TCA)9 | ACAGAAGGCGTTTGAGTCAA | GGCTTCTTCTTCGGAACCCA | 165 | FAM |
| Locus | Product Size (bp) | Number of Alleles | Ne | h | I | Gst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoA007 | 176–257 | 16 | 1.0072–1.6880 | 0.0071–0.4076 | 0.0237–0.5976 | 0.0037–0.7133 | 0.2010–134.0618 |
| CoA008 | 138–230 | 26 | 1.0072–1.7521 | 0.0071–0.4293 | 0.0237–0.6206 | 0.0037–0.7981 | 0.0029–134.0618 |
| CoA011 | 167–206 | 12 | 1.0072–1.5542 | 0.0071–0.3566 | 0.0237–0.5393 | 0.0037–1.0000 | 0–134.0618 |
| CoA016 | 208–367 | 17 | 1.0072–1.7183 | 0.0071–0.3833 | 0.0237–0.6088 | 0.0037–0.7853 | 0.1367–134.0618 |
| CoA020 | 164–256 | 21 | 1.0072–2.0000 | 0.0071–0.5000 | 0.0237–0.6931 | 0.0037–0.6424 | 0.2783–134.0618 |
| CoA022 | 127–184 | 31 | 1.0072–1.9468 | 0.0071–0.4863 | 0.0237–0.6794 | 0.0037–0.7032 | 0.2110–134.0618 |
| CoA032 | 130–204 | 22 | 1.0072–1.9872 | 0.0071–0.4968 | 0.0237–0.6899 | 0.0037–0.6555 | 0.2628–134.0618 |
| CoA038 | 192–221 | 13 | 1.0072–1.9619 | 0.0071–0.4903 | 0.0237–0.6834 | 0.0037–0.6220 | 0.3038–134.0618 |
| CoA039 | 103–126 | 13 | 1.0073–1.5290 | 0.0072–0.3460 | 0.0240–0.4973 | 0.0162–0.6118 | 0.3172–30.4262 |
| CoA045 | 237–288 | 14 | 1.0072–1.9993 | 0.0071–0.4998 | 0.0237–0.6930 | 0.0037–0.7650 | 0.1536–134.0618 |
| CoA046 | 169–208 | 17 | 1.0072–1.9983 | 0.0071–0.4996 | 0.0237–0.6927 | 0.0037–0.5994 | 0.3126–134.0618 |
| CoA055 | 151–313 | 22 | 1.0073–1.2904 | 0.0072–0.2250 | 0.0240–0.3849 | 0.0112–1.0000 | 0–44.0603 |
| CoA069 | 211–266 | 18 | 1.0072–1.9155 | 0.0071–0.4779 | 0.0237–0.6709 | 0.0037–0.8486 | 0.1211–134.0618 |
| CoA081 | 150–184 | 7 | 1.0073–1.9835 | 0.0072–0.4959 | 0.0240–0.6890 | 0.0112–0.5857 | 0.3537–44.0603 |
| CoA084 | 106–119 | 6 | 1.0072–1.6058 | 0.0071–0.3773 | 0.0237–0.5648 | 0.0037–0.4816 | 0.5381–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa003 | 126–167 | 12 | 1.0072–1.9971 | 0.0071–0.4993 | 0.0237–0.6924 | 0.0037–0.6596 | 0.2581–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa007 | 224–311 | 23 | 1.0072–1.9989 | 0.0071–0.4997 | 0.0237–0.6929 | 0.0037–0.4972 | 1.0755–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa030 | 238–277 | 14 | 1.0072–1.7639 | 0.0071–0.4331 | 0.0237–0.6246 | 0.0037–1 | 0–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa038 | 273–304 | 18 | 1.0072–1.8695 | 0.0071–0.4651 | 0.0237–0.6578 | 0.0037–0.2993 | 1.1705–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa045 | 291–317 | 19 | 1.0073–1.9215 | 0.0072–0.4796 | 0.0240–0.6726 | 0.0075–0.3244 | 1.0415–66.5610 |
| SJMCoa049 | 270–286 | 7 | 1.0072–1.9989 | 0.0071–0.4997 | 0.0237–0.6929 | 0.0037–0.3559 | 0.9048–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa050 | 253–273 | 10 | 1.0072–1.3412 | 0.0071–0.2544 | 0.0237–0.4219 | 0.0037–1.0000 | 0–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa058 | 197–266 | 16 | 1.0072–1.5438 | 0.0071–0.3522 | 0.0237–0.5371 | 0.0037–0.2238 | 1.7344–134.0618 |
| SJMCoa090 | 173–203 | 11 | 1.0218–1.9829 | 0.0213–0.4957 | 0.0596–0.6888 | 0.0112–0.5934 | 0.3426–44.0603 |
| Mean | 16.0417 | 1.1676 | 0.1104 | 0.1890 | 0.3948 | 0.7666 |
| Group | N | Na | Ne | Is | h | uh | P (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 108 | 1.605 | 1.197 | 0.214 | 0.128 | 0.130 | 79.48 |
| S2 | 17 | 0.969 | 1.195 | 0.193 | 0.121 | 0.122 | 45.97 |
| S3 | 5 | 0.434 | 1.140 | 0.119 | 0.081 | 0.101 | 20.52 |
| S4 | 5 | 0.200 | 1.041 | 0.041 | 0.027 | 0.033 | 7.79 |
| S5 | 5 | 0.468 | 1.116 | 0.104 | 0.070 | 0.087 | 18.70 |
| Mean | 28 | 0.735 | 1.138 | 0.134 | 0.086 | 0.096 | 34.49 |
| Variation Source | df | SS | MS | Est. Var. | PMV (%) | Fst | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among Pops | 4 | 485.260 | 121.315 | 7.197 | 23 | 0.231 | 0.001 |
| Within Pops | 135 | 3240.862 | 24.006 | 24.006 | 77 | ||
| Total | 139 | 3726.121 | 31.203 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Qi, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, J. Assessment of the Genetic Relationship and Population Structure in Oil-Tea Camellia Species Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers. Genes 2022, 13, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112162
Yan H, Qi H, Li Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Yu J. Assessment of the Genetic Relationship and Population Structure in Oil-Tea Camellia Species Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers. Genes. 2022; 13(11):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112162
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Heqin, Huasha Qi, Yang Li, Yougen Wu, Yong Wang, Jianmiao Chen, and Jing Yu. 2022. "Assessment of the Genetic Relationship and Population Structure in Oil-Tea Camellia Species Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers" Genes 13, no. 11: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112162
APA StyleYan, H., Qi, H., Li, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, J., & Yu, J. (2022). Assessment of the Genetic Relationship and Population Structure in Oil-Tea Camellia Species Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers. Genes, 13(11), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112162







