Abstract
Physalis angulata var. villosa, rich in withanolides, has been used as a traditional Chinese medicine for many years. To date, few extensive molecular studies of this plant have been conducted. In the present study, the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was sequenced, characterized and compared with that of other Physalis species, and a phylogenetic analysis was conducted in the family Solanaceae. The plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was 156,898 bp in length with a GC content of 37.52%, and exhibited a quadripartite structure typical of land plants, consisting of a large single-copy (LSC, 87,108 bp) region, a small single-copy (SSC, 18,462 bp) region and a pair of inverted repeats (IR: IRA and IRB, 25,664 bp each). The plastome contained 131 genes, of which 114 were unique and 17 were duplicated in IR regions. The genome consisted of 85 protein-coding genes, eight rRNA genes and 38 tRNA genes. A total of 38 long, repeat sequences of three types were identified in the plastome, of which forward repeats had the highest frequency. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) analysis revealed a total of 57 SSRs, of which the T mononucleotide constituted the majority, with most of SSRs being located in the intergenic spacer regions. Comparative genomic analysis among nine Physalis species revealed that the single-copy regions were less conserved than the pair of inverted repeats, with most of the variation being found in the intergenic spacer regions rather than in the coding regions. Phylogenetic analysis indicated a close relationship between Physalis and Withania. In addition, Iochroma, Dunalia, Saracha and Eriolarynx were paraphyletic, and clustered together in the phylogenetic tree. Our study published the first sequence and assembly of the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa, reported its basic resources for evolutionary studies and provided an important tool for evaluating the phylogenetic relationship within the family Solanaceae.
1. Introduction
Physalis angulata L. var. villosa Bonati belongs to the family Solanaceae and has important potential pharmaceutical value [1,2]. It is distributed mainly in Vietnam and the Hubei, Jiangxi and Yunnan Provinces of China [3]. It is interesting to note that, unlike other Physalis plants, P. angulata var. villosa has a remarkable characteristic: its whole body is covered with short white fluff (Figure 1) [1]. Additionally, more importantly, P. angulata var. villosa has been widely used for various traditional medicinal treatments in China. P. angulata var. villosa is rich not only in minerals and antioxidants, but also in a range of pharmacologically-active withanolides, including physagulins A–Q, withangulatins A−I, physangulidines A−C, physalins B, D, F, G, and H, withaminimin, physangulatins A−N, and withaphysalins Y and Z, and many of them have anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial or anti-cancer activities [2,4]. P. angulata var. villosa also has important edible and ornamental values, so it is much appreciated by people in China [1,5].

Figure 1.
Plant morphology of P. angulata var. villosa in natural habitats.
Although studies into several pharmacologically active ingredients and their functions have been carried out in P. angulata var. villosa over the past few decades, no exclusive genetic or genomic studies of this plant have been conducted to date. Plastomes (or named chloroplast genomes) play an important role in carbon fixation and stress response in plants, and the plastome is an important organelle in plant cells [6]. The plastomes of most land plants have typical, highly conserved four-part structures: one large single-copy (LSC) region, one small single-copy (SSC) region and a pair of inverted repeats (IR), with the plastome size ranging from 120 to 170 kb [7,8]. Compared with nuclear DNA sequences, the gene content and gene composition of plastomes are relatively conservative, and their evolutionary rate is relatively slow [9,10]. In addition, many studies have observed expansion, contraction, and reversal or gene rearrangement events in the plastomes of angiosperms, which may be the result of differential rates of insertions/deletions (indels) and substitutions during plant evolution [11,12,13,14]. With the rapid development of next-generation sequencing technology, more and more plant plastomes have been sequenced and have been widely used in plant phylogeny, taxonomy and identification [15,16,17,18,19].
In recent years, the identification and systematic classification of Physalis species and the phylogenetic relationships within Solanaceae have become a focus of attention for researchers [1,20,21]. Olmstead et al. (2008) studied the phylogenic relationships of Solanaceae based on the chloroplast DNA regions ndhF and trnLF, the results of which not only provided a framework phylogeny of Solanaceae, but also reveal some problems that still require further study [21]. For example, the study showed that genera appear to be non-monophyletic, including Lycianthes, Lycium and Physalis, etc. [21]. Prior to the current study, universal DNA barcoding sequences, such as the plastid psbA–trnH intergenic spacer region [22], nuclear internal transcribed spacers (ITSs) [1,20] and some traditional molecular markers, such as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) [23] and inter simple sequence repeats (ISSRs) [24,25], have been used to identify species and to construct phylogenies of Physalis species. However, specific nuclear or plastid gene sequences are relatively short, providing only limited genetic information, and have proved unsuccessful for distinguishing very closely related species [6]. Thus, the phylogenetic trees constructed from such sequences need more advanced techniques and methods for verification. By contrast, most plant plastomes can provide significant quantities of genetic information at the genome-wide evolutionary level and can improve the identification of plant species and better elucidate the relationship between plant taxonomy and phylogeny [26,27,28]. The abundance of plastome sequencing data has accelerated the progress of research into the relationship between plant evolution and phylogeny [6,29]. Increasingly, plastome sequences have been used by researchers to study phylogenetic relationships at different taxonomic levels [27,30,31,32].
In the present study, we sequenced and characterized the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa and compared the genome with plastomes from other solanaceous species. The purpose of our study was to examine both the phylogenetic relationships and the plastome evolution of P. angulata var. villosa within the Solanaceae. In addition, we also identified SSRs, repeat sequences and the hotspots of sequence variation in Physalis species, which might provide some important information for the development of polymorphic molecular markers for germplasm identification and evolutionary studies of Physalis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
P. angulata var. villosa plants were collected from Hangzhou (30°20′84′′ N, 120°21′20.1′′ E) in Zhejiang Province, China and their identity was confirmed by Prof. Huizhong Wang (Hangzhou Normal University). The voucher sample was deposited in the Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Genetic Improvement and Quality Control of Medicinal Plants, Hangzhou Normal University, China (Voucher specimen PHZ002). No permission was necessary for the collection of P. angulata var. villosa, which is widely distributed in China and is not listed among the national key protected plants.
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
Total genomic DNA was extracted from 0.15 g of fresh leaf material (pooled equal weights of leaves from six individual P. angulata var. villosa plants) using the Plant Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Technology and Service Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.3. Library Construction, Sequencing and Assembly
The genomic DNA was sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform. The sequencing work was carried out at the Germplasm Bank of Wild Species in Southwest China, Kunming Institution of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China. Raw reads were filtered using the NGS QC Toolkit v. 2.3.3 [33] with a cut-off value of 80 for the percentage of read lengths and a cut-off value of 30 for PHRED quality scores. The plastome assembly, using the high-quality clean reads, was conducted using CLC genomics workbench 8 [34] and SOAPdenovo [35] with a k mer of 63 and a minimum overlap length of 1 kb. The plastome of Physalis peruviana (GenBank accession number: MH019242) was used as the reference sequence for genome assembly.
2.4. Genome Annotation and Sequence Analysis
The online plastid genome annotation program Dual Organellar GenoMe Annotator (DOGMA) [36] was used to annotate the genes in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome. The positions of the start and stop codons were checked manually. The tRNAscan-SE v2.0 [37] software was used to confirm the tRNA genes. Organellar Genome Draw (ORGDRAW) [38] was used to draw the map of the plastome. The complete plastome sequence of P. angulata var. villosa was submitted to GenBank (Accession number OM257167). MEGA7 [39] was used to analyze the relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU), codon usage and base composition. The RNA editing sites in the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was predicted using the PREP suite with a cut-off value of 8.0 [40].
2.5. Repeat Sequence Analysis
Long repeat sequences were detected using the online program REPuter [41] with the following parameters: cut-off n ≥ 30 bp, a Hamming distance of 3, and a 90% similarity among repeat units. The Perl script MIcroSAtellite (MISA) program [42] was used to detect SSRs with the following settings: ten repeat units for mononucleotide, five for dinucleotide, four for trinucleotide, and three for tetra-, penta-, or hexanucleotide SSR motifs.
2.6. Genome Comparison
The online software mVISTA was used to compare the variation in the complete plastomes of nine Physalis species, using the annotation of P. angulata var. villosa as a reference in the global alignment Shuffle-LAGAN mode [43]. The structure variation in SC/IRs borders between nine Physalis species were visualized by using the R script of IRscope software (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/irapp/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
For phylogenetic analysis, 80 plastomes of Solanaceae species, representing 23 genera deposited in GenBank, were downloaded (Table S1). The plastomes of four non-solanaceous species, namely Bacopa monnieri, Digitalis lanata, Rehmannia glutinosa, and Scrophularia buergeriana, were also downloaded and designated as outgroups (Table S1). MAFFT version 7 [44] was used for the alignment of these selected, complete, solanaceous plastome sequences. Maximum likelihood (ML) and neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic analyses were performed in MEGA7 [39]. The most suitable models were selected after model testing in MEGA7, and the general time reversible (GTR+G+I) substitution model for evolution was used with 1000 bootstrap repeats to ascertain branch support.
3. Results
3.1. Chloroplast Assembly and Genome Feature
The complete plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was 156,898 bp in size, with a typical quadripartite structure containing a large single-copy region (LSC, 87,108 bp), a small single-copy region (SSC, 18,462 bp), and a pair of inverted repeats (IRA and IRB, 25,664 bp for each) (Figure 2 and Table 1). GC content in the entire P. angulata var. villosa plastome was 37.52%, whereas the LSC, SSC and IR regions had GC values of 35.58%, 31.33% and 43.05%, respectively (Table 1). The results suggested that IR regions had higher GC contents than did the LSC and SSC regions (Table 1).
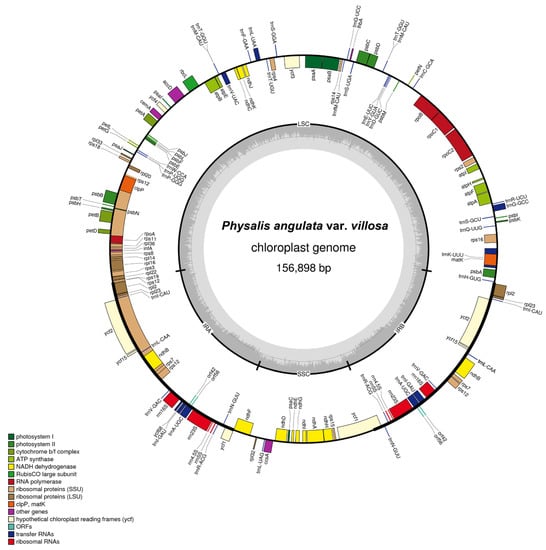
Figure 2.
Gene map of the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa. Genes outside the circles are transcribed in a counterclockwise direction, and genes inside the circles in a clockwise direction. Known functional genes are color coded. AT and GC contents are denoted by the light and dark grays in the inner circle, respectively. LSC indicates large single-copy region and SSC indicates small single-copy region, whereas IRA and IRB indicate inverted repeats.

Table 1.
Summaries of complete plastome of P. angulata var. villosa.
The complete plastome P. angulata var. villosa contains 131 genes, including 114 different genes and 17 genes duplicated in IR regions. The number of protein-coding genes, rRNA genes and tRNA genes in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome is 85, eight and 38, respectively (Figure 2, Table 1 and Table 2). Four rRNA, seven tRNA and six protein-coding genes are duplicated in the two copies of the IR regions, whereas 61 protein-coding genes and 23 tRNA genes are in the LSC region, with the remaining 11 protein-coding genes and one tRNA gene being in the SSC region. There are 19 different genes containing introns (Table 3), including seven tRNA genes and 12 protein-coding genes, six of which (ndhB, rpl2, trnA-UGC, trnE-UUC, trnI-GAU and trnV-UAC) are located in the pair of IR regions, whereas only one intron-containing gene (ndhA) is located in the SSC region, with the other 11 being in the LSC region. In addition to that, the rps12 gene is divided into 5′-rps12 in the LSC region and 3′-rps12 in the pair of IR regions. Two genes, namely clpP and ycf3, have two introns each, whereas the other 16 genes have one intron. The trnK-UUU gene has the largest intron (2509 bp in length), with the matK gene harbored within it (Table 2 and Table 3).

Table 2.
Genes in the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa.

Table 3.
Genes with intron in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome and length of exons and intron.
The codon usage and codon-anticodon recognition patterns of the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa were analyzed using the nucleotide sequences of protein-coding genes and tRNA genes (Table 4). The genes in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome are encoded by 52,299 codons. The frequency rates of the individual amino acids encoded in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome range from 1.25% to 10.83% (Figure 3). The codons that code for the amino acid leucine are the most frequent, with 5144 of the total codons (10.83%), followed by arginine (4558 codons, 9.60%), isoleucine (4399 codons, 9.26%), phenylalanine (3721 codons, 7.84%), serine (3585 codons, 7.55%) and lysine (3119 codons, 6.57%) having relatively high usage rates, while the codons that code for the amino acid glycine appeared to be the least frequent, at 594 codons (1.25%). The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values ranged from 0.41 (CGC) to 1.94 (AGA) (Table 4). Almost all A- or U-ending codons (28 codons) had RSCU values >1, except for CGU, CUA, AGU and AUA (RSCU = 0.73, 0.85, 0.86 and 0.97, respectively), whereas almost all G- or C-ending codons had RSCU values < 1 except for ACC, CCC, UCC and UUG (1.03, 1.04, 1.15 and 1.26, respectively). The amino acids tryptophan and methionine did not exhibit codon bias because they had RSCU values = 1.

Table 4.
Codon—anticodon recognition patterns and codon usage of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome.
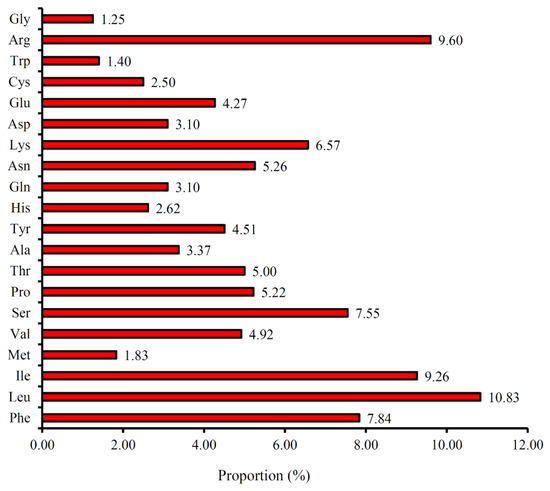
Figure 3.
Amino acid frequencies in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome protein-coding sequences.
The RNA editing sites present in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome were predicted (Table S2). The highest number of conversions in the codon positions are from proline to leucine (28 sites), followed by proline to serine (23 sites), threonine to isoleucine (21 sites), histidine to tyrosine (20 sites) and serine to leucine (20 sites), whereas proline to leucine and arginine to tryptophan have the lowest number of conversions, with only one site each (Table S2). The total number of editing sites observed in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome is 150, distributed between 25 of the protein-coding genes. The gene with the highest number of editing sites is psaB (18 sites), followed by rpoB (14 sites), ndhB (13 sites), rpoC1 (11 sites), rpoC2 (11 sites) and ndhF (ten sites). In contrast, the petB, ndhG, psbE, psbF and rpl20 genes have the lowest number of editing sites, with only one editing site each.
3.2. Repeat Element Analysis
Repeat element sequences in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome were analyzed, and the results are shown in Table 5. In total, three types of repeats, namely forward, palindromic and reverse repeats, were detected, except for the complementary repeats (Table 5). The results showed that a total of 38 repeats, namely 22 forward repeats, 14 palindromic repeats and two reverse repeats, was identified in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome (Table 5). Most of the repeats (84.21%), including 19 forward, 11 palindromic and two reverse repeats, had sizes of 30–39 bp, followed by 13.16% of the repeats being 40–49 bp (including three forward and two palindromic repeats), whereas 50–59 bp repeats were the least frequent (2.63%), including only one palindromic repeat. Most (55.26%) of the repeats were distributed in the intergenic spacers (IGS), but only two repeats (5.26%) were located in tRNA genes. The other 15 repeats were found in the protein-coding genes psbT, psaB, ndhA, ycf1, ycf2, and ycf3. The repeats in the plastomes of the eight other Physalis species were also analyzed (Figure 4). Compared with P. angulata var. villosa, 42, 43, 42, 39, 44, 34, 40 and 35 repeats were detected in the Physalis angulata, Physalis minima, Physalis pubescens, Physalis peruviana, Physalis chenopodifolia, Physalis philadelphica, Physalis pruinosa and Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii (synonyms for Alkekengi officinarum) plastomes, respectively (Figure 4A). Although the number and length of the repeats differed among the nine Physalis species, most of the repeats in the nine species were distributed in the length range 30–39 bp (Figure 4B).

Table 5.
Repeat sequences present in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome.
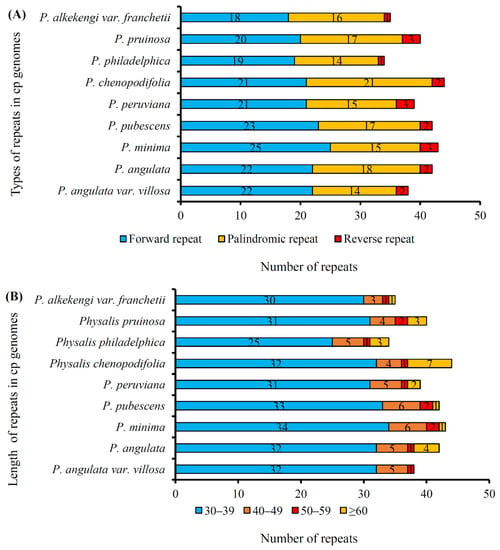
Figure 4.
Repeated sequences in the plastomes of nine Physalis species. (A), Three repeat types (forward, reverse and palindromic repeats) in the nine Physalis plastomes; (B), Numbers of repeat (forward, reverse and palindromic) sequences by length.
3.3. SSR Analysis
SSRs are a very important class of molecular marker, which are widely distributed in plastome. In the current study, a total number of 57 SSRs was detected in the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa (Figure 5A). Most of the SSRs were mononucleotide (39, 68.42%), followed by seven tetranucleotide SSRs (12.28%), six dinucleotides SSRs (10.53%) and five trinucleotides SSRs (8.77%). Among them, the mononucleotide SSRs were composed of A, T or C, of which T constituted the majority (61.54%). Most of the SSRs were detected in the intergenic spacer (IGS) regions (68.42%), followed by 29.82% of SSRs detected in the protein-coding regions (Figure 5B), whereas SSRs located in the tRNA genes showed the lowest frequency (1.75%). The results also showed that most SSRs were in the LSC region (71.93%), compared with the IR (14.04%) and the SSC regions (8.77%) (Figure 5C).
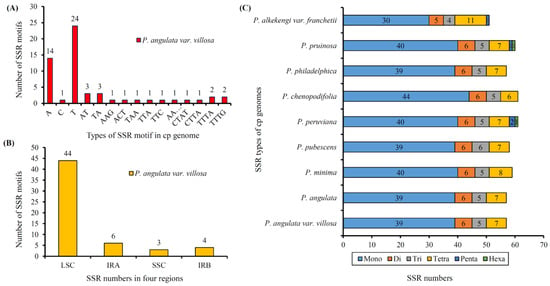
Figure 5.
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) types, distribution and presence in P. angulata var. villosa and other representative species from Physalis. (A), Numbers of different SSR motifs in different repeat types detected in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome. (B), Numbers of SSRs in different regions (IRA, IRB, LSC, and SSC) of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome. (C), Numbers of different SSR types detected in the genomes of the nine Physalis species.
3.4. Comparative Genomics Analysis
The plastome sequences of nine Physalis species were compared, including P. angulata var. villosa (156,898 bp), P. angulata (156,905 bp), P. minima (156,692 bp), P. pubescens (157,007 bp), P. peruviana (156,706 bp), P. chenopodifolia (156,888 bp), P. philadelphica (156,804 bp), P. pruinosa (156,706 bp) and P. alkekengi var. franchetii (156,578 bp). To investigate the level of plastome sequences variation between P. angulata var. villosa and the eight other Physalis species, mVISTA software was used to align the sequences, with the annotation of P. angulata var. villosa being used as the reference (Figure 6). The results showed that the Physalis plastomes were highly conserved, but some level of variation was detected. Compared with the LSC and SSC regions, the pair of IR regions showed low levels of variation. Furthermore, the protein-coding genes showed less divergence than did the non-coding regions, especially the intergenic spacer regions. The intergenic spacer regions with a high variation level included petN–psbM, trnL-UAA–trnF-GAA, ndhC–trnV-UAC, rbcL–accD, accD–psbI, petA–psbJ, trnL-UAG–ccsA, trnQ-UUG–psbK, atpH–atpI and rpl32–trnL-UAG. In addition to that, protein-coding genes, such as ycf1, ycf2, ndhF, rps19 and ccsA, also showed high sequence variation.
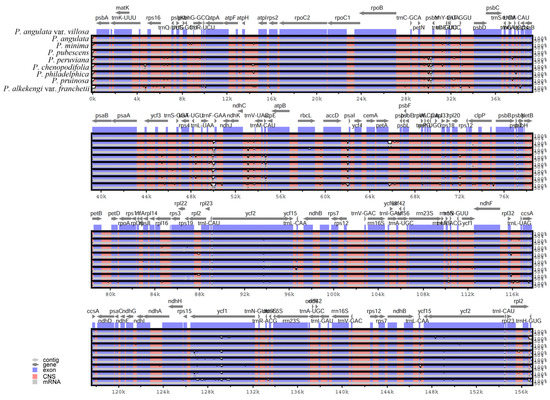
Figure 6.
Sequence alignment of nine plastomes in the genus Physalis performed with mVISTA, using annotation of P. angulata var. villosa as reference. The y-axis presents the percentage identity, within 50–100%. Protein-encoding regions are indicated in blue and non-coding regions in red. A reduction in sequence identity is indicated by a reduction in the blue/red shadowing (white spaces).
The main factors determining plastome size variation are the expansion and contraction of IR regions, which play an important role in plant evolutionary history. In our study, the sizes and the boundaries of the LSC, SSC, and IR regions of the nine Physalis plastomes were compared (Figure 7). The lengths of the IR regions ranged from 24,777 bp to 25,685 bp between the nine Physalis plastomes, indicating some potential expansion and contraction had occurred in the IR regions, which might be the main reasons for the differences in genome length of Physalis plastomes. The rps19, rpl2, rpl23 and trnH genes were located near the LSC/IR border of the nine Physalis plastomes and exhibited slight variation in the number of nucleotides, whereas the ycf1 and ndhF genes were found near the IR/SSC border. The rps19 gene crossed the LSC/IRB regions in the six Physalis plastomes (P. angulata var. villosa, P. minima, P. pubescens, P. chenopodifolia, P. philadelphica and P. alkekengi var. franchetii), but it was located in the LSC region near the LSC/IRB border in P. angulata, and at the IRA/LSC border in only the plastome of P. minima. The rpl2 gene was located at the IRA/LSC boundary in P. angulata var. villosa, P. angulata, P. minima, P. pubescens and P. alkekengi var. franchetii, but was absent from the IRA/LSC boundary in P. peruviana, P. chenopodifolia, P. philadelphica and P. pruinosa. Notably, the rpl2 gene crossed the LSC/IRB borders and extended to the LSC region in P. peruviana and P. pruinosa, which is different from the other seven species.
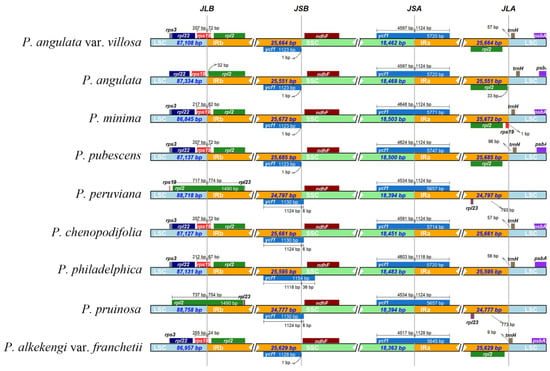
Figure 7.
Comparison of the borders of the IR, SSC and LSC regions among nine Physalis plastomes. Numbers above indicate the distances in bp between the ends of the genes and the border sites.
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
To determine the phylogenetic relationship and tribal positions among P. angulata var. villosa and the eight other Physalis species within the Solanaceae, we used the plastomes of 80 Solanaceae species, representing 23 genera of seven tribes (Physaleae, Capsiceae, Solaneae, Datureae, Lycieae, Hyoscyameae and Nicotianeae) from three subfamilies (Solanoideae, Nicotianoideae and Petunioideae), to construct phylogenetic trees. The two phylogenetic analyses were performed using the maximum likelihood (ML) or the neighbor-joining (NJ) methods, with Bacopa monnieri, Digitalis lanata, Rehmannia glutinosa and Scrophularia buergeriana as outgroups. The phylogenetic results from the ML and NJ analyses were similar and divided all the species into seven groups with very high support (Bootstrap (BS) = 100%) (Figure 8 and Figure S1).
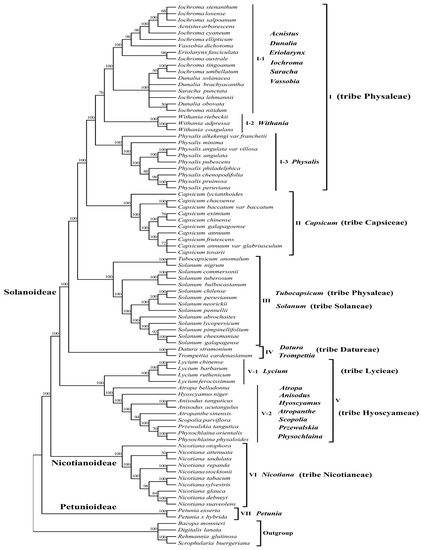
Figure 8.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of the complete plastomes of 80 species of seven tribes (Physaleae, Capsiceae, Solaneae, Datureae, Lycieae, Hyoscyameae and Nicotianeae) from three subfamily (Solanoideae, Nicotianoideae and Petunioideae) of Solanaceae. Numbers above branches indicate bootstrap support levels.
As described in Figure 8 and Figure S1, group I was the most complex group, comprising 29 species of eight genera from tribe Physaleae of subfamily Solanoideae, which could be further divided into three subgroups (I-1, I-2 and I-3). Subgroup I-1 contained 17 species: three species from genus Dunalia, ten species from genus Iochroma and one each from genera Acnistus, Eriolarynx, Saracha and Vassobia. Subgroup I-2 contained three Withania species: Withania riebeckii, Withania adpressa and Withania coagulans. Nevertheless, we found that P. angulata var. villosa and the eight other Physalis species were closely related to these genera and were grouped separately into subgroup I-3. Group II contained all 10 species from the genus Capsicum of tribe Capsiceae of subfamily Solanoideae. Group III contained all the 13 Solanum species from tribe Solaneae and one species from tribe Physaleae (Tubocapsicum anomalum). Two species, Datura stramonium and Trompettia cardenasianum from tribe Datureae of subfamily Solanoideae, were grouped into group IV. Group V included 13 species from eight genera, and was further divided into two subgroups, V-1 and V-2. Subgroup V-1 contained four Lycium species from tirbe Lycieae of subfamily Solanoideae, whereas subgroup V-2 contained two Anisodus species (Anisodus tanguticus and Anisodus acutangulus), two Physochlaina species (Physochlaina orientalis and Physochlaina physaloides), and one species each from the genera Atropa, Atropanthe, Hyoscyamus, Przewalskia and Scopolia within tribe Hyoscyameae of subfamily Solanoideae. All 10 species from genus Nicotiana of tribe Nicotianeae of subfamily Nicotianoideae were classified in group VI, whereas the two Petunia species from subfamily Petunioideae analyzed were distant from any other Solanaceae species tested and were assigned into group VII.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we sequenced the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa using Illumina sequencing technology and compared it with the published plastomes of the other eight Physalis species. The analysis of the plastome showed that the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa had a typical quadripartite structure, which contained a pair of IR regions (IRA and IRB), one SSC region and one LSC region. The organization and structure of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome was similar to that of the other Physalis plastomes [45]. The size of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome (156,898 bp) was comparable to that of other sequenced plastomes of members of the Solanaceae, being longer than those of Datura stramonium [46], Solanum brevicaule [47] and Withania somnifera [48], but shorter than those of Iochroma ellipticum (GenBank accession: KU323367), P. pubescens [45] and Eriolarynx fasciculata (GenBank accession: KU306938). The GC content of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome was 37.52%, which was similar to that of many other Solanaceae species [45,49,50,51]. In addition, the rps12 gene in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome was found to be a trans-spliced gene, as had been reported in other species [48,52]. Although the length of the P. angulata var. villosa plastome was different from that of other Solanaceae species, the arrangement and gene contents of the plastomes were similar [45,53,54].
Repeat elements are widely present in plant plastomes and are associated with recombination and rearrangement events [10,55,56]. Furthermore, these repeat sequences are the basis of population and phylogenetic studies [28,57]. A total of 38 repeats were identified in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome, which was more than of the corresponding number in Withania somnifera [48], but significantly fewer than that in Physalis chenopodifolia [53]. The lengths of 84.21% of the repeat elements in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome was between 30 and 39 bp, a finding similar to that of most other Solanaceae plastomes [45,48,54]. Interestingly, although P. angulata var. villosa and P. angulata are genetically closely related, we found some differences in repeat sequences within the number and length between these two species, which might help us understand their phylogenetic differences. Chloroplast SSRs (cpSSRs) are short repeats distributed in plastomes and inherited from a single parent and are often used as DNA molecular makers in genetic diversity, species identification and phylogenetic studies [58,59,60]. CpSSR analysis revealed a total of 57 SSRs in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome, most of which were mononucleotides, primarily A and T, a finding similar to that reported in many other plants [45,61,62]. Most (77.19%) of the cpSSRs of P. angulata var. villosa were in the LSC region, whereas the number of cpSSRs distributed in the SSC region was the lowest (5.26%). The cpSSRs detected in the present study will be useful in genetic diversity and population structure studies of P. angulata var. villosa, as well as with respect to genetic relationship and species identification investigations of the genus Physalis.
The variation in plastome size is mainly due to the expansion and contraction of IR regions [63]. After comparing the plastomes among the nine Physalis species in the current study, contraction and expansion of the IR regions were detected in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome and other sequenced Physalis plastomes. The boundary regions between the SSC and the two IR regions were relatively highly conserved, and the distribution and location of genes in these regions were consistent. However, the boundary regions between the LSC and the two IR regions varied greatly, which were similar with the finding in many angiosperm plants [64,65]. The contraction and expansion of IR borders can reflect the genetic relationship of plant species [66,67]. Despite the similar size of the IR regions between P. angulata var. villosa and the other Physalis species, some level of expansion and contraction was detected. There were variations in the border of the LSC and IR regions among the nine Physalis species, mainly based on the position of rps19, rpl2 and trnH. In P. angulata var. villosa, P. angulata, P. pubescens and P. alkekengi var. franchetii, one rpl2 gene was located in the IRA region, whereas only one rps19 gene spanned the LSC/IRB boundary, with most of the sequence being present in the LSC region. In P. minima, one of the duplicated rps19 copies spanned the LSC/IRB boundary, whereas the other was located in the IRA region. In P. peruviana, P. chenopodifolia, P. pruinosa and P. philadelphica, no rpl2 genes were found in the IRA/LSC border. It was observed that there were extensions of the IR region into the LSC regions for P. peruviana and P. pruinosa, resulting in these two species having relatively long LSC regions with 88,718 bp and 88,758 bp, respectively.
The result of the comparative genomic analysis using mVISTA showed that the genomes of P. angulata var. villosa and other eight Physalis species were relatively highly conserved, with a low degree of sequence divergence. Any variations mainly occurred in the non-coding regions of the plastomes due to the results of insertion and deletion, a finding which is consistent with most angiosperm plants [11,64]. The comparative genome analysis results also revealed some variable regions in the tested Physalis species, namely petN–psbM, trnL-UAA–trnF-GAA, ndhC–trnV-UAC, rbcL–accD, accD–psbI, petA–psbJ, trnL-UAG–ccsA, trnQ-UUG–psbK, atpH–atpI, trnL-UAG, ycf1, ycf2, ndhF, rps19 and ccsA, which could be used as potential DNA barcodes for the identification of Physalis species, as well as for resolving phylogenetic relationships in the family Solanaceae.
Many previous studies have indicated that the phylogenetic classification of the genus Physalis is complex, due to the large number of species, wide distribution, and relatively similar morphological characteristics [1,20,21]. In the present study, phylogenetic trees were constructed from the plastomes of 80 species representing 23 genera of seven tribes from three subfamily of the family Solanaceae, using NJ and ML methods. The two phylogenetic trees showed similar topology with a very high support rate of 100% for all the groups. The results revealed that all the species in the genus Physalis were grouped into a separate subgroup, with the genetic relationship between P. angulata var. villosa and P. angulata being the closest, whereas that between P. angulata var. villosa and P. alkekengi var. franchetii was the most distant. The finding not only corresponded to current taxonomy of genus Physalis, but also further confirmed the relatively distant genetic relationship between P. alkekengi var. franchetii and other Physalis species [1,20]. The results also showed that the tested Physalis species have relatively close genetic relationships with the solanaceous genera Withania, Iochroma, Dunalia, Saracha, Eriolarynx, Vassobia, and Acnistus, whereas the Physalis species studied were most distantly related to the Petunia species tested from subfamily Petunioideae, which confirms some previous studies and improves the phylogenetic map of the Solanaceae [1,20,21,45]. The clustering results showed that most species from the same genus of the family Solanaceae were monophyletic, but interestingly, a few species of some genera were paraphyletic in the phylogenetic evolution of the Solanaceae. For example, the genetic relationships among Iochroma, Dunalia, Saracha and Eriolarynx species were complex, confirming earlier findings [20,21,45]. In addition, interestingly, our study also showed that at the tribe level, all species from the same tribe tended to cluster together, except Tubocapsicum anomalum from tribe Physaleae. We speculated that the reason why T. anomalum were distant from the other species of tribe Physaleae might be that the plastome sequence of this species was downloaded from the GenBank database and there was only one sequence; it was debatable whether the sequence information and species were consistent due to the similar morphological characteristics of some Solanaceae species. Therefore, the phylogenetic position of this species may need to be further verified by more plastome sequences.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we sequenced and reported the complete plastome of P. angulata var. villosa, providing new, valuable plastid genomic resources for the genus Physalis. The plastome of P. angulata var. villosa has a typical angiosperm plastome structure and gene content and is comparable to other Physalis plastomes. The repeat sequences and SSRs identified in this study could be used as valuable tools for evolutionary research within the genus Physalis in the future. The comparative genomic analyses of nine Physalis species showed that some variable hotspots could be used to develop DNA barcodes for the identification of the species. The present study also revealed the taxonomic position and genetic relationships of major genera in the Solanaceae, showing that several species of some genera were paraphyletic during phylogenetic evolution.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13122291/s1, Figure S1: Neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree of complete plastomes from 80 species of Solanaceae. Numbers above branches indicate bootstrap support levels; Table S1: The 80 species belonging to 23 genera of Solanaceae, and four species used as outgroups; Table S2. Predicted RNA editing site in the P. angulata var. villosa plastome.
Author Contributions
S.F. and X.Z. conceived and designed the experiments, participated in the analysis and drafted the manuscript; Z.Z., Y.G. and Y.J. carried out the molecular studies; Y.Z. and C.S. performed the statistical analysis; S.F. and H.W. secured funding and helped to revise the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Our work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31970346, 32000255); the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY20H280012); the key project at the central government level for the ability establishment of sustainable use for valuable Chinese medicine resources (2060302), the Zhejiang Provincial Key Research & Development Project Grants (2018C02030).
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in the manuscript, and the complete plastome of Physalis angulata var. villosa were submitted to the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 13 January 2022)) with GenBank accession numbers OM257167.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com (accessed on 12 August 2022) for editing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feng, S.; Jiang, M.; Shi, Y.; Jiao, K.; Shen, C.; Lu, J.; Ying, Q.; Wang, H. Application of the ribosomal DNA ITS2 region of Physalis (Solanaceae): DNA barcoding and phylogenetic study. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Hu, Z.; Yu, L.; Ma, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X. Induction of quinone reductase (QR) by withanolides isolated from Physalis angulata L. var. villosa Bonati (Solanaceae). Steroids 2014, 86, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese academy of sciences. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; Volume 67, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, W.N.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Lin, R.; Shan, S.M.; Zhu, M.D.; Luo, J.G.; Kong, L.Y. Cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulata var. villosa and the apoptosis-inducing effect via ROS generation and the activation of MAPK in human osteosarcoma cells. Rsc. Adv. 2016, 6, 53089–53100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Kong, L.Y.; Luo, J.G. Target discovery of cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulata var. villosa via reactivity-based screening. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 151, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, K.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Wolfe, K.H.; van den Bekerom, R.; Dix, P.J.; Barth, S. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major allogamous forage species, perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). DNA Res. 2009, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, H.; Shen, H. Chloroplast genome sequence of Chongming lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) and comparative analyses with other legume chloroplast genomes. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Li, W.H.; Sharp, P.M. Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. CHAPTER 2—Plastid Chromosomes: Structure and Evolution. In The Molecular Biology of Plastids; Bogorad, L., Vasil, I.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 5–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Cullis, C. A novel inversion in the chloroplast genome of marama (Tylosema esculentum). J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, G.; Park, K.T.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S. Characteristics of the completed chloroplast genome sequence of Xanthium spinosum: Comparative analyses, identification of mutational hotspots and phylogenetic implications. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Shi, T.; Luo, W.; Ni, X.; Iqbal, S.; Ni, Z.; Huang, X.; Yao, D.; Shen, Z.; Gao, Z. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome among Prunus mume, P. armeniaca, and P. salicina. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.D.; Thompson, W.F. Rearrangements in the chloroplast genomes of mung bean and pea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 5533–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Koo, H.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, D.Y.; Giang, V.N.L.; Kim, M.; Shim, H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoo, K.O.; et al. Authentication of Zanthoxylum species based on integrated analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences and metabolite profiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10350–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.A.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H. The complete chloroplast genome of colchicine plants (Colchicum autumnale L. and Gloriosa superba L.) and its application for identifying the genus. Planta 2015, 242, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Ma, Q.; Liang, L.; Wang, G. Comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis revealed the chloroplast genome variation and interspecific relationships of Corylus (Betulaceae) species. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.Y.; Tong, L.; Sun, M.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wen, J.; Lin, Q.W.; Liu, B. Phylogeny and divergence time estimation of the walnut family (Juglandaceae) based on nuclear RAD-Seq and chloroplast genome data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 147, 106802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.J.; Wu, S.; Zhai, J. Comparative analysis of plastomes in Oxalidaceae: Phylogenetic relationships and potential molecular markers. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitson, M.; Manos, P.S. Untangling Physalis (Solanaceae) from the Physaloids: A two-gene phylogeny of the Physalinae. Syst. Bot. 2005, 30, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmstead, R.G.; Bohs, L.; Migid, H.A.; Santiago-Valentin, E.; Garcia, V.F.; Collier, S.M. A molecular phylogeny of the Solanaceae. Taxon 2008, 57, 1159–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Jiao, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, H. Molecular identification of species of Physalis (Solanaceae) using a candidate DNA barcode: The chloroplast psbA-trnH intergenic region. Genome 2018, 61, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbaqueba, J.; Sanchez, P.; Sanchez, E.; Zarantes, V.M.N.; Chacon, M.I.; Barrero, L.S.; Marino-Ramirez, L. Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for the cape gooseberry Physalis peruviana. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Ponce, O.; Perez-Alvarez, L.F.; Zamora-Tavares, P.; Rodriguez, A. Assessing genetic diversity in Mexican Husk tomato species. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 29, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Tavares, P.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Sanchez-Martinez, J.; Cabrera-Toledo, D. Diversity and genetic structure of the husk tomato (Physalis philadelphica Lam.) in Western Mexico. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2015, 62, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Alonso, R.; Ibanez, V.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Dopazo, J. A Phylogenetic analysis of 34 chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships between wild and domestic species within the genus Citrus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2015–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Duan, L.; Liu, P.L.; Liu, J.; Chang, Z.Y.; Wen, J. Chloroplast phylogenomics and character evolution of eastern Asian Astragalus (Leguminosae): Tackling the phylogenetic structure of the largest genus of flowering plants in Asia. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2021, 156, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of Avena: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogeny. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Harris, A.J.; Kalburgi, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Ickert-Bond, S.M.; Johnson, G.; Zimmer, E.A. Chloroplast phylogenomics of the New World grape species (Vitis, Vitaceae). J. Syst. Evol. 2018, 56, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Yonezawa, T.; Zhong, Y.; Hasegawa, M. The position of gnetales among seed plants: Overcoming pitfalls of chloroplast phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, J.B.; Ma, W.Z.; Pressel, S.; Liu, H.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Schneider, H. Chloroplast phylogenomics of liverworts: A reappraisal of the backbone phylogeny of liverworts with emphasis on Ptilidiales. Cladistics 2020, 36, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Harris, A.J.; Su, C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Arslan, E.; Ertugrul, K.; Loc, P.K.; Hayashi, H.; Wen, J.; Chen, H.F. Chloroplast phylogenomics reveals the intercontinental biogeographic history of the Liquorice genus (Leguminosae:Glycyrrhiza). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.K.; Jain, M. NGS QC Toolkit: A toolkit for quality control of next generation sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.U.; Park, S.K.; Kang, S.A.; Park, M.K.; Cho, M.K.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Yu, H.S. Comparison of functional gene annotation of Toxascaris leonina and Toxocara canis using CLC genomics workbench. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, G.; Tang, J.; Luo, R.; Patterson, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; He, G.; Gu, S.; Li, S.; et al. SOAPdenovo-Trans: De novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gile, G.H.; Moog, D.; Slamovits, C.H.; Maier, U.G.; Archibald, J.M. Dual organellar targeting of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in diatoms and cryptophytes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW--a suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Munch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Zheng, K.; Jiao, K.; Cai, Y.; Chen, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhan, X.; Ying, Q.; Wang, H. Complete chloroplast genomes of four Physalis species (Solanaceae): Lights into genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Cruz, I.M.; Nunez-Farfan, J. The complete chloroplast genomes of two Mexican plants of the annual herb Datura stramonium (Solanaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 2823–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Ruess, H.; Liang, Q.; Colleoni, C.; Spooner, D.M. Analyses of 202 plastid genomes elucidate the phylogeny of Solanum section Petota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Mirza, B. Characterization of Withania somnifera chloroplast genome and its comparison with other selected species of Solanaceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.J.; Jung, J.D.; Park, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Cha, H.W.; Min, S.R.; Jeong, W.J.; Liu, J.R. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Solanum tuberosum and comparative analysis with Solanaceae species identified the presence of a 241-bp deletion in cultivated potato chloroplast DNA sequence. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yisilam, G.; Mamut, R.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Fu, C.X. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Lycium ruthenicum (Solanaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2018, 3, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, C.L.; Garcia, L.E.; Abbona, C.C.; Sanchez-Puerta, M.V. The complete organelle genomes of Physochlaina orientalis: Insights into short sequence repeats across seed plant mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2019, 137, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Puerta, M.V.; Abbona, C.C. The chloroplast genome of Hyoscyamus niger and a phylogenetic study of the tribe Hyoscyameae (Solanaceae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Tavares, M.D.; Sandoval-Padilla, I.; Chavez Zendejas, A.; Perez-Alquicira, J.; Vargas-Ponce, O. Complete chloroplast genome of Physalis chenopodifolia Lam. (Solanaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvonen, J.; Poczai, P. The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): Plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogihara, Y.; Terachi, T.; Sasakuma, T. Intramolecular recombination of chloroplast genome mediated by short direct-repeat sequences in wheat species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8573–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumley, T.W.; Palmer, J.D.; Mower, J.P.; Fourcade, H.M.; Calie, P.J.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium x hortorum: Organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.F.; Yu, H.X.; Price, M.; Xie, C.; Deng, Y.Q.; Chen, J.P.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. Phylogeny of chinese Allium species in section Daghestanica and adaptive evolution of Allium (Amaryllidaceae, Allioideae) species revealed by the chloroplast complete genome. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, S.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y. Inferring genetic variation and demographic history of Michelia yunnanensis Franch. (Magnoliaceae) from chloroplast DNA sequences and microsatellite markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Jin, Y.Q.; Gao, Q.; Hu, X.G.; Gao, F.L.; Yang, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Mao, J.F. Development of high transferability cpSSR markers for individual identification and genetic investigation in Cupressaceae species. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4967–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, S.L.; Pei, S.Y.; Ning, M.M.; Tang, S.Q. Genetic diversity and population structure of Camellia huana (Theaceae), a limestone species with narrow geographic range, based on chloroplast DNA sequence and microsatellite markers. Plant Divers. 2020, 42, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ren, B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Comparison of chloroplast genomes of Gynura species: Sequence variation, genome rearrangement and divergence studies. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Li, H.K.; Zhao, H.S. Chloroplast genomes of two species of Cypripedium: Expanded genome size and proliferation of AT-biased repeat sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 609729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Chung, M.G.; Park, S. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of three Veroniceae Species (Plantaginaceae): Comparative analysis and highly divergent regions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Qu, G.Z. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Betula platyphylla: Gene organization, RNA editing, and comparative and phylogenetic analyses. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wu, F. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fagus longipetiolata Seemen (Fagaceae): Genome structure, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. Life 2022, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; Kanwal, N.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, G.; Zhao, G. Completion of eight gynostemma BL. (Cucurbitaceae) chloroplast genomes: Characterization, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jing, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Kai, G. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Anisodus Acutangulus and a comparison with other Solanaceae species. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2021, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).