Identification of QTLs Controlling Resistance to Anthracnose Disease in Water Yam (Dioscorea alata)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Phenotyping
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Data Analyses
2.4.1. Phenotype Data
2.4.2. SNP Calling and Quality Assessment
2.4.3. Genetic Map Construction
2.4.4. QTL Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Variability
3.2. SNP Filtering
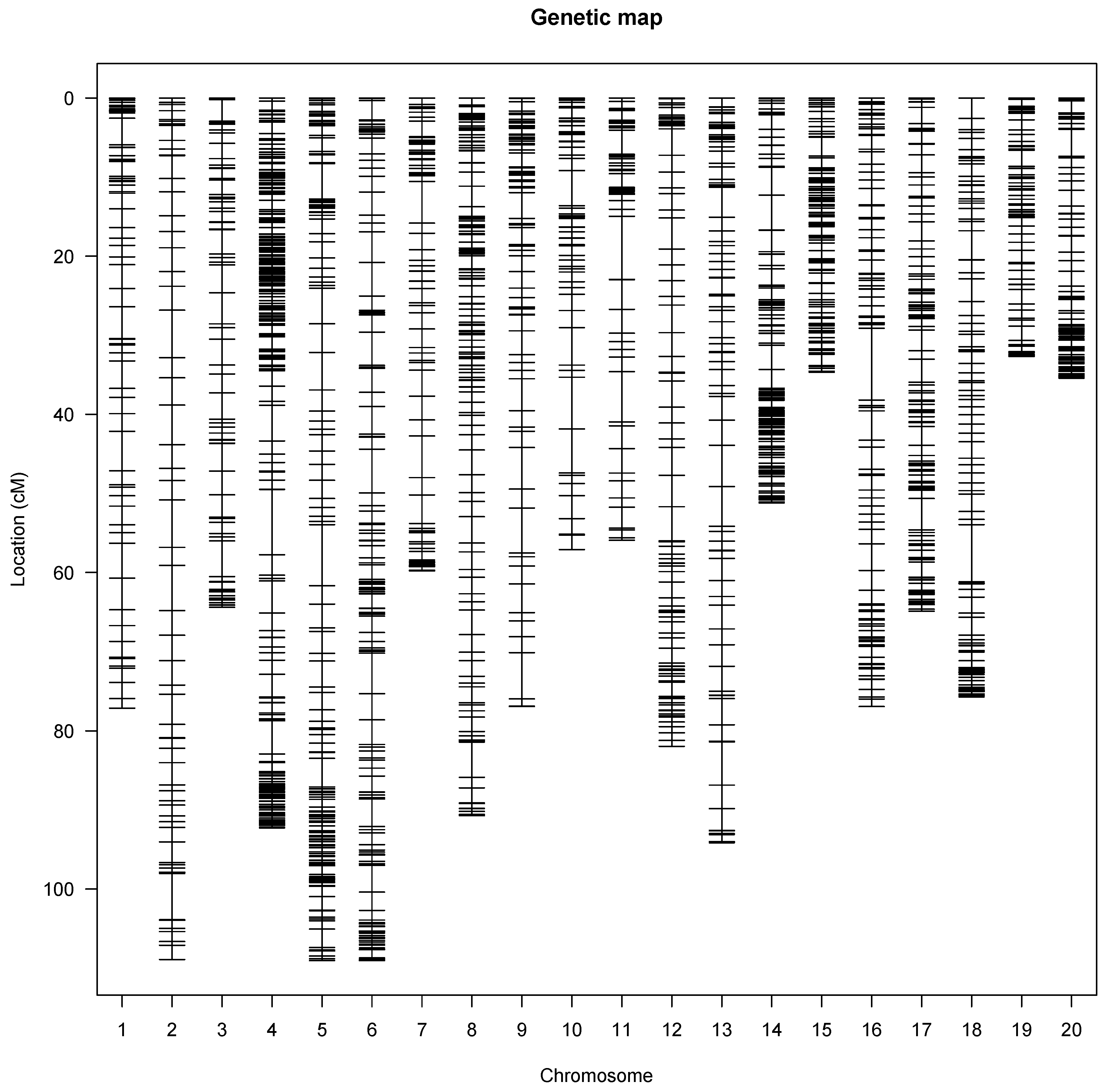
3.3. Linkage Mapping
3.4. QTL Identification
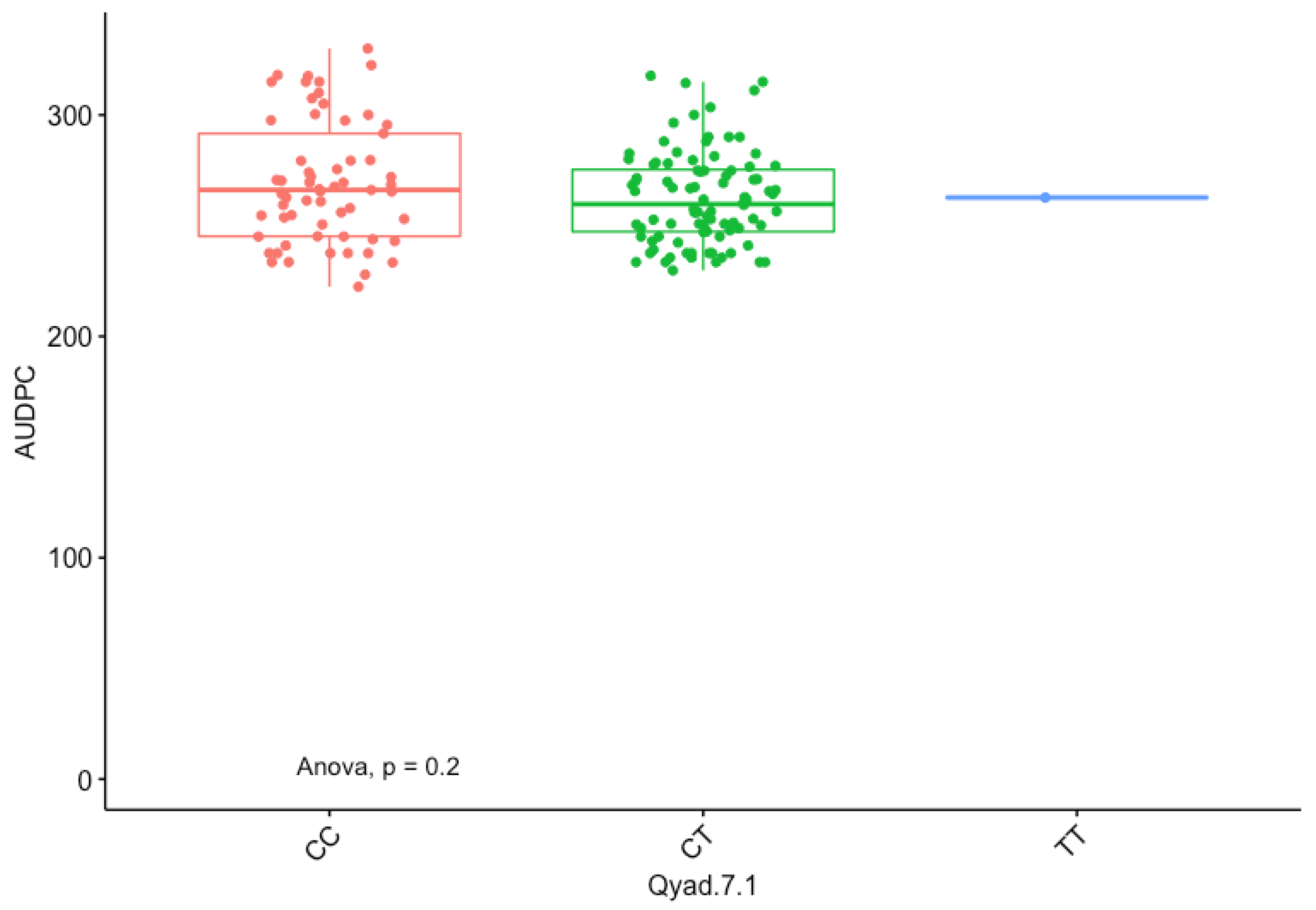
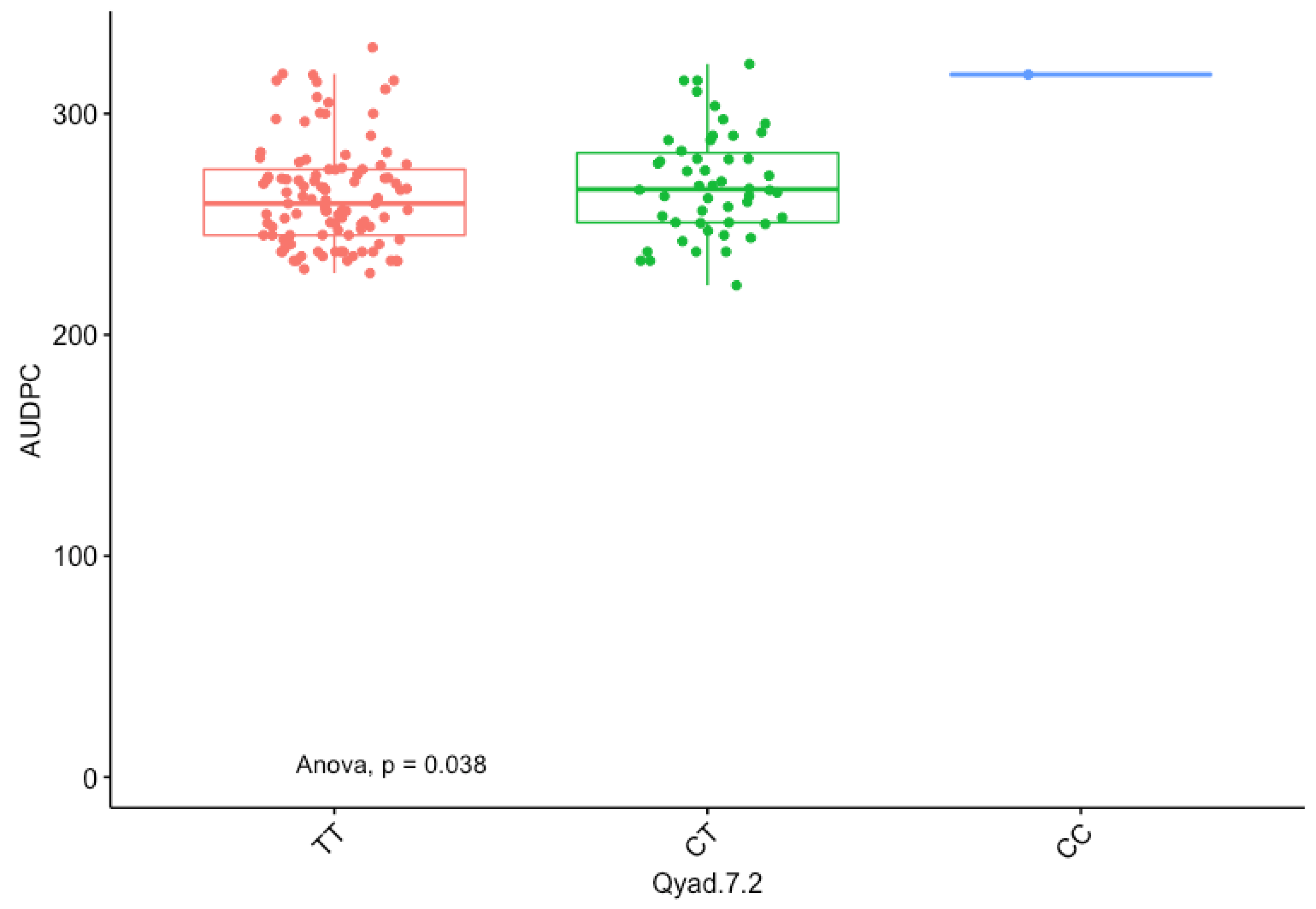
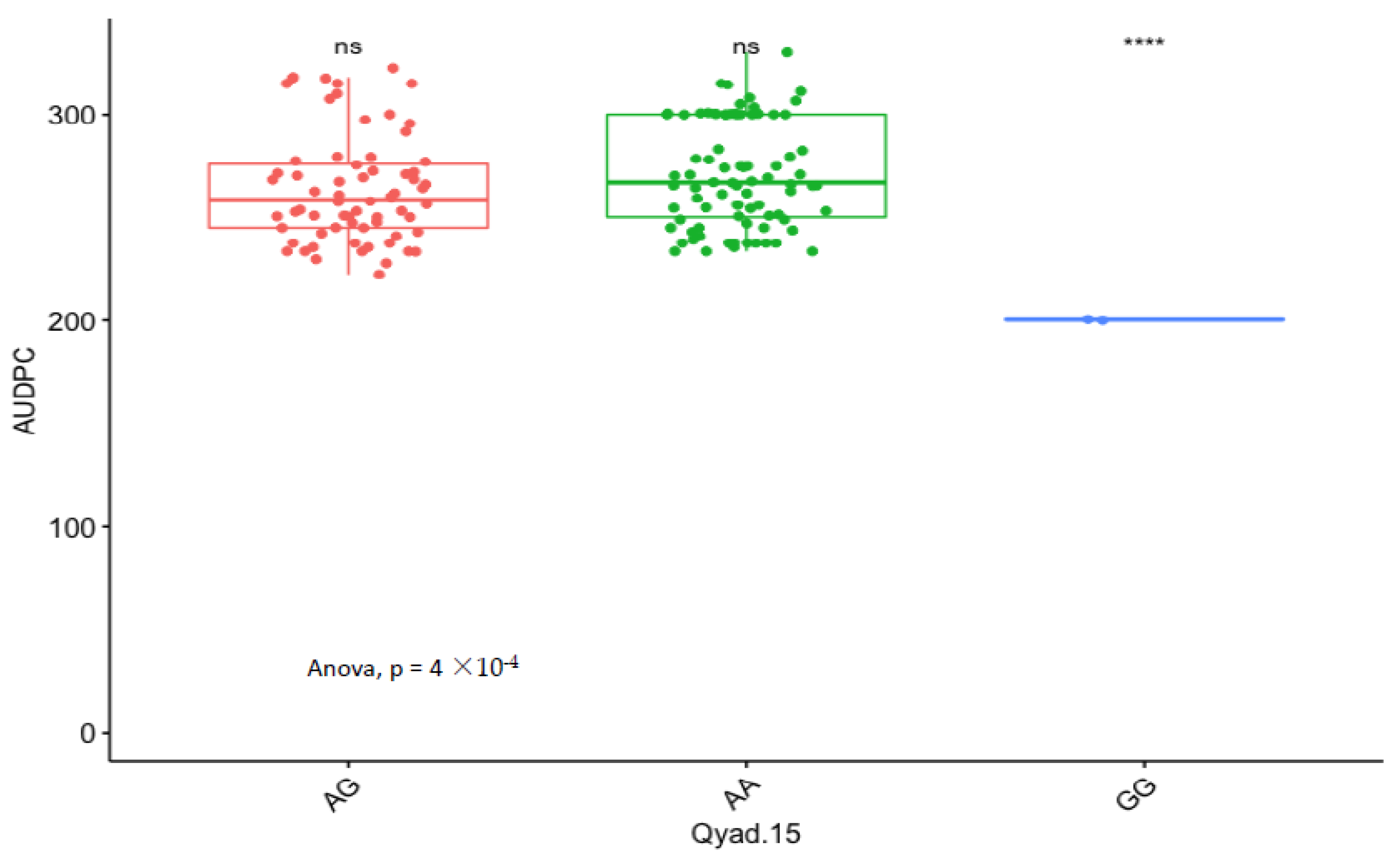
3.5. Marker Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asiedu, R.; Sartie, A. Crops that feed the world 1. Yams. Food Secur. 2010, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarcelli, N.; Cubry, P.; Akakpo, R.; Thuillet, A.C.; Obidiegwu, J.; Baco, M.N.; Otoo, E.; Sonké, B.; Dansi, A.; Djedatin, G.; et al. Yam genomics supports West Africa as a major cradle of crop domestication. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darkwa, K.; Olasanmi, D.; Asiedu, R.; Asfaw, A. Review of empirical and emerging breeding methods and tools for yam (Dioscorea spp.) improvement: Status and prospects. Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 474–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidiegwu, J.E.; Akpabio, E.M. The geography of yam cultivation in southern Nigeria: Exploring its social meanings and cultural functions. J. Ethn. Foods 2017, 4, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignouna, H.; Mank, R.; Ellis, T.; Van den Bosch, N.; Asiedu, R.; Abang, M.; Peleman, J. A genetic linkage map of water yam (Dioscorea alata L.) based on AFLP markers and QTL analysis for anthracnose resistance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah, F.D.; Maziya-Dixon, B.; Asiedu, R.; Oduro, I.; Ellis, W.O. Nutritional and biochemical composition of D. alata (Dioscorea spp.) tubers. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Abang, M.M.; Fagbola, O.; Smalla, K.; Winter, S. Two genetically distinct populations of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz. causing anthracnose disease of yam (Dioscorea spp.). J. Phytopathol. 2005, 153, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntui, V.O.; Uyoh, E.A.; Ita, E.E.; Markson, A.-A.A.; Tripathi, J.N.; Okon, N.I.; Akpan, M.O.; Phillip, J.O.; Brisibe, E.A.; Ene-Obong, E.; et al. Strategies to combat the problem of yam anthracnose disease: Status and prospects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abang, M.M.; Green, K.R.; Wanyera, N.W.; Iloba, C. Characterization of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz. from yam (Dioscorea spp.) in Nigeria. In Root Crops in the 21st Century, Proceedings of the 7th Triennial Symposium of the International Society for Tropical Root Crops–Africa Branch, Cotonou, Benin, 11–17 October 1998; ISTRC Acra: Kent, UK; pp. 613–615.
- Akem, C.N. Yam die-back and its principal cause in the yam belt of Nigeria. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 1999, 2, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Appiah-Kubi, Z.; Apetorgbor, A.K.; Moses, E.; Appiah-Kubi, D. Farmers Knowledge of Anthracnose Disease of Cassava and Yam in Four Ecological Zones in Ghana. Greener J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 5, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwadili, C.O.; Augusto, J.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Atehnkeng, J.; Lopez-Montes., A.; Onyeka, T.J.; Kumar, P.L.; Asiedu, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Comparative reliability of screening parameters for anthracnose resistance in water yam (Dioscorea alata). Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezal, L.; Jacqua, G.; Neema, C. Study of the genetic diversity of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, causative agent of anthracnose of white yam in Guadeloupe. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Plant Diseases, Tours, France, 3–5 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Abang, M.M.; Hoffmann, P.; Winter, S.; Green, K.R.; Wolf, G.A. Vegetative compatibility among isolates of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from yam (Dioscorea spp.) in Nigeria. J. Phytopathol. 2004, 152, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.A.; Linde, C. The population genetics of plant pathogens and breeding strategies for durable resistance. Euphytica 2002, 124, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, S.A.; Green, K.R. Epidemiology of yam anthracnose: Sources of inoculum. In Proceedings of the 4th International Confeence of Plant Protection, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–31 March 1994; pp. 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, E.M.; Casa, R.T.; Blum, M.M.; dos Santos, H.P.; Medeiros, C.A. Effects of cultural practices on the severity of leaf blotches of wheat and their relationship to the incidence of pathogenic fungi in the harvested seed. Fitopatol. Bras. 1997, 22, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniyandi, S.A.; Yang, S.H.; Cheng, J.H.; Meng, L.; Suh, J.W. Biological control of anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) in yam by Streptomyces sp. MJM5763. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 111, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepperly, P.; Vazquez, F. Resistance and scouting in the control of yam anthracnose of the winged yam (Dioscorea alata). In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Meeting of the Caribbean Food Crops Society Gosier, Guadeloupe, France, 1–6 July 1989; pp. 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Bayart, J.D.; Pallas, B. Tolerance of yam anthracnose of a benzimidazole. Results of the first study conducted in Guadeloupe. Phytoma 1994, 461, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lebot, V.; Abraham, K.; Kaoh, J.; Rogers, C.; Molisalé, T. Development of anthracnose resistant hybrids of the greater yam (Dioscorea alata L.) and interspecific hybrids with D. nummularia Lam. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2019, 66, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, A.R.; Adedibu, B.O.; Ganiyu, S.A. Rapid assessment of resistance to tissue-cultured water yam (Dioscorea alata) and white yam (Dioscorea rotundata) to anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz.). Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2013, 46, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.S.; Sheela, M.N.; Jeeva, M.L.; Abhilash, P.V. Identification of host plant resistance to anthracnose in greater yam (Dioscorea alata L.). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, R.; Ng, N.G.; Bai, K.V.; Ekanayake, I.J.; Wanyera, N.M. Genetic Improvement. In Food Yams: Advances in Research; IITA and NCRI: Ibadan, Nigeria, 1998; pp. 63–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mignouna, H.D.; Abang, M.M.; Green, K.R.; Asiedu, R. Inheritance of resistance in water yam (Dioscorea alata) to anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petro, D.; Onyeka, T.J.; Etienne, S.; Rubens, S. An intraspecific genetic map of water yam (Dioscorea alata L.) based on AFLP markers and QTL analysis for anthracnose resistance. Euphytica 2001, 179, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narina, S.S.; Buyyarapu, R.; Kottapalli, K.R.; Sartie, A.M.; Ali, M.I.; Robert, A.; Hodeba, M.J.D.; Sayre, B.; Scheffler, B.E. Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) for marker development in yam (Dioscorea alata L.). BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saski, C.A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Scheffler, B.E.; Asiedu, R. Genomic resources for water yam (Dioscorea alata L.): Analyses of EST-sequences, de novo sequencing and GBS libraries. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Nwadili, C.O.; Saski, C.A.; Paterne, A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Augusto, J.; Lopez-Montes, A.; Onyeka, J.D.; Kumar, P.L.; Bandyopadhyay, R. An EST-SSR based genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs for anthracnose disease resistance in water yam (Dioscorea alata L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, A. Standard Operating Protocol for Yam Variety Performance Evaluation Trial; IITA: Ibadan, Nigeria, 2016; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.L.; Madden, L.V. Introduction to Plant Disease Epidemiology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cormier, F.; Lawac, F.; Maledon, E.; Gravillon, M.C.; Nudol, E.; Mournet, P.; Vignes, H.; Arnau, G. A reference high-density genetic map of greater yam (Dioscorea alata L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Scarcelli, N.; Mariac, C.; Couvreur, T.L.; Faye, A.; Richard, D.; Sabot, F.; Berthouly-Salazar, C.; Vigouroux, Y. Intra-individual polymorphism in chloroplasts from NGS data: Where does it come from and how to handle it? Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, G.; Homa, F.; Pointet, S.; Contreras, S.; Sabot, F.; Nabholz, B.; Santoni, S.; Sauné, L.; Ardisson, M.; Chantret, N.; et al. A large set of 26 new reference transcriptomes dedicated to comparative population genomics in crops and wild relatives. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredeson, J.V.; Lyons, J.B.; Oniyinde, I.O.; Okereke, N.R.; Kolade, O.; Nnabue, I.; Nwadili, C.O.; Hřibová, E.; Parker, M.; Nwogha, J.; et al. Chromosome Evolution and the Genetic Basis of Agronomically Important Traits in Greater Yam. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.14.439117 (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollinari, M.; Olukolu, B.A.; Pereira, G.D.; Khan, A.; Gemenet, D.; Yencho, G.C.; Zen, Z.B. Unraveling the hexaploid sweetpotato inheritance using ultra-dense multilocus mapping. G3-Genes Genom. Genet. 2020, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ma, C.; Hong, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H. Construction and analysis of high-density linkage map using high-throughput sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, K.W.; Gatti, D.M.; Simecek, P.; Furlotte, N.A.; Prins, P.; Sen, S.; Yandell, B.S.; Churchill, G.A. R/qtl2: Software for mapping quantitative trait loci with high-dimensional data and multiparent populations. Genetics 2019, 211, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, G.A.; Doerge, R.W. Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 1994, 138, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Zhao, J.; Zuo, K.; Qiu, C.; Yao, H.; Qin, J.; Sun, X.; Tang, K. Isolation and expression analysis of a GDSL-like lipase gene from Brassica napus L. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 39, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Jin, H.C.; Lee, S.; Nam, M.H.; Chung, J.H.; Kwon, S.S.I.; Ryu, C.M.; Park, O.K. GDSL lipase-like 1 regulates systemic resistance associated with ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 58, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.K.; Choi, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, B.K. Function of a novel GDSL-type pepper lipase gene, CaGLIP1, in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 2008, 227, 539–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J. 2004, 37, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, F.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Sánchez-Rodriguez, C.; Jorda, L.; Molina, A. ERECTA receptor-like kinase and heterotrimeric G protein from Arabidopsis are required for resistance to the necrotrophic fungus Plectosphaerella cucumerina. Plant J. 2005, 43, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, M.; Bourdais, G.; Gervasi, F.; Beck, M.; Zhou, J.; Spallek, T.; Bartels, S.; Boller, T.; Ueda, T.; Kuhn, H.; et al. Clathrin-dependent endocytosis is required for immunity mediated by pattern recognition receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11034–11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, F.; Gaffoor, I.; Chopra, S. Flavonoid phytoalexin-dependent resistance to anthracnose leaf blight requires a functional yellow seed1 in Sorghum bicolor. Genetics 2010, 184, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, F.; Gaffoor, I.; Tan, Q.; Shyu, C.R.; Chopra, S. A sorghum MYB transcription factor induces 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and enhances resistance against leaf blights in maize. Molecules 2015, 20, 2388–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Burg, H.A.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Rowland, O.; Lo, J.; Rallapalli, G.; MacLean, D.; Takken, F.L.; Jones, J.D. The F-box protein ACRE189/ACIF1 regulates cell death and defense responses activated during pathogen recognition in tobacco and tomato. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 697–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, D.; Rafiqi, M.; Hurley, U.; Lawrence, G.I.; Bernoux, M.; Hardham, A.R.; Ellis, J.G.; Dodds, P.N.; Jones, D.A. N-terminal motifs in some plant disease resistance proteins function in membrane attachment and contribute to disease resistance. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mean Squares | CV | Broad Sense Heritability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Genotype | Year | Genotype × Year | (%) | (%) |
| AUDPC | 163.01 * | 2190.01 ** | 3371.8 *** | 17.6 | 70.64 |
| Chromosomes | Number of SNPs | Chromosome Length (cM) | Average SNP Distance | Maximum Gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 80 | 80.93 | 1.95 | 5.00 |
| Chr2 | 84 | 109.17 | 1.28 | 6.01 |
| Chr3 | 115 | 64.63 | 0.56 | 4.48 |
| Chr4 | 520 | 92.32 | 0.16 | 8.26 |
| Chr5 | 199 | 109.19 | 0.50 | 7.71 |
| Chr6 | 191 | 109.52 | 0.57 | 5.54 |
| Chr7 | 127 | 59.84 | 0.48 | 5.26 |
| Chr8 | 200 | 91.39 | 0.48 | 4.44 |
| Chr9 | 124 | 77.12 | 0.62 | 5.80 |
| Chr10 | 104 | 57.13 | 0.55 | 5.52 |
| Chr11 | 85 | 55.95 | 0.66 | 7.94 |
| Chr12 | 125 | 83.22 | 0.65 | 4.30 |
| Chr13 | 116 | 95.55 | 0.78 | 5.47 |
| Chr14 | 208 | 51.447 | 0.25 | 4.40 |
| Chr15 | 180 | 34.70 | 0.18 | 2.39 |
| Chr16 | 139 | 77.16 | 0.61 | 9.07 |
| Chr17 | 208 | 67.44 | 0.31 | 3.95 |
| Chr18 | 129 | 75.71 | 0.54 | 7.23 |
| Chr19 | 111 | 33.09 | 0.28 | 2.03 |
| Chr20 | 139 | 35.48 | 0.23 | 3.41 |
| Total | 3184 | 1,460.98 |
| Markers | Chr | Pos (cM) | LOD | Add/Dom | CI. Low | CI. High | R2 (%) | Putative Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qyad-7-1 | 7 | 10.60 | 4.51 | −2.56 | 10.596 | 19.217 | 33.7 | DRNTG_08663.1 |
| QTL-7-2 | 7 | 19.21 | 5.28 | −5.98 | 10.596 | 19.218 | 29.54 | DRNTG_08664.1, DRNTG_23336.1 |
| Qyad-15 | 15 | 28.80 | 4.43 | −10.12 | 10.171 | 28.817 | 30.90 | DRNTG_14305.1 |
| Qyad-18 | 18 | 61.4 | 4.65 | −3.48 | 61.345 | 61.432 | 39.40 | DRNTG_18245.1, DRNTG_29617.1 |
| Marker Interactions | df | MS | p-Value | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qyad-7-1: QTL-7-2 | 1 | 55.9 | 0.835 | 0.04147 |
| Qyad-7-1: Qyad-15 | 1 | 5303.5 | 0.0456 * | 0.02544 |
| Qyad7-1: Qyad-18 | 1 | 155.2 | 0.734 | −0.0002131 |
| QTL-7-2: Qyad-15 | 1 | 2580.7 | 0.158 | 0.04395 |
| Qyad-7-2: Qyad-18 | 1 | 6341.0 | 0.026 * | 0.06074 |
| Qyad-15: Qyad-18 | 1 | 1408.4 | 0.309 | −0.01079 |
| Qyad-7-1: QTL-7-2: Qyad-15: Qyad-18 | 3 | 1247.7 | 0.068 | 0.04413 |
| Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 174,125 | 87,062 | 370.9525 |
| Qyad-7-1 | 12.25 | 12.25 | 0.0002 *** |
| QTL-7-2 | 101 | 101 | 0.0003 *** |
| Qyad-15 | 129 | 129 | 0.0001 *** |
| Qyad-18 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 0.0002 *** |
| Year × Qyad-7-2 | 275 | 112 | 0.789ns |
| Year × QTL-7-2 | 342 | 78 | 0.02 * |
| Year × Qyad-15 | 278 | 110 | 0.226ns |
| Year × Qyad-18 | 178 | 89 | 0.567ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agre, P.A.; Darkwa, K.; Olasanmi, B.; Kolade, O.; Mournet, P.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Lopez-Montes, A.; De Koeyer, D.; Adebola, P.; Kumar, L.; et al. Identification of QTLs Controlling Resistance to Anthracnose Disease in Water Yam (Dioscorea alata). Genes 2022, 13, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020347
Agre PA, Darkwa K, Olasanmi B, Kolade O, Mournet P, Bhattacharjee R, Lopez-Montes A, De Koeyer D, Adebola P, Kumar L, et al. Identification of QTLs Controlling Resistance to Anthracnose Disease in Water Yam (Dioscorea alata). Genes. 2022; 13(2):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020347
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgre, Paterne Angelot, Kwabena Darkwa, Bunmi Olasanmi, Olufisayo Kolade, Pierre Mournet, Ranjana Bhattacharjee, Antonio Lopez-Montes, David De Koeyer, Patrick Adebola, Lava Kumar, and et al. 2022. "Identification of QTLs Controlling Resistance to Anthracnose Disease in Water Yam (Dioscorea alata)" Genes 13, no. 2: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020347
APA StyleAgre, P. A., Darkwa, K., Olasanmi, B., Kolade, O., Mournet, P., Bhattacharjee, R., Lopez-Montes, A., De Koeyer, D., Adebola, P., Kumar, L., Asiedu, R., & Asfaw, A. (2022). Identification of QTLs Controlling Resistance to Anthracnose Disease in Water Yam (Dioscorea alata). Genes, 13(2), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020347









