Abstract
Suicide is multifactorial and polygenic phenotype, affected by environmental and genetic factors. Among epigenetic mechanisms, miRNAs have been studied, but so far no very concise results exist. To overcome limitations of candidate miRNA and whole genome sequencing approaches, we created an in silico analysis algorithm that would help select the best suitable miRNAs that target the most interesting genes associated with suicidality. We used databases/web algorithms DIANA microT, miRDB, miRmap, miRWalk, and TargetScan and candidate genes SLC6A4, HTR1A, BDNF, NR3C1, ZNF714, and NRIP3. Based on a prediction algorithm, we have chosen miRNAs that are targeting regulation of the genes listed, and are at the same time being expressed in the brain. The highest ranking scores were obtained for hsa-miR-4516, hsa-miR-3135b, hsa-miR-124-3p, hsa-miR-129-5p, hsa-miR-27b-3p, hsa-miR-381-3p, hsa-miR-4286. Expression of these miRNAs was tested in the brain tissue of 40 suicide completers and controls, and hsa-miR-4516 and hsa-miR-381-3p showed a trend for statistical significance. We also checked the expression of the target genes of these miRNAs, and for NR3C1 expression was lower in suicide completers compared to controls, which is in accordance with the available literature results. To determine the miRNAs that are most suitable for further suicidality research, more studies, combining in silico analysis and wet lab experiments, should be performed.
1. Introduction
Suicide is a major public health issue, with more than 700,000 or 1.3% of deaths every year [1]. Although public awareness regarding suicidality has been rising over the past years, the goal of the international public health community to reduce the global suicide mortality rate by one third by 2030 will not be achieved [2]. In order to address the issue of suicidality comprehensively, many actions have been taken, and the available literature addressing the suicidality aetiology is growing every year. Suicidality is a complex behavioural phenotype, affected by many different risk and protective factors, including social, cultural, psychological, clinical, biological and environmental factors. To better understand the suicide risk, several different models have been proposed. One of them is the biopsychosocial model, which takes into account all of the previously listed factors and how they are connected [3]. Through family, twin and adoption studies, it has been identified that both environmental and genetic components make a significant contribution to the suicidality phenotype [4,5,6,7]. Over the past four decades, the genetic contribution to suicidality has been researched mostly on a DNA level, addressing the differences in genotype and allele frequencies distributions between different shapes of suicidality. The results of these studies were further evaluated in meta-analyses of several candidate genes for suicidality. These genes were recognised inside the neurotransmitter signaling pathways that were identified through studies of the neurobiological background of suicidality. The most dissected has been the serotonergic system and the polymorphisms in the genes for serotonin transporter (SLC6A4) [8], serotonin receptors (HTR), and tryptophan hydroxylase [9,10]. The physiological functions of serotonin are involved in the regulation of the development and plasticity of neural circuits, and are closely associated with actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a neurotrophin and member of a nervous growth factor family. BDNF, another important candidate gene for suicidality, promotes survival and differentiation of serotonergic neurons, while on the other hand elevated synaptic levels of serotonin positively regulate transcription of BDNF [11,12]. The functional polymorphism of BDNF has been researched extensively and it was associated with the possibility for increased risk for suicidal behaviour [13]. The results of the studies of candidate genes and polymorphisms on suicidality did not provide a clear answer to the causality of it, but it became evident that suicidality has a multifactorial and polygenic background. The search for novel genes associated with suicidality was advanced through genome-wide association studies interrogating hundreds of thousands of polymorphisms. However, this attempt did not provide consistent results, and previously identified candidate genes were frequently failing to pass rigorous reproducibility and significance testing [3,14].
Due to the multifaceted nature of suicidality and the insufficient clarification of the genetic background of suicidality, the studies were further oriented towards the simultaneous investigation of several factors and, in this case, the epigenetic studies aimed to link the environmental and genetic factors. Among the genes in epigenetic studies, very notable results were obtained for glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1). It is a part of the negative loop regulating the stress response axis hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal gland (HPA), often disturbed in mental disorders and suicidality [15]. In the brains of the suicide completers, lower expression of the NR3C1 was determined, and this could be the cause for the higher activity of the HPA axis [15,16]. Epigenetic regulation of the NR3C1 was also determined in the subjects that experienced early adverse events [17], pointing out the possible environmental effects on gene expression.
Through epigenetics, we study the differences in gene expression patterns, which are under very precise spatiotemporal control. The three most common epigenetic mechanisms are noncoding RNA, DNA methylation and modifications of histone proteins. Micro RNAs (miRNAs) belong to the short noncoding RNAs and are about 22 nucleotides in length. In humans, there are more than 2500 different miRNAs whose presence was also experimentally confirmed [18,19]. However, some estimates predict, in human genomes, the existence of up to one million corresponding sequences that could, after transcription, enter into the process of miRNA biogenesis [20]. MiRNA biogenesis is a multistep process that starts in the nucleus and completes in the cytoplasm with mature miRNAs [21]. Biogenesis initiates with RNA polymerase II that synthesises the first primary pri-miRNA transcript of about 70 nucleotides. The pri-miRNA has the typical hairpin loop structure, which is the substrate for microprocessor. The latter is a heterotrimeric complex protein that contains one molecule of the Drosha endonuclease and two molecules of its partner protein, DGCR8, and it catalyses the first step of enzymatic cleavage of pri-miRNA to pre-miRNA [16,22,23]. After cleavage, the pre-miRNA is transported to the cytoplasm via a transporter protein exportin 5. In the cytoplasm, further enzymatic cleavage of the hairpin structured pre-miRNA is catalysed by endoribonuclease Dicer. This results in a double-stranded RNA molecule, with mature miRNA and its complementary, passenger strand [23]. In most cases, only one strand of the double-stranded molecule is functionally active and becomes miRNA, while the other is degraded; however, sometimes both strands can be retained and become miRNAs [23,24]. Mature miRNA, bound to its complementary strand, with some assistance from chaperone proteins, is eventually loaded into an Argonaute (Ago) protein. At this point, the selection of the miRNA that will serve as the guide strand of the of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) is performed, while the complementary strand is degraded [23]. The role of the RISC molecule is a recognition of the short sequence within the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of target genes, to which miRNA molecules bind and cause messenger RNA (mRNA) silencing [16] through three possible different mechanisms. These are either degradation of mRNA through endoribonuclease activity of protein Ago3, which is part of the RISC [16,21,25], shortening of the polyadenilated tail at the 3′-end of the mRNA leading to lower stability of mRNA and accelerated degradation with cytoplasmic RNases [21], or inhibition of the ribosome binding to the mRNA, resulting in a reduction in translation efficiency [21,25].
The miRNAs’ main function is, therefore, post-transcriptional gene regulation at the level of mRNA, and miRNAs thus act as an important epigenetic mechanism of gene downregulation [26]. MiRNA molecules are of specific interest in the study of psychiatric disorders, since neuronal miRNA represent 70% of the total miRNAs in our body, and they are involved in neurogenesis and neuroplasticity [27]; hence, they represent a promising biomarker potential. However, one target mRNA can be regulated through several miRNAs, while one particular miRNA can regulate several different mRNAs [16,19,22,28]. This makes the identification of the potential miRNAs as a biomarker a quite elaborate task, but the use of modern in silico approaches could facilitate the work greatly.
In order for miRNAs to accomplish their goal, a specific intermolecular interaction occurs between miRNA and mRNA molecules. The probability and strength of such an interaction depends primarily on the nucleotide sequence of both molecules. With in silico analysis, it is possible to evaluate miRNAs and their role in gene expression. Several different databases/web algorithms, such as DIANA microT [29], miRDB [30], miRmap [31], miRWalk [32], and TargetScan [33], which collect and store data on miRNA are available. However, these databases use different algorithms and therefore the annotation of miRNA-mRNA pairs can vary. In order to minimise the type I and type II errors, it is advisable to use more independent sources, since a significant number of miRNA–mRNA interactions are false positives or negatives [34].
Since different databases do not necessarily predict the action of specific miRNAs in the same way, and because miRNAs are very abundant in the brain where they fine-tune explicit gene expression, we aimed to design an algorithm that would enable the evaluation the robustness of the results of particular miRNAs targeting and their expression in the brain from several distinct data sources (databases) [29,30,31,32,33,35] which could serve as potential biomarkers in suicidality. As target genes, we have selected several already well recognised candidate genes for suicidality (SLC6A4, HTR1A, BDNF, NR3C1), identified through the search of rather comprehensive available literature results, and additionally two genes (ZNF714, NRIP3) that we have identified as differentially methylated and expressed in a study on genome-wide DNA methylation in the brains of suicide completers [36]. We performed the miRNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis on the samples of Brodmann area 10 (BA10) on suicide completers and controls.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Altogether our study included 40 male subjects, 20 suicide completers and 20 control group subjects. The cause of death, determined by the medical examiner after completed autopsy, was hanging for suicide victims and sudden cardiac arrest for the control group subjects. Exclusion criteria (in addition to other causes of death and female sex) were age over 65 (to avoid age-related neurodegeneration) and alcohol dependence syndrome, which could cause age- or alcohol-related epigenetic changes, and insufficient body preservation that could be associated with poor RNA isolation yields and integrity. In blood and urine, basic toxicology and alcoholometry screening were performed. To rule out alcohol misuse status, histological changes in the liver that could be attributed exclusively to excessive alcohol consumption (fatty liver disease with >60% of hepatocytes showing macrovesicular hepatocyte fatty change, alcohol hepatitis and hepatic cirrhosis) with simultaneous exclusion of causal factors for histologic changes in the liver (abnormalities of hepatic tissue due to obesity, diabetes and/or congestive heart failure) were determined. Average age, postmortem interval and RIN value of suicide completers and control group subjects are presented in Table 1. Detailed subject information can be found in the Supplementary Table S1. Imaging and molecular studies have implicated the prefrontal cortex in suicidality. Brodmann area 10 is a region located in the frontopolar/rostrolateral prefrontal cortex, and is thought to be involved in memory recall, cognitive awareness and various executive functions [37]. Brain tissue samples of prefrontal cortex (BA10) were collected during routine autopsy performed at the Institute of Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ljubljana. All samples were collected by the same medical examiner, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further processing. The institutional review board of the Slovenian National Medical Ethics Committee approved our study, code 0120-392/2020-6.

Table 1.
Subject information and group comparison, including age, postmortem interval and RNA integrity number (mean ± SD).
2.2. Algorithm Design and in Silico Selection of miRNAs
To select the miRNAs for biochemical analysis, we designed a sorting algorithm that enabled us to order a list of miRNAs into a sequence based on the probability of having differential expression in suicide completers. This probability was evaluated by calculating a score for each miRNA which consisted of two components: target interaction score (from in silico target interaction analysis) and expression score (from in silico miRNA expression analysis). Each of those two components on average provided 50% to the total score.
For target interaction analysis, we selected six target genes that are characterised by differential expression in suicide completers (target genes being BDNF, HTR1A, SLC6A4, NR3C1, ZNF714, and NRIP3) based on literature research and results of our previous study [36]. Several online biological databases and algorithms exist, which evaluate which miRNAs are involved in regulation of target gene expression based on molecular interaction with the mRNA. We collected the data from five such biological databases/web algorithms (called databases below): DIANA microT (version 5.0, released in 2013) [29], miRDB (version 6.0, released in 2020) [30], miRmap (version 1.1, released in 2013) [31], miRWalk (version 3.0, released in 2018) [32] and TargetScan (version 7.2, released in 2018) [33]. Each database provided a set of miRNAs that could regulate the expression of a target gene, while some of them also provided a score that evaluated the probability/strength of intermolecular interaction. Table 2 includes the information about the predicted number of miRNAs targeting each of the selected target genes. In total, we collected more than 20,000 data entities, each of them providing an evaluation of a specific interaction between a miRNA and one of the target genes.

Table 2.
Number of predicted miRNAs involved in each target gene regulation.
As the data from different databases were not given in an identical format, data standardisation was performed. A 4-dimensional vector (containing miRNA identifier, target gene symbol, interaction evaluation, and database name) was selected as the standard data model. The major challenge was to reduce every data entity to a value in the interval (0, 1) where 0 or 1 would imply a low or a high probability of intermolecular interaction, respectively. Firstly, we converted the category given by databases miRWalk and TargetScan into a numerical value: 0 (database has not predicted regulation of target gene); 1 (database has predicted regulation of target gene). Next, the databases miRDB and miRmap provided values on a numerical scale that was two orders of magnitude higher than desired. A linear transformation with a normalisation factor of 0.01 was performed to fit the standard data model. Finally, to correct systemic differences between databases, we added a constant of 0.5 to all values from databases miRDB, miRmap and DIANA microT. This resulted in some values reaching as high as 1.5, but this was still acceptable.
The second component of the score was obtained from in silico expression analysis. Expression of miRNA is not universal throughout the body, each tissue has a specific miRNA expression profile, and this is something that we corrected for to decrease the proportion of false positive matches. A study by Ludwig et al. measured the expression of 1997 miRNAs using RNA-microarray analysis. Authors mapped the miRNA expression profile in 61 different tissues of two human subjects. Furthermore, in the study, the raw experimental data were normalised using variance-stabilised normalisation and corrected for negative values by adding a constant. This sequence of processes rendered the values that were directly used by our algorithm. We selected only the normalised expression data from regions “brain_1” and “brain_cerebral_coretex_2” [35]. These brain regions were selected because they contain BA10, which was the source of the biological samples we studied.
There were a total of 2511 miRNA included in in silico analysis; some of them had full and some only partial data available. For every miRNA, six distinct target interaction scores were calculated, one for each target gene, by adding together the values from all five databases. To determine the interaction score that a miRNA has with the whole group of target genes, we added together interaction scores for every target gene and obtained the overall interaction score represented by a number in the interval (0, 39) (5 databases × 6 genes, 30 values combined). The other part of the total score (expression score) provided values in the interval (0, 10). To ensure that each score component would provide 50% to the total score, we performed a linear transformation on expression data with normalisation factor of 2.4 (0.4 for each gene). By finally adding together the overall target interaction score and normalised expression score, we determine the total score of a miRNA. Based on this score, the sorting algorithm can determine which miRNAs have the highest probability to be involved in gene regulation of (differentially expressed) target genes. For the biochemical analysis, we selected 10 miRNAs with the highest total scores, but later reduced the selection to 7 miRNAs due to qPCR reagent quality issues. Detailed information and algorithm source codes are available at https://github.com/ualich/miRNAtpa (accessed on 21 January 2022).
2.3. Isolation and Gene Expression of miRNA and Target Gene mRNA
To isolate RNA, we used 50 mg of frozen and ground BA10 tissue. We isolated both miRNA and mRNA simultaneously using mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), following the manufacturer instructions. Isolated RNA was quantified using Synergy H4 and 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). RIN values (mean ± SD) were 7.7 ± 0.22 for suicide completers and 7.26 ± 0.27 for control group subjects.
For miRNA analysis, RNA underwent reverse transcription using TaqMan Advanced miRNA cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), following the manufacturer instructions. For mRNA analysis, RNA underwent reverse transcription using Maxima H Minus cDNA Synthesis Master Mix kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), following the manufacturer instructions.
Gene expression levels were quantified using qPCR following the MIQE guidelines [38]. All qPCR reactions were run using Viia 7 real-time PCR system and hydrolysis probes (both Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). All hydrolysis probes were validated beforehand and negative control was used for each qPCR. We used has-miR-99a-5p and GAPDH as reference genes for miRNA and mRNA quantificatiohashsa-miR-99a-5p was selected based on the qualities needed for a good reference gene: stable expression level through various tissue, sufficient level of expression in the brain tissue and it ranked low on our algorithm. GAPDH was chosen as it is one of the most commonly used reference genes for RNA gene expression analysis.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Gene expression data were analysed relative to the corresponding reference gene, following the 2−ΔΔCq method by Livak et al. [39]. Based on the value of sample’s quantification cycle (Cq), we compared relative changes in gene expression between suicide completers and control group subjects. Next, the distribution of data set was assessed using the D’Agostino and Pearson test. As all data did not follow normal distribution, data set values were further analysed using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. The results are presented and considered without correction for multiple testing as the study was explorative in nature. Statistical tests and figures were made using GraphPad Prism version 8.4.3 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA, www.graphpad.com, accessed on 21 January 2022). p-values < 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. MiRNA Gene Expression
Final miRNA selection was based on the total algorithm score (comprised of interaction scores and expression score). The total score was calculated for all 2511 miRNAs included in in silico analysis. Based on this in silico analysis, we selected seven miRNAs for experimental validation (Table 3).

Table 3.
Final miRNA selection. MiRNAs were selected by an in silico algorithm. The table contains separated values of target gene analysis and expression analysis, as well as combined values.
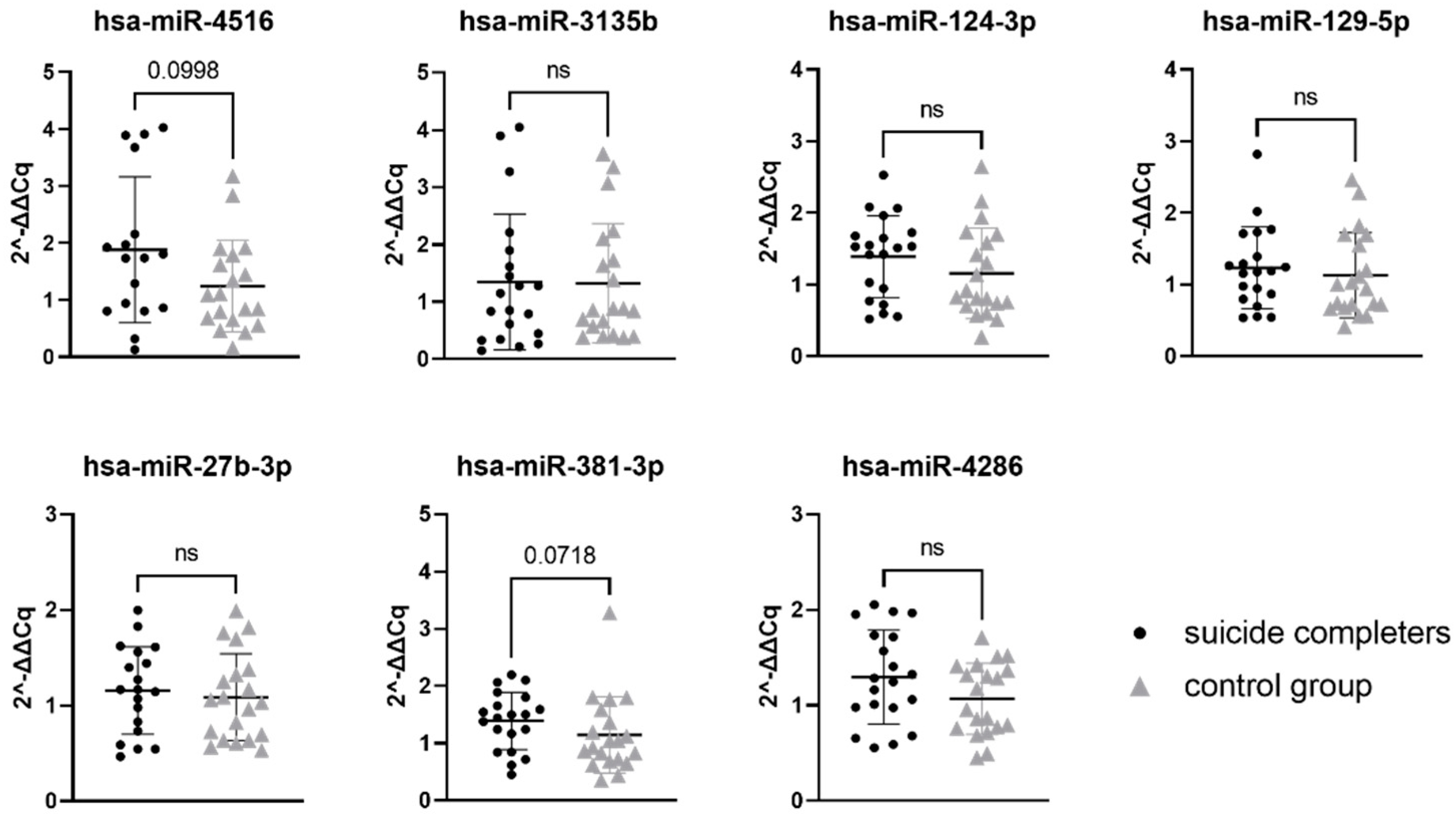
Relative gene expression data of seven miRNAs were compared between suicide completers and control group subjects. While none of the seven tested miRNAs reached statistical significance, two of them showed a trend towards statistical significance (hsa-miR-4516 with p-value 0.0998 and hsa-miR-381-3p with p-value 0.0718). Gene expression of both miRNAs was on average higher in suicide completers compared to the control group subjects. Detailed statistical information is presented in Table 4. Graphical representation of miRNA expression results can be found in Figure 1.

Table 4.
Relative gene expression of miRNAs between suicide completers and control group subjects, determined using the Mann–Whitney U test.
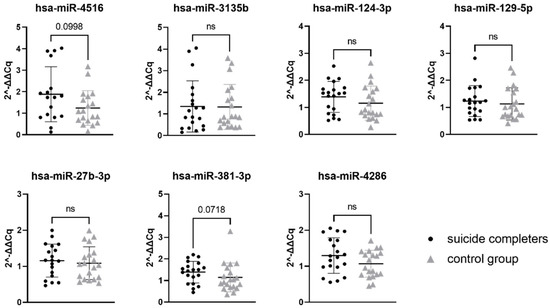
Figure 1.
Relative gene expression of selected miRNAs in Brodmann area 10. Data are presented as a scatter plot, with each point being a measure of relative gene expression per subject for both studied groups. Horizontal lines represent mean value ± standard deviation. Data were analysed using the Mann–Whitney U test, with p-values below 0.05 as significant. ns stands for not significant.
3.2. Target Gene mRNA Expression
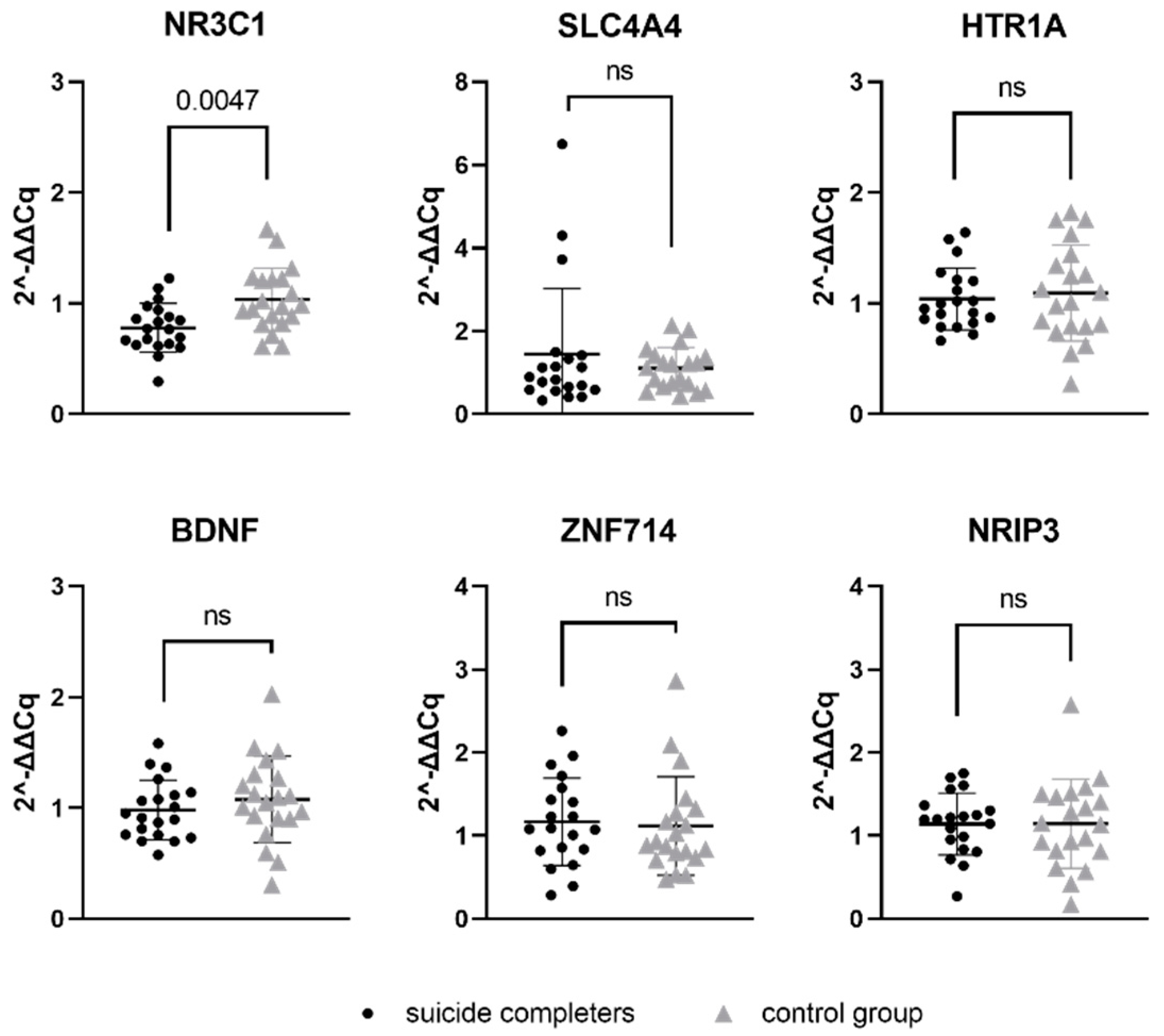
Relative gene expression data of six genes, which represent a potential target for previously mentioned seven miRNAs, were compared between suicide completers and control group subjects. One of the studied genes, NR3C1, reached statistical significance (p-value 0.0047). Gene expression of NR3C1 was lower in suicide completers compared to control group subjects. Detailed statistical information are presented in Table 5. Graphical representation of mRNA expression results can be found in Figure 2.

Table 5.
Relative gene expression of target gene mRNAs between suicide completers and control group subjects, determined using the Mann–Whitney U test.
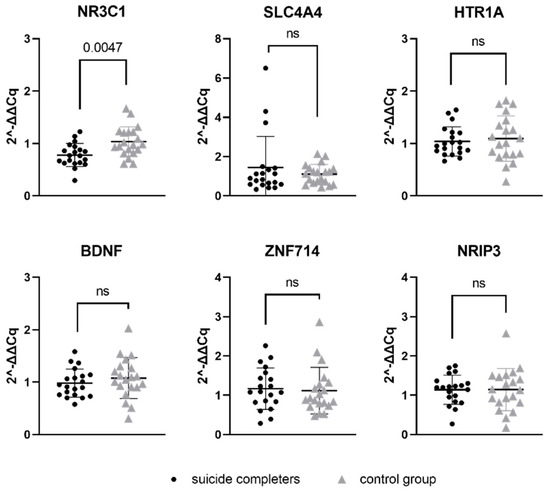
Figure 2.
Relative gene expression of target gene mRNAs in Brodmann area 10. Data are presented as a scatter plot, with each point being a measure of relative gene expression per subject for both studied groups. Horizontal lines represent mean value ± standard deviation. Data were analysed using Mann–Whitney U test, with p-values below 0.05 as significant. ns stands for not significant.
4. Discussion
Disposition to suicidality is determined by genetic as well as by environmental factors, while one of the main connecting links between these two factors could be epigenetics [15]. Numerous studies exist, connecting epigenetic mechanisms with suicidal behaviour, with DNA methylation being predominately studied [15]. With our study, we aimed to design an algorithm that could efficiently select miRNAs that potentially target our genes of interest, and analyse whether or not the selected miRNAs exhibit altered expression levels in the brain of suicide completers.
We selected miRNAs using integrated data of five miRNA databases/web algorithms: DIANA microT-CDS, miRDB, miRmap, miRWalk and TargetScan. We developed a custom sorting algorithm that ranked miRNAs into an order according to the probability of target gene interaction and potential expression in the brain. For each miRNA, a total score was calculated by combining interaction scores and expression scores. Using qPCR, we tested the association between expression of miRNAs (hsa-miR-4516, hsa-miR-3135b, hsa-miR-124-3p, hsa-miR-129-5p, hsa-miR-27b-3p, hsa-miR-381-3p, and hsa-miR-4286) and their potential target mRNAs (SLC6A4, HTR1A, BDNF, NR3C1, ZNF714, and NRIP3) that have been previously recognised as important candidate genes for suicidality. None of the seven studied miRNA reached statistical significance of p-value below 0.05. However, two of the studied miRNAs, hsa-miR-4516 and hsa-miR-381-3p, did show a trend towards statistical significance with the p-value below 0.1.
Interestingly, according to our algorithm, hsa-miR-4516 was the highest ranked miRNA, with a strong association to SLC6A4 gene. Experimental data showed a high expression rate in the brain of our subjects, compared to the expression rate of the other six miRNAs we analysed. Hsa-miR-4516 has already been described in the literature as associated with mental disorders. In subjects diagnosed with bipolar disorder, there was an increased level of hsa-miR-4516 expression in peripheral blood exosomes [40]. The second miRNA we observed with a trend towards significance, hsa-miR-381-3p, has not yet been associated with suicidality. A study did, however, observe hsa-miR-381-3p as potentially involved in brain state and inflammation, where a decreased expression of has-miR-381-3p was observed in the serum of patients with Alzheimer’s disease [41]. Taking both hsa-miR-4516 and has-miR-381-3p into account, together they target too few genes to look at a common gene ontology assessment. This is the reason that we looked at the gene ontology of hsa-miR-4516 and hsa-miR-381-3p separately. Both miRNAs have numerous other target genes in addition to the six target genes that we selected in our analysis [42]. Hsa-miR-4516 appears to be targeting genes involved in cell adhesion and synaptic signalling, while hsa-miR-381-3p targets genes involved in transcription regulation and neurogenesis [42]. The altered expression of miRNAs could therefore have a broader effect on the cell functioning.
The remaining five miRNAs that we analysed (hsa-miR-3135b, hsa-miR-124-3p, hsa-miR-129-5p, hsa-miR-27b-3p, and hsa-miR-4286) showed no difference in expression levels between suicide completers and control group subjects. Of these, hsa-miR-124-3p appears to be the most studied in regard to brain states. It belongs to the miR-124 family, which is highly neuron-specific and it is thought to be important for the functioning and development of the nervous system (however, it so far lacks sensitivity to be a useful biomarker) [43,44]. Hsa-miR-124-3p has been associated with depression-like states. Cell and animal models indicate that miR-124-3p binds to the 3′UTR region of NR3C1, leading into decreased levels of NR3C1 gene expression [45]. Similarly, it is increased in subjects with major depressive disorder (both in living subjects and in those deceased from causes other than suicide) [46].
MiRNAs work by binding to target gene mRNA and subsequently decrease the expression of the target gene. Therefore, we hypothesised that if there are present changes in miRNA expression in suicide completers, that the changes in expression could also be observed at the level of the target genes. Our study revealed decreased expression of NR3C1 gene in suicide completers. NR3C1 is a gene that codes for glucocorticoid receptor and is, thus, heavily involved in the stress response. The HPA axis and its dysfunction is known to be an important risk factor for suicidal behaviour. Dysfunction of the stress axis and poor adaptation to stress may also be associated with changes in epigenetic regulation and gene expression of involved genes. Cortisol, also known as the stress hormone, binds to the glucocorticoid receptor, which has an anti-inflammatory effect. If the number of glucocorticoid receptors is adequate, the stress response is appropriate. However, if the number of glucocorticoid receptors is reduced, the stress response can be prolonged [47]. In animal studies, the separation of a pup from its mother is associated with increased DNA methylation in the NR3C1 promoter region. This leads to reduced expression of the NR3C1 gene and, consequently, a more pronounced response of the organism to stress [48]. Similarly, hypermethylation on NR3C1 promoter in downregulated gene expression was determined to be more likely in suicidal patients with a major depressive disorder compared to in the control subjects [49]. Numerous mechanisms exist inside the cell which can influence gene expression. Studies show that miRNA can also greatly affect the glucocorticoid response system [50], which could lead us to believe that one possible explanation for a decreased level of NR3C1 mRNA in suicide completers could be the increased expression of has-miR-4516 ahashsa-miR-381-3p. Decreased levels of NR3C1 mRNA have already been associated with suicidal behaviour [17,51,52].
The first miRNAs were discovered in the 1990s, and about a decade later, they have been adopted as a separate class of biological regulators. Through numerous studies, miRNAs were recognised as one of the most important mechanisms for gene expression regulation [22,23,53]. This is also the reason why today miRNAs are tested as biological markers to be used in the diagnosis and prognosis of various neuropsychiatric disorders [54]. The great potential of miRNAs for clinical medicine is their presence and biological activity not only in the cell they were generated in, but also in other, neighbouring cells or distant tissues. One of the mechanisms for miRNAs transportation are extracellular vesicles (EVs) [28,55].
Although miRNAs appear to be a promising biomarker, there are some limitations associated with their study. One of the main limitations at the stage of miRNA selection is the non-uniform nomenclature of miRNAs between different data sources. This was an important issue in our study, as we used five different data sources/web algorithms to extract the data on miRNAs. We treated all the miRNAs with the same sequence as identical (for example, hsa-mir-125b-1-3p and hsa-mir-125b-2-3p have the same sequence), as the miRNA sequence was the most important factor in databases/web algorithms.
The limitation of our study is the sample size, which was rather small; on the other hand, the inclusion criteria were rather strict, resulting in a homogenous sample in which even smaller changes could be more likely detected. The significant difference in age between suicide completers and control group subjects also needs to be taken into consideration. The difference in age can be attributed to the cause of death. Middle-aged men tend to be most at risk of suicide, while the risk of sudden cardiac death tends to increase with age. If subjects over the age of 65 would be included, the age difference between the two groups examined would be possibly lower (due to older suicide completers), but this could then present another problem as after the age of 65, age-related neurodegeneration can start occurring. Still, subjects who died from sudden cardiac arrest present a control group with a high homogeneity within the group. In the end, we have to be careful with the interpretation of the results. Namely, miRNAs represent just one of the possible levels of gene expression regulation. Therefore, if a miRNA is determined as the regulatory miRNA based on a database/web algorithm, its role in the particular physiologic state of a cell still has to be demonstrated, suggesting the importance of coordinated use of in silico and experimental procedures.
More general limitations are related to the studies on miRNAs in association with mental disorders and suicide, as there is a lot of overlap in the nature of both phenotypes. Currently, there is a clear lack of studies in which the result of miRNAs expression could be associated only to suicidality; therefore, we can more or less treat the miRNAs as the biomarkers for mental disorders, and not really just as the biomarkers for suicidality specifically.
While the algorithm had many beneficial properties, such as integration of five different databases and gene expression data integration, the results of the expression of the identified miRNAs were not significant when comparing suicide completers and controls. This could be due to various reasons such as the selection of candidate genes and algorithm weaknesses which have to be further identified and improved.
5. Conclusions
The aim of our study was to confirm the listed miRNAs as potential biomarkers for suicide, as miRNAs are, in addition to being an important gene expression regulator, also very stable molecules in terms of their chemical stability (higher resistance to RNase degradation, pH and temperature changes), with tissue-specific expression, and could, therefore, also be a suitable biomarker from a technical point of view. Because of their characteristics and their presence in body fluids, miRNA testing in the future could also advance to the clinical setting. Namely, one of the important cargos of the EVs are miRNAs. It has been shown that EVs can cross the blood–brain barrier [56], thus bringing the information from the central nervous system to the periphery (e.g., blood), where sampling can be performed with minimally invasive protocols. Therefore, miRNAs represent a great potential for central nervous system biomarkers for tackling the brain’s (patho)physiological status.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13040562/s1, Table S1: Study subject information.
Author Contributions
Conceiving and designing the experiments, A.V.P.; collection of the samples and data, T.Z.; performed the experiments, K.K. and U.A.; analysis of the data, K.K. and U.A.; writing of the paper, A.V.P., K.K. and U.A. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovenian Research Agency, grants for Research Programme P1-0390 and Research Project J3-7132 and Z3-2653.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the Council of Europe Conventions, Oviedo Convention, and Slovenian Code of Medical Ethics, and approved by the Slovenian National Medical Ethics Committee (0120-392/2020-6).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived as the samples were taken at routine autopsy.
Data Availability Statement
Available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mojca Katrašnik and Iris Šalamon for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Suicide in the World: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Live Life: An Implementation Guide for Suicide Prevention in Countries; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Turecki, G.; Brent, D.A.; Gunnell, D.; O’Connor, R.C.; Oquendo, M.A.; Pirkis, J.; Stanley, B.H. Suicide and suicide risk. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, B.; Buettner, A.; Zill, P. Genetics of suicide. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, D.A.; Melhem, N. Familial transmission of suicidal behavior. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voracek, M. Genetic factors in suicide: Reassessment of adoption studies and individuals’ beliefs about adoption study findings. Psychiatr. Danub. 2007, 19, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Voracek, M.; Loibl, L.M. Genetics of suicide: A systematic review of twin studies. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2007, 119, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, G.; Serretti, A. The influence of the serotonin transporter gene 5-httlpr polymorphism on suicidal behaviors: A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 88, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkovic, B.; Laurent, C.; Podlipski, M.A.; Frebourg, T.; Cohen, D.; Gerardin, P. Genetic association studies of suicidal behavior: A review of the past 10 years, progress, limitations, and future directions. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Jia, C.X.; Lian, Y.; Sun, S.H.; Lyu, M.; Wu, A. Association of the htr2a 102t/c polymorphism with attempted suicide: A meta-analysis. Psychiatr. Genet. 2015, 25, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinowich, K.; Lu, B. Interaction between bdnf and serotonin: Role in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. Neuronal and behavioral plasticity: The role of serotonin and bdnf systems tandem. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castro, T.B.; Salas-Magaña, M.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; López-Narváez, M.L.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.A.; Hernández-Díaz, Y. Exploring the association between bdnf val66met polymorphism and suicidal behavior: Meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 94, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castro, T.B.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.A.; Genis-Mendoza, A.D.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; Nicolini, H.; López-Narváez, M.L.; Martínez-Magaña, J.J. Identification of gene ontology and pathways implicated in suicide behavior: Systematic review and enrichment analysis of gwas studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2019, 180, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.; Woo, J.; Maes, M.S.; Zai, C.C. Suicide epigenetics, a review of recent progress. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, Y. Micrornas in depression and suicide: Recent insights and future perspectives. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 240, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P.O.; Sasaki, A.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Dymov, S.; Labonte, B.; Szyf, M.; Turecki, G.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Fischer, U.; Backes, C.; Galata, V.; Minet, M.; Hart, M.; Abu-Halima, M.; Grässer, F.A.; Lenhof, H.-P.; et al. An estimate of the total number of true human mirnas. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slota, J.A.; Booth, S.A. Micrornas in neuroinflammation: Implications in disease pathogenesis, biomarker discovery and therapeutic applications. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saçar, M.D.; Allmer, J. Data mining for microrna gene prediction: On the impact of class imbalance and feature number for microrna gene prediction. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, Ankara, Turkey, 25–27 September 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vishnoi, A.; Rani, S. Mirna biogenesis and regulation of diseases: An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1509, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gantier, M.P.; McCoy, C.E.; Rusinova, I.; Saulep, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, D.; Irving, A.T.; Behlke, M.A.; Hertzog, P.J.; Mackay, F.; et al. Analysis of microrna turnover in mammalian cells following dicer1 ablation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5692–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan micrornas. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. Mirbase: Microrna sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conaco, C.; Otto, S.; Han, J.J.; Mandel, G. Reciprocal actions of rest and a microrna promote neuronal identity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geaghan, M.; Cairns, M.J. Microrna and posttranscriptional dysregulation in psychiatry. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruzdev, S.K.; Yakovlev, A.A.; Druzhkova, T.A.; Guekht, A.B.; Gulyaeva, N.V. The missing link: How exosomes and mirnas can help in bridging psychiatry and molecular biology in the context of depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.M.J.; Krauskopf, J.; Ramaekers, J.G.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; Prickaerts, J.; Briedé, J.J. Circulating micrornas as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 185, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kostoulas, N.; Vlachos, I.S.; Vergoulis, T.; Reczko, M.; Filippidis, C.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. Diana-microt web server v5.0: Service integration into mirna functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W169–W173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Mirdb: An online database for prediction of functional microrna targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejnar, C.E.; Zdobnov, E.M. Mirmap: Comprehensive prediction of microrna target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. Mirwalk: An online resource for prediction of microrna binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microrna target sites in mammalian mrnas. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.P.; Fiori, L.M.; Gross, J.A.; Labonte, B.; Yerko, V.; Mechawar, N.; Turecki, G. Regulatory role of mirnas in polyamine gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide completers. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of mirna expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouter, K.; Zupanc, T.; Videtič Paska, A. Genome-wide DNA methylation in suicide victims revealing impact on gene expression. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 253, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaal, L.; van Harmelen, A.-L.; Chatzi, V.; Lippard, E.T.C.; Toenders, Y.J.; Averill, L.A.; Mazure, C.M.; Blumberg, H.P. Imaging suicidal thoughts and behaviors: A comprehensive review of 2 decades of neuroimaging studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The miqe guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time pcr experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2−ΔΔc(t) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, G.R.; Lima, C.N.C.; Valvassori, S.S.; Zunta-Soares, G.; Soares, J.C.; Quevedo, J. Preliminary investigation of peripheral extracellular vesicles’ micrornas in bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 255, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Teng, P.; Yang, Q. Differential expression of mir-381-3p in alzheimer’s disease patients and its role in beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and inflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. G:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Piperi, C. Mir-124 and parkinson’s disease: A biomarker with therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Innamorati, M.; Giordano, G.; Montebovi, F.; Sher, L.; Dwivedi, Y.; Girardi, P. The role of micrornas in synaptic plasticity, major affective disorders and suicidal behavior. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 73, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Mu, R.H.; Li, C.F.; Dong, S.Q.; Geng, D.; Liu, Q.; Yi, L.T. Microrna-124 targets glucocorticoid receptor and is involved in depression-like behaviors. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 79, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Dunbar, M.; Shelton, R.C.; Dwivedi, Y. Identification of microrna-124-3p as a putative epigenetic signature of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadmiel, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, I.C.; Cervoni, N.; Champagne, F.A.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Sharma, S.; Seckl, J.R.; Dymov, S.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Shelton, R.C.; Dwivedi, Y. DNA methylation and expression of stress related genes in pbmc of mdd patients with and without serious suicidal ideation. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 89, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gou, X.; Jiang, T.; Ouyang, J. The effects of micrornas on glucocorticoid responsiveness. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonté, B.; Suderman, M.; Maussion, G.; Navaro, L.; Yerko, V.; Mahar, I.; Bureau, A.; Mechawar, N.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J.; et al. Genome-wide epigenetic regulation by early-life trauma. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Díaz, Y.; Genis-Mendoza, A.D.; González-Castro, T.B.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.A.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; López-Narváez, M.L.; Nicolini, H. Association and genetic expression between genes involved in hpa axis and suicide behavior: A systematic review. Genes 2021, 12, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.J. New human and mouse microrna genes found by homology search. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Yoshino, Y.; Allen, L.; Prall, K.; Schell, G.; Dwivedi, Y. Exploiting circulating micrornas as biomarkers in psychiatric disorders. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Hansen, K.; Obrietan, K.; Dwivedi, Y.; Amore, M.; Shomron, N.; Girardi, P. Micrornas: Fundamental regulators of gene expression in major affective disorders and suicidal behavior? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).