miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Isolation of the Thymus Tissues and TECs
2.3. Culture of the MTEC1 and HEK-293T Cells
2.4. RT-qPCR Assays
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Cell Cycle Assay
2.8. Target Genes Prediction
2.9. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
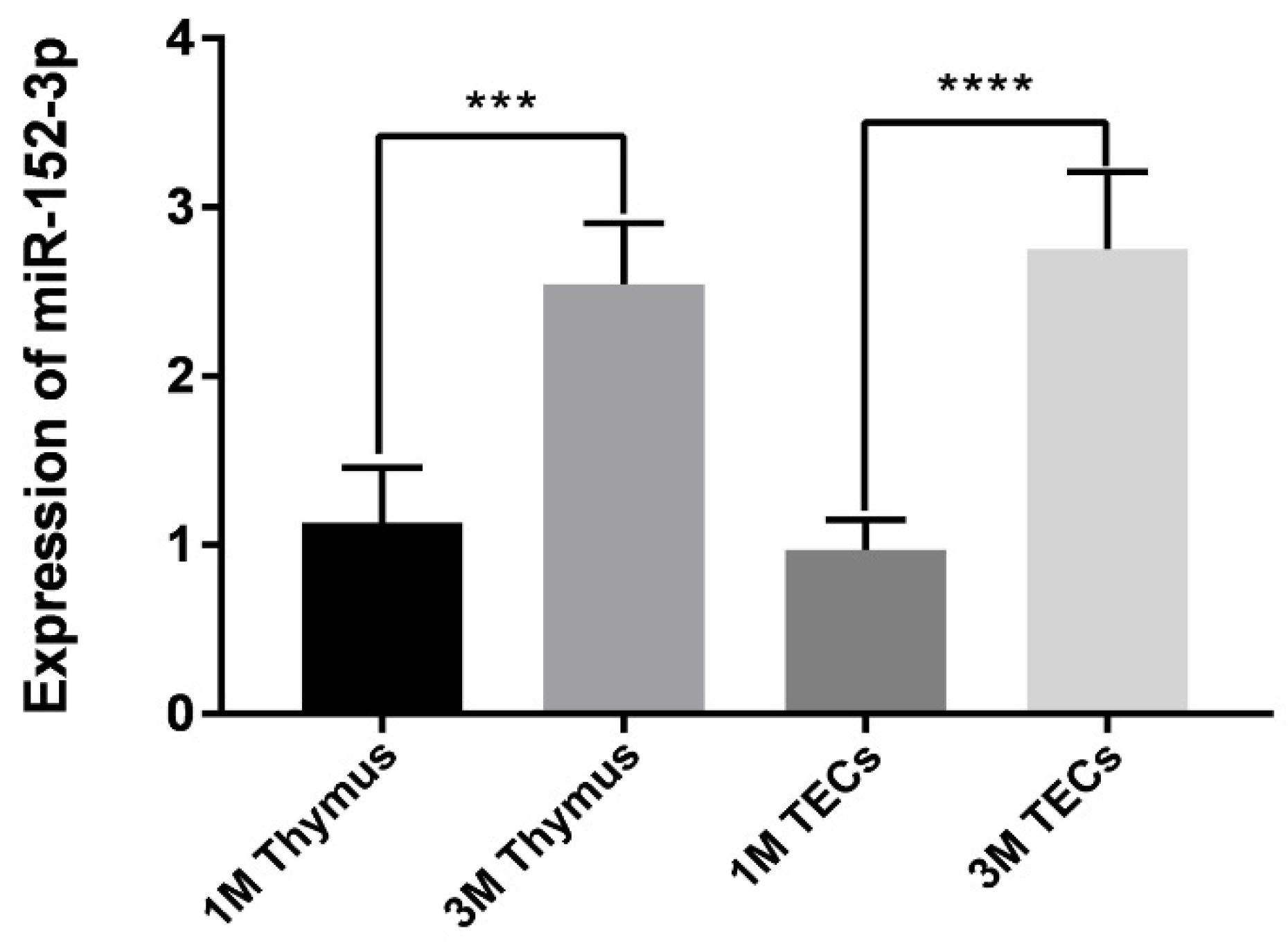
3.1. The Expression of miR-152-3p in the Mice Thymus and TECs
3.2. miR-152-3p Inhibits the Viability and Proliferation of MTEC1 Cells
3.3. miR-152-3p Represses the Cell Cycle of MTEC1 Cells
3.4. Putative Target Genes of miR-152-3p
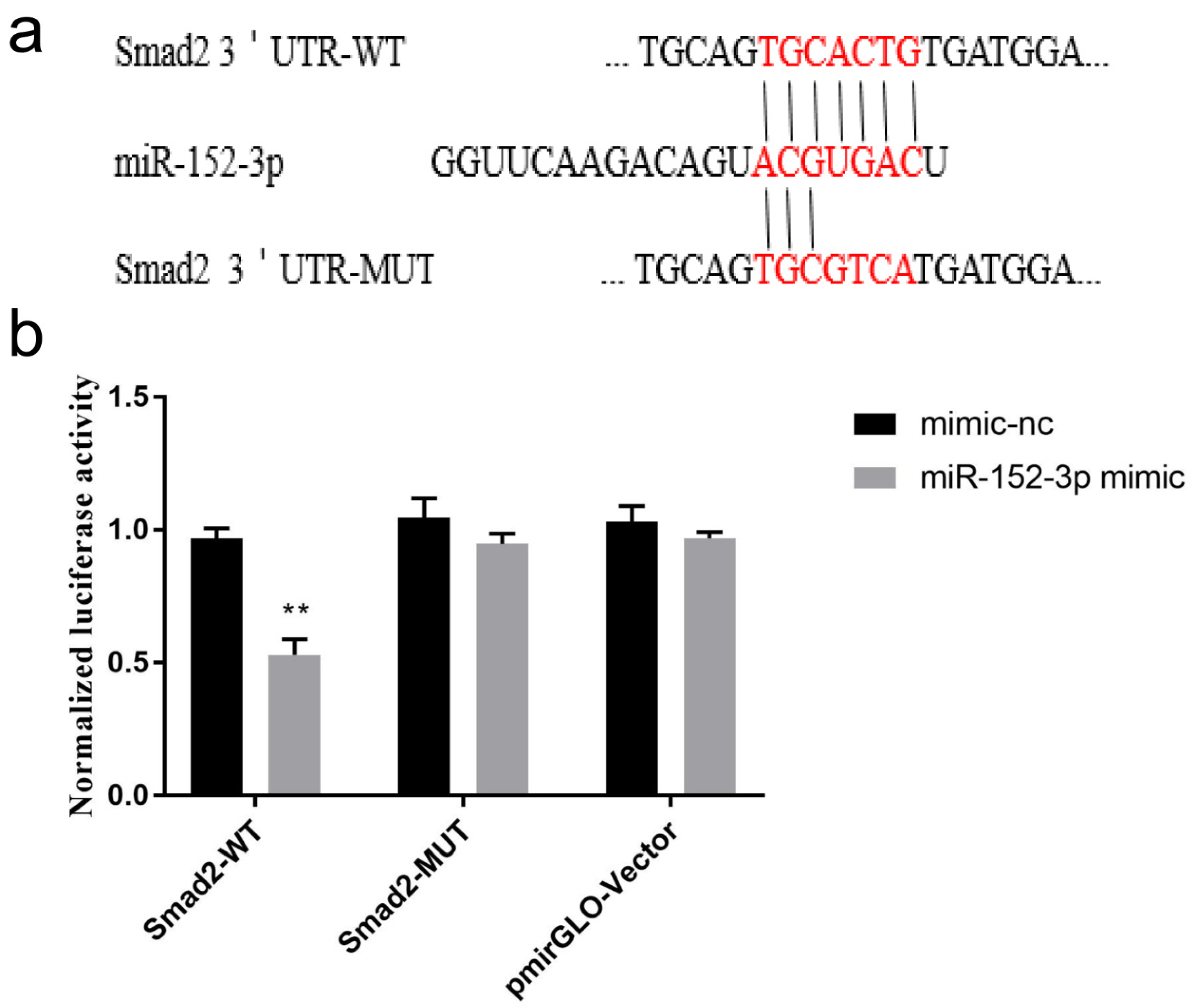
3.5. Validation of the Target Gene Smad2
3.6. miR-152-3p Regulated the Proliferation of MTEC1 Cells by Targeting Smad2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Pan, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhong, X.-P.; Tan, L.; Liang, Z.; He, J.; Feng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.-R. Thymic Epithelial Cells Contribute to Thymopoiesis and T Cell Development. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D.B. The effect of age on thymic function. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akha, A.A.S. Aging and the immune system: An overview. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 463, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Morales, A.J.; Maxey, S.E.; Bessette, K.A.; Ratcliffe, N.R.; Kelly, J.A.; Craig, R.W. MCL1 increases primitive thymocyte viability in female mice and promotes thymic expansion into adulthood. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Mustachio, L.M.; Su, D.-M.; Craig, R.W. Thymus Size and Age-related Thymic Involution: Early Programming, Sexual Dimorphism, Progenitors and Stroma. Aging Dis. 2012, 3, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.; Zhu, X.; Dohkan, J.; Cheng, L.; Barnes, P.F.; Su, D.-M. The aged thymus shows normal recruitment of lymphohematopoietic progenitors but has defects in thymic epithelial cells. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Brown, R.; Amagai, T.; Zhao, Y.; Su, D.-M. Declining expression of a single epithelial cell-autonomous gene accelerates age-related thymic involution. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zook, E.C.; Krishack, P.A.; Zhang, S.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J.; Firulli, A.B.; Witte, P.L.; Le, P.T. Overexpression of Foxn1 attenuates age-associated thymic involution and prevents the expansion of peripheral CD4 memory T cells. Blood 2011, 118, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfin, P.M.; Min, D.; Bryson, J.L.; Serwold, T.; Edris, B.; Blackburn, C.; Richie, E.; Weinberg, K.I.; Manley, N.R.; Sage, J.; et al. Inactivation of the RB family prevents thymus involution and promotes thymic function by direct control of Foxn1 expression. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaka, C.; Hauri-Hohl, M.; Takizawa, K.; Nishikawa, Y.; Yano, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Boyd, R.; Holländer, G.A. TGF-β type II receptor expression in thymic epithelial cells inhibits the development of Hassall’s corpuscles in mice. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Enright, A.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human MicroRNA Targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fortin, K.; Mourelatos, Z. MicroRNAs: Biogenesis and Molecular Functions. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gan, T.; Ning, H.; Wang, L. MicroRNA Functions in Thymic Biology: Thymic Development and Involution. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, A.S.; Dooley, J.; Linterman, M.; Pierson, W.; Ucar, O.; Kyewski, B.; Zuklys, S.; A Hollander, G.; Matthys, P.; Gray, D.; et al. The thymic epithelial microRNA network elevates the threshold for infection-associated thymic involution via miR-29a mediated suppression of the IFN-α receptor. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Ye, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Tan, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-181a-5p enhances cell proliferation in medullary thymic epithelial cells via regulating TGF-β signaling. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Ye, Y.; Qi, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Tan, X.; Tan, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-195a-5p inhibits mouse medullary thymic epithelial cells proliferation by directly targeting Smad7. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. miR-205-5p inhibits thymic epithelial cell proliferation via FA2H-TFAP2A feedback regulation in age-associated thymus involution. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 122, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, B.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. miR-199b-5p enhances the proliferation of medullary thymic epithelial cells via regulating Wnt signaling by targeting Fzd6. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2020, 53, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, D.; Ouyang, D.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. MicroRNA expression in the aging mouse thymus. Gene 2014, 547, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Ye, Y.; Qi, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Age and sex differences in microRNAs expression during the process of thymus aging. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.-L.; Zeng, X.-Q.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.-M.; Gong, B.-S.; Zhang, K.-Z.; Zeng, J.-H.; Guo, D.-G.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-G. Integrated microRNA and mRNA sequencing analysis of age-related changes to mouse thymic epithelial cells. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Ye, Y.; Xing, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of Castration on miRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA Profiles in Mice Thymus. Genes 2020, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamato, D.; Burch, M.L.; Piva, T.J.; Rezaei, H.B.; Rostam, M.A.; Xu, S.; Zheng, W.; Little, P.J.; Osman, N. Transforming growth factor-β signalling: Role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, P. Activation of SIRT3 by resveratrol ameliorates cardiac fibrosis and improves cardiac function via the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2015, 308, H424–H434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Luo, J.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Zeng, O.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Hydrogen sulfide exhibits cardioprotective effects by decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stress in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ran, Q. Nuclear SMAD2 Restrains Proliferation of Glioblastoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhou, D.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Smad2 increases the apoptosis of activated human hepatic stellate cells induced by TRAIL. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 32, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, W.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y. Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 regulates human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via sponging miR-205 and modulating Smad2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6919–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, É.; AlSudais, H.; Rajgara, R.; Fu, D.; Omaiche, S.; Wiper-Bergeron, N. SMAD2 promotes myogenin expression and terminal myogenic differentiation. Development 2021, 148, dev195495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Chi, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Wei, T.; Gui, J.; Zhu, X. Transcriptome analysis of murine thymic epithelial cells reveals age-associated changes in microRNA expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, A.; Chen, W. Cytological identification of the murine MTEC1 thymus epithelial cell line. ACTA Anat. Sin. 1990, 21, 408–410, 463. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Sizova, O.; Wang, L.; Su, D.-M. A Fine-Tune Role of Mir-125a-5p on Foxn1 During Age-Associated Changes in the Thymus. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geenen, V. The thymus and the science of self. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Bai, Z.; Wen, X.; Du, H.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ma, W. MiR-152-3p regulates cell proliferation, invasion and extracellular matrix expression through by targeting FOXF1 in keloid fibroblasts. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Liu, M.-M.; Jin, R.-T.; Kong, J.; Wang, S.-H.; Sun, W.-B. miR-152-3p Modulates hepatic carcinogenesis by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 8. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, Z.; Man, D.; Ruan, H.; Huang, S. miR-152-3p Affects the Progression of Colon Cancer via the KLF4/IFITM3 Axis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 8209504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, M.J.; Martin-Malpartida, P.; Massagué, J. Structural determinants of Smad function in TGF-β signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, C.; Zaromytidou, A.-I.; Xi, Q.; Gao, S.; Yu, J.; Fujisawa, S.; Barlas, A.; Miller, A.N.; Manova-Todorova, K.; Macias, M.J.; et al. Nuclear CDKs Drive Smad Transcriptional Activation and Turnover in BMP and TGF-β Pathways. Cell 2009, 139, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Alarcón, C.; Sapkota, G.; Rahman, S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Goerner, N.; Macias, M.J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Massagué, J. Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4L Targets Activated Smad2/3 to Limit TGF-β Signaling. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Q. Lnc-LFAR1 affects intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma proliferation, invasion, and EMT by regulating the TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hobson, K.G.; Cho, K.; Adamson, L.K.; Greenhalgh, D.G. Burn-Induced Thymic Apoptosis Corresponds with Altered TGF-β1 and Smad 2/3. J. Surg. Res. 2002, 105, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenneth, N.S.; White, R.J. Regulation by c-Myc of ncRNA expression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Genes | Forward and Reverse Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| C-myc | F: GCAACTTCTCCACCGCCGAT | |
| NM_010849.4 | R: AACCGCTCCACATACAGTCCT | 141 |
| Ccnd1 | F: CATGAACTACCTGGACCGCTT | |
| NM_007631.2 | R: TGCTTGTTCTCATCCGCCTCT | 285 |
| Ccne1 | F: GTGCGAAGTCTATAAGCTCCA | |
| NM_007633.2 | R: CGCCATCTGTAACATAAGCAA | 194 |
| Cdk4 | F: CTACATACGCAACACCCG | |
| NM_009870 | R: TCAAAGATTTTCCCCAACT | 118 |
| Ywhab | F: CCGGAGAAAATAAACAAACCAC | |
| NM_018753.6 | R: CAATCGCCTCATCAAATGCC | 201 |
| Tgif2 | F: TCTGCACCGCTACAACGCCTA | |
| NM_173396.3 | R: ACTGATTAGGGTCTTTGCCAT | 158 |
| Ltbp1 | F: GCTCTTTCCGCTGCCTCTGTTATC | |
| NM_019919.4 | R: AGTTCACACTCGTTCACATCCACAC | 82 |
| Fbn1 | F: GAGTGCCAAGAAATCCCGAAC | |
| NM_007993.2 | R: AATCGTGTTTCTGCAAGTCCC | 174 |
| Acvr1 | F: ATCGCTTCAGACATGACCTCC | |
| NM_001110204.1 | R: TCCGAAGGCAGCTAACCGTA | 127 |
| Mdm4 | F: TTGTTTCAGACACTACGGATGA | |
| NM_001302801.1 | R: GTTTGCTCAGAATTAGCAGCTT | 100 |
| Smad2 | F: CTCTCCAACGTTAACCGAAATG | |
| NM_010754.5 | R: CACCTATGTAATACAAGCGCAC | 82 |
| Cdc14a | F: CTTACAACCTCACCGTCCT | |
| NM_001080818.2 | R: TATTCTTCCGCATCAAACGTCT | 94 |
| Dnmt1 | F: GAGACGAAAAACGACACGTAAA | |
| NM_001199432.1 | R: CACTTTGGTGAGTTGATCTTCG | 117 |
| Tgfb2 | F: CTGTACCTTCGTGCCGTCT | |
| NM_009367.4 | R: GCCATCAATACCTGCAAATCTCG | 82 |
| β-actin | F: CATCCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCCAA | |
| NM_007393.5 | R: ATGGAGCCACCGATCCACA | 171 |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Accession No. | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smad2 3′UTR | F: GAGCTCTCTTGTAACAGAAACCGTGTG R: GTCGACAATAGTGTCCACCTTCCGAG | NM_010754.5 | 671 bp |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Gong, B.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2. Genes 2022, 13, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040576
Li Y, Wang X, Wu Q, Liu F, Yang L, Gong B, Zhang K, Ma Y, Li Y. miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2. Genes. 2022; 13(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Xintong Wang, Qingru Wu, Fenfen Liu, Lin Yang, Bishuang Gong, Kaizhao Zhang, Yongjiang Ma, and Yugu Li. 2022. "miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2" Genes 13, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040576
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, X., Wu, Q., Liu, F., Yang, L., Gong, B., Zhang, K., Ma, Y., & Li, Y. (2022). miR-152-3p Represses the Proliferation of the Thymic Epithelial Cells by Targeting Smad2. Genes, 13(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040576






