Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Techniques Used
3. Principal Results
3.1. Genetic Features
3.2. Main Details of Karyotype Structure
3.3. Chromosomal Rearrangements
3.4. Karyotype Evolution
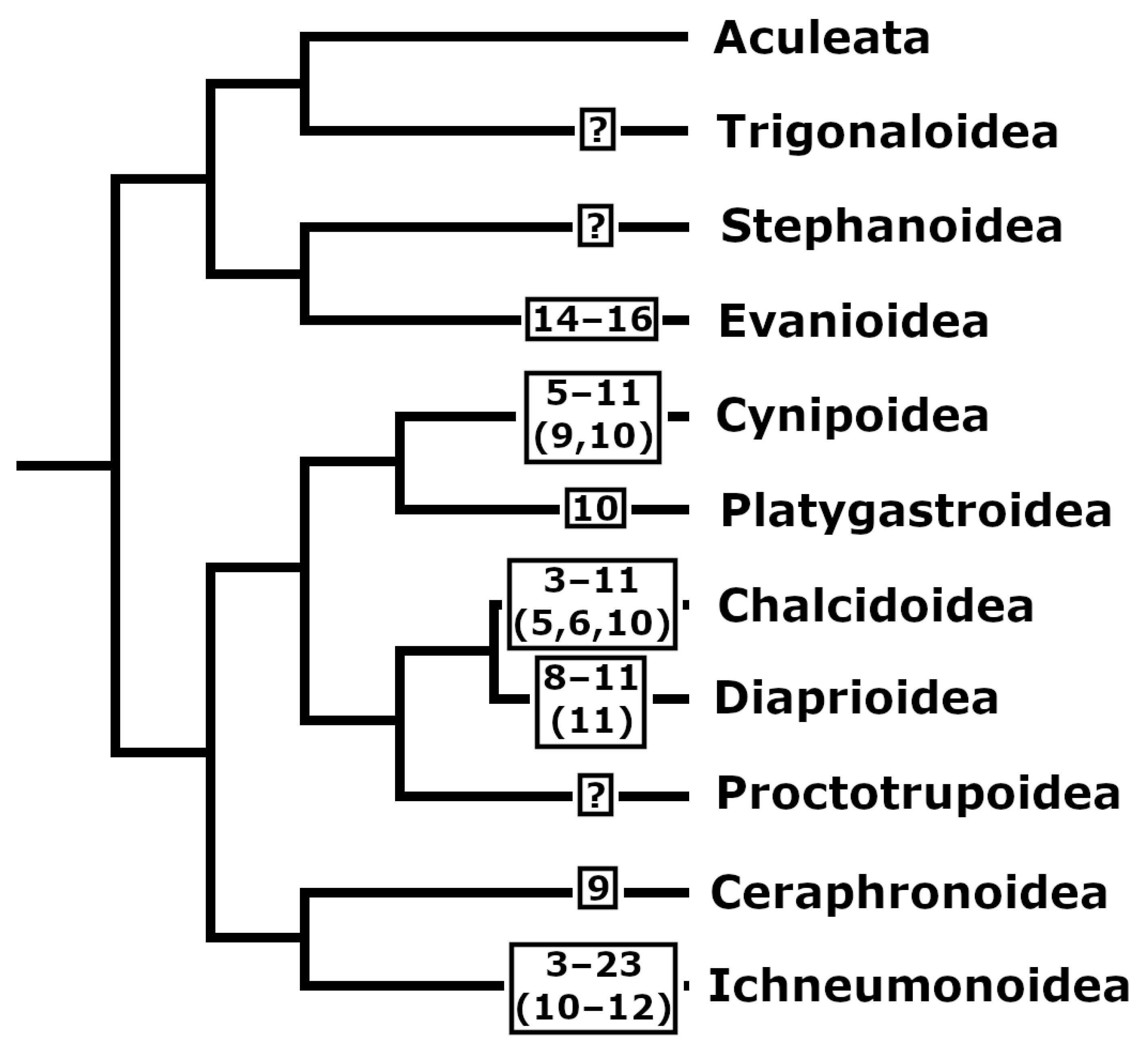
3.5. Taxonomic Implications
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huber, J.T. Biodiversity of Hymenoptera. In Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society, 2nd ed.; Foottit, R.G., Adler, P.H., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 419–462. [Google Scholar]
- Gauld, I.D.; Bolton, B. The Hymenoptera; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1988; p. 332. [Google Scholar]
- Rasnitsyn, A.P. Origin and Evolution of Hymenopterous Insects; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1980; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Bebber, D.P.; Polaszek, A.; Wood, J.R.I.; Barker, C.; Scotland, R.W. Taxonomic Capacity and Author Inflation. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 741–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, A.A.; Bagley, R.K.; Beer, M.A.; Hippee, A.C.; Widmayer, H.A. Quantifying the Unquantifiable: Why Hymenoptera, not Coleoptera, Is the Most Speciose Animal Order. BMC Ecol. 2018, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; p. 475. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Karyotypes of Parasitic Hymenoptera; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Comparative Karyology of Parasitic Hymenoptera: Between the Past and the Future. Proc. Russ. Entomol. Soc. 2015, 86, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Integrative Taxonomy and Its Implications for Species-Level Systematics of Parasitoid Hymenoptera. Entomol. Rev. 2018, 98, 834–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, R.H. Hymenoptera. Animal Cytogenetics 3(7); Gebrüder Borntraeger: Berlin–Stuttgart, Germany, 1975; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, A.R. The Cytology of Parthenogenesis in Tenthredinidae. Genetica 1932, 14, 321–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpasture, C. Comparative courtship behavior and karyology in Monodontomerus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1975, 68, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpasture, C.; Grissell, E.E. A Karyological Study of Nine Species of Torymus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae). Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 1975, 17, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.C.F. Chromosome and Isozyme Studies in Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 1982, 84, 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, M.R.; Ode, P.J. Chromosome Number of the Polyembryonic Parasitoid Copidosoma floridanum (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1990, 83, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, R.H. An Acetic Acid Dissociation, Air-Drying Technique for Insect Chromosomes, with Aceto-Lactic Orcein Staining. Stain Technol. 1968, 43, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.T.; Taylor, R.W.; Crosland, M.W.J.; Crozier, R.H. Modes of Spontaneous Chromosomal Mutation and Karyotype Evolution in Ants with Reference to the Minimum Interaction Hypothesis. Jpn. J. Genet. 1988, 63, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abe, Y. Karyotype Differences and Speciation in the Gall Wasp Andricus mukaigawae (s.lat.) (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae), with Description of the New Species A. kashiwaphilus. Entomol. Scand. 1988, 29, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odierna, G.; Baldanza, F.; Aprea, G.; Olmo, E. Occurrence of G-Banding in Metaphase Chromosomes of Encarsia berlesei (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Genome 1993, 36, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levan, A.; Fredga, K.; Sandberg, A.A. Nomenclature for Centromeric Position on Chromosomes. Hereditas 1964, 52, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altınordu, F.; Peruzzi, L.; Yu, Y.; He, X. A Tool for the Analysis of Chromosomes: KaryoType. Taxon 2016, 65, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Mikhailenko, A.P. Karyotypic Diversity in the Subfamily Eurytominae (Hymenoptera: Eurytomidae). Folia Biol. 2008, 56, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Johnston, J.S.; Small, C.; Rajwani, R.; Hanrahan, S.J.; Govind, S. Genomic and Karyotypic Variation in Drosophila Parasitoids (Hymenoptera, Cynipoidea, Figitidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2011, 5, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Kuhn, K.L.; Woolley, J.B.; Hopper, K.R. Variation in Genome Size and Karyotype among Closely Related Aphid Parasitoids (Hymenoptera, Aphelinidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2017, 11, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hare, E.E.; Johnston, J.S. Genome Size Determination Using Flow Cytometry of Propidium Iodide-Stained Nuclei. Mol. Methods Evol. Genet. 2011, 772, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Chromosomes of Parasitic Wasps of the Superfamily Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera): An Overview. Comp. Cytogenet. 2020, 14, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, B.; Sarti Chiarelli, M.; Shafer, D.A. Chromosome Banding with Trypsin. Genetica 1972, 43, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, A.T. A Simple Technique for Demonstrating Centromeric Heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Black, D.A. Controlled Silver Staining of Nucleolus Organizer Regions with a Protective Colloidal Developer: A 1-Step Method. Experientia 1980, 36, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, D.; Ambros, P.F. Chromosome Banding. Stain Combinations for Specific Regions. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994, 29, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sharakhov, I.V. (Ed.) Protocols for Cytogenetic Mapping of Arthropod Genomes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; p. 470. [Google Scholar]
- Liehr, T. (Ed.) Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH): Application Guide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; p. 606. [Google Scholar]
- Speicher, M.R.; Carter, N.P. The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology. Nature Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burry, R.W. Immunocytochemistry. A Practical Guide for Biomedical Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.J.D. Animal Cytology and Evolution; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; p. 961. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Kuznetsova, V.G. Parthenogenesis in Hexapoda: Holometabolous Insects. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2018, 56, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpur, B.A.; Sobhani, M.; Zayed, A. A Review of the Consequences of Complementary Sex Determination and Diploid Male Production on Mating Failures in the Hymenoptera. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 146, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E. Parallel Pathways of Karyotype Evolution in the Superfamily Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera). Russ. Entomol. J. 2013, 22, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Morphotypes of Chromosome Sets and Pathways of Karyotype Evolution of Parasitic Hymenoptera. Russ. Entomol. J. 2011, 20, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanderson, A.R. Cytological Investigation of Parthenogenesis in Gall Wasps (Cynipidae, Hymenoptera). Genetica 1988, 77, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Yefremova, Z.A.; Yegorenkova, E.N. Karyotypes of Parasitic Wasps of the Family Eulophidae (Hymenoptera) Attacking Leaf-Mining Lepidoptera (Gracillariidae, Gelechiidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2014, 8, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebiola, M.; Giorgini, M.; Navone, P.; Bernardo, U. A Karyological Study of the Genus Pnigalio Schrank (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): Assessing the Taxonomic Utility of Chromosomes at the Species Level. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2012, 102, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur, U.; Werren, J.H.; Eickbush, D.G.; Burke, W.D.; Eickbush, T.H. A “Selfish” B Chromosome that Enhances Its Transmission by Eliminating the Paternal Genome. Science 1988, 240, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vugt, J.J.F.A.; de Nooijer, S.; Stouthamer, R.; de Jong, H. NOR Activity and Repeat Sequences of the Paternal Sex Ratio Chromosome of the Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma kaykai. Chromosoma 2005, 114, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vugt, J.J.F.A.; de Jong, H.; Stouthamer, R. The Origin of a Selfish B Chromosome Triggering Paternal Sex Ratio in the Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma kaykai. Proc. R. Soc. B 2009, 276, 4149–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Westendorff, M. Chromosomes of Aphidius ervi Haliday, 1834 (Hymenoptera, Braconidae). Beitr. Entomol. 2003, 53, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, T.R. Animal Genome Size Database. Available online: http://www.genomesize.com (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Baldanza, F.; Gaudio, L.; Viggiani, G. Cytotaxonomic Studies of Encarsia Foerster (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1999, 89, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E. Differential Chromosome Staining in Parasitic Wasps of the Genus Dirophanes (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae). Entomol. Rev. 1997, 77, 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Carabajal Paladino, L.; Papeschi, A.; Lanzavecchia, S.; Cladera, J.; Bressa, M.J. Cytogenetic Characterization of Diachasmimorpha longicaudata (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a Parasitoid Wasp Used as a Biological Control Agent. Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Anokhin, B.A.; Kuznetsova, V.G. Distribution of 18S rDNA Sites and Absence of the Canonical TTAGG Insect Telomeric Repeat in Parasitoid Hymenoptera. Genetica 2014, 142, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Bolsheva, N.L.; Govind, S.; Muravenko, O.V. A Comparative Cytogenetic Study of Drosophila Parasitoids (Hymenoptera, Figitidae) Using DNA-Binding Fluorochromes and FISH with 45S RDNA Probe. Genetica 2016, 144, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanza, F.; Giorgini, M. Karyotype and NOR Localization Differences between Encarsia formosa Gahan and Encarsia luteola Howard (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Boll. Lab. Entomol. Agrar. “Filippo Silvestri” 2001, 56, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgini, M.; Baldanza, F. Species Status of Two Populations of Encarsia sophia (Girault & Dodd) (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) Native to Different Geographic Areas. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bolsheva, N.L.; Gokhman, V.E.; Muravenko, O.V.; Gumovsky, A.V.; Zelenin, A.V. Comparative Cytogenetic Study on Two Species of the Genus Entedon Dalman, 1820 (Hymenoptera, Eulophidae) Using DNA-Binding Fluorochromes and Molecular and Immunofluorescent Markers. Comp. Cytogenet. 2012, 6, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E. Chromosomes of Three Gall Wasps of the Tribe Aylacini (Hymenoptera, Cynipidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2021, 15, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Pereira, F.F.; Costa, M.A. A Cytogenetic Study of Three Parasitic Wasp Species (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea, Eulophidae, Trichogrammatidae) from Brazil Using Chromosome Morphometrics and Base-Specific Fluorochrome Staining. Comp. Cytogenet. 2017, 11, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rütten, K.B.; Pietsch, C.; Olek, K.; Neusser, M.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Gadau, J. Chromosomal Anchoring of Linkage Groups and Identification of Wing Size QTL Using Markers and FISH Probes Derived from Microdissected Chromosomes in Nasonia (Pteromalidae: Hymenoptera). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2004, 105, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Jing, X.A.; Aldrich, J.C.; Clifford, C.; Chen, J.; Akbari, O.S.; Ferree, P.M. Unique sequence organization and small RNA expression of a “selfish” B chromosome. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belle, E.; Beckage, N.E.; Rousselet, J.; Poirié, M.; Lemeunier, F.; Drezen, J.-M. Visualization of Polydnavirus Sequences in a Parasitoid Wasp Chromosome. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5793–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Kuznetsova, V.G. Presence of the Canonical TTAGG Insect Telomeric Repeat in the Tenthredinidae (Symphyta) Suggests Its Ancestral Nature in the Order Hymenoptera. Genetica 2018, 146, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, R.S.T.; Bardella, V.B.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Lucena, D.A.A.; Almeida, E.A.B. Are the TTAGG and TTAGGG Telomeric Repeats Phylogenetically Conserved in Aculeate Hymenoptera? Sci. Nat. 2017, 104, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Benetta, E.; Antoshechkin, I.; Yang, T.; Nguyen, H.Q.M.; Ferree, P.M.; Akbari, O.S. Genome Elimination Mediated by Gene Expression from a Selfish Chromosome. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Appel, A.G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Profiles of Telomeric Repeats in Insecta Reveal Diverse Forms of Telomeric Motifs in Hymenopterans. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukhtanov, V.A. Diversity and Evolution of Telomere and Subtelomere DNA Sequences in Insects. BioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E. Chromosomes of Parasitic Wasps of the Genus Metaphycus (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Encyrtidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2010, 4, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E. New Species of Ichneumoninae of the Tribe Phaeogenini from the European Part of the USSR. Zool. Zh. 1991, 70, 73–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- König, C.; Paschke, S.; Pollmann, M.; Reinisch, R.; Gantert, C.; Weber, J.; Krogmann, L.; Steidle, J.L.M.; Gokhman, V.E. Molecular and Cytogenetic Differentiation within the Lariophagus distinguendus (Förster, 1841) Species Complex (Hymenoptera, Pteromalidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2019, 13, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Cioffi, M.B.; König, C.; Pollmann, M.; Gantert, C.; Krogmann, L.; Steidle, J.L.M.; Kosyakova, N.; Liehr, T.; Al-Rikabi, A. Microdissection and Whole Chromosome Painting Confirm Karyotype Transformation in Cryptic Species of the Lariophagus distinguendus (Förster, 1841) Complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, M.J.; Jiggins, C.D. Supergenes and Their Role in Evolution. Heredity 2014, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wurm, Y.; Nipitwattanaphon, M.; Riba-Grognuz, O.; Huang, Y.-C.; Shoemaker, D.; Keller, L. A Y-like Social Chromosome Causes Alternative Colony Organization in Fire Ants. Nature 2013, 493, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.; van de Zande, L.; Beukeboom, L.W. Life-history Traits of the Whiting Polyploid Line of the Parasitoid Nasonia vitripennis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2019, 167, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, R.S.; Krogmann, R.; Mayer, C.; Donath, A.; Gunkel, S.; Meusemann, K.; Kozlov, A.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Petersen, M.; Lanfear, R.; et al. Evolutionary History of the Hymenoptera. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Timokhov, A.V.; Fedina, T.Y. First Evidence for Sibling Species in Anisopteromalus calandrae (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Russ. Entomol. J. 1998, 7, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman, V.E.; Fedina, T.Y.; Timokhov, A.V. Life-history Strategies in Parasitic Wasps of the Anisopteromalus calandrae Complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Russ. Entomol. J. 1999, 8, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Timokhov, A.V.; Gokhman, V.E. Host Preferences of Parasitic Wasps of the Anisopteromalus calandrae Species Complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 2003, 67, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, H.; Kranz-Baltensperger, Y.; Cruaud, A.; Rasplus, J.-Y.; Timokhov, A.V.; Gokhman, V.E. Morphometric Analysis and Taxonomic Revision of Anisopteromalus Ruschka (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Pteromalidae)—An Integrative Approach. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fusu, L. An Integrative Taxonomic Study of European Eupelmus (Macroneura) (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Eupelmidae), with a Molecular and Cytogenetic Analysis of Eupelmus (Macroneura) vesicularis: Several Species Hiding under One Name for 240 Years. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 181, 519–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, F.; Eroğlu, H.E.; Nozari, J.; Hosseininaveh, V. Karyotype Analysis of Trichogramma embryophagum Htg. (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) Using a New Method and Estimate Its Karyotype Symmetry. Caryologia 2020, 73, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Farsi, F.; Nozari, J. Status of Cell Division, Cytogenetical Index, and Chromosome Details on the Immature Stage of Trichogramma brassicae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Arthropods 2021, 10, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmeyer, K.T.; Oppenheim, S.J.; Hopper, K.R. Assemblies of the Genomes of Parasitic Wasps Using Meta-assembly and Scaffolding with Genetic Linkage. Genes Genomes Genet. 2022, 12, jkab386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gokhman, V.E. Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results. Genes 2022, 13, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050751
Gokhman VE. Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results. Genes. 2022; 13(5):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050751
Chicago/Turabian StyleGokhman, Vladimir E. 2022. "Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results" Genes 13, no. 5: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050751
APA StyleGokhman, V. E. (2022). Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results. Genes, 13(5), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050751





