SSR-Based Molecular Identification and Population Structure Analysis for Forage Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Landraces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. PCR Reaction and Genotyping
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genetic Variation in Forage Pea (P. sativum ssp. arvense L.) Landrace Accessions Using SSR Primers
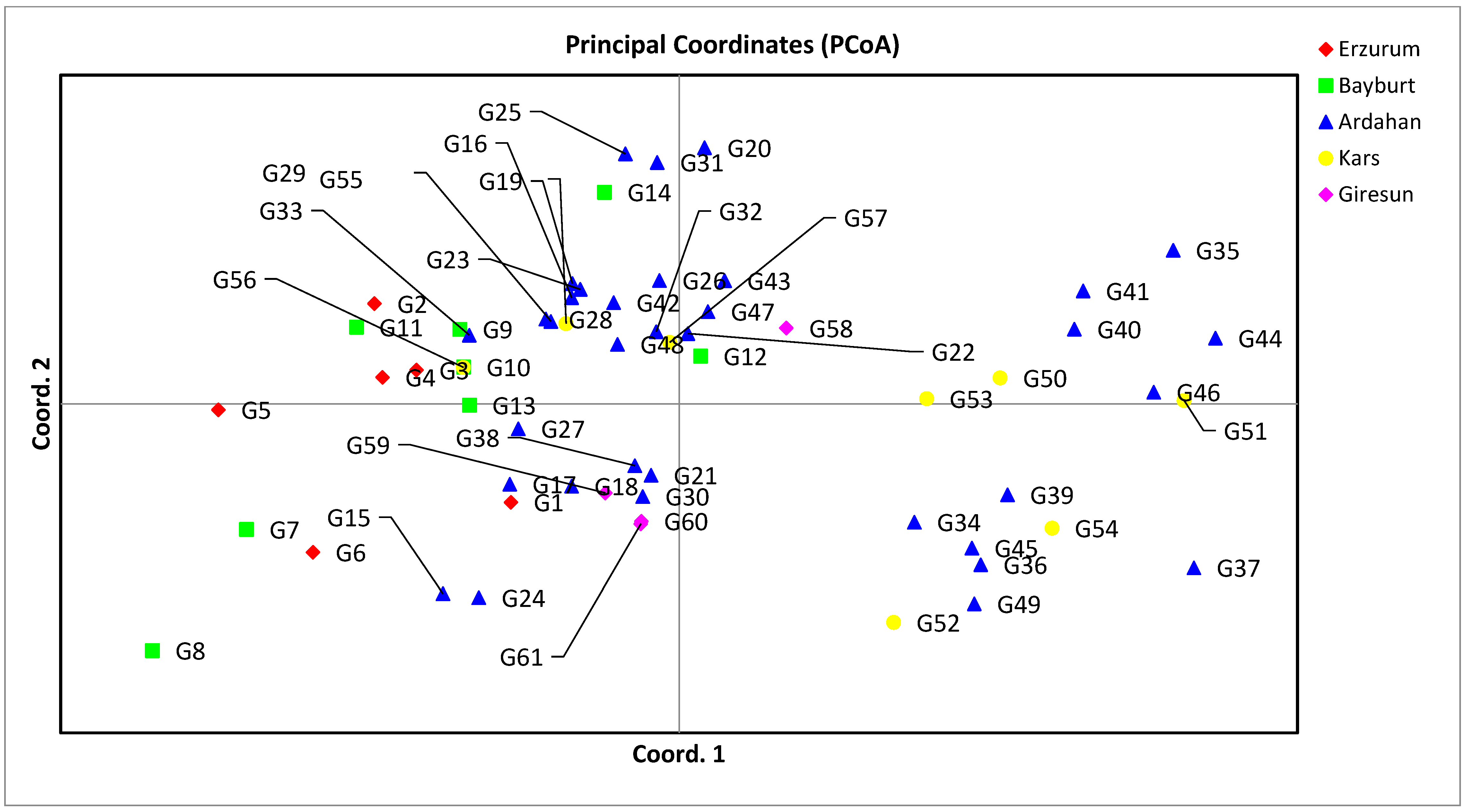
3.2. Genetic Distance, Cluster Analysis, Molecular Variance Analysis (AMOVA), and Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) for SSR Markers
3.3. Population Structure among 61 Forage Peas (P. sativum ssp. arvense L.) Landrace Accessions Using SSR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acikbas, S.; Ozyazici, M.A.; Bektas, H. Root system architecture and seed weight relations in forage pea (Pisum sativum ssp. arvense L. Poir.). Cienc. Rural 2021, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, R.; Marker, S.; Kumar, K.Y.; Taranum, S.A. Genetic Variability Parameters for Quantitative Traits in Farmers’ Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Varieties. Biol. Forum Int. J. 2021, 13, 320–325. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, E.; Shana, F.; Hans, K.; Julie, P.; Michael, W.; Janet, K.; Kenneth, H. Field Pea Production A1166 (Revised); N.D.S.U. Extension Service: Fargo, ND, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ceyhan, E.; Avci, M.A. Combining ability and heterosis for grain yield and some yield components in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2005, 8, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Acikgoz, E.; Ustun, A.; Gul, I.; Anlarsal, E.; Tekeli, A.; Nizam, I.; Avcioglu, R.; Geren, H.; Cakmakci, S.; Aydinoglu, B. Genotype x environment interaction and stability analysis for dry matter and seed yield in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 7, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Addisu, F.; Shumet, T. Variability, heritability and genetic advance for some yield and yield related traits in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) landraces in Ethiopia. Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2015, 9, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzahib, R.H.; Migdadi, H.M.; Ghamdi, A.A.A.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Afzal, M.; Elharty, E.H.; Alghamdi, S.S. Exploring genetic variability among and within hail tomato landraces based on sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Diversity 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, G.; Caramante, M.; Piffanelli, P.; Rao, R. Genetic diversity in Italian tomato landraces: Implications for the development of a core collection. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 168, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondani, C.; Borba, T.C.O.; Rangel, P.H.N.; Brondani, R.P.V. Determination of genetic variability of traditional varieties of Brazilian rice using microsatellite markers. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2006, 29, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, S. Landraces: Importance and use in breeding and environmentally friendly agronomic systems. In Agrobiodiversity Conservation: Securing the Diversity of Crop Wild Relatives and Landraces; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2012; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Gixhari, B.; Pavelkova, M.; Ismaili, H.; Vrapi, H.; Jaupi, A.; Smýkal, P. Genetic diversity of Albanian pea (Pisum sativum L.) landraces assessed by morphological traits and molecular markers. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2014, 50, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Singh, B.; Sharma, V.R.; Kumar, M.; Sirohi, U. Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Germplasm based on Morphological Traits and SSR Markers. Legume Res. 2021, 4751, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, F.S.; Alsaleh, A.; de Miera, L.E.S.; Hatipoğlu, R.; Çiftçi, V.; Karaköy, T.; Yıldız, M.; Özkan, H. DNA based iPBS-retrotransposon markers for investigating the population structure of pea (Pisum sativum) germplasm from Turkey. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 61, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, A.; Bryngelsson, T.; Dagne, K.; Geleta, M. Assessment of genetic diversity in Ethiopian field pea (Pisum sativum L.) accessions with newly developed EST-SSR markers. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demirkol, G.; Yilmaz, N. Forage pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) landraces reveal morphological and genetic diversities. Turk. J. Bot. 2019, 43, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalzadehtabrizi, H.; Hosseinpour, A.; Aydin, M.; Haliloglu, K. A modified genomic DNA extraction method from leaves of sunflower for PCR based analyzes. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2015, 7, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.-X.; Guan, J.-P.; Wang, S.-M.; Liu, Q.-C.; Redden, R.R.; Ford, F. Genetic diversity and core collection of aliens Pisum sativum L. germplasm. Acta Agron. Sin. 2008, 34, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Smýkal, P.; Hýbl, M.; Corander, J.; Jarkovský, J.; Flavell, A.J.; Griga, M. Genetic diversity and population structure of pea (Pisum sativum L.) varieties derived from combined retrotransposon, microsatellite and morphological marker analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Redden, R.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Guan, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Yan, L. Analysis of a diverse global Pisum sp. collection and comparison to a Chinese local P. sativum collection with microsatellite markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.X.; Ford, R.; Redden, R.R.; Guan, J.P.; Wang, S.M. Identification and analysis of genetic diversity structure within Pisum genus based on microsatellite markers. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslarová, J.; Smýkal, P.; Dočkalová, Z.; Hanáček, P.; Procházka, S.; Hýbl, M.; Griga, M. Molecular evidence of genetic diversity changes in pea (Pisum sativum L.) germplasm after long-term maintenance. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2011, 58, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, A.; Karahan, F.; İlhan, E.; İlçim, A.; Haliloğlu, K. Genetic structure and diversity of Adonis L. (Ranunculaceae) populations collected from Turkey by inter-primer binding site (iPBS) retrotransposon markers. Turk. J. Bot. 2019, 43, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. J. Bioinform. 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, F.C.; Yang, R.; Boyle, T.B.; Ye, Z.; Mao, J.X. POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. Cent. Univ. Alta. Can. 1997, 10, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. An empirical comparison of three ordination techniques in numerical taxonomy. Syst. Zool. 1972, 21, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Donnelly, P. Association mapping in structured populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earl, D.A.; VonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loridon, K.; McPhee, K.; Morin, J.; Dubreuil, P.; Pilet-Nayel, M.L.; Aubert, G.; Rameau, C.; Baranger, A.; Coyne, C.; Lejeune-Henaut, I. Microsatellite marker polymorphism and mapping in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smýkal, P.; Horáček, J.; Dostálová, R.; Hýbl, M. Variety discrimination in pea (Pisum sativum L.) by molecular, biochemical and morphological markers. J. Appl. Genet. 2008, 49, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, J.; Haghnazari, A.; Saba, J. Genetic diversity among varieties and wild species accessions of pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on SSR markers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; McPhee, K.E.; Coram, T.E.; Peever, T.L.; Chilvers, M.I. Development and characterization of 37 novel EST-SSR markers in Pisum sativum (Fabaceae). Appl. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 1200249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstin, J.; Deniot, G.; Potier, J.; Weinachter, C.; Aubert, G.; Barranger, A. Microsatellite polymorphism in Pisum sativum. Plant Breed. 2001, 120, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.-M.; Xu, S.-C.; Mao, W.-H.; Hu, Q.-Z.; Zhang, G.-W.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.-D. Developing new SSR markers from ESTs of pea (Pisum sativum L.). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cupic, T.; Tucak, M.; Popovic, S.; Bolaric, S.; Grljusic, S.; Kozumplik, V. Genetic diversity of pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes assessed by pedigree, morphological and molecular data. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, R.; Le Roux, K.; Itman, C.; Brouwer, J.B.; Taylor, P.W. Diversity analysis and genotyping in Pisum with sequence tagged microsatellite site (STMS) primers. Euphytica 2002, 124, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranger, A.; Aubert, G.; Arnau, G.; Lainé, A.; Deniot, G.; Potier, J.; Weinachter, C.; Lejeune-Henaut, I.; Lallemand, J.; Burstin, J. Genetic diversity within Pisum sativum using protein-and PCR-based markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnazari, A.; Samimifard, R.; Najafi, J.; Mardi, M. Genetic diversity in pea (Pisum sativum L.) accessions detected by sequence tagged microsatellite markers. J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2005, 59, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Tar’an, B.; Zhang, C.; Warkentin, T.; Tullu, A.; Vandenberg, A. Genetic diversity among varieties and wild species accessions of pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on molecular markers, and morphological and physiological characters. Genome 2005, 48, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.; Tanveer, H.; Dixit, G. Identification and detection of genetic relatedness among important varieties of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown in India. Genetica 2007, 130, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikamis, G.; Yanmaz, R.; Ermis, S.; Bakir, M.; Yuksel, C. Genetic characterization of pea (Pisum sativum) germplasm from Turkey using morphological and SSR markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 2010, 9, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cömertpay, G.; Baloch, F.S.; Kilian, B.; Ülger, A.C.; Özkan, H. Diversity assessment of Turkish maize landraces based on fluorescent labelled SSR markers. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 30, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handerson, C.; Noren, S.; Wricha, T.; Meetei, N.; Khanna, V.; Pattanayak, A.; Datt, S.; Choudhury, P.R.; Kumar, M. Assessment of genetic diversity in pea (Pisum sativum L.) using morphological and molecular markers. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2014, 74, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Kumar, A.; Mamidi, S.; McPhee, K. Genetic diversity and population structure among pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars as revealed by simple sequence repeat and novel genic markers. Mol. Biotechnol. 2014, 56, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslarová, J.; Hýbl, M.; Griga, M.; Smýkal, P. Molecular analysis of temporal genetic structuring in pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars bred in the Czech Republic and in former Czechoslovakia since the mid-20th century. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2012, 48, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; Kaur, S.; Lamb-Palmer, N.D.; Lefsrud, M.; Singh, J. Genetic diversity and population structure of Pisum sativum accessions for marker-trait association of lipid content. Crop J. 2015, 3, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, N.; Kumar, R.; Choudhary, V.; Singh, C.M. Molecular assessment of genetic divergence in pea genotypes using microsatellite markers. Legume Res. Int. J. 2016, 39, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisar, M.; Khan, A.; Wadood, S.F.; Shah, A.A.; Hanci, F. Molecular characterization of edible pea through EST-SSR markers. Turk. J. Bot. 2017, 41, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, N.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Blair, M.W. Genetic diversity of Chinese and global pea (Pisum sativum L.) collections. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, H.; Acar, Z.; Ayan, I.; Kurt, O. Genetic diversity of Turkish Lathyrus L. landraces using ISSR markers. Genetika 2018, 50, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, J.C.; Rana, M.; Sharma, V.; Nag, A.; Chahota, R.K.; Sharma, T.R. Genetic diversity and structure of pea (Pisum sativum L.) germplasm based on morphological and SSR markers. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 35, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegay, S.; Geleta, M.; Bryngelsson, T.; Gustavsson, L.; Persson-Hovmalm, H.; Ortiz, R. Comparing genetic diversity and population structure of common beans grown in Kyrgyzstan using microsatellites. Sci. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 1, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, M.W.; Soler, A.; Cortes, A.J. Diversification and population structure in common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, S.A.; Prasanna, B. Analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants—salient statistical tools and considerations. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klaedtke, S.; Jacques, M.A.; Raggi, L.; Préveaux, A.; Bonneau, S.; Negri, V.; Chable, V.; Barret, M. Terroir is a key driver of seed-associated microbial assemblages. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1792–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Burlyaeva, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Fang, L.; Redden, R.; Zong, X. Genetic diversity of grass pea and its relative species revealed by SSR markers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118542. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, G.T.; Lee, J.R.; Moon, J.K.; Yoon, M.S.; Baek, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Paek, N.C. Genetic diversity and population structure of Korean soybean landrace [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. J. Crop. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 11, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Harmankaya, M.; Özcan, M.M.; Karadaş, S.; Ceyhan, E. Protein and mineral contents of pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes grown in Central Anatolian region of Turkey. South-West. J. Hortic. Biol. Environ. 2010, 1, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hanci, F.; Cebeci, E. Determination of morphological variability of different pisum genotypes using principal component analysis. Legum. Res. 2019, 42, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanci, F. Genetic variability in peas (Pisum sativum L.) from Turkey assessed with molecular and morphological markers. Folia Hortic. 2019, 31, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirbas, A. Micro and macronutrients diversity in Turkish pea (Pisum sativum) germplasm. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Ton, A.; Mart, D.; Karaköy, T.; Türkeri, M.; Torun, A.A.; Anlarsal, A.E. Characterization of some local pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes for agro-morphological traits and mineral concentrations. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2022, 46, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Code Number | Association No | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Ovaçevirme-1 | Erzurum | 39.19.57 N | 41.47.51 E | 1586 |
| G2 | Ovaçevirme-2 | Erzurum | 39.19.57 N | 41.47.51 E | 1586 |
| G3 | Ovaçevirme-3 | Erzurum | 39.19.57 N | 41.47.51 E | 1586 |
| G4 | Ovaçevirme-4 | Erzurum | 39.19.57 N | 41.47.51 E | 1586 |
| G5 | Ovaçevirme-5 | Erzurum | 39.19.57 N | 41.47.51 E | 1586 |
| G6 | Şenkaya Merkez | Erzurum | 40.33.27 N | 42.20.37 E | 1826 |
| G7 | İncili-1 | Bayburt | 40.23.24 N | 40.12.16 E | 1579 |
| G8 | İncili-2 | Bayburt | 40.23.22 N | 40.12.14 E | 1578 |
| G9 | İncili-3 | Bayburt | 40.23.22 N | 40.12.14 E | 1575 |
| G10 | Çiğdemtepe | Bayburt | 40.19.50 N | 40.08.16 E | 1564 |
| G11 | Arpalı | Bayburt | 40.21.56 N | 40.06.17 E | 1538 |
| G12 | Aşağıkırzı | Bayburt | 40.23.23 N | 40.08.48 E | 1535 |
| G13 | Değirmencik-1 | Bayburt | 40.21.29 N | 40.14.30 E | 1532 |
| G14 | Değirmencik-2 | Bayburt | 40.21.29 N | 40.14.30 E | 1532 |
| G15 | Ardahan Merkez-1 | Ardahan | 41.09.45 N | 42.56.15 E | 1905 |
| G16 | Ardahan Merkez-2 | Ardahan | 41.09.45 N | 42.56.15 E | 1905 |
| G17 | Ardahan Merkez-3 | Ardahan | 41.09.45 N | 42.56.15 E | 1905 |
| G18 | Çamlıçatak-1 | Ardahan | 41.07.42 N | 42.49.59 E | 1798 |
| G19 | Çamlıçatak-2 | Ardahan | 41.07.42 N | 42.49.59 E | 1798 |
| G20 | Sulakyurt | Ardahan | 41.09.50 N | 42.36.59 E | 1920 |
| G21 | Döşeli-1 | Ardahan | 41.08.59 N | 42.44.45 E | 1815 |
| G22 | Döşeli-2 | Ardahan | 41.08.59 N | 42.44.45 E | 1815 |
| G23 | Kartalpınar | Ardahan | 41.08.59 N | 42.44.45 E | 2063 |
| G24 | Tepeler | Ardahan | 41.03.51 N | 42.34.30 E | 2044 |
| G25 | Oburcak | Ardahan | 41.20.59 N | 42.52.10 E | 2100 |
| G26 | Seyitören | Ardahan | 41.23.18 N | 42.48.35 E | 2224 |
| G27 | Serhat | Ardahan | 41.20.31 N | 42.85.11 E | 1950 |
| G28 | Cumhuriyet | Ardahan | 41.20.57 N | 42.52.16 E | 1922 |
| G29 | Burmadere | Ardahan | 41.18.09 N | 42.47.05 E | 2044 |
| G30 | Tepeköy | Ardahan | 41.20.50 N | 42.48.26 E | 2076 |
| G31 | Selamverdi | Ardahan | 41.14.06 N | 42.51.44 E | 1810 |
| G32 | Ortakent | Ardahan | 41.13.45 N | 42.56.05 E | 1819 |
| G33 | Yamçılı | Ardahan | 42.20.29 N | 42.80.12 E | 2034 |
| G34 | Koyunpınarı | Ardahan | 41.14.20 N | 42.46.40 E | 1860 |
| G35 | Çayağzı | Ardahan | 41.11.34 N | 42.51.02 E | 1813 |
| G36 | Avcılar | Ardahan | 41.15.02 N | 42.49.33 E | 1801 |
| G37 | Öncül | Ardahan | 41.14.18 N | 43.09.59 E | 1793 |
| G38 | Aşağıcambaz | Ardahan | 41.14.41 N | 43.24.10 E | 2044 |
| G39 | Eşmepınar | Ardahan | 41.06.50 N | 43.09.07 E | 1889 |
| G40 | Eskibeyrehatun | Ardahan | 41.07.42 N | 42.57.30 E | 2040 |
| G41 | Kaşlıkaya | Ardahan | 41.09.38 N | 43.04.12 E | 1857 |
| G42 | Sazlısu | Ardahan | 41.06.16 N | 43.06.58 E | 1913 |
| G43 | Kenarbel | Ardahan | 41.11.26 N | 43.09.53 E | 1788 |
| G44 | Tahtakıran | Ardahan | 40.30.32 N | 42.35.23 E | 2042 |
| G45 | Dedekılıç | Ardahan | 40.51.45 N | 42.33.31 E | 2040 |
| G46 | Yiğitkonağı | Ardahan | 40.57.16 N | 42.34.04 E | 2048 |
| G47 | Çayırbaşı-1 | Ardahan | 40.52.24 N | 43.37.56 E | 2045 |
| G48 | Çayırbaşı-2 | Ardahan | 40.52.24 N | 43.37.56 E | 2045 |
| G49 | Balçeşme | Ardahan | 40.49.54 N | 42.49.29 E | 2165 |
| G50 | Subatan | Kars | 40.36.12 N | 43.26.07 E | 1788 |
| G51 | Doğruyol | Kars | 41.03.00 N | 43.20.10 E | 2031 |
| G52 | Paslı | Kars | 40.17.05 N | 42.57.32 E | 1838 |
| G53 | Yolgeçmez | Kars | 40.25.07 N | 42.45.11 E | 1898 |
| G54 | Iğdır | Kars | 40.21.12 N | 42.45.11 E | 1815 |
| G55 | Gölbaşı | Kars | 40.76.57 N | 42.98.47 E | 2015 |
| G56 | Yukarışallıpınar-1 | Kars | 40.43.63 N | 42.61.42 E | 2081 |
| G57 | Yukarışallıpınar-2 | Kars | 40.43.63 N | 42.61.42 E | 2081 |
| G58 | Sarvan | Giresun | 40.53.03 N | 38.27.19 E | 266 |
| G59 | Görele-1 | Giresun | 41.01.54 N | 39.00.04 E | 24 |
| G60 | Görele-2 | Giresun | 41.01.54 N | 39.00.04 E | 24 |
| G61 | Giresun Merkez | Giresun | 40.52.07 N | 38.23.38 E | 18 |
| Primer No. | Marker Name | Forward (5′–3′) | Backward (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PB14 | GAGTGAGCTTTTTAGCTTGCAGCCT | TGCTTGAGAACAGTGACTCGCA |
| 2 | PSAA18 | CTGTAGACCAAGCCCAAAAGAT | TGAGACACTTTTGACAAGGAGG |
| 3 | PSAA175 | TTGAAGGAACACAATCAGCGAC | TGCGCACCAAACTACCATAATC |
| 4 | PSAC58 | TCCGCAATTTGGTAACACTG | CGTCCATTTCTTTTATGCTGAG |
| 5 | PSAC75 | CGCTCACCAAATGTAGATGATAA | TCATGCATCAATGAAAGTGATAAA |
| 6 | PSAA219 | ATTTGTGCAATTGCAATTTCATT | CGAAAACGCTTTGCATCCTA |
| 7 | PSAD83 | CACATGAGCGTGTGTATGGTAA | GGGATAAGAAGAGGGAGCAAAT |
| 8 | PSAD270 | CTCATCTGATGCGTTGGATTAG | AGGTTGGATTTGTTGTTTGTTG |
| 9 | PSAA456 | TGTAGAAGCATAAGAGCGGGTG | TGCAACGCTCTTGTTGATGATT |
| 10 | PSAB23 | TCAGCCTTTATCCTCCGAACTA | GAACCCTTGTGCAGAAGCATTA |
| 11 | PSAB47 | TCCACAATACCATCTAAATGCCA | AATTTGTTCAGTTGAAATTTCGTTTC |
| 12 | PSAA497 | TTGTGACTGATTTAGAAGTTTCCCAC | TTGATGAGTTGCAATTTCGTTTC |
| 13 | PSAD280 | TGGTGCTCGTGATTAATTTCACATA | ACTAAACAACCAACTGCCAAAACTG |
| 14 | PSAB72 | ATCTCATGTTCAACTTGCAACCTTTA | TTCAAAACACGCAAGTTTTCTGA |
| 15 | PSAB109 | GAACCCTTGTGTAGAAGCATTTGTG | GAGCTACTGTGAGTCTGATGCCATTAT |
| 16 | PSAB141 | ATCCCAATACTCCCACCAATGTT | AGACTTAGGCTTCCCTTCTACGACTT |
| 17 | PSAB161 | CTCAAGTGAAGACTTGGAATTTCGTT | TTTGGTCTTCCTCAAGTGATAAGATG |
| 18 | AD100 | TACACCCAAGACGACAAGCCT | GGAGCTTCCGCTTGATTCTCT |
| 19 | AD134 | TTTATTTTTCCATATATTACAGACCCG | ACACCTTTATCTCCCGAAGACTTAG |
| 20 | AA303 | GGGTGAAGGAAAATCGTGA | GCATCCCATAAAATTGGTTCT |
| 21 | AA315 | AGTGGGAAGTAAAAGGTGTAG | TTTCACTAGATGATATTTCGTT |
| 22 | AA-67 | CCCATGTGAAATTCTCTTGAAGA | GCATTTCACTTGATGAAATTTCG |
| 23 | AA-321 | CTGCAGCCTGTACAAGTGG | CCAGTTACAAGATTGATGTTTATGG |
| 24 | AD-186 | TCAATGACGTGTTGATCGAGGA | CCATGCTTTGCACCGAAAGTAA |
| 25 | AA-278 | CCAAGAAAGGCTTATCAACAGG | TGCTTGTGTCAAGTGATCAGTG |
| 26 | A-9 | GTGCAGAAGCATTTGTTCAGAT | CCCACATATATTTGGTTGGTCA |
| 27 | AD-141 | AATTTGAAAGAGGCGGATGTG | ACTTCTCTCCAACATCCAACGA |
| 28 | AD-237 | AGATCATTTGGTGTCATCAGTG | TGTTTAATACAACGTGCTCCTC |
| Marker | Na | Maf | Ob-Het | Ex-Het | GD | h | ne | I | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB14 | 2.00 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 1.96 | 0.68 | 0.37 |
| PSAA18 | 4.00 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 2.60 | 1.07 | 0.54 |
| PSAA175 | 5.00 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 2.62 | 1.20 | 0.58 |
| PSAC58 | 5.00 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 4.07 | 1.47 | 0.70 |
| PSAC75 | 3.00 | 0.51 | 0.58 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 2.52 | 0.99 | 0.52 |
| PSAA219 | 4.00 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 2.19 | 0.97 | 0.48 |
| PSAD83 | 3.00 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 2.66 | 1.03 | 0.55 |
| PSAD270 | 3.00 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 2.24 | 0.91 | 0.52 |
| PSAA456 | 3.00 | 0.59 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 2.05 | 0.81 | 0.42 |
| PSAB23 | 3.00 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 2.78 | 1.06 | 0.57 |
| PSAB47 | 3.00 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 2.48 | 0.99 | 0.52 |
| PSAA497 | 3.00 | 0.80 | 0.23 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 1.51 | 0.55 | 0.28 |
| PSAD280 | 3.00 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 2.97 | 1.09 | 0.59 |
| PSAB72 | 3.00 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 2.60 | 1.01 | 0.53 |
| PSAB109 | 2.00 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 1.60 | 0.56 | 0.30 |
| PSAB141 | 3.00 | 0.52 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 2.16 | 0.84 | 0.43 |
| PSAB161 | 3.00 | 0.52 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 2.20 | 0.86 | 0.45 |
| AD100 | 2.00 | 0.54 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 0.69 | 0.37 |
| AD134 | 3.00 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 1.99 | 0.79 | 0.38 |
| AA303 | 2.00 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 1.79 | 0.63 | 0.34 |
| AA315 | 2.00 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 1.27 | 0.37 | 0.19 |
| AA-67 | 2.00 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 1.97 | 0.69 | 0.37 |
| AA-321 | 2.00 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 1.27 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| AD-186 | 2.00 | 0.53 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.99 | 0.69 | 0.37 |
| AA-278 | 2.00 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 1.18 | 0.29 | 0.03 |
| A-9 | 2.00 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| AD-141 | 3.00 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 1.86 | 0.73 | 0.38 |
| AD-237 | 4.00 | 0.57 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 2.51 | 1.11 | 0.55 |
| Mean | 2.89 | 0.60 | 0.22 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 2.15 | 0.81 | 0.41 |
| Source | Degree of Freedom (DF) | Sum of Squares (SS) | Variance Component | % Of Total Variance | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among Population | 4 | 78.52 | 1.40 | 18 | 0.18 |
| Within Population | 56 | 351.06 | 6.26 | 82 | 0.001 |
| Total | 60 | 429.59 | 7.67 | 100 | - |
| Axis | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| % | 21.59 | 16.67 | 13.28 |
| Cum % | 21.59 | 38.26 | 51.54 |
| Sub-Population (K) | Expected Heterozygosity | Fst Value |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.2969 | 0.2351 |
| B | 0.2581 | 0.3838 |
| C | 0.3223 | 0.2506 |
| Mean | 0.2924 | 0.2898 |
| Sub-Populations (K) | Sub-Population A | Sub-Population B | Sub-Population C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-population A | - | 0.1024 | 0.0690 |
| Sub-population B | 0.1024 | - | 0.1087 |
| Sub-population C | 0.0690 | 0.1087 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haliloglu, K.; Turkoglu, A.; Tan, M.; Poczai, P. SSR-Based Molecular Identification and Population Structure Analysis for Forage Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Landraces. Genes 2022, 13, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061086
Haliloglu K, Turkoglu A, Tan M, Poczai P. SSR-Based Molecular Identification and Population Structure Analysis for Forage Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Landraces. Genes. 2022; 13(6):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061086
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaliloglu, Kamil, Aras Turkoglu, Mustafa Tan, and Peter Poczai. 2022. "SSR-Based Molecular Identification and Population Structure Analysis for Forage Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Landraces" Genes 13, no. 6: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061086
APA StyleHaliloglu, K., Turkoglu, A., Tan, M., & Poczai, P. (2022). SSR-Based Molecular Identification and Population Structure Analysis for Forage Pea (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.) Landraces. Genes, 13(6), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061086








