MicrobiomeGWAS: A Tool for Identifying Host Genetic Variants Associated with Microbiome Composition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. A Score Statistic for Testing Main Effect
2.2. A Score Statistic for Testing Gene–Environment Interaction
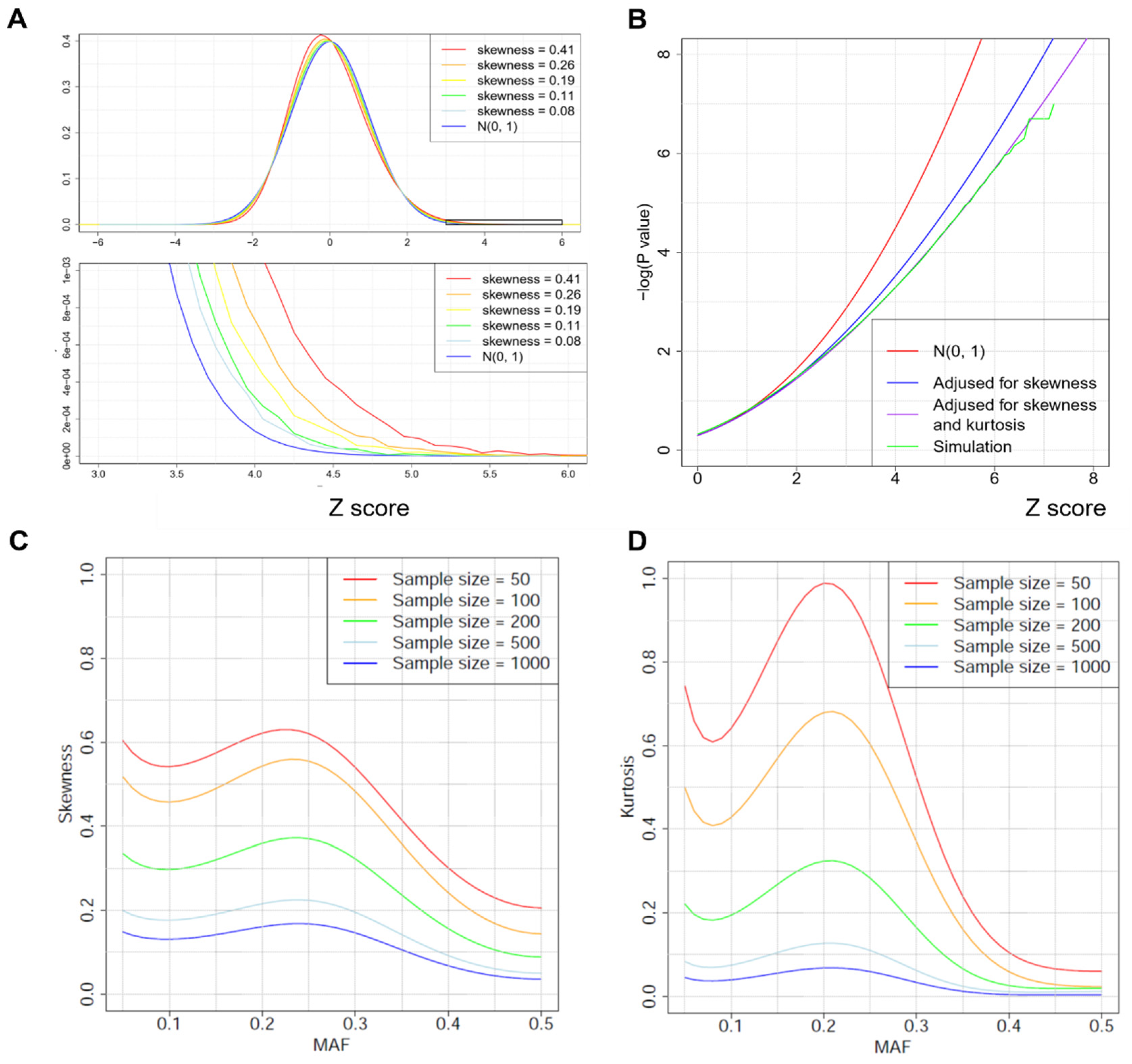
2.3. Improved p-Value Approximations by Correcting for Skewness and Kurtosis
3. Results
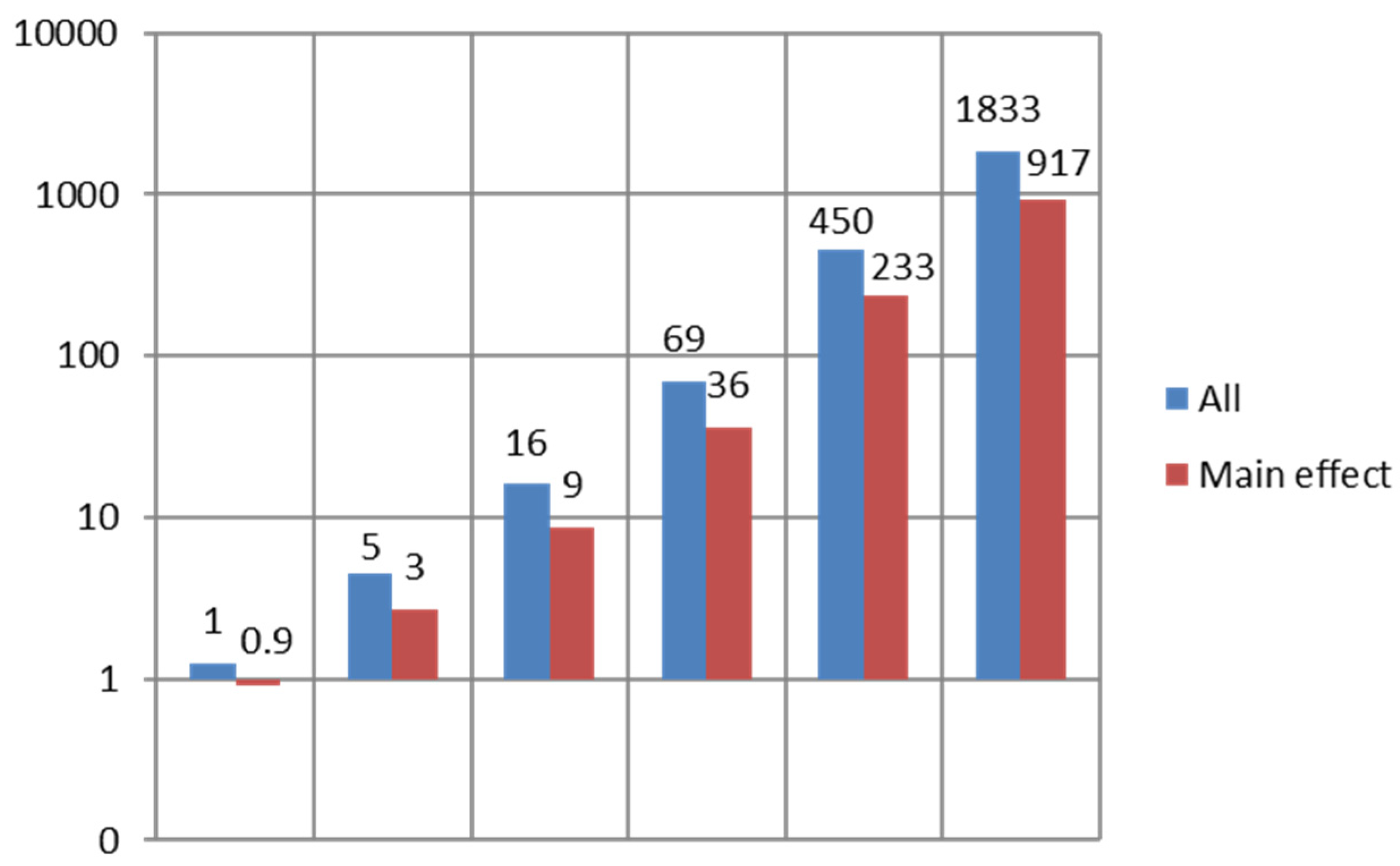
3.1. Simulation Results
3.2. Software Implementation, Memory Requirement, and Computational Complexity
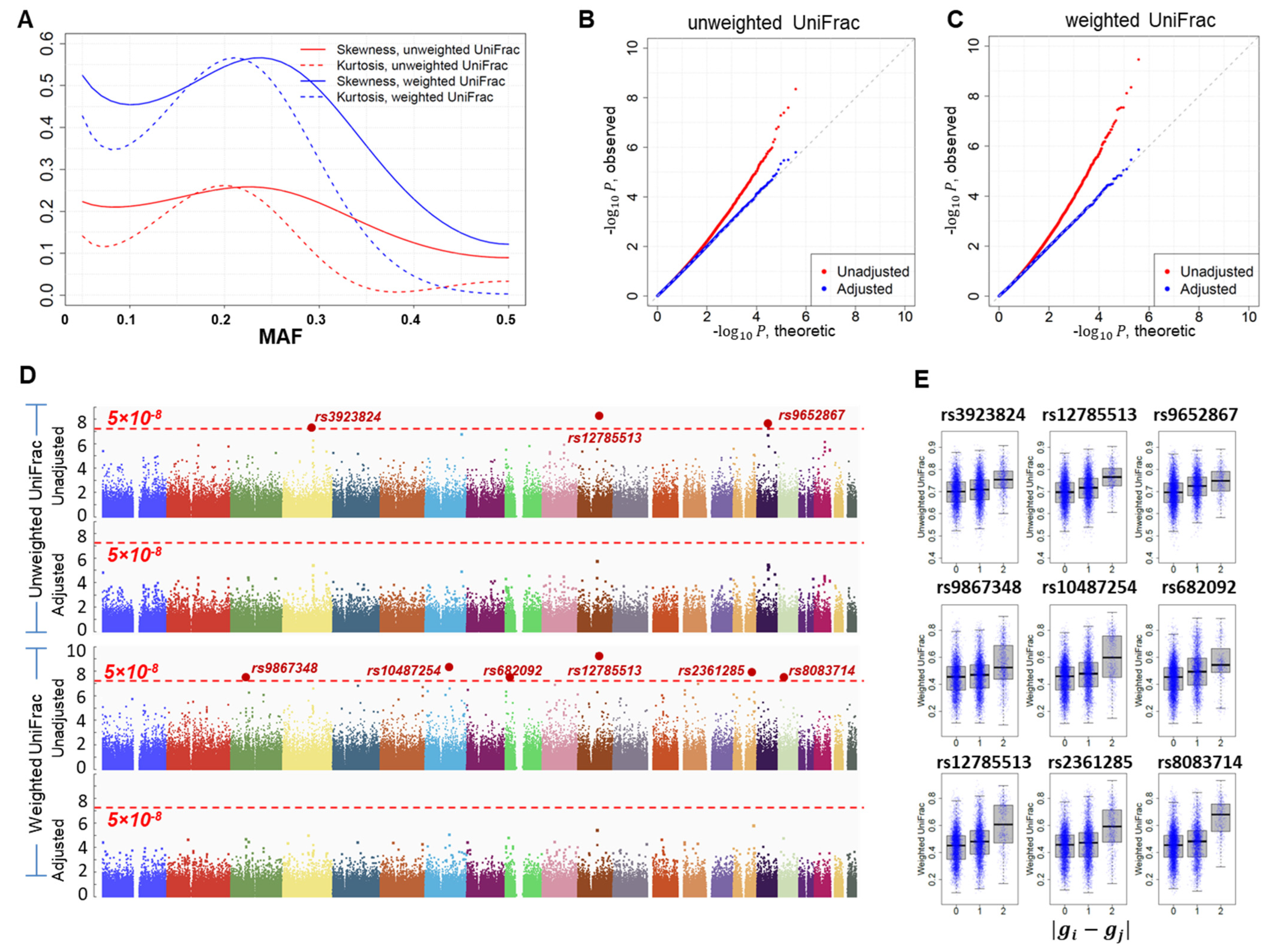
3.3. GWAS of Microbiome Diversity in Adjacent Normal Lung Tissues
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
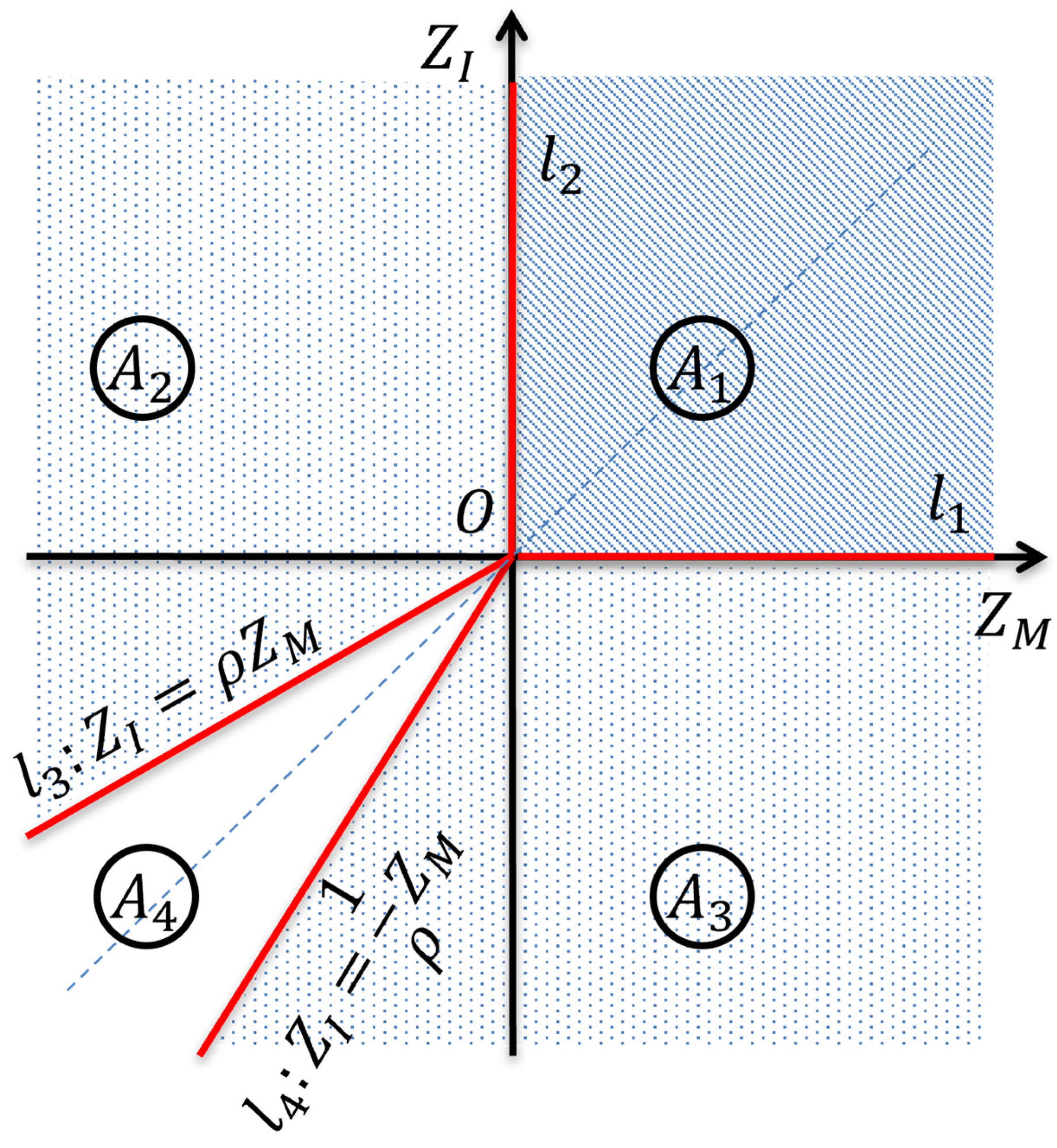
Appendix A. Calculating Calculating , , and
Appendix B. Calculating
Appendix C. A Statistic for Testing
Appendix D. Calculating Skewness and Kurtosis under
Appendix E. Improve p-Value Approximations by Adjusting for Skewness and Kurtosis
References
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.L.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; LeLeiko, N.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Sinha, R.; Pei, Z.; Dominianni, C.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Hayes, R.B.; Yang, L. Human gut microbiome and risk for colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goedert, J.J.; Jones, G.; Hua, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, G.; Flores, R.; Falk, R.T.; Gail, M.H.; Shi, J.; Ravel, J.; et al. Investigation of the Association Between the Fecal Microbiota and Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women: A Population-Based Case-Control Pilot Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, S.; Smith, D.P.; Hampton-Marcell, J.; Owens, S.M.; Handley, K.M.; Scott, N.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Larsen, P.; Shogan, B.D.; Weiss, S.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of microbial interaction between humans and the indoor environment. Science 2014, 345, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.; McHardy, I.; Ruegger, P.; Goudarzi, M.; Kashyap, P.C.; Haritunians, T.; Li, X.; Graeber, T.G.; Schwager, E.; Huttenhower, C.; et al. Reprograming of gut microbiome energy metabolism by the FUT2 Crohn’s disease risk polymorphism. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2193–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knights, D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Weersma, R.K.; Gevers, D.; Dijkstra, G.; Huang, H.; Tyler, A.D.; van Sommeren, S.; Imhann, F.; Stempak, J.M.; et al. Complex host genetics influence the microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKnite, A.M.; Perez-Munoz, M.E.; Lu, L.; Williams, E.G.; Brewer, S.; Andreux, P.A.; Bastiaansen, J.W.M.; Wang, X.; Kachman, S.D.; Auwerx, J.; et al. Murine Gut Microbiota Is Defined by Host Genetics and Modulates Variation of Metabolic Traits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, A.K.; Kelly, S.A.; Legge, R.; Ma, F.; Low, S.J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Nehrenberg, D.; Hua, K.; et al. Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18933–18938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davenport, E.R.; Cusanovich, D.A.; Michelini, K.; Barreiro, L.B.; Ober, C.; Gilad, Y. Genome-Wide Association Studies of the Human Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: Multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 2015, 348, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battle, A.; Mostafavi, S.; Zhu, X.; Potash, J.B.; Weissman, M.M.; McCormick, C.; Haudenschild, C.D.; Beckman, K.B.; Shi, J.; Mei, R.; et al. Characterizing the genetic basis of transcriptome diversity through RNA-sequencing of 922 individuals. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, J.T.; Pai, A.A.; Pickrell, J.K.; Gaffney, D.J.; Pique-Regi, R.; Degner, J.F.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. DNA methylation patterns associate with genetic and gene expression variation in HapMap cell lines. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Marconett, C.N.; Duan, J.; Hyland, P.L.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Wheeler, W.; Zhou, B.; Campan, M.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Characterizing the genetic basis of methylome diversity in histologically normal human lung tissue. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVicker, G.; van de Geijn, B.; Degner, J.F.; Cain, C.E.; Banovich, N.E.; Raj, A.; Lewellen, N.; Myrthil, M.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. Identification of Genetic Variants That Affect Histone Modifications in Human Cells. Science 2013, 342, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilpinen, H.; Waszak, S.M.; Gschwind, A.R.; Raghav, S.K.; Witwicki, R.M.; Orioli, A.; Migliavacca, E.; Wiederkehr, M.; Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Panousis, N.I.; et al. Coordinated Effects of Sequence Variation on DNA Binding, Chromatin Structure, and Transcription. Science 2013, 342, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suhre, K.; Wallaschofski, H.; Raffler, J.; Friedrich, N.; Haring, R.; Michael, K.; Wasner, C.; Krebs, A.; Kronenberg, F.; Chang, D.; et al. A genome-wide association study of metabolic traits in human urine. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatti, C.; Service, S.K.; Hartikainen, A.L.; Pouta, A.; Ripatti, S.; Brodsky, J.; Jones, C.G.; Zaitlen, N.A.; Varilo, T.; Kaakinen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of metabolic traits in a birth cohort from a founder population. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and qualitative β diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R. UniFrac--an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generalized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Thingholm, L.B.; Skieceviciene, J.; Rausch, P.; Kummen, M.; Hov, J.R.; Degenhardt, F.; Heinsen, F.A.; Ruhlemann, M.C.; Szymczak, S.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variation in vitamin D receptor and other host factors influencing the gut microbiota. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Petrosino, J.F.; Huang, K.; McGuire, A.L.; Birren, B.W.; Nelson, K.E.; White, O.; Methe, B.A.; Huttenhower, C. The Human Microbiome Project: A community resource for the healthy human microbiome. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MicrobiomeGWAS. Available online: https://github.com/lsncibb/microbiomeGWAS (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Landi, M.T.; Consonni, D.; Rotunno, M.; Bergen, A.W.; Goldstein, A.M.; Lubin, J.H.; Goldin, L.; Alavanja, M.; Morgan, G.; Subar, A.F.; et al. Environment And Genetics in Lung cancer Etiology (EAGLE) study: An integrative population-based case-control study of lung cancer. BMC Public Health 2008, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, M.T.; Chatterjee, N.; Yu, K.; Goldin, L.R.; Goldstein, A.M.; Rotunno, M.; Mirabello, L.; Jacobs, K.; Wheeler, W.; Yeager, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study of lung cancer identifies a region of chromosome 5p15 associated with risk for adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Tu, I.P.; Siegmund, D.O. The maximum of a function of a Markov chain and application to linkage analysis. Adv. Appl. Probab. 1999, 31, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, D. Sequential Analysis: Tests and Confidence Intervals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, D.; Hyde, E.; Debelius, J.W.; Morton, J.T.; Gonzalez, A.; Ackermann, G.; Aksenov, A.A.; Behsaz, B.; Brennan, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. American Gut: An Open Platform for Citizen Science Microbiome Research. mSystems 2018, 3, e00031-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rühlemann, M.C.; Hermes, B.M.; Bang, C.; Doms, S.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Thingholm, L.B.; Frost, F.; Degenhardt, F.; Wittig, M.; Kässens, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study in 8956 German individuals identifies influence of ABO histo-blood groups on gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Dubosarskiy, I.; Murray, S.R.; Andersen, G.L. Comprehensive aligned sequence construction for automated design of effective probes (CASCADE-P) using 16S rDNA. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devlin, B.; Roeder, K. Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999, 55, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, R.J.; McKay, J.D.; Gaborieau, V.; Boffetta, P.; Hashibe, M.; Zaridze, D.; Mukeria, A.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Lissowska, J.; Rudnai, P.; et al. A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25. Nature 2008, 452, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKay, J.D.; Hung, R.J.; Gaborieau, V.; Boffetta, P.; Chabrier, A.; Byrnes, G.; Zaridze, D.; Mukeria, A.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Lissowska, J.; et al. Lung cancer susceptibility locus at 5p15.33. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Geller, F.; Sulem, P.; Rafnar, T.; Wiste, A.; Magnusson, K.P.; Manolescu, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Stefansson, H.; Ingason, A.; et al. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature 2008, 452, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amos, C.I.; Wu, X.; Broderick, P.; Gorlov, I.P.; Gu, J.; Eisen, T.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Vijayakrishnan, J.; et al. Genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility locus for lung cancer at 15q25.1. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Broderick, P.; Webb, E.; Wu, X.; Vijayakrishnan, J.; Matakidou, A.; Qureshi, M.; Dong, Q.; Gu, X.; Chen, W.V.; et al. Common 5p15.33 and 6p21.33 variants influence lung cancer risk. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chatterjee, N.; Rotunno, M.; Wang, Y.; Pesatori, A.C.; Consonni, D.; Li, P.; Wheeler, W.; Broderick, P.; Henrion, M.; et al. Inherited variation at chromosome 12p13.33, including RAD52, influences the risk of squamous cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timofeeva, M.N.; Hung, R.J.; Rafnar, T.; Christiani, D.C.; Field, J.K.; Bickeboller, H.; Risch, A.; McKay, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; et al. Influence of common genetic variation on lung cancer risk: Meta-analysis of 14 900 cases and 29 485 controls. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Chen, J.; Carroll, I.M.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Epstein, M.P.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J.J.; Ringel, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, M.C. Testing in Microbiome-Profiling Studies with MiRKAT, the Microbiome Regression-Based Kernel Association Test. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 96, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X. D-MANOVA: Fast distance-based multivariate analysis of variance for large-scale microbiome association studies. Bioinformatics. 2021, 38, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, V.A.; Cham, C.M.; Chang, E.B. Diet, gut microbes, and genetics in immune function: Can we leverage our current knowledge to achieve better outcomes in inflammatory bowel diseases? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Vangay, P.; McKinlay, C.E.; Knights, D. Multi-omics analysis of inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troncone, R.; Discepolo, V. Celiac disease and autoimmunity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59 (Suppl. S1), S9–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, N.; Burton, J.P.; Suppiah, P.; Reid, G.; Stebbings, S. The role of the microbiome in rheumatic diseases. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.A.; Costenbader, K.H. Genetics, environment, and gene-environment interactions in the development of systemic rheumatic diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 40, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.A. Update on ankylosing spondylitis: Current concepts in pathogenesis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.S.; Krych, L.; Buschard, K.; Hansen, C.H.; Hansen, A.K. Beyond genetics. Influence of dietary factors and gut microbiota on type 1 diabetes. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4234–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birt, D.F.; Phillips, G.J. Diet, genes, and microbes: Complexities of colon cancer prevention. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 42, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marietta, E.; Rishi, A.; Taneja, V. Immunogenetic control of the intestinal microbiota. Immunology 2015, 145, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ZM | ZI | Q | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | α = 10−3 | 10−5 | 10−7 | 10−3 | 10−5 | 10−7 | 10−3 | 10−5 | 10−7 | |
| Asymptotic approximation | 100 | 5.5 | 51.6 | 610.0 | 4.7 | 36.1 | 342.8 | 7.3 | 80.9 | 1148.0 |
| 200 | 3.7 | 23.0 | 187.3 | 3.1 | 15.8 | 105.5 | 4.6 | 33.0 | 316.7 | |
| 500 | 2.4 | 9.4 | 45.2 | 2.1 | 6.7 | 25.5 | 2.8 | 11.9 | 64.1 | |
| 1000 | 2.0 | 5.7 | 21.3 | 1.8 | 4.4 | 14.0 | 2.2 | 6.9 | 28.5 | |
| Adjusted for skewness and kurtosis | 100 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| 200 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.8 | |
| 500 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.7 | |
| 1000 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | |
| SNP | Chr | Annotated Genes | Unweighted UniFrac | Weighted UniFrac |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2036534 | 15q25.1 | CHRNA3/4/5 | 0.425 | 0.167 |
| rs1051730 | 15q25.1 | CHRNA3/4/5 | 0.020 | 0.401 |
| rs2736100 | 5p15.33 | TERT | 0.089 | 0.267 |
| rs401681 | 5p15.33 | CLPTM1L | 0.056 | 0.005 |
| rs6489769 | 12p13.3 | RAD52 | 0.197 | 0.329 |
| rs1333040 | 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B | 0.249 | 0.224 |
| Overall test | 0.0032 | 0.011 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, X.; Song, L.; Yu, G.; Vogtmann, E.; Goedert, J.J.; Abnet, C.C.; Landi, M.T.; Shi, J. MicrobiomeGWAS: A Tool for Identifying Host Genetic Variants Associated with Microbiome Composition. Genes 2022, 13, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071224
Hua X, Song L, Yu G, Vogtmann E, Goedert JJ, Abnet CC, Landi MT, Shi J. MicrobiomeGWAS: A Tool for Identifying Host Genetic Variants Associated with Microbiome Composition. Genes. 2022; 13(7):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071224
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Xing, Lei Song, Guoqin Yu, Emily Vogtmann, James J. Goedert, Christian C. Abnet, Maria Teresa Landi, and Jianxin Shi. 2022. "MicrobiomeGWAS: A Tool for Identifying Host Genetic Variants Associated with Microbiome Composition" Genes 13, no. 7: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071224
APA StyleHua, X., Song, L., Yu, G., Vogtmann, E., Goedert, J. J., Abnet, C. C., Landi, M. T., & Shi, J. (2022). MicrobiomeGWAS: A Tool for Identifying Host Genetic Variants Associated with Microbiome Composition. Genes, 13(7), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071224





