Identification of New Toxicity Mechanisms in Drug-Induced Liver Injury through Systems Pharmacology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gathering Drug, Proteins and Domain Data
2.1.1. Drug-Protein Association
2.1.2. Drug-Domain Associations
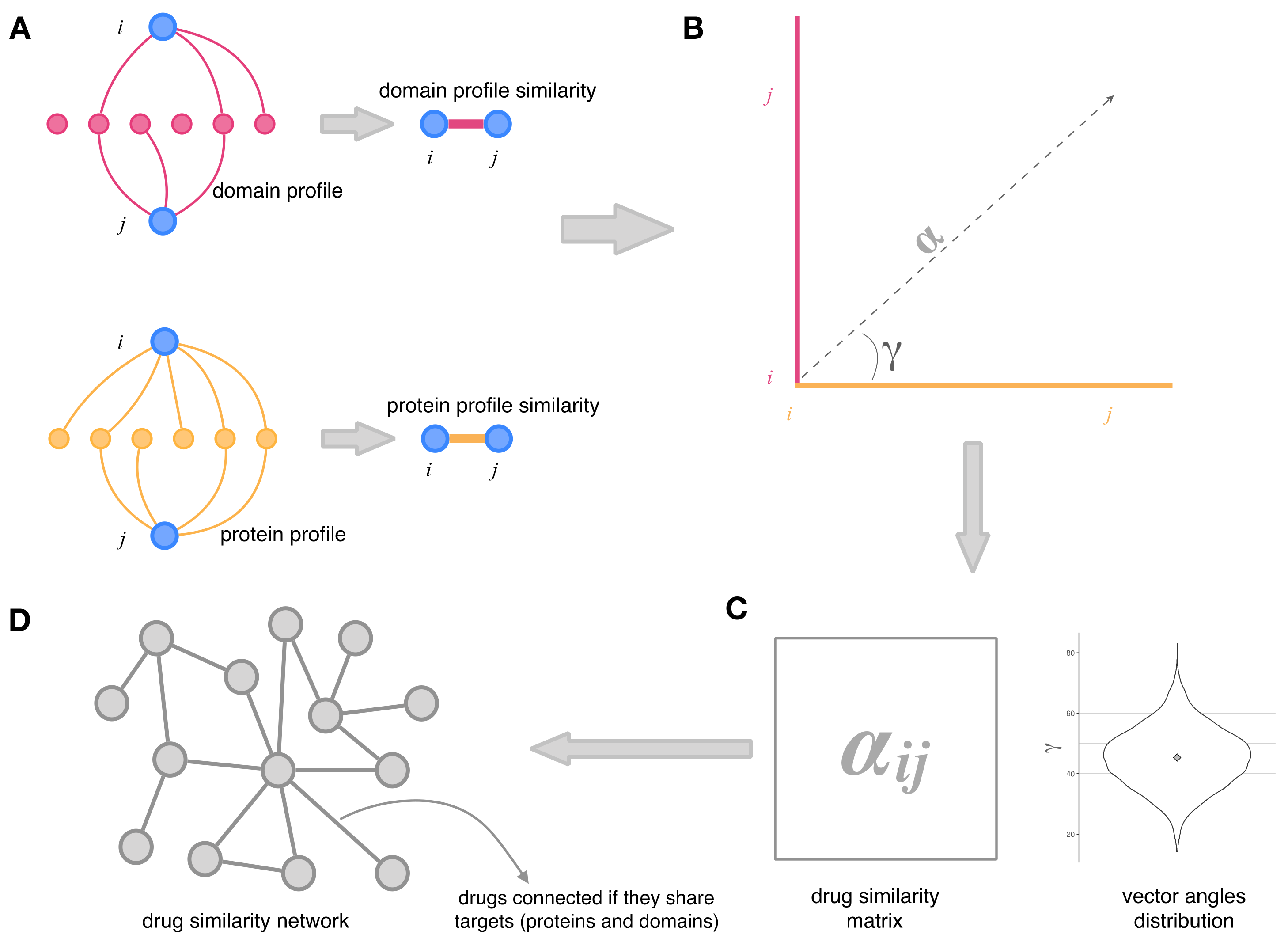
2.2. Integration of Drug–Protein and Drug–Domain Data. Drug Similarity Network
2.3. Topology and Community Analysis of the Drug Similarity Network
3. Results and Discussion
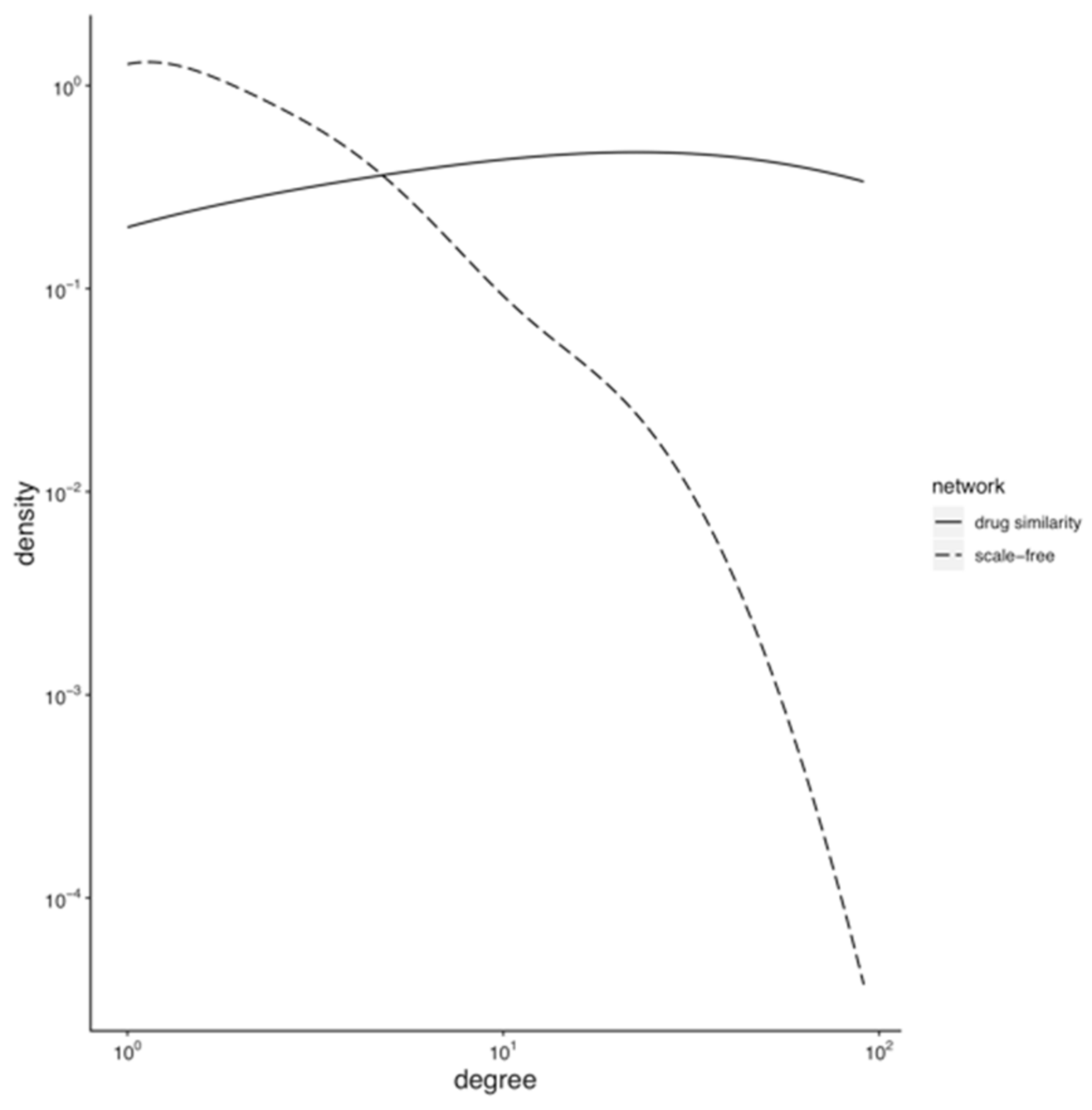
3.1. Topology of the Drug Similarity Network
3.1.1. Hubs and Drug-Target Data Completion
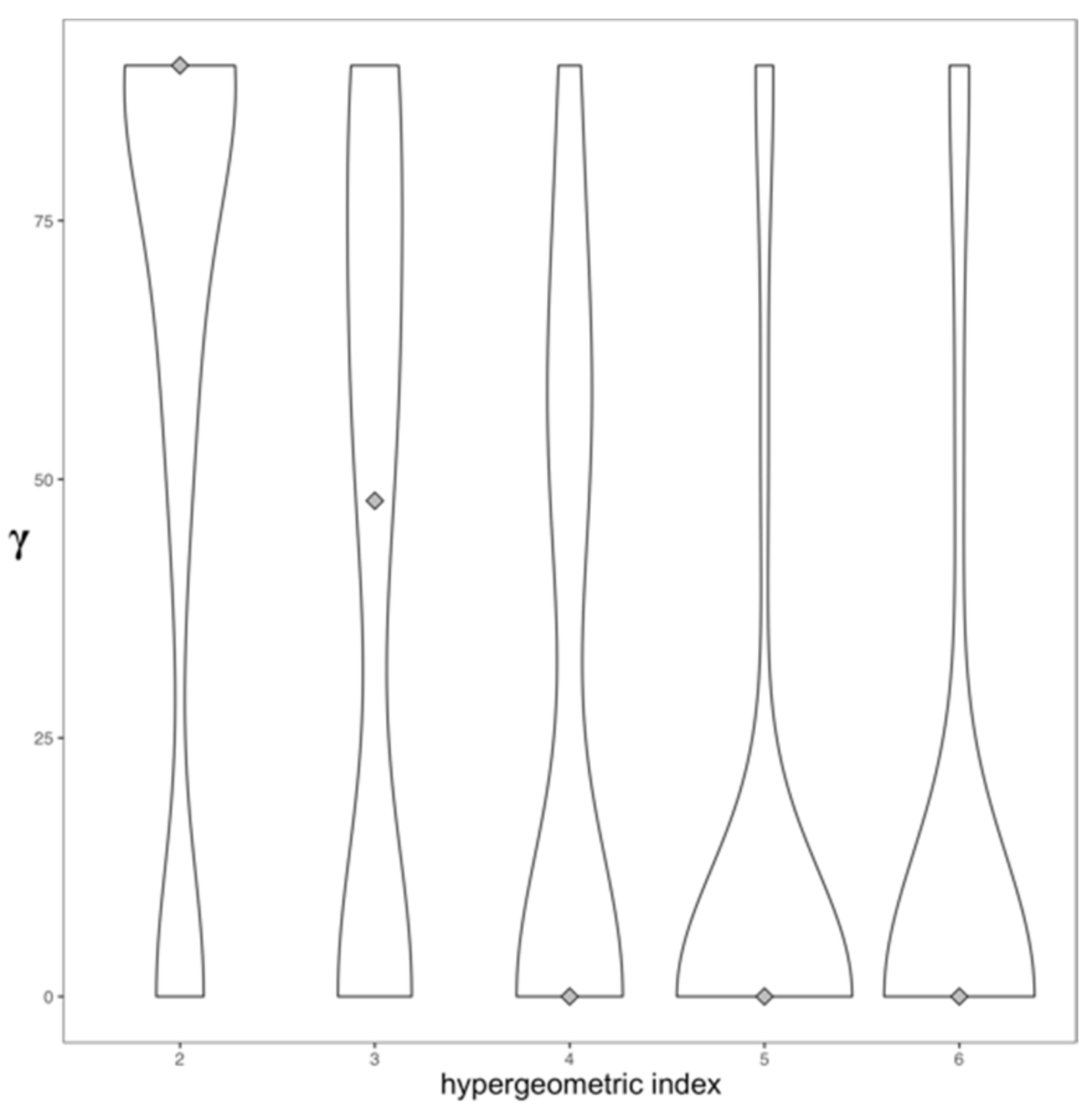
3.1.2. Assortative Mixing in the Drug Similarity Network
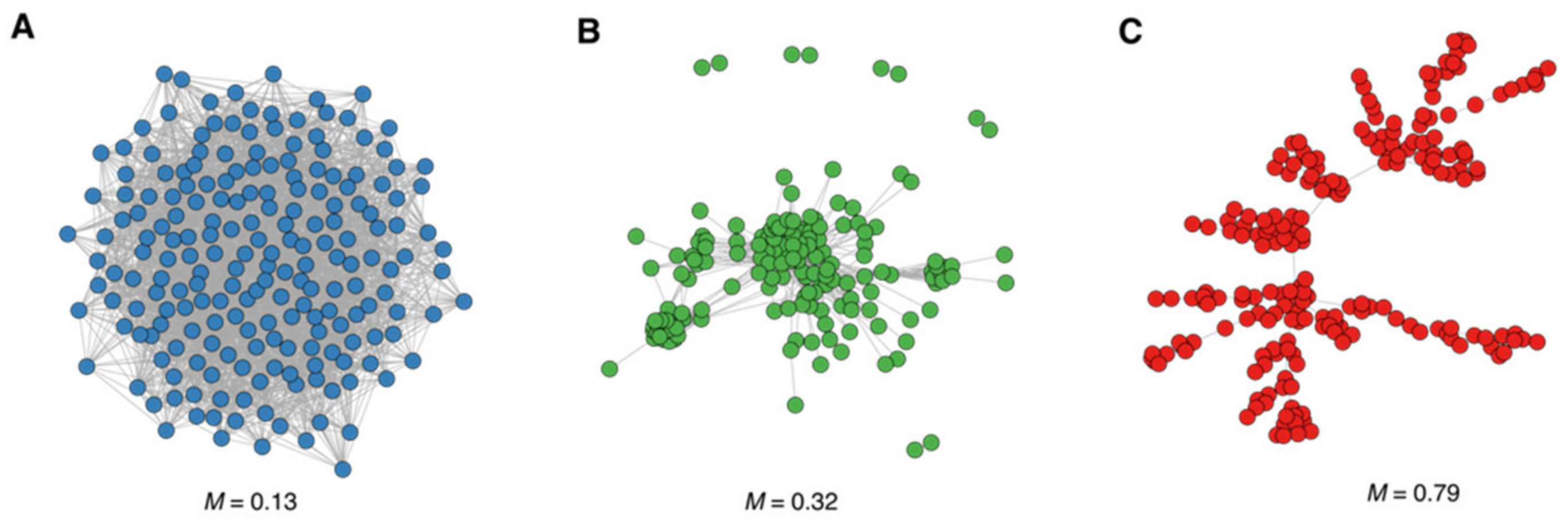
3.2. Modularity and Community Structure of the Drug Similarity Network
3.2.1. Animal-Haem Peroxidase and EGF-Like Drug Community
3.2.2. Sodium-Neurotransmitter Symporter Drug Community
3.2.3. Olfactory Receptors (ORs) Drug Community
3.2.4. Drug Communities with a Low Number of Drugs
3.3. Drug Communities and Demographic-Clinical Characteristics
3.4. Drug Communities and Drug Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouvy, J.C.; Bruin, M.L.D.; Koopmanschap, M.A. Epidemiology of Adverse Drug Reactions in Europe: A Review of Recent Observational Studies. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Heneghan, C.J.; Aronson, J.K. Worldwide Withdrawal of Medicinal Products Because of Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuikkala, J.; Vähämaa, H.; Salmela, P.; Nevalainen, O.S.; Aittokallio, T. A Multilevel Layout Algorithm for Visualizing Physical and Genetic Interaction Networks, with Emphasis on Their Modular Organization. BioData Min. 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalasani, N.P.; Hayashi, P.H.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Navarro, V.J.; Lee, W.M.; Fontana, R.J. ACG Clinical Guideline: The Diagnosis and Management of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdmanis, P.N.; Gu, S.; Chu, K.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Munding, E.M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kutay, H.; Ghoshal, K.; et al. RNA Interference–Induced Hepatotoxicity Results from Loss of the First Synthesized Isoform of MicroRNA-122 in Mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoine, D.J.; Harrill, A.H.; Watkins, P.B.; Park, B.K. Safety Biomarkers for Drug-Induced Liver Injury—Current Status and Future Perspectives. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 3, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I.; Alonso, A.; García-Cortes, M.; García-Ruiz, E.; Benitez, R.; Fernandez, M.C.; Pelaez, G.; Romero, M.; Corpas, R.; et al. HLA Class II Genotype Influences the Type of Liver Injury in Drug-Induced Idiosyncratic Liver Disease. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; López-Nevot, M.-Á.; Cabello, F.R.; Ulzurrun, E.; Soriano, G.; Gomez, M.R.; Moreno-Casares, A.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J. HLA Alleles Influence the Clinical Signature of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate Hepatotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J.; Nez, C.M.I.; Ulzurrun, E.; García-Martín, E.; Borraz, Y.; Fernández, M.C.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Castiella, A.; Planas, R.; et al. Glutathione S-Transferase M1 and T1 Null Genotypes Increase Susceptibility to Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Hepatology 2008, 48, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulzurrun, E.; Stephens, C.; Crespo, E.; Cabello, F.R.; Ruiz-Nuñez, J.; Saenz-López, P.; Moreno-Herrera, I.; Robles-Díaz, M.; Hallal, H.; Moreno-Planas, J.M.; et al. Role of Chemical Structures and the 1331TC Bile Salt Export Pump Polymorphism in Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredj, N.B.; Gam, R.; Kerkni, E.; Chaabane, A.; Chadly, Z.; Boughattas, N.; Aouam, K. Risk Factors of Isoniazid-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Tunisian Tuberculosis Patients. Pharm. J. 2016, 17, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, G.P.; Ramsay, L.; Daly, A.K.; Sonchit, N.; Leathart, J.B.S.; Alexander, G.; Kenna, J.G.; Caldwell, J.; Day, C.P. Hepatic Adducts, Circulating Antibodies, and Cytokine Polymorphisms in Patients with Diclofenac Hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.; Hapani, S.; Choueiri, T.K.; Wu, S. Risk of Liver Toxicity with the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Pazopanib in Cancer Patients. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosedale, M.; Watkins, P. Drug-induced Liver Injury: Advances in Mechanistic Understanding That Will Inform Risk Management. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strebhardt, K.; Ullrich, A. Paul Ehrlich’s Magic Bullet Concept: 100 Years of Progress. Nature reviews. Cancer 2008, 8, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L. Harnessing Polypharmacology with Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moya-García, A.; Adeyelu, T.; Kruger, F.A.; Dawson, N.L.; Lees, J.G.; Overington, J.P.; Orengo, C.; Ranea, J.A.G. Structural and Functional View of Polypharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campillos, M.; Kuhn, M.; Gavin, A.C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. Drug Target Identification Using Side-Effect Similarity. Science 2008, 321, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, M.; Banchaabouchi, M.A.; Campillos, M.; Jensen, L.J.; Gross, C.; Gavin, A.-C.; Bork, P. Systematic Identification of Proteins That Elicit Drug Side Effects. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.H.; Tokheim, C.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Sengupta, S.; Bertrand, D.; Weerasinghe, A.; Colaprico, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Driver Genes and Mutations. Cell 2018, 173, 371–376.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duran-Frigola, M.; Aloy, P. Analysis of Chemical and Biological Features Yields Mechanistic Insights into Drug Side Effects. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mestres, J.; Gregori-Puigjané, E.; Valverde, S.; Solé, R.V. Data Completeness—The Achilles Heel of Drug-Target Networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 983–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I.; Fernandez, M.C.; Pelaez, G.; Pachkoria, K.; García-Ruiz, E.; García-Muñoz, B.; González-Grande, R.; Pizarro, A.; Durán, J.A.; et al. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: An Analysis of 461 Incidences Submitted to the Spanish Registry over a 10-Year Period. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Vijay, V.; Shi, Q.; Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Tong, W. FDA-Approved Drug Labeling for the Study of Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, N.; Fisk, L.; Naven, R.T.; Note, R.R.; Patel, M.L.; Pelletier, D.J. Developing Structure-Activity Relationships for the Prediction of Hepatotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Chen, F.; Gao, S.; Pei, J.; Lai, L. Deep Learning for Drug-Induced Liver Injury. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; Robles-Diaz, M.; Medina-Caliz, I.; Garcia-Cortes, M.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Sanabria-Cabrera, J.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, A.; Alvarez-Alvarez, I.; Slim, M.; Jimenez-Perez, M.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis and Insights Gained from Long-Term Experience of the Spanish DILI Registry. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsson, E.S. Incidence and Outcomes of DILI in Western Patients. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 4, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessone, F.; Hernandez, N.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J.; Latin Dili Network Latindilin And Spanish Dili Registry. The Latin American DILI Registry Experience: A Successful Ongoing Collaborative Strategic Initiative. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontana, R.J.; Watkins, P.B.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Chalasani, N.; Davern, T.; Serrano, J.; Rochon, J.; Group, D.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN) Prospective Study. Drug Saf. 2009, 32, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL Database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Alpi, E.; Bely, B.; Bingley, M.; Britto, R.; Bursteinas, B.; Busiello, G.; et al. UniProt: A Worldwide Hub of Protein Knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Bajorath, J. Influence of Search Parameters and Criteria on Compound Selection, Promiscuity, and Pan Assay Interference Characteristics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3056–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, C.A.; Michie, A.D.; Jones, S.; Jones, D.T.; Swindells, M.B.; Thornton, J.M. CATH—A Hierarchic Classification of Protein Domain Structures. Struct./Fold. Des. 1997, 5, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kummerfeld, S.K.; Teichmann, S.A. Protein Domain Organisation: Adding Order. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, E.; Tan, T.; Lin, K. Promiscuous Domains: Facilitating Stability of the Yeast Protein—Protein Interaction Network. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 8, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, F.A.; Gaulton, A.; Nowotka, M.; Overington, J.P. PPDMs—A Resource for Mapping Small Molecule Bioactivities from ChEMBL to Pfam—A Protein Domains. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bass, J.I.F.; Diallo, A.; Nelson, J.; Soto, J.M.; Myers, C.L.; Walhout, A.J.M. Using Networks to Measure Similarity between Genes: Association Index Selection. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research; Complex Systems: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006; p. 1695. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell, L.H.; Hopfield, J.J.; Leibler, S.; Murray, A.W. From Molecular to Modular Cell Biology. Nature 1999, 402, C47–C52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-Y.; Bagrow, J.P.; Lehmann, S. Link Communities Reveal Multiscale Complexity in Networks. Nature 2010, 466, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New Perspectives on Genomes, Pathways, Diseases and Drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabasi, A.-L.; Albert, R. Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, U.T.; Waldron, T.T.; Springer, T.A. Remodeling of the Lectin–EGF-like Domain Interface in P- and L-Selectin Increases Adhesiveness and Shear Resistance under Hydrodynamic Force. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, J.; Flemmig, J. Human Myeloperoxidase in Innate and Acquired Immunity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 500, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Raja, K.; Schweizer, U.; Mugesh, G. Chemistry and Biology in the Biosynthesis and Action of Thyroid Hormones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7606–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-J.; Oh, D.-K. Prostaglandin Synthases: Molecular Characterization and Involvement in Prostaglandin Biosynthesis. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 66, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tian, Y.; Lian, X.; Jin, Y.; Jin, T.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, B.; Shen, X.; Fan, X. Integrated Systems Toxicology Approaches Identified the Possible Involvement of ABC Transporters Pathway in Erythromycin Estolate-Induced Liver Injury in Rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, F.-L.; Zheng, Z.-W.; Fan, Z.-D.; Zhu, S.-M.; Qian, X.-F.; Liu, N.-N. Clinical Characteristics of Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Related Risk Factors. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2606–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, C.; Castiella, A.; Gomez-Moreno, E.M.; Otazua, P.; López-Nevot, M.-Á.; Zapata, E.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; Medina-Cáliz, I.; Robles-Díaz, M.; et al. Autoantibody Presentation in Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Idiopathic Autoimmune Hepatitis. Pharm. Genom. 2016, 26, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.D.; Michot, J.-M.; Rosmorduc, O.; Guettier, C.; Samuel, D. Liver Toxicity as a Limiting Factor to the Increasing Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Vilarnau, N.; Hankeova, S.; Vorrink, S.U.; Mkrtchian, S.; Andersson, E.R.; Lauschke, V.M. Calcium Signaling in Liver Injury and Regeneration. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.E.; van Staden, C.J.; Chen, Y.; Kalyanaraman, N.; Kalanzi, J.; Dunn, R.T.; Afshari, C.A.; Hamadeh, H.K. A Multifactorial Approach to Hepatobiliary Transporter Assessment Enables Improved Therapeutic Compound Development. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 136, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, D.; Lynn, A.; Wang, S.; Johnson, D.E. Evidence for a Potential Protective Effect of Carnitine-Pantothenic Acid Co-Treatment on Valproic Acid-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 7, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maßberg, D.; Hatt, H. Human Olfactory Receptors: Novel Cellular Functions Outside of the Nose. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1739–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jia, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Sekharan, S.; Batista, V.S.; Lee, S.-J. Activation of OR1A1 Suppresses PPAR-γ Expression by Inducing HES-1 in Cultured Hepatocytes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 64, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Fu, N.; Chen, L. The Diversified Function and Potential Therapy of Ectopic Olfactory Receptors in Non-olfactory Tissues. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maßberg, D.; Simon, A.; Häussinger, D.; Keitel, V.; Gisselmann, G.; Conrad, H.; Hatt, H. Monoterpene (−)-Citronellal Affects Hepatocarcinoma Cell Signaling via an Olfactory Receptor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 566, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kelly, R.; Zhou, G.; Fang, H.; Borlak, J.; Tong, W. The Liver Toxicity Knowledge Base: A Systems Approach to a Complex End Point. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Domain Name | Pfam ID | Toxic Drugs, n | Non-Toxic Drugs, n | DILI Score | Therapeutics Categories (n Drugs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGF-like domain | PF00008 | 12 | 0 | 101 | NSAIDs | (12) |
| Animal haem peroxidase | PF03098 | 12 | 0 | 101 | NSAIDs | (12) |
| Sodium-neurotransmitter symporter domain | PF00209 | 20 | 9 | 75 | Nervous system | (12) |
| Cardiac system | (8) | |||||
| Respiratory | (2) | |||||
| Antineoplastic | (2) | |||||
| Gynecological | (2) | |||||
| Alimentary | (1) | |||||
| Blood formation | (1) | |||||
| Dermatological | (1) | |||||
| Ligand-binding domain of nuclear hormone receptor | PF00104 | 2 | 1 | 67 | Sexual hormone | (2) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| ABC transporter transmembrane region | PF00664 | 2 | 1 | 67 | Nervous system | (1) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| Antineoplastic | (1) | |||||
| Olfactory receptor | PF13853 | 18 | 18 | 62 | Nervous system | (20) |
| Cardiac system | (6) | |||||
| Respiratory | (6) | |||||
| Alimentary | (2) | |||||
| Gynaecological | (1) | |||||
| Dermatological | (1) | |||||
| Eukaryotic-type carbonic anhydrase | PF00194 | 2 | 2 | 50 | Cardiac system | (2) |
| Antineoplastic | (1) | |||||
| Nervous system | (1) | |||||
| Multi-antimicrobial extrusion protein | PF01554 | 2 | 2 | 50 | Anti-infective | (2) |
| Antineoplastic | (1) | |||||
| Respiratory | (1) | |||||
| Cytochrome P450 | PF00067 | 2 | 2 | 50 | Dermatological | (3) |
| Various | (1) | |||||
| 7 transmembrane receptor (rhodopsin family) | PF00001 | 19 | 25 | 62 | Nervous system | (18) |
| Respiratory | (8) | |||||
| Alimentary | (5) | |||||
| Gynaecological | (5) | |||||
| Cardiac system | (4) | |||||
| Dermatological | (2) | |||||
| Antineoplastic | (1) | |||||
| Hormonal | (1) | |||||
| Sugar (and other) transporter | PF00083 | 1 | 2 | 33 | Alimentary | (1) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| Anti-infective | (1) | |||||
| Major Facilitator Superfamily | PF07690 | 1 | 2 | 33 | Alimentary | (1) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| Anti-infective | (1) | |||||
| FAD-binding domain | PF00890 | 1 | 2 | 33 | Nervous system | (2) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-like domain | PF13450 | 1 | 2 | 33 | Nervous system | (2) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| DEAD/DEAH box helicase | PF00270 | 1 | 4 | 21 | Nervous system | (2) |
| Cardiac system | (1) | |||||
| Respiratory | (1) | |||||
| Antineoplastic | (1) | |||||
| PF00209 | p-Value * | PF03098 | p-Value * | PF13853 | p-Value * | Remaining DILI Cases | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 141) | (n = 40) | (n = 757) | ||||
| Demographics | |||||||
| Age, median (IQR) | 49 (41–68) | 0.6285 | 55 (40–69) | 0.3496 | 56 (43–69) | 0.9831 | 58 (42–69) |
| Women, n (%) | 24 (53) | 0.4828 | 71 (50) | 0.6002 | 20 (50) | 0.8006 | 363 (48) |
| Clinical parameters | |||||||
| Duration of treatment, median days (IQR) | 62 (29–150) | 0.0001 | 23 (8–58) | 0.4333 | 37 (15–77) | 0.0559 | 22 (8–63) |
| Time to onset, median days (IQR) | 38 (19–122) | 0.0092 | 25 (7–61) | 0.3342 | 24 (8–78) | 0.5889 | 22 (9–60) |
| Severity, n (%) | 0.1921 | 0.1254 | 0.0165 | ||||
| Mild | 20 (45) | 43 (32) | 21 (55) | 230 (31) | |||
| Moderate | 19 (43) | 79 (59) | 13 (34) | 429 (58) | |||
| Severe | 4 (9) | 3 (2) | 3 (8) | 52 (7.0) | |||
| Fatal/Transplant | 1 (2) | 8 (6) | 1 (2) | 27 (3.6) | |||
| Eosinophilia, n (%) | 7 (17) | 0.3127 | 21 (16) | 0.0416 | 8 (28) | 0.5376 | 178 (24) |
| Lymphopenia, n (%) | 9 (26) | 0.6801 | 23 (20) | 0.5260 | 6 (16) | 0.2495 | 146 (23) |
| Positive autoantibody titres §, n (%) | 4 (11) | 0.0394 | 29 (25) | 0.9494 | 5 (16) | 0.2617 | 148 (24) |
| Type of liver injury, n (%) | 0.0413 | 0.8202 | 0.3628 | ||||
| Hepatocellular | 34 (76) | 84 (61) | 27 (67) | 448 (62) | |||
| Cholestastic & Mixed | 11 (24) | 53 (38) | 13 (32) | 273 (30) | |||
| Liver profile values at onset xULN, median (IQR) | |||||||
| TBL | 2.14 (0.7–6.2) | 0.0900 | 4.2 (1.2–9.3) | 0.3855 | 1.5 (0.6–4.4) | 0.0099 | 5 (1.15–10) |
| AST | 5.6 (2.1–15) | 0.5378 | 8.4 (2.7–26) | 0.2773 | 5.0 (2.4–13) | 0.2405 | 6.4 (3.0–19) |
| ALT | 7.3 (4.0–28) | 0.5619 | 9.5 (4.5–30) | 0.2847 | 8.1 (4.3–16) | 0.0582 | 9.8 (4.7–24) |
| GGT | 4.0 (2.1–10) | 0.5000 | 6.6 (2.8–20) | 0.1910 | 5.9 (2.2–9.4) | 0.3671 | 5.4 (2.7–10) |
| ALP | 1.2 (0.7–4.7) | 0.0420 | 1.7 (1.1–2.9) | 0.0818 | 1.0 (0.7–2.0) | 0.0316 | 1.6 (1.0–4.2) |
| PF00209 | p-Value * | PF03098 | p-Value * | PF13853 | p-Value * | Remaining DILI Drugs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 20) | (n = 15) | (n = 22) | (n = 141) | ||||
| Physicochemical | |||||||
| Molecular weight, mean | 331 | 0.3577 | 261 | 0.0124 | 364 | 0.7271 | 377 |
| Number of rings, mean | 3.09 | 0.3118 | 2.0 | 0.0213 | 3.63 | 0.0104 | 2.76 |
| Heterorings, mean | 0.90 | 0.1069 | 0.53 | 0.0089 | 1.63 | 0.2390 | 1.32 |
| Pharmacokinetics | |||||||
| Half-life, median h | 11 | 0.0234 | 2.2 | 0.2913 | 14.1 | 0.0130 | 6.5 |
| Lipophilicity (LogP), median (range) | 4.01 | 0.0008 | 2.87 | 0.4447 | 3.9 | 0.001 | 2.27 |
| (0.51–6.3) | (−0.9–4.3) | (−6.8–8.3) | |||||
| Plasma protein binding (%), median (range) | 95 | 0.0204 | 99 | 0.0001 | 93 | 0.0099 | 84 |
| (27–99.3) | (55–99.5) | (56–99.98) | (1–99.9) | ||||
| Hepatic metabolism | 20 (100) | 0.0039 | 13 (87) | 0.1630 | 20 (95) | 0.0134 | 98 (65) |
| ≥50%, n (%) | |||||||
| Enterohepatic circulation, n (%) | 8 (42) | 0.1908 | 2 (13) | 0.2345 | 10 (47) | 0.0618 | 38 (27) |
| Reactive metabolite formation, n (%) | 8 (40) | 0.7871 | 7 (46) | 0.4574 | 9 (41) | 0.7164 | 52 (37) |
| Mitochondrial liability, n (%) | 13 (65) | 0.2198 | 13 (87) | 0.0073 | 13 (59) | 0.4457 | 71 (50) |
| Lipoaffinity, mean | 8.54 | 0.0003 | 4.68 | 0.6014 | 8.6 | 0.0006 | 5.28 |
| BDDCS | 0.0090 | 0.5158 | 0.0048 | ||||
| Class 1 (↑solub/↑hep met) | 12 (60) | 4 (57) | 14 (64) | 39 (28) | |||
| Class 2 (↓solub/↑hep met) | 8 (40) | 8 (29) | 8 (36) | 60 (43) | |||
| Class 3 (↑solub/↓hep met) | - | 2 (14) | - | 25 (18) | |||
| Class 4 (↓solub/↓ hep met) | 16 (11) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moya-García, A.A.; González-Jiménez, A.; Moreno, F.; Stephens, C.; Lucena, M.I.; Ranea, J.A.G. Identification of New Toxicity Mechanisms in Drug-Induced Liver Injury through Systems Pharmacology. Genes 2022, 13, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071292
Moya-García AA, González-Jiménez A, Moreno F, Stephens C, Lucena MI, Ranea JAG. Identification of New Toxicity Mechanisms in Drug-Induced Liver Injury through Systems Pharmacology. Genes. 2022; 13(7):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071292
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoya-García, Aurelio A., Andrés González-Jiménez, Fernando Moreno, Camilla Stephens, María Isabel Lucena, and Juan A. G. Ranea. 2022. "Identification of New Toxicity Mechanisms in Drug-Induced Liver Injury through Systems Pharmacology" Genes 13, no. 7: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071292
APA StyleMoya-García, A. A., González-Jiménez, A., Moreno, F., Stephens, C., Lucena, M. I., & Ranea, J. A. G. (2022). Identification of New Toxicity Mechanisms in Drug-Induced Liver Injury through Systems Pharmacology. Genes, 13(7), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13071292







