Genomic Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from 2011 to 2020 Based on Data from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Analysis of Virulence Genes, Resistance Genes, and Plasmids
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
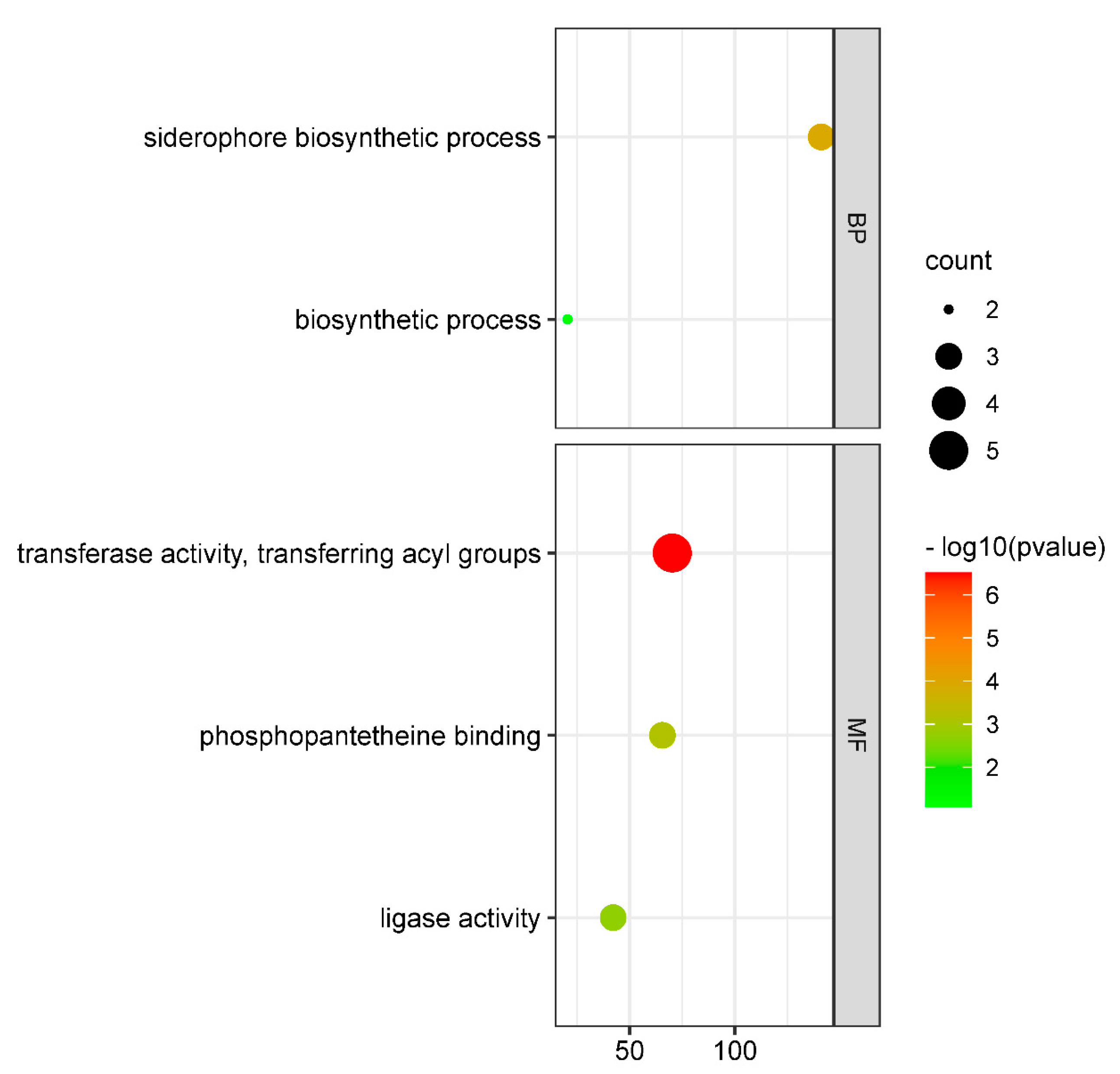
2.4. Differential Gene Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
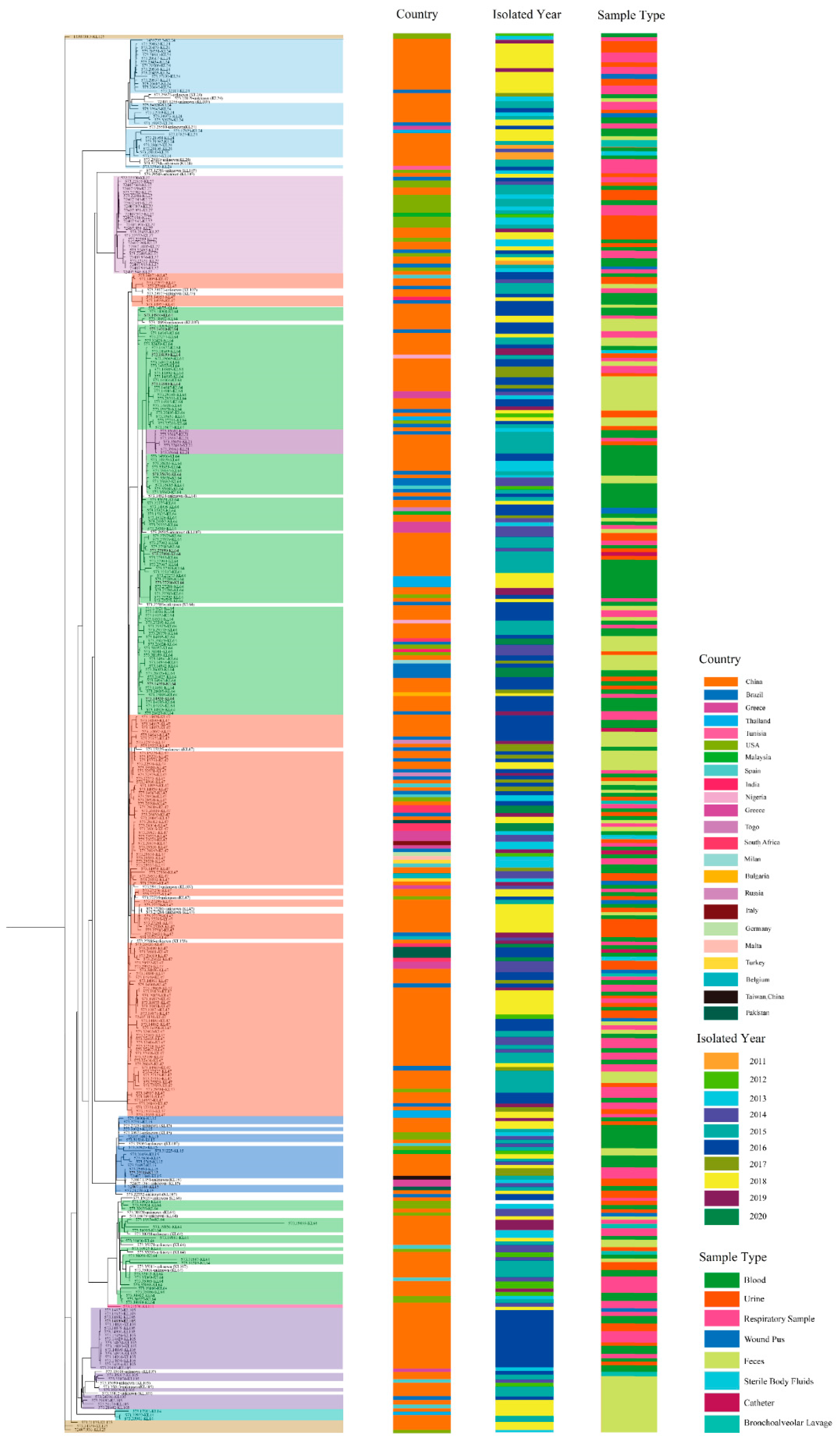
3.1. Clinical and Molecular Characterizations of ST11 CRKP
3.2. Presence of Carbapenem Resistance and Virulence Genes in KL47 and KL64
3.3. Comparison of the Virulence Genes Distribution between KL47 and KL64
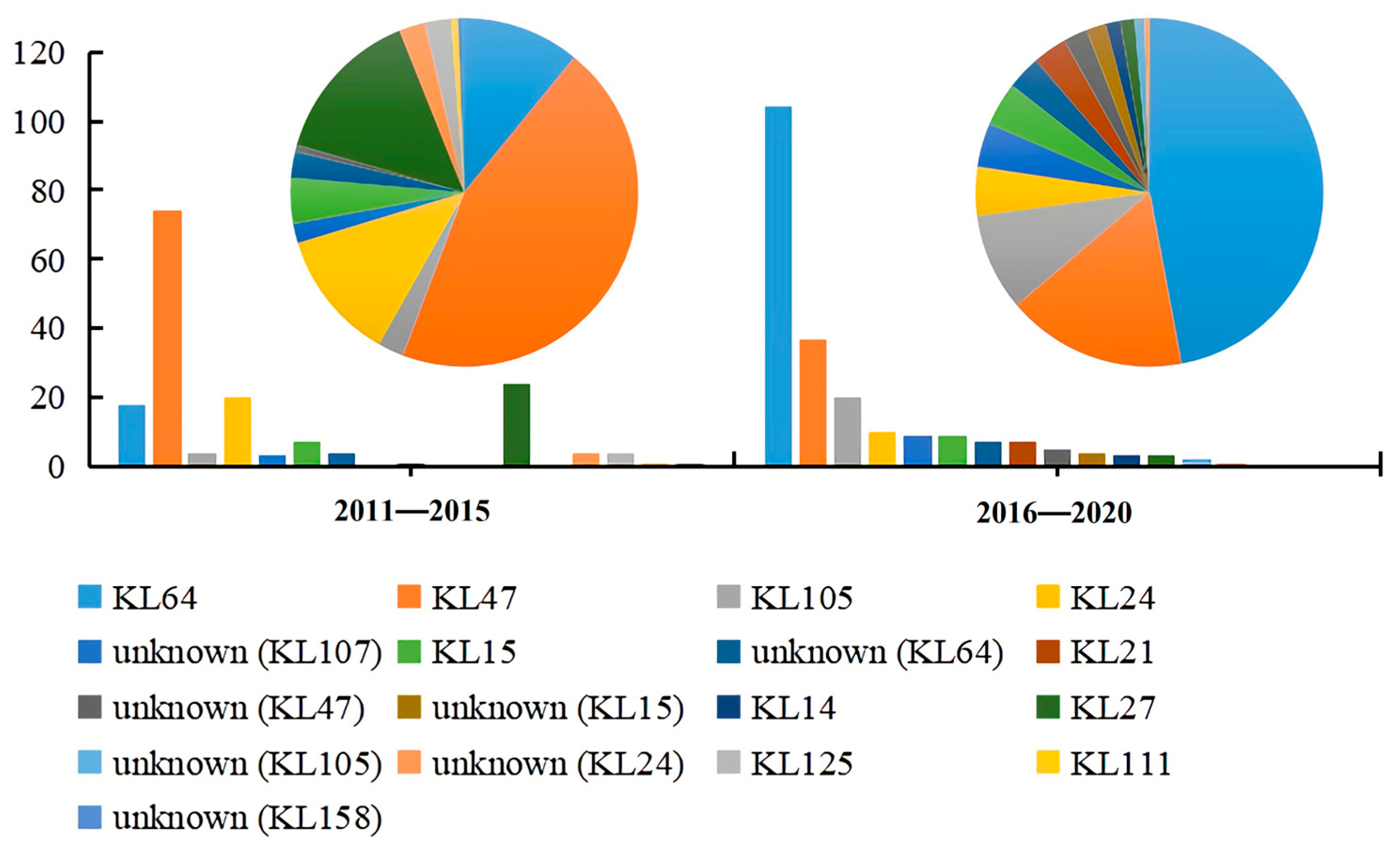
3.4. Serotype Evolutionary Characterization of ST11 CRKP
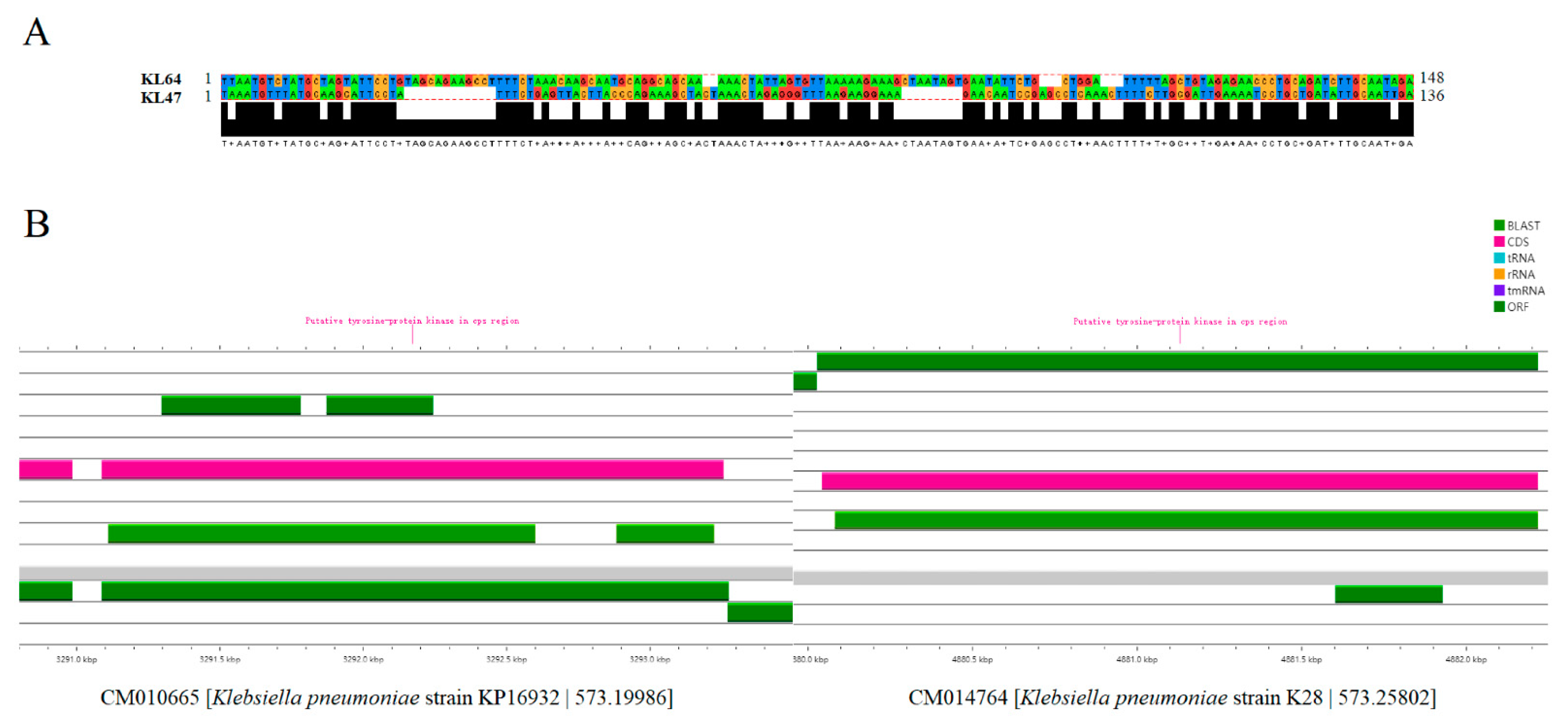
3.5. The Potential Mechanisms for the Evolution of ST11 CRKP from KL47 to KL64
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, Y.; He, F. Rapid Emergence of a Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Isolate in an Inpatient in a Teaching Hospital in China After Treatment with Multiple Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Torres, V.V.L.; Liu, H.; Rocker, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Bi, W.; Lin, J.; et al. An Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in an Intensive Care Unit of a Major Teaching Hospital in Wenzhou, China. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormicanm, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, A.A.; Bergen, P.J.; Rao, G.G.; Nation, R.L.; Landersdorfer, C.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment outcomes following antibiotic therapy among patients with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Lin, D.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S. Genome analysis of clinical multilocus sequence Type 11 Klebsiella pneumoniae from China. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsu, C.R.; Hsieh, P.F.; Wu, M.C.; Wang, J.T. Capsular types of Klebsiella pneumoniae revisited by wzc sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zou, X.; Lu, B.; Cao, B. Genomic characteristics of clinically important ST11 Klebsiella pneumoniae strains worldwide. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, L.; Ye, K.; Ma, Y.; Shen, D.; Yang, J. Genomic Analysis of KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Isolates at the Respiratory Department of a Tertiary Care Hospital in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Xiao, T.; David, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, L.; Aanensen, D.; Holt, K.E.; Thomson, N.R.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Novel Subclone of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 11 with Enhanced Virulence and Transmissibility, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, J.J.; Wattam, A.R.; Cammer, S.A.; Gabbard, J.L.; Shukla, M.P.; Dalay, O.; Driscoll, T.; Hix, D.; Mane, S.P.; Mao, C.; et al. PATRIC: The comprehensive bacterial bioinformatics resource with a focus on human pathogenic species. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4286–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis–10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didelot, X.; Wilson, D.J.; ClonalFrame, M.L. Efficient inference of recombination in whole bacterial genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procter, J.B.; Carstairs, G.M.; Soares, B.; Mourão, K.; Ofoegbu, T.C.; Barton, D.; Lui, L.; Menard, A.; Sherstnev, N.; Roldan-Martinez, D.; et al. Correction to: Alignment of Biological Sequences with Jalview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2231, C1. [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W181–W184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shi, Q.; Hu, D.; Fang, L.; Mao, Y.; Lan, P.; Han, X.; Zhang, P.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. The Emergence of Novel Sequence Type Strains Reveals an Evolutionary Process of Intraspecies Clone Shifting in ICU-Spreading Car-bapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 691406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Bi, R.; Cao, X.; Qian, H.; Hu, R.; Ma, P. Clonal dissemination of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and ST48 clone among multiple departments in a tertiary teaching hospital in Jiangsu Province, China. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Sun, C. Epidemiological Study of Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Open Med. 2018, 13, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Guo, M.K.; Ke, S.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Li, C.R.; Vy Nguyen, H.T.; Wu, L.T. Emergence and nosocomial spread of ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae co-producing OXA-48 and KPC-2 in a regional hospital in Taiwan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Simner, P.; Tamma, P.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L. Emergence and establishment of KPC-2-producing ST11 Klebsiella pneumoniae in a general hospital in Shanghai, China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Zou, C.; Qin, J.; Tao, J.; Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Du, H.; Shen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Emergence of Hypervirulent ST11-K64 Klebsiella pneumoniae Poses a Serious Clinical Threat in Older Patients. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 765624. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, P.; Jiang, B.; Peng, N.; Wang, J.; Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tan, C.; et al. Characteristics of ST11 KPC-2-producing carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae causing nosocomial infection in a Chinese hospital. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24476. [Google Scholar]


| Variables | Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| KL47 | KL64 | ||
| n = 111 | n = 122 | ||
| Number of Cabarpenemase genes | 15 (14, 18) | 15 (14, 18) | 0.380 |
| Number of plasmids | 4 (3, 4) | 3 (3, 4) | 0.003 |
| Number of virulence genes | 63 (63, 69) | 78 (72, 79.25) | <0.001 |
| Virulence Genes | Group | χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL47 | KL64 | |||
| n = 111 | n = 122 | |||
| acrA | 105 | 122 | 4.786 | 0.029 |
| clbA | 1 | 19 | 15.946 | <0.001 |
| clbB/clbC/clbD/clbE/clbF/clbG/clbH | 1 | 20 | 17.011 | <0.001 |
| clbI/clbN/clbO | 1 | 19 | 15.946 | <0.001 |
| clbL/clbM/clbP/clbQ/clbS | 1 | 20 | 17.011 | <0.001 |
| entF | 111 | 113 | 6.647 | 0.010 |
| glf | 3 | 117 | 202.116 | <0.001 |
| gnd | 3 | 122 | 221.262 | <0.001 |
| iucA | 32 | 60 | 10.075 | 0.002 |
| iucB | 34 | 62 | 9.779 | 0.002 |
| iucC/iucD/iutA | 34 | 61 | 9.030 | 0.003 |
| mrkI | 101 | 121 | 8.665 | 0.003 |
| rmpA | 1 | 45 | 47.497 | <0.001 |
| rmpA2 | 30 | 59 | 11.205 | 0.001 |
| senB | 0 | 8 | 5.689 | 0.017 |
| vipA/tssB | 106 | 73 | 41.509 | <0.001 |
| wbbM | 0 | 114 | 203.085 | <0.001 |
| wbbN | 0 | 117 | 213.819 | <0.001 |
| wbbO | 0 | 110 | 189.586 | <0.001 |
| wzm | 0 | 118 | 217.522 | <0.001 |
| wzt | 0 | 117 | 213.819 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jin, M.; Chen, J.; Qin, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Genomic Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from 2011 to 2020 Based on Data from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center. Genes 2022, 13, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091624
Zhang N, Tang Y, Yang X, Jin M, Chen J, Qin S, Liu F, Liu X, Guo J, Wang C, et al. Genomic Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from 2011 to 2020 Based on Data from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091624
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Na, Yue Tang, Xiaojing Yang, Meiling Jin, Jiali Chen, Shiyu Qin, Fangni Liu, Xiong Liu, Jinpeng Guo, Changjun Wang, and et al. 2022. "Genomic Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from 2011 to 2020 Based on Data from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center" Genes 13, no. 9: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091624
APA StyleZhang, N., Tang, Y., Yang, X., Jin, M., Chen, J., Qin, S., Liu, F., Liu, X., Guo, J., Wang, C., & Chen, Y. (2022). Genomic Evolution of ST11 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from 2011 to 2020 Based on Data from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center. Genes, 13(9), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091624





