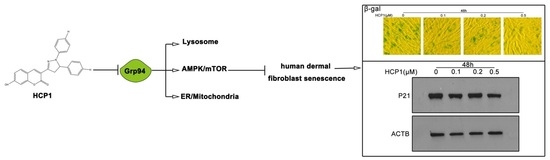
Grp94 Inhibitor HCP1 Inhibits Human Dermal Fibroblast Senescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Morphology
2.3. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase Assay
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Immunoprecipitation (IP)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Lysosomal pH Sensing Experiment
2.9. The Staining of Ca2+ in Mitochondria
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. HCP1 Inhibits the Senescence of HDFs
3.2. HCP1 Regulated Cell Cycle in Senescent HDFs
3.3. HCP1 Improved the Protein Level of Type I Collagen and Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF)
3.4. HCP1 Failed to Function in Nucleus during the Suppression of HDFs Senescence
3.5. HCP1 Regulated the AMPK/mTOR Signal Pathway
3.6. HCP1 Protected and Enhanced the Activity of Lysosome via Protecting the V0 Proton Channel of v-ATPase
3.7. HCP1 Reduced the Concentration of Ca2+ in Mitochondria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niedernhofer, L.J.; Kirkland, J.L.; Ladiges, W. Molecular pathology endpoints useful for aging studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcinotto, A.; Kohli, J.; Zagato, E.; Pellegrini, L.; Demaria, M.; Alimonti, A. Cellular Senescence: Aging, Cancer, and Injury. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1047–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Micco, R.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Baker, D.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence in ageing: From mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, E.; Steinbauer, J.; Landthaler, M.; Szeimies, R.M. Skin ageing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2011, 25, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. A role for estrogen in skin ageing and dermal biomechanics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 197, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.Y.; Dreesen, O. Faces of cellular senescence in skin aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 198, 111525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasymchuk, M.; Cherkasova, V.; Kovalchuk, O.; Kovalchuk, I. The Role of microRNAs in Organismal and Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y. Biomarkers, oxidative stress and autophagy in skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 59, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csekes, E.; Rackova, L. Skin Aging, Cellular Senescence and Natural Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, J.L.; Tchkonia, T. Cellular Senescence: A Translational Perspective. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHugh, D.; Gil, J. Senescence and aging: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, J.; Su, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J.; Lin, Z. Low-concentration HCP1 inhibits apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, W.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J. An Inhibitor of Grp94 Inhibits OxLDL-Induced Autophagy and Apoptosis in VECs and Stabilized Atherosclerotic Plaques. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 757591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Q.; Kumar, A.V.; Mills, J.; Lapierre, L.R. Autophagy in aging and longevity. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Zimmermann, A.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Essential role for autophagy in life span extension. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y.; Han, J.A.; Im, J.S.; Morrone, A.; Johung, K.; Goodwin, E.C.; Kleijer, W.J.; DiMaio, D.; Hwang, E.S. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase is lysosomal β-galactosidase. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Fielder, E.; Passos, J.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and cell senescence: Deciphering a complex relationship. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Scott, L., Jr.; Washenik, K.; Stenn, K. Full-thickness skin with mature hair follicles generated from tissue culture expanded human cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, M. Cellular aging beyond cellular senescence: Markers of senescence prior to cell cycle arrest in vitro and in vivo. Aging cell 2021, 20, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y. Deacetylation of MRTF-A by SIRT1 defies senescence induced down-regulation of collagen type I in fibroblast cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpet, A.; Stucki, M. Chromatin maintenance and dynamics in senescence: A spotlight on SAHF formation and the epigenome of senescent cells. Chromosoma 2014, 123, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Kong, W.; Yan, F.; Han, F.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Y. Effect of Jiajian Guishen Formula on the senescence-associated heterochromatic foci in mouse ovaria after induction of premature ovarian aging by the endocrine-disrupting agent 4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.L.; Liu, K.Y.; Chen, H.; Mao, Z.B. PIM-1 modulates cellular senescence and links IL-6 signaling to heterochromatin formation. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ning, J.Y.; Dai, X.; Gao, Y.D.; Su, L.; Zhao, B.X.; Miao, J.Y. Discovery of novel HSP90 inhibitors that induced apoptosis and impaired autophagic flux in A549 lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colacurcio, D.J.; Nixon, R.A. Disorders of lysosomal acidification-The emerging role of v-ATPase in aging and neurodegenerative disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.M.; Zoncu, R. The Lysosome as a Regulatory Hub. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Qu, G.; Su, L.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J. A pH probe inhibits senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletto, D.; Dersh, D.; Argon, Y. GRP94 in ER quality control and stress responses. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiel, C.; Lallet-Daher, H.; Gitenay, D.; Gras, B.; Le Calve, B.; Augert, A.; Ferrand, M.; Prevarskaya, N.; Simonnet, H.; Vindrieux, D.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum calcium release through ITPR2 channels leads to mitochondrial calcium accumulation and senescence. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckhart, L.; Zeeuwen, P. The skin barrier: Epidermis vs. environment. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognoni, E.; Watt, F.M. Skin Cell Heterogeneity in Development, Wound Healing, and Cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.I.; Choi, S.; Roh, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.G. Cellular Senescence and Inflammaging in the Skin Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydont, V.; Bernard, B.A.; Fortunel, N.O. Age-related evolutions of the dermis: Clinical signs, fibroblast and extracellular matrix dynamics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 177, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tower, J. Effects of light on aging and longevity. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 53, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.F.; Cervantes, E.L.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; Mojica, L. Food-derived bioactive compounds with anti-aging potential for nutricosmetic and cosmeceutical products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3740–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.A.D.; Oliveira de Souza, R.; Ghislain Rogez, H.L.; Masaki, H.; Fonseca, M.J.V. Cecropia obtusa extract and chlorogenic acid exhibit anti aging effect in human fibroblasts and keratinocytes cells exposed to UV radiation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fryatt, G.L.; Ghorbani, M.; Obst, J.; Menassa, D.A.; Martin-Estebane, M.; Muntslag, T.A.O.; Olmos-Alonso, A.; Guerrero-Carrasco, M.; Thomas, D.; et al. Replicative senescence dictates the emergence of disease-associated microglia and contributes to Abeta pathology. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despres, J.; Ramdani, Y.; di Giovanni, M.; Benard, M.; Zahid, A.; Montero-Hadjadje, M.; Yvergnaux, F.; Saguet, T.; Driouich, A.; Follet-Gueye, M.L. Replicative senescence of human dermal fibroblasts affects structural and functional aspects of the Golgi apparatus. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Martinez, L.; Ozturk, M.; Butter, F.; Luke, B. Npl3 stabilizes R-loops at telomeres to prevent accelerated replicative senescence. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, R.; Wang, E. Replicative senescence revisited. J. Gerontology. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, B257–B269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Kamal, N.S.; Safuan, S.; Shamsuddin, S.; Foroozandeh, P. Aging of the cells: Insight into cellular senescence and detection Methods. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraldi, F.; Annovi, G.; Tiozzo, R.; Sommer, P.; Quaglino, D. Comparison of ex vivo and in vitro human fibroblast ageing models. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2010, 131, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, K.S.; Chan, C.C.; Chiu, H.Y.; Tsai, R.Y.; Chan, J.Y.; Lin, S.J. Stress-induced premature senescence of dermal papilla cells compromises hair follicle epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Jung, T.; Grune, T.; Hohn, A. SIPS as a model to study age-related changes in proteolysis and aggregate formation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 170, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasymchuk, M.; Robinson, G.I.; Kovalchuk, O.; Kovalchuk, I. Modeling of the Senescence-Associated Phenotype in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertschmann, J.; Thalappilly, S.; Riabowol, K. The ING1a model of rapid cell senescence. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 177, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasymchuk, M.; Robinson, G.I.; Kovalchuk, O.; Kovalchuk, I. The Effects of Nutrient Signaling Regulators in Combination with Phytocannabinoids on the Senescence-Associated Phenotype in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Munk, R.; Kim, K.M.; Piao, Y.; De, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Transcriptome signature of cellular senescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 7294–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, B.; Dunlop, E.A. The lysosome: A crucial hub for AMPK and mTORC1 signalling. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, B.; Platt, F.M. Bridging the age spectrum of neurodegenerative storage diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Marino, G.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy and aging. Cell 2011, 146, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindell, J.A. Lysosomal acidification mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012, 74, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Hao, X.; Wen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J. Grp94 Inhibitor HCP1 Inhibits Human Dermal Fibroblast Senescence. Genes 2022, 13, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091651
Cui X, Hao X, Wen J, Zhang S, Zhao B, Miao J. Grp94 Inhibitor HCP1 Inhibits Human Dermal Fibroblast Senescence. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091651
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xiaoling, Xuxiao Hao, Jie Wen, Shangli Zhang, Baoxiang Zhao, and Junying Miao. 2022. "Grp94 Inhibitor HCP1 Inhibits Human Dermal Fibroblast Senescence" Genes 13, no. 9: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091651
APA StyleCui, X., Hao, X., Wen, J., Zhang, S., Zhao, B., & Miao, J. (2022). Grp94 Inhibitor HCP1 Inhibits Human Dermal Fibroblast Senescence. Genes, 13(9), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091651