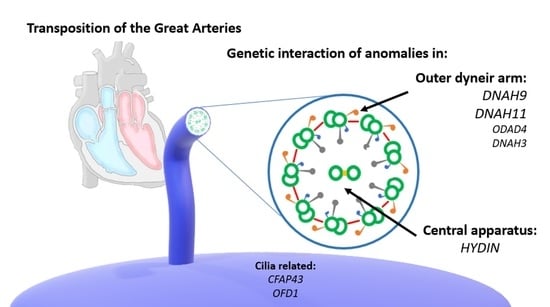
Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing DNA Extraction
2.3. Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.4. Variant Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Analysis Related to Syndromic Entities
3.2. NGD and Previously TGA-Related Genes
3.3. Motile and Non-Motile Genes, Ciliogenesis, and Cilia Trafficking Gene Analysis
3.4. Interaction and Clustering Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unolt, M.; Putotto, C.; Silvestri, L.M.; Marino, D.; Scarabotti, A.; Massaccesi, V.; Caiaro, A.; Versacci, P.; Marino, B. Transposition of great arteries: New insights into the pathogenesis. Front. Pediatr. 2013, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versacci, P.; Pugnaloni, F.; Digilio, M.C.; Putotto, C.; Unolt, M.; Calcagni, G.; Baban, A.; Marino, B. Some Isolated Cardiac Malformations Can Be Related to Laterality Defects. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ita, M.; Cisneros, B.; Rosas-Vargas, H. Genetics of Transposition of Great Arteries: Between Laterality Abnormality and Outflow Tract Defect. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Amack, J.D. Cilia in vertebrate left-right patterning. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottereau, E.; Mortemousque, I.; Moizard, M.-P.; Bürglen, L.; Lacombe, D.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Sigaudy, S.; Boute, O.; David, A.; Faivre, L.; et al. Phenotypic Spectrum of Simpson-Golabi-Behmel Syndrome in a Series of 42 Cases with a Mutation in GPC 3 and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2013, 163, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-P.; Su, Y.-N.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chern, S.-R.; Tsai, F.-J.; Wu, P.-C.; Chen, P.-T.; Wang, W. Ellis-van Creveld syndrome: Prenatal diagnosis, molecular analysis and genetic counseling. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 49, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chern, S.-R.; Su, J.-W.; Wang, W. First-trimester prenatal diagnosis of Ellis-van Creveld syndrome. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 51, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Priest, J.R.; Fu, Y.; Pang, K.-J.; Ma, B.; Han, B.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.; et al. Exome-Based Case-Control Analysis Highlights the Pathogenic Role of Ciliary Genes in Transposition of the Great Arteries. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.S.; Chaturvedi, R.R.; Jobling, R.K.; Pellecchia, G.; Hamdan, O.; Sung, W.W.; Nalpathamkalam, T.; Attaluri, P.; Silversides, C.K.; Wald, R.M.; et al. Clinical Genetic Risk Variants Inform a Functional Protein Interaction Network for Tetralogy of Fallot. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, e003410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; Zhou, M.M. The PHD finger: A versatile epigenome reader. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, J.F.; Leroux, M.R. Genes and molecular pathways underpinning ciliopathies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patir, A.; Fraser, A.M.; Barnett, M.W.; McTeir, L.; Rainger, J.; Davey, M.G.; Freeman, T.C. The transcriptional signature associated with human motile cilia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusapati, G.; Hughes, C.E.; Dorn, K.V.; Zhang, D.; Sugianto, P.; Aravind, L.; Rohatgi, R. EFCAB7 and IQCE Regulate Hedgehog Signaling by Tethering the EVC-EVC2 Complex to the Base of Primary Cilia. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, J.M.; Conduit, S.E.; Feeney, S.J.; Hakim, S.; DiTommaso, T.; Fulcher, A.J.; Sriratana, A.; Ramm, G.; Horan, K.A.; Gurung, R.; et al. INPP5E regulates phosphoinositide-dependent cilia transition zone function. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 216, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoak, I.W.; Byrd, N.A.; Abu-Issa, R.; Goddeeris, M.M.; Anderson, R.; Morris, J.; Yamamura, K.; Klingensmith, J.; Meyers, E.N. Sonic hedgehog is required for cardiac outflow tract and neural crest cell development. Dev. Biol. 2005, 283, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, C.; Ismail, T.; Kim, Y.-K.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, O.-S.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, D.-S.; Park, T.-J.; et al. IFT46 plays crucial roles in craniofacial and cilia development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Shi, X.; Shen, Y. Intraflagellar transport 46 (IFT46) is essential for trafficking IFT proteins between cilia and cytoplasm in Paramecium. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Hwang, K.-S.; Oh, H.-W.; Ji-Ae, K.; Kim, H.-T.; Cho, H.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Ko, J.Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.-M.; et al. IFT46 plays an essential role in cilia development. Dev. Biol. 2015, 400, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanska, P.; Joachimiak, E.; Bazan, R.; Fu, G.; Poprzeczko, M.; Fabczak, H.; Nicastro, D.; Wloga, D. Ciliary proteins Fap43 and Fap44 interact with each other and are essential for proper cilia and flagella beating. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4479–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubo, T.; Hou, Y.; Cochran, D.A.; Witman, G.B.; Oda, T. A microtubule-dynein tethering complex regulates the axonemal inner dynein f (I1). Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Kinoshita, A.; Satoh, C.; Mishima, H.; Yamaguchi, N.; Matsuda, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Komohara, Y.; et al. Nonsense mutation in CFAP43 causes normal-pressure hydrocephalus with ciliary abnormalities. Neurology 2019, 92, e2364–e2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, W.; Pettersson, M.; Kurtoglu, D.; Armenio, M.; Eisfeldt, J.; Papadogiannakis, N.; Gustavsson, P.; Lindstrand, A. Targeted copy number screening highlights an intragenic deletion of WDR63 as the likely cause of human occipital encephalocele and abnormal CNS development in zebrafish. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Biallelic Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 Cause Male Infertility with Multiple Morphological Abnormalities of the Sperm Flagella. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.-H.; Khan, I.; Shah, B.; Dil, S.; Ullah, N.; Zhou, J.-T.; Zhao, D.-R.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Jiang, X.-H.; et al. Novel biallelic loss-of-function mutations in CFAP43 cause multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagellum in Pakistani families. Asian J. Androl. 2021, 23, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhu, J.; Cai, K.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X. Biallelic DNAH9 mutations are identified in Chinese patients with defective left–right patterning and cilia-related complex congenital heart disease. Qual. Life Res. 2022, 141, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loges, N.T.; Antony, D.; Maver, A.; Deardorff, M.A.; Güleç, E.Y.; Gezdirici, A.; Nöthe-Menchen, T.; Höben, I.M.; Jelten, L.; Frank, D.; et al. Recessive DNAH9 Loss-of-Function Mutations Cause Laterality Defects and Subtle Respiratory Ciliary-Beating Defects. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamoto, N.; Narita, K.; Kubo, T.; Oda, T.; Takeda, S. CFAP70 Is a Novel Axoneme-Binding Protein That Localizes at the Base of the Outer Dynein Arm and Regulates Ciliary Motility. Cells 2018, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachev, E.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Fuhl, F.; Ott, T.; Tveriakhina, L.; Beckers, A.; Hegermann, J.; Boldt, K.; Mai, M.; Kremmer, E.; et al. CFAP43 modulates ciliary beating in mouse and Xenopus. Dev. Biol. 2019, 459, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, G.W.; Loges, N.T.; Klinkenbusch, J.A.; Olbrich, H.; Pennekamp, P.; Menchen, T.; Raidt, J.; Wallmeier, J.; Werner, C.; Westermann, C.; et al. DNAH11 Localization in the Proximal Region of Respiratory Cilia Defines Distinct Outer Dynein Arm Complexes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, R.; Yang, W.; Wen, Y.; Xie, L.; Shi, F.; Lu, D.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; et al. Dnah9 mutant mice and organoid models recapitulate the clinical features of patients with PCD and provide an excellent platform for drug screening. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, L.E.; Yin, W.; Rogers, T.D.; Busalacchi, K.B.; Chua, M.; O’Neal, W.K.; Grubb, B.R. Conditional Deletion of Dnaic1 in a Murine Model of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Causes Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechtreck, K.F.; Delmotte, P.; Robinson, M.L.; Sanderson, M.J.; Witman, G.B. Mutations in Hydin impair ciliary motility in mice. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.I.; Zullo, A.; Barra, A.; Bimonte, S.; Messaddeq, N.; Studer, M.; Dollé, P.; Franco, B. Oral-facial-digital type I protein is required for primary cilia formation and left-right axis specification. Nat. Genet. 2005, 38, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, K.; Rhee, K. CEP90 is required for the assembly and centrosomal accumulation of centriolar satellites, which is essential for primary cilia formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teves, M.E.; Zhang, Z.; Costanzo, R.M.; Henderson, S.C.; Corwin, F.D.; Zweit, J.; Sundaresan, G.; Subler, M.; Salloum, F.N.; Rubin, B.K.; et al. Sperm-Associated Antigen–17 Gene Is Essential for Motile Cilia Function and Neonatal Survival. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbari, N.F.; Kin, N.W.; Sharma, N.; Michaud, E.J.; Kesterson, R.A.; Yoder, B.K. Mutations in Traf3ip1 reveal defects in ciliogenesis, embryonic development, and altered cell size regulation. Dev. Biol. 2011, 360, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muncke, N.; Jung, C.; Rüdiger, H.; Ulmer, H.; Roeth, R.; Hubert, A.; Goldmuntz, E.; Driscoll, D.; Goodship, J.; Schön, K.; et al. Missense Mutations and Gene Interruption in PROSIT240, a Novel TRAP240-like Gene, in Patients with Congenital Heart Defect (Transposition of the Great Arteries). Circulation 2003, 108, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Luo, M.; Ma, S.; Lu, C.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Cai, R.; Chen, C.; et al. Identification of two novel pathogenic variants of PIBF1 by whole exome sequencing in a 2-year-old boy with Joubert syndrome. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Lin, H.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.-X.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, J. Analysis of mutations in 7 candidate genes for dextro-Transposition of the great arteries in Chinese population. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digilio, M.C.; Casey, B.; Toscano, A.; Calabrò, R.; Pacileo, G.; Marasini, M.; Banaudi, E.; Giannotti, A.; Dallapiccola, B.; Marino, B. Complete transposition of the great arteries: Patterns of congenital heart disease in familial precurrence. Circulation 2001, 104, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, W.S.; Hernandez, E.J.; Wesolowski, S.; Bisgrove, B.W.; Sunderland, R.T.; Lin, E.; Lemmon, G.; Demarest, B.L.; Miller, T.A.; Bernstein, D.; et al. De novo and recessive forms of congenital heart disease have distinct genetic and phenotypic landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Garrod, A.S.; Madan-Khetarpal, S.; Sreedher, G.; McGuire, M.; Yagi, H.; Klena, N.T.; Gabriel, G.C.; Khalifa, O.; Zahid, M.; et al. Respiratory motile cilia dysfunction in a patient with cranioectodermal dysplasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2015, 167, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, F.F.; Shbaro, R.; Mroueh, S.; Yunis, K.; Obeid, M. Dextrocardia and corrected transposition of the great arteries (I,D,D) in a case of Kartagener’s syndrome: A unique association. Clin. Cardiol. 1998, 21, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Zhan, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Ma, D.; Sheng, W.; Huang, G. DNAH11 variants and its association with congenital heart disease and heterotaxy syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassad, M.R.; Shoemark, A.; Legendre, M.; Hirst, R.A.; Koll, F.; le Borgne, P.; Louis, B.; Daudvohra, F.; Patel, M.P.; Thomas, L.; et al. Mutations in Outer Dynein Arm Heavy Chain DNAH9 Cause Motile Cilia Defects and Situs Inversus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmeier, J.; Shiratori, H.; Dougherty, G.W.; Edelbusch, C.; Hjeij, R.; Loges, N.T.; Menchen, T.; Olbrich, H.; Pennekamp, P.; Raidt, J.; et al. TTC25 Deficiency Results in Defects of the Outer Dynein Arm Docking Machinery and Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia with Left-Right Body Asymmetry Randomization. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukic, I.; Rivera-Molina, F.; Toomre, D. The IN/OUT assay: A new tool to study ciliogenesis. Cilia 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, B.A.; Navarro, F.M.; Winey, M. Motile Cilia: Innovation and Insight from Ciliate Model Organisms. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.Y.; Jekely, G. On the unity and diversity of cilia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutton, C.; Vargas, A.S.; Amiri-Yekta, A.; Kherraf, Z.-E.; Ben Mustapha, S.F.; Le Tanno, P.; Wambergue-Legrand, C.; Karaouzène, T.; Martinez, G.; Crouzy, S.; et al. Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 cause male infertility and flagellum defects in Trypanosoma and human. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louka, P.; Vasudevan, K.K.; Guha, M.; Joachimiak, E.; Wloga, D.; Tomasi, R.F.-X.; Baroud, C.N.; Dupuis-Williams, P.; Galati, D.F.; Pearson, C.G.; et al. Proteins that control the geometry of microtubules at the ends of cilia. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4298–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanian, H.; Cho, Y.K.; Rizer, N.W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Degenhardt, K.; Jain, R. Pdgfralpha functions in endothelial-derived cells to regulate neural crest cells and the development of the great arteries. Dis. Model Mech. 2017, 10, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, C.; Lier, J.M.; Kuschel, S.; Ruther, U. The ciliary protein Ftm is required for ventricular wall and septal development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, M.; Bais, A.; Tian, X.; Devine, W.; Lee, D.M.; Yau, C.; Sonnenberg, D.; Beerman, L.; Khalifa, O.; Lo, C.W. Airway ciliary dysfunction and respiratory symptoms in patients with transposition of the great arteries. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blue, G.M.; Mekel, M.; Das, D.; Troup, M.; Rath, E.; Ip, E.; Gudkov, M.; Perumal, G.; Harvey, R.P.; Sholler, G.F.; et al. Whole genome sequencing in transposition of the great arteries and associations with clinically relevant heart, brain and laterality genes. Am. Heart J. 2022, 244, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortigue, M.; Nield, L.E.; Karakachoff, M.; McLeod, C.J.; Belli, E.; Babu-Narayan, S.V.; Prigent, S.; Boet, A.; Conway, M.; Elder, R.W.; et al. Familial Recurrence Patterns in Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries: An International Study. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2022, 15, e003464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteche-López, A.; Ávila-Fernández, A.; Romero, R.; Riveiro-Álvarez, R.; López-Martínez, M.A.; Giménez-Pardo, A.; Vélez-Monsalve, C.; Gallego-Merlo, J.; García-Vara, I.; Almoguera, B.; et al. Sanger sequencing is no longer always necessary based on a single-center validation of 1109 NGS variants in 825 clinical exomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Lu, H.M.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Elliott, A.M. Sanger Confirmation Is Required to Achieve Optimal Sensitivity and Specificity in Next-Generation Sequencing Panel Testing. J. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 18, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudhuin, L.M.; Lagerstedt, S.A.; Klee, E.W.; Fadra, N.; Oglesbee, D.; Ferber, M.J. Confirming Variants in Next-Generation Sequencing Panel Testing by Sanger Sequencing. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patients | Gene | dbSNP | NT Change | CQ | AA Change | SIFT | PP2. HumDiv | PP2. HumVar | Mutation Assessor | Allele Freq | Mend | OMIM | Del |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T180101 | KDM6A | rs780238270 | c.232C>T | M | p.R78C | T (0.15) | B (0.05) | B (0.009) | L (1.31) | 3.95 × 10−4 * | HEMY | XLD | No |
| FOXH1 | rs899189505 | c.187G>A | M | p.V63I | T (0.69) | B (0.251) | B (0.083) | N (−1.435) | 5.81 × 10−5 | HE | NR | No | |
| T180201 | GDF1 | rs944730356 | c.404C>T | M | p.A135V | T (0.54) | B (0.015) | B (0.008) | N (0.6) | 0.001301 | HE | AD/AR | No |
| KMT2D | New | c.547C>T | M | p.P183S | T (0.62) | PD (0.959) | PD (0.6) | N (0.55) | New | HE | AD | Yes | |
| MEGF8 | rs769862975 | c.1315C>T | M | p.R439W | D (0) | PD (1) | PD (0.948) | M (2.27) | 6.13 × 10−4 | HE | AR | Yes | |
| T180301 | KMT2D | rs201628357 | c.15686G>A | M | p.R5229H | D(0.04) | PD (1) | PD (0.98) | N (0.255) | 2.49 × 10−5 * | HE | AD | Yes |
| T181001 | MEGF8 | rs1281253733 | c.2344C>T | M | p.R782W | D (0.085) | PD (0.962) | D (0.898) | N (0.345) | 8.11 × 10−6 | HE | AR | Yes |
| T181101 | DNAI1 | rs771320807 | c.203G>A | M | p.R68Q | D (0.0) | PD (0.998) | PD (0.917) | M (2.455) | 2.89 × 10−5 | HE | AR | Yes |
| DISC1 | rs753171376 | c.1852C>G | M | p.P618A | T (0.08) | PD (0.995) | PD (0.865) | M (2.24) | 2.83 × 10−4 * | HE | AR | Yes | |
| CCDC65 | rs200575863 | c.470+3A>G | S | Splice acceptor | 16.55 CAD PHRED (No deleterious) | 8.52 × 10−4 | HE | AR | No | ||||
| T181201 | SLC4A1 | rs2285644 | c.2561C>T | M | p.P854L | D (0.04) | PD (0.823) | B (0.140) | M (2.66) | 0.04128 | HE | Yes | Yes |
| CLASP1 | rs373752835 | c.170C>T | M | p.S57F | T (0.08) | PD (0.985) | PD (0.55) | M (2.08) | 2.89 × 10−5 | HE | No | Yes | |
| T181401 | PLB1 | rs745799206 | c.2089-2A>G | S | Splice acceptor | 33 CAD PHRED (Deleterious) | 8.674 × 10−5 | HE | NR | Yes | |||
| CLASP1 | New | c.1110T>G | M | p.D370E | T (0.92) | B (0) | B (0.001) | N (−0.175) | New | HE | No | No | |
| Patient | Gene | dbSNP | NT Change | CQ | AA Change | SIFT | PP2. HumDiv | PP2. HumVar | Mutation Assessor | Allele Freq | OMIM | Mend | Variant Associated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T180101 Male | DRC7 | rs199828087 | c.1819C>T | M | p.R607C | D (0.04) | D (0.91) | PD (0.99) | L (1.81) | 2.83 × 10−5 | NR | HE | No |
| TTC25 | rs782333806 | c.218C>T | M | p.S73L | D (0) | PD (1) | PD (0.97) | M (2.54) | 5.94 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| RSPH14 | rs780971104 | c.488A>G | M | p.E163G | D (0) | B (0.02) | B (0.02) | M (2.71) | 4.63 × 10−4 | NR | HE | No | |
| T180201 Male | NEK5 | rs35465612 | c.1420C>T | M | p.R474C | D (0) | PD (1) | PD (0.95) | M (2.44) | 9.27 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No |
| LRGUK | rs140175129 | c.2044C>T | M | p.R682C | D (0) | PD (0.96) | B (0.27) | N (0) | 3.44 × 10−2 | NR | HE | No | |
| CFAP43 | rs150378110 | c.3935G>A | M | p.R1312H | T (0.12) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.85) | M (2.59) | 1.21 × 10−3 | AD/R | HE | No | |
| DNAH11 | rs1243678738 | c.12577C>T | N | p.Q4193/Stop | 48 CAD PHRED (Deleterious) | 2.897 ×10−5 | HE | AR | No | ||||
| T180301 Male | DNAH10 | rs779897384 | c.1468C>A | M | p.P490T | D (0.01) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.97) | M (3.04) | 1.98 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No |
| DNAH3 | rs182462514 | c.608T>C | M | p.M203T | T (0.1) | PD (0.45) | B (0.07) | M (2.17) | 3.95 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No | |
| T180401 Male | HYDIN | New | c.3332C>T | M | p.P1111L | D (0) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.98) | M (2.76) | New | AR | HO | No |
| DNAH9 | rs139596704 | c.3050A>G | M | p.Y1017C | D (0) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.82) | M (2.93) | 5.30 × 10−2 | AR | HE | No | |
| DNAH9 | rs777167537 | c.5151+1G>A | S | Splice acceptor | 34 CAD PHRED (Deleterious) | 1.1 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | ||||
| T180701 Female | WDR63 | rs1056616254 | c.1742C>A | M | p.T581N | D (0) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.64) | M (2.58) | 1.19 × 10−5 * | NR | HE | No |
| CFAP43 | rs117768807 | c.589G>A | M | p.V197M | D (0) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.97) | L (1.76) | 3.05 × 10−4 | AD/R | HE | No | |
| CCDC113 | rs144246110 | c.300A>T | M | p.K100N | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.85) | 2.03 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No | |
| T180801 Male | DNAH10 | rs755673190 | c.8228C>T | M | p.P2743L | D (0.05) | B (0.005) | B (0.005) | M (2.53) | 2.83 × 10−5 | NR | HE | No |
| OFD1 | rs779051357 | c.2482T>G | M | p.F828V | T (0.07) | PD (0.90) | PD (0.59) | M (2.43) | 5.17 × 10−5 | XLD | HEMY | No | |
| T180901 Male | WDR63 | rs138379333 | c.922G>A | M | p.A308T | D (0.04) | PD (0.79) | B (0.14) | M (2.49) | 5.39 × 10−2 | NR | HE | No |
| CFAP70 | rs575812060 | c.3079T>A | M | p.C1027S | D (0.02) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.90) | M (2.43) | 2.60 × 10−3 | AR | HE | No | |
| DNAH3 | rs141197402 | c.8597A>G | M | p.H2866R | D (0) | PD (0.83) | PD (0.49) | L (1.29) | 1.87 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No | |
| DNAH9 | rs267604735 | c.7150G>A | M | p.G2384R | D (0.04) | PD (0.99) | D (0.91) | H (3.71) | 5.79 × 10−5 | AR | HE | No | |
| ARMC9 | rs386656198 | c.878C>T | M | p.T293M | T (1) | PD (1.0) | D (0.98) | M (2.33) | 5.24 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| T181001 Female | DNAH11 | rs199789835 | c.8521A>G | M | p.S2841G | D (0.02) | PD (0.95) | PD (0.79) | M (2.95) | 2.23 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No |
| OFD1 | New | c.2610G>C | M | p.Q870H | D (0.04) | PD (0.89) | PD (0.63) | M (2.12) | New | XL | HEMY | No | |
| CEP295 | rs763108226 | c.512C>T | M | p.P171L | D (0.04) | PD (0.72) | B (0.25) | NF | 5.37 × 10−3 | ND | HE | No | |
| T181101 Male | SPAG17 | rs140959339 | c.430C>T | M | p.R144W | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.70) | 2.37 × 10−2 | NR | HE | No |
| DNAI1 | rs771320807 | c.203G>A | M | p.R68Q | D (0) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.91) | M (2.45) | 2.89 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| MNS1 | rs549395315 | c.605delA | F | p.L202SfsTer | 29.2 CAD PHRED (Deleterious) | NF | AR | HE | No | ||||
| T181201 Male | SPAG17 | rs1028261558 | c.1700C>A | M | p.P567Q | D (0.01) | PD (0.97) | PD (0.84) | M (2.62) | 1.74 × 10−4 | NR | HE | No |
| DNAH9 | rs139596704 | c.3050A>G | M | p.Y1017C | D (0) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.82) | M (2.93) | 5.30 × 10−2 | AR | HE | No | |
| T181401 Male | TEKT2 | rs144497984 | c.1114C>T | M | p.R372W | D (0.01) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.86) | 2.21 × 10−2 | NR | HE | No |
| Patient | Gene | dbSNP | NT Change | CQ | AA Change | SIFT | PP2. HumDiv | PP2. HumVar | Mutation Assessor | Allele Freq | OMIM | Mend | Variant Associated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T180101 Male | PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1) | PD (0.99) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HE | Jb |
| T180201 Male | IQCE | rs200648086 | c.1688T>C | M | p.L563S | D (0) | B (0.19) | B (0.20) | M (2.31) | 5.23 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No |
| T180301 Male | TTLL6 | rs184362955 | c.517C>T | M | p.R173W | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (1.0) | H (4.64) | 8.89 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No |
| T180401 Male | CFAP100 | rs149511023 | c.589G>A | M | p.A197T | T (0.04) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.85) | M (2.71) | 6.85 × 10−3 | ND | HE | No |
| T180701 Female | CFAP77 | rs11243798 | c.551G>A | M | p.R184H | D (0.04) | PD (1) | PD (0.99) | M (2.65) | 5.03 × 10−3 | ND | HE | No |
| CFAP100 | rs754767651 | c.1292G>C | M | p.R430T | D (0) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.84) | L (1.76) | 3.76 × 10−4 | ND | HE | No | |
| T180801 Male | PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.96) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HO | Jb |
| IQCE | rs375144768 | c.784C>T | M | p.L262F | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.59) | 2.60 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| INPP5E | rs138150684 | c.1360G>A | M | p.D454N | T (0.06) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.88) | M (1.99) | 1.96 × 10−4 * | AR | HE | No | |
| OFD1 | rs779051357 | c.2482T>G | M | p.F828V | T (0.07) | PD (0.90) | PD (0.59) | M (2.43) | 5.17 × 10−5 | XLD | HEMY | No | |
| T181001 Female | OFD1 | New | c.2610G>C | M | p.Q870H | D (0.04) | PD (0.89) | PD (0.63) | M (2.12) | New | XL | HEMY | No |
| AK7 | rs746369518 | c.159_170del | F | p.(Glu53_Glu56del) | 0.514 LoF-Tool PD | 3 × 10−3 | AR | HE | No | ||||
| T181201 Male | PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HO | Jb |
| Patient | Gene | dbSNP | NT Change | CQ | AA Change | SIFT | PP2. HumDiv | PP2. HumVar | Mutation Assesor | Allele Freq | OMIM | Mend | Variant Associated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T180101 Male | SAXO2 | rs116324279 | c.1111T>C | M | p.S371P | T (0.04) | PD (0.87) | PD (0.63) | M (2.14) | 5.65 × 10−4 | ND | HE | No |
| T180201 Male | PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1) | PD (0.99) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HE | Jb |
| UBXN10 | rs11556959 | c.794A>G | M | p.H265R | D (0.01) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.82) | M (2.32) | 2.60 × 10−4 | NR | HE | No | |
| T180301 Male | TTLL6 | rs184362955 | c.517C>T | M | p.R173W | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (1.0) | H (4.64) | 8.89 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No |
| T180701 Female | TRPV4 | rs187864727 | c.649G>T | M | p.A217S | T (0.13) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.00) | 6.85 × 10−2 | AD | HE | NEDY |
| IFT46 | rs145438119 | c.454C>G | M | p.P152A | D (0.01) | PD (1.0) | PD (1.0) | M (3.25) | 3.16 × 10−3 | AR | HE | No | |
| MORN3 | rs782293129 | c.616G>C | M | p.A206P | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (1.0) | M (2.87) | 2.03 × 10−4 | ND | HE | No | |
| TRAF3IP1 | rs761035757 | c.838C>T | M | p.R280W | D (0.01) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.91) | L (1.79) | 2.56 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| T180801 Male | TRPV4 | rs187864727 | c.649G>T | M | p.A217S | T (0.13) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.00) | 6.85 × 10−2 | AD | HE | NEDY |
| PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.96) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HO | Jb | |
| OFD1 | rs779051357 | c.2482T>G | M | p.F828V | T (0.07) | PD (0.90) | PD (0.59) | M (2.43) | 5.17 × 10−5 | XLD | HEMY | No | |
| T180901 Male | MORN1 | rs34587196 | c.757C>T | M | p.R253W | D(0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.25) | 6.57 × 10−3 | NR | HE | No |
| ARMC9 | rs386656198 | c.878C>T | M | p.T293M | T (1) | PD (1.0) | D (0.98) | M (2.33) | 5.24 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No | |
| T181001 Female | NEK11 | rs140058289 | c.127G>C | M | p.V43L | D (0.01) | PD (0.93) | PD (0.52) | M (3.41) | 4.80 × 10−2 | NR | HE | No |
| OFD1 | New | c.2610G>C | M | p.Q870H | D (0.04) | PD (0.89) | PD (0.63) | M (2.12) | New | XL | HEMY | No | |
| T181201 Male | AGBL2 | rs7941404 | c.956G>A | M | p.R319H | T (0.09) | PD (0.99) | PD (0.91) | M (2.49) | 9.9 × 10−5 * | NR | HE | No |
| PIBF1 | rs17089782 | c.1214G>A | M | p.R405Q | D (0) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.56) | 0.1021 | AR | HO | Jb | |
| T181401 Male | BBS7 | rs199891330 | c.508A>G | M | p.R170G | D (0.02) | PD (1.0) | PD (0.99) | M (2.66) | 9.84 × 10−4 | AR | HE | No |
| SPATA4 | rs765034017 | c.599A>C | M | p.N200T | D (0.02) | PD (0.98) | PD (0.88) | M (2.17) | 8.67 × 10−5 | ND | HE | No |
| Cilia Gene | Region Affected | Genetic Alteration Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFAP43 | Axonemal | Lower beating frequency | [29] |
| CFAP70/TTC18 | ODA-Central pair | Reduced beating frequency | [28] |
| DNAH11 | ODA | Hyperkinetic beating | [30] |
| DNAH9 | ODA | Lower beating frequency, loss of outer dynein arm structures | [27,31] |
| DNAI1 | ODA | Fewer actively beating cilia, loss of outer dynein arm structures | [32] |
| HYDIN | Central pair | Cilia is unable to bend normally; reduced beat frequency | [33] |
| IFT46 | IFT subcomplex B | Reduced length and number of cilia | [18] |
| OFD1 | Centriole | Lack of cilia in the embryonic node | [34] |
| PIBF1 | Cilia assembly | Non-motile cilia assembly, Reduced number of cilia | [35] |
| SPAG17 | Central pair | Central pair structural abnormalities | [36] |
| TRAF3IP1/IFT154 | IFT subcomplex B | Absence of cilia, abnormal ciliogenesis | [37] |
| WDR63/DNAI3 | IDA | Disorganization of cilia | [23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Ita, M.; Gaytán-Cervantes, J.; Cisneros, B.; Araujo, M.A.; Huicochea-Montiel, J.C.; Cárdenas-Conejo, A.; Lazo-Cárdenas, C.C.; Ramírez-Portillo, C.I.; Feria-Kaiser, C.; Peregrino-Bejarano, L.; et al. Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries. Genes 2022, 13, 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091662
De Ita M, Gaytán-Cervantes J, Cisneros B, Araujo MA, Huicochea-Montiel JC, Cárdenas-Conejo A, Lazo-Cárdenas CC, Ramírez-Portillo CI, Feria-Kaiser C, Peregrino-Bejarano L, et al. Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091662
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Ita, Marlon, Javier Gaytán-Cervantes, Bulmaro Cisneros, María Antonieta Araujo, Juan Carlos Huicochea-Montiel, Alan Cárdenas-Conejo, Charles César Lazo-Cárdenas, César Iván Ramírez-Portillo, Carina Feria-Kaiser, Leoncio Peregrino-Bejarano, and et al. 2022. "Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries" Genes 13, no. 9: 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091662
APA StyleDe Ita, M., Gaytán-Cervantes, J., Cisneros, B., Araujo, M. A., Huicochea-Montiel, J. C., Cárdenas-Conejo, A., Lazo-Cárdenas, C. C., Ramírez-Portillo, C. I., Feria-Kaiser, C., Peregrino-Bejarano, L., Yáñez-Gutiérrez, L., González-Torres, C., & Rosas-Vargas, H. (2022). Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries. Genes, 13(9), 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091662