Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Strains
2.2. Mapping of the P White+ (Pw+) Reporters
2.3. Complementation Test with Df(2Rh)MS41-10
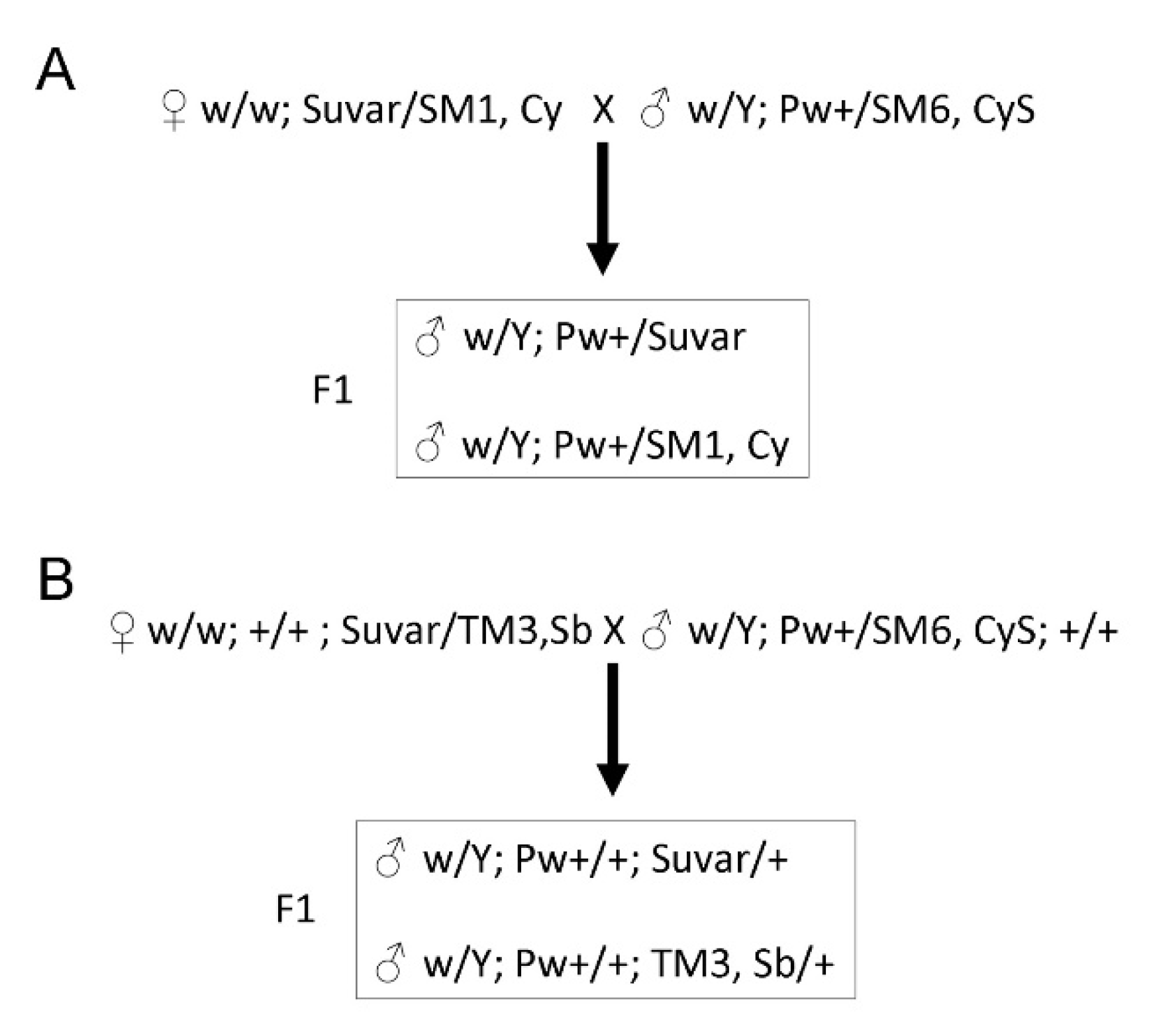
2.4. Genetic Crosses with PEV Suppressors
2.5. Eye Pigment Assays
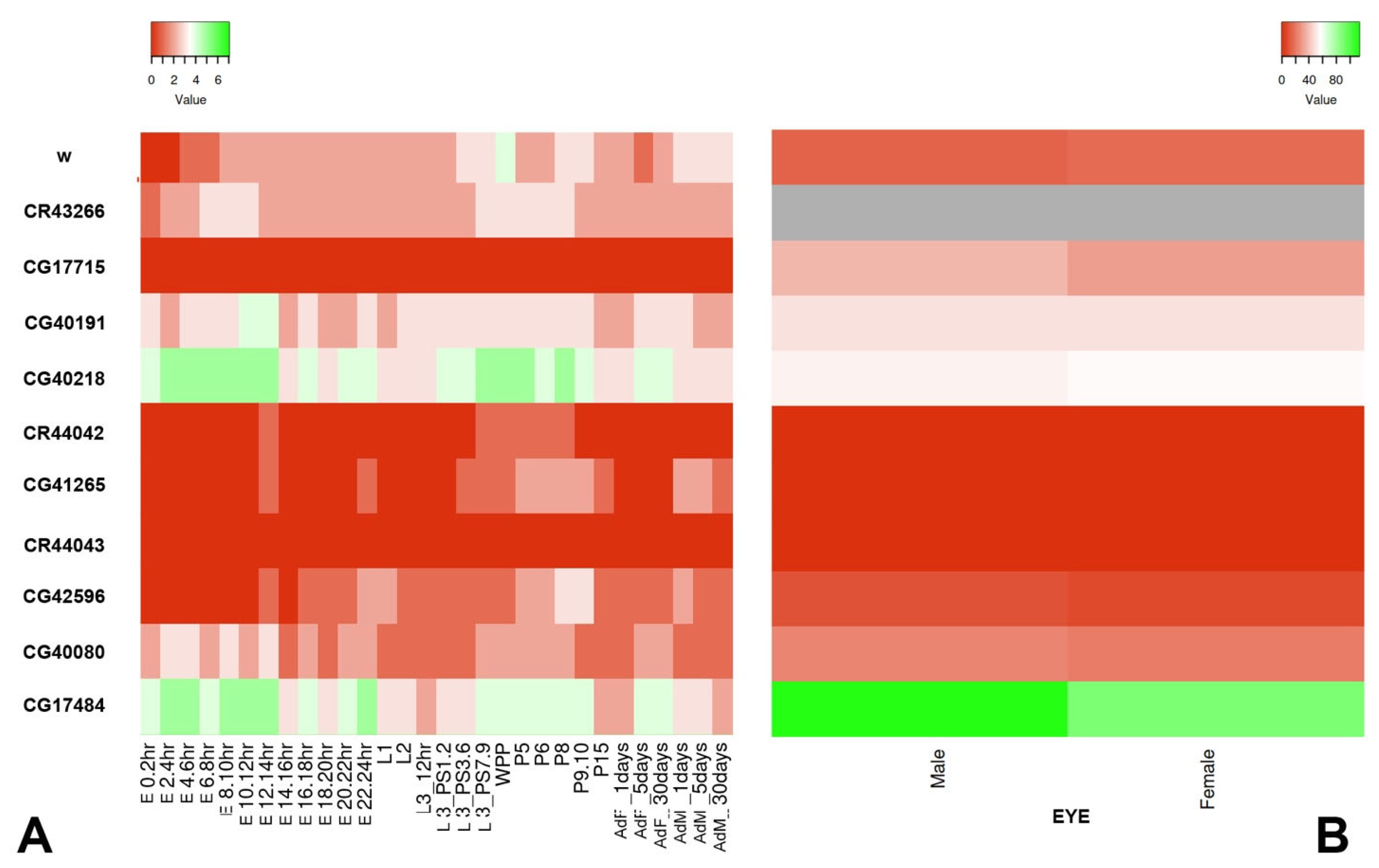
2.6. Distribution of Epigenetic Marks
3. Results
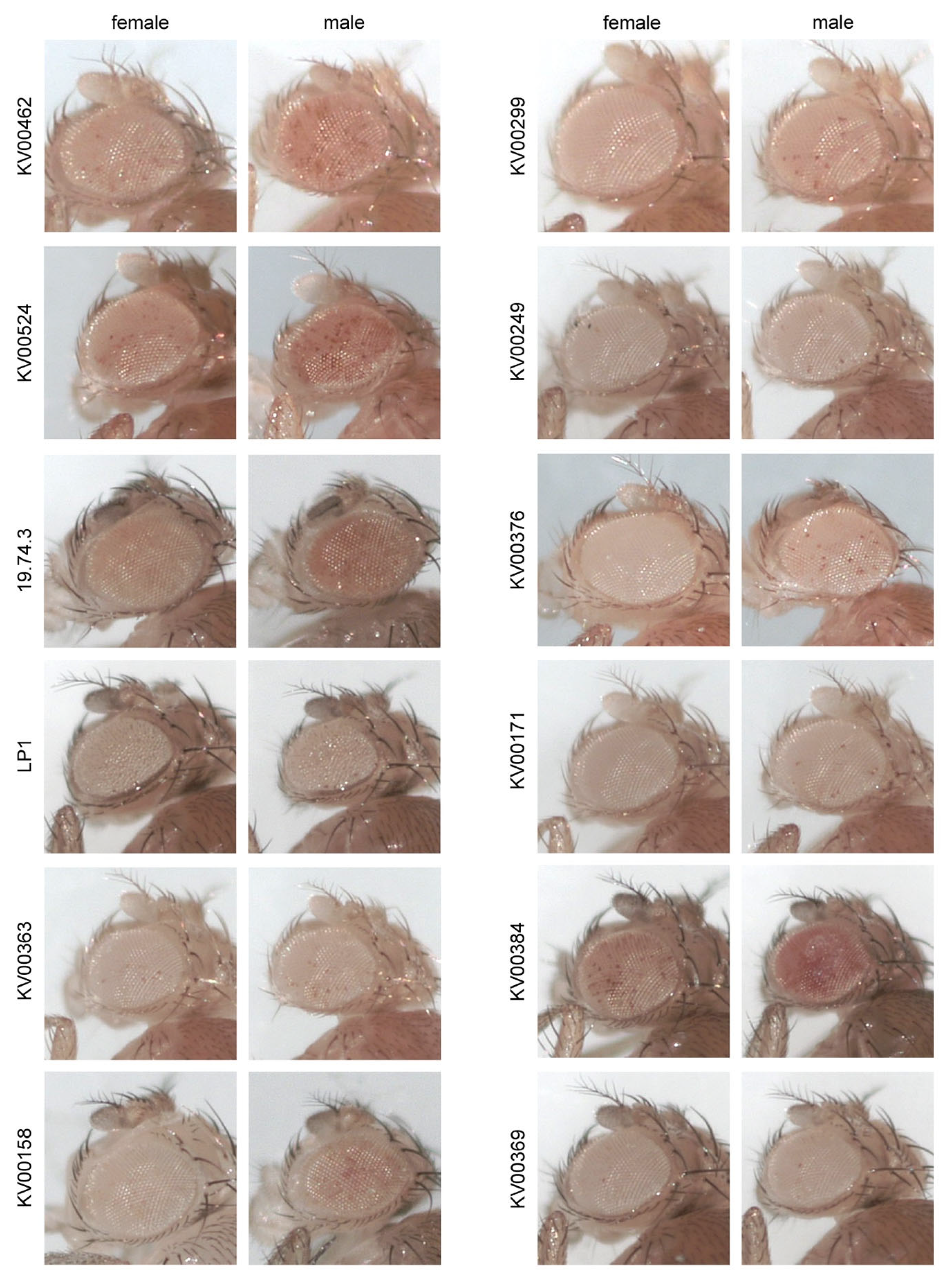
3.1. Analysis of P-Element Insertions
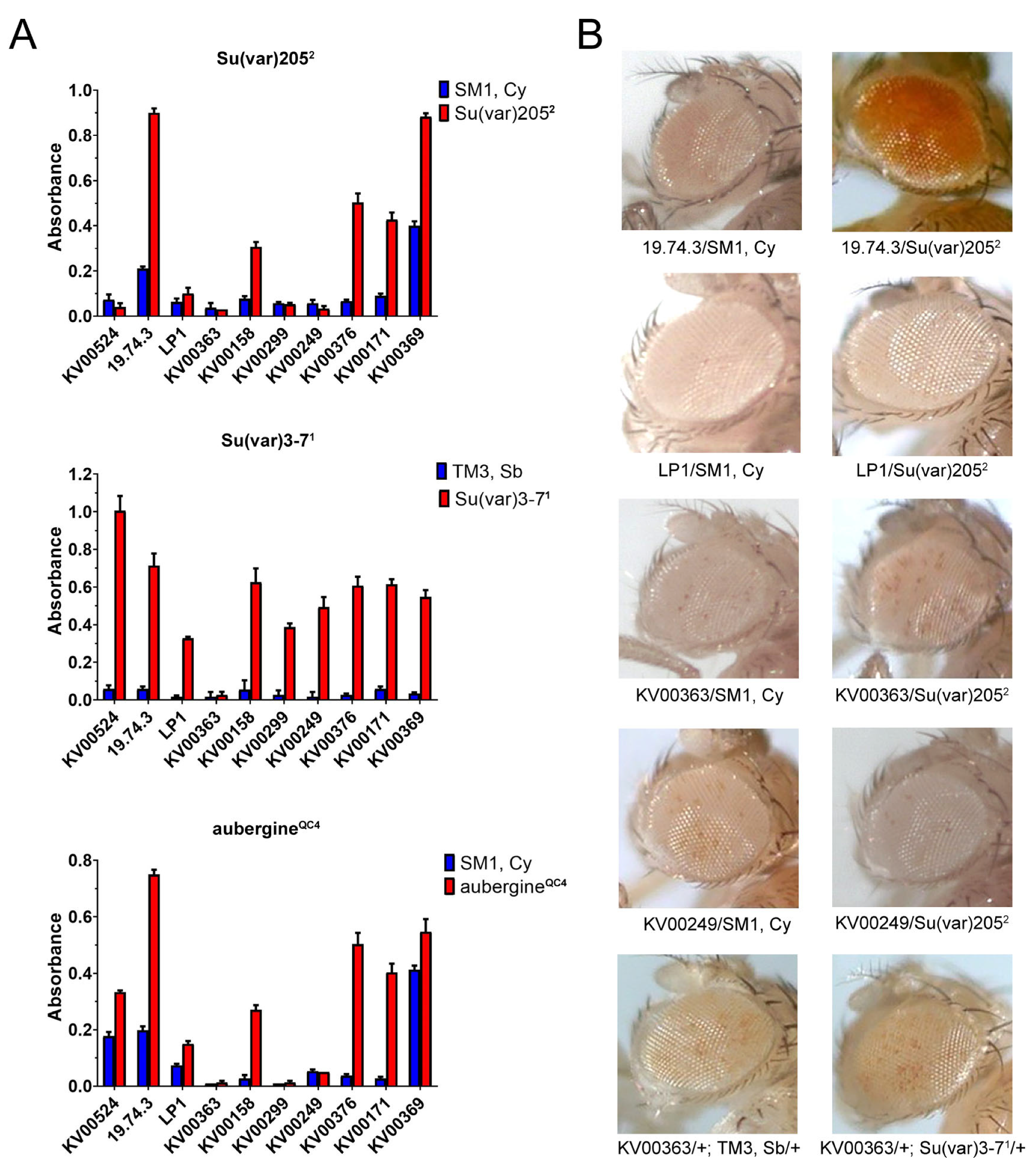
3.2. Experiments with Genetic Modifiers of PEV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flavell, R.B. Repetitive DNA and chromosome evolution in plants. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1986, 312, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SanMiguel, P.; Tikhonov, A.; Jin, Y.-K.; Motchoulskaia, N.; Zakharov, D.; Melake-Berhan, A.; Springer, P.S.; Edwards, K.J.; Lee, M.; Avramova, Z.; et al. Nested Retrotransposons in the Intergenic Regions of the Maize Genome. Science 1996, 274, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kidwell, M.G.; Lisch, D. Transposable elements as sources of variation in animals and plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 1997, 94, 7704–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaminker, J.S.; Bergman, C.; Kronmiller, B.; Carlson, J.; Svirskas, R.; Patel, S.; Frise, E.; A Wheeler, D.; E Lewis, S.; Rubin, G.; et al. The transposable elements of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatin: A genomics perspective. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0084.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.N.; Feschotte, C. A Field Guide to Eukaryotic Transposable Elements. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. Rolling-circle transposons in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8714–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. Self-synthesizing DNA transposons in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4540–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, N.C.; Fanti, L. Transposable Elements: Major Players in Shaping Genomic and Evolutionary Patterns. Cells 2022, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitri, P.; Corradini, N.; Rossi, F.; Mei, E.; Zhimulev, I.; Vernì, F. Transposable elements as artisans of the heterochromatic genome in Drosophila melanogaster. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsano, R.M.; Dimitri, P. Constitutive Heterochromatin in Eukaryotic Genomes: A Mine of Transposable Elements. Cells 2022, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsano, R.M.; Giordano, E.; Messina, G.; Dimitri, P. A New Portrait of Constitutive Heterochromatin: Lessons from Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Hoskins, R.; Smith, C.D.; Carlson, J.W.; Carvalho, A.B.; Halpern, A.; Kaminker, J.S.; Kennedy, C.; Mungall, C.J.; A Sullivan, B.; Sutton, G.G.; et al. Heterochromatic sequences in a Drosophila whole-genome shotgun assembly. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, Rresearch0085.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoskins, R.A.; Carlson, J.W.; Kennedy, C.; Acevedo, D.; Evans-Holm, M.; Frise, E.; Wan, K.H.; Park, S.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Rossi, F.; et al. Sequence Finishing and Mapping of Drosophila melanogaster Heterochromatin. Science 2007, 316, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoskins, R.A.; Carlson, J.W.; Wan, K.H.; Park, S.; Mendez, I.; Galle, S.E.; Booth, B.W.; Pfeiffer, B.D.; George, R.A.; Svirskas, R.; et al. The Release 6 reference sequence of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kidwell, M.G.; Kidwell, J.F.; Sved, J.A. Hybrid Dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: A Syndrome of Aberrant Traits Including Mutation, Sterility and Male Recombination. Genetics 1977, 86, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.; Kidwell, M.G.; Bingham, P.M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: The nature of induced mutations. Cell 1982, 29, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Pélisson, A.; Bucheton, A.; Finnegan, D. Molecular lesions associated with white gene mutations induced by I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984, 3, 3079–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bucheton, A. I transposable elements and I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Spradling, A.C. Insertional mutagenesis of Drosophila heterochromatin with single P elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3539–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitri, P.; Arcà, B.; Berghella, L.; Mei, E. High genetic instability of heterochromatin after transposition of the LINE-like I factor in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8052–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konev, A.Y.; Yan, C.M.; Acevedo, D.; Kennedy, C.; Ward, E.; Lim, A.; Tickoo, S.; Karpen, G.H. Genetics of P-element transposition into Drosophila melanogaster centric heterochromatin. Genetics 2003, 165, 2039–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitri, P.; Bucheton, A. I element distribution in mitotic heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster reactive strains: Identification of a specific site which is correlated with the reactivity levels. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.M.; Spradling, A.C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 1982, 218, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, H.M.; Preston, C.R.; Phillis, R.W.; Johnson-Schlitz, D.M.; Benz, W.K.; Engels, W.R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1988, 118, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, L.; Kelley, R.; Spradling, A. Insertional Mutagenesis of the Drosophila Genome with Single P Elements. Science 1988, 239, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, L.; Berg, C.; Kelley, R.; McKearin, D.; Spradling, A. Identifying and cloning Drosophila genes by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1989, 36, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, A.C.; Stern, D.; Beaton, A.; Rhem, E.J.; Laverty, T.; Mozden, N.; Misra, S.; Rubin, G. The Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project Gene Disruption Project: Single P-Element Insertions Mutating 25% of Vital Drosophila Genes. Genetics 1999, 153, 135–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.G.; Hiesinger, P.R.; Koh, T.-W.; Verstreken, P.; Schulze, K.L.; Cao, Y.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Norga, K.K.; Pan, H.; Bayat, V.; et al. Mapping Drosophila mutations with molecularly defined P element insertions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10860–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Kane, C.J.; Gehring, W.J. Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9123–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, C.; Pearson, R.K.; Bellen, H.J.; O’Kane, C.J.; Grossniklaus, U.; Gehring, W.J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: An efficient method for isolating and characterizing developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelrigg, T.; Levis, R.; Rubin, G.M. Transformation of white locus DNA in Drosophila: Dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell 1984, 36, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellen, H.; Levis, R.; Liao, G.; He, Y.; Carlson, J.W.; Tsang, G.; Evans-Holm, M.; Hiesinger, P.R.; Schulze, K.L.; Rubin, G.; et al. The BDGP Gene Disruption Project. Genetics 2004, 167, 761–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levis, R.; Hazelrigg, T.; Rubin, G.M. Effects of Genomic Position on the Expression of Transduced Copies of the white Gene of Drosophila. Science 1985, 229, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpen, G.H.; Spradling, A.C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics 1992, 132, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseman, R.; Pirrotta, V.; Geyer, P. The su(Hw) protein insulates expression of the Drosophila melanogaster white gene from chromosomal position-effects. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgin, S.C.; Reuter, G. Position-Effect Variegation, Heterochromatin Formation, and Gene Silencing in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a017780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitri, P.; Pisano, C. Position effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster: Relationship between suppression effect and the amount of Y chromosome. Genetics 1989, 122, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.-L.; Haynes, K.; Simpson, C.L.; Lee, S.D.; Collins, L.; Wuller, J.; Eissenberg, J.C.; Elgin, S.C.R. cis -Acting Determinants of Heterochromatin Formation on Drosophila melanogaster Chromosome Four. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8210–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riddle, N.C.; Leung, W.; Haynes, K.A.; Granok, H.; Wuller, J.; Elgin, S.C.R. An Investigation of Heterochromatin Domains on the Fourth Chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2008, 178, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallrath, L.L.; Elgin, S.C. Position effect variegation in Drosophila is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, A.; Dura, J.-M. In Vivo Chromatin Accessibility Correlates with Gene Silencing in Drosophila. Genetics 1998, 150, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.-L.; Cuaycong, M.H.; Elgin, S.C.R. Long-Range Nucleosome Ordering Is Associated with Gene Silencing in Drosophila melanogaster Pericentric Heterochromatin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 2867–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, M.; Dimitri, P.; Berloco, M.; Wakimoto, B.T. Cis-effects of heterochromatin on heterochromatic and euchromatic gene activity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1995, 140, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greil, F.; van der Kraan, I.; Delrow, J.; Smothers, J.F.; de Wit, E.; Bussemaker, H.J.; van Driel, R.; Henikoff, S.; van Steensel, B. Distinct HP1 and Su(var)3-9 complexes bind to sets of developmentally coexpressed genes depending on chromosomal location. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuhara, J.C.; Wakimoto, B.T. Molecular landscape of modified histones in Drosophila heterochromatic genes and euchromatin-heterochromatin transition zones. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Wit, E.; Greil, F.; van Steensel, B. Genome-wide HP1 binding in Drosophila: Developmental plasticity and genomic targeting signals. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Wit, E.; Greil, F.; Van Steensel, B. High-Resolution Mapping Reveals Links of HP1 with Active and Inactive Chromatin Components. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanti, L.; Pimpinelli, S. HP1: A functionally multifaceted protein. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, N.C.; Minoda, A.; Kharchenko, P.V.; Alekseyenko, A.A.; Schwartz, Y.B.; Tolstorukov, M.Y.; Gorchakov, A.A.; Jaffe, J.D.; Kennedy, C.; Linder-Basso, D.; et al. Plasticity in patterns of histone modifications and chromosomal proteins in Drosophila heterochromatin. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, P.; Sowpati, D.T.; Mishra, R.K. Epigenomic and genomic landscape of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatic genes. Genomics 2019, 111, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Sowpati, D.T.; Soujanya, M.; Srivastava, I.; Mishra, R.K. Interplay of pericentromeric genome organization and chromatin landscape regulates the expression of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatic genes. Epigenetics Chromatin 2020, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrath, L.L.; Rodriguez-Tirado, F.; Geyer, P.K. Shining Light on the Dark Side of the Genome. Cells 2022, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Damia, E.; Fanti, L.; Atterrato, M.T.; Celauro, E.; Mariotti, F.R.; Accardo, M.C.; Walther, M.; Verni, F.; Picchioni, D.; et al. Yeti, an essential Drosophila melanogaster gene, encodes a protein required for chromatin organization. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharchenko, P.V.; Alekseyenko, A.A.; Schwartz, Y.B.; Minoda, A.; Riddle, N.C.; Ernst, J.; Sabo, P.J.; Larschan, E.; Gorchakov, A.A.; Gu, T.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the chromatin landscape in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 2011, 471, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ephrussi, B.; Herold, J.L. Studies of Eye Pigments of Drosophila. I. Methods of Extraction and Quantitative Estimation of the Pigment Components. Genetics 1944, 29, 148–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozzillo, Y.; Cuticone, S.; Ferreri, D.; Fattorini, G.; Messina, G.; Dimitri, P. In Vivo Silencing of Genes Coding for dTip60 Chromatin Remodeling Complex Subunits Affects Polytene Chromosome Organization and Proper Development in Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliker, A.J. Genetic analysis of the centromeric heterochromatin of chromosome 2 of Drosophila melanogaster: Deficiency mapping of EMS-induced lethal complementation groups. Genetics 1976, 83, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitri, P. Cytogenetic analysis of the second chromosome heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1991, 127, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, N.; Rossi, F.; Verni, F.; Dimitri, P. FISH analysis of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin using BACs and P elements. Chromosoma 2003, 112, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Moschetti, R.; Caizzi, R.; Corradini, N.; Dimitri, P. Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of heterochromatin gene models in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2007, 175, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, A.B.; Alm, C.; Cealiac, I.; Sinclair, D.A.R.S.A.; Honda, B.M.H.M.; Rossi, F.; Dimitri, P.; Hilliker, A.J. Essential Loci in Centromeric Heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. I: The Right Arm of Chromosome 2. Genetics 2010, 185, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roseman, R.R.; Johnson, E.A.; Rodesch, C.K.; Bjerke, M.; Nagoshi, R.N.; Geyer, P.K. A P element containing suppressor of hairy-wing binding regions has novel properties for mutagenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1995, 141, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.M.; Dobie, K.W.; Le, H.D.; Konev, A.Y.; Karpen, G.H. Efficient Recovery of Centric Heterochromatin P-Element Insertions in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2002, 161, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, K.; Muller, M.; Schedl, P. Fab-7 functions as a chromatin domain boundary to ensure proper segment specification by the Drosophila bithorax complex. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 3202–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreyeva, E.N.; Kolesnikova, T.D.; Demakova, O.V.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Pokholkova, G.V.; Belyaeva, E.S.; Rossi, F.; Dimitri, P.; Villasante, A.; Zhimulev, I.F. High-resolution analysis of Drosophila heterochromatin organization using SuUR Su(var)3-9 double mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12819–12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal-Bhadra, M.; Leibovitch, B.A.; Gandhi, S.G.; Rao, M.; Bhadra, U.; Birchler, J.A.; Elgin, S.C.R. Heterochromatic Silencing and HP1 Localization in Drosophila Are Dependent on the RNAi Machinery. Science 2004, 303, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishida, K.M.; Saito, K.; Mori, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Nagami-Okada, T.; Inagaki, S.; Siomi, H.; Siomi, M.C. Gene silencing mechanisms mediated by Aubergine–piRNA complexes in Drosophila male gonad. RNA 2007, 13, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bannister, A.J.; Zegerman, P.; Partridge, J.F.; Miska, E.A.; Thomas, J.O.; Allshire, R.C.; Kouzarides, T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 2001, 410, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachner, M.; O’Carroll, D.; Rea, S.; Mechtler, K.; Jenuwein, T. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 2001, 410, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.-I.; Rice, J.C.; Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D.; Grewal, S.I.S. Role of Histone H3 Lysine 9 Methylation in Epigenetic Control of Heterochromatin Assembly. Science 2001, 292, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, D.F.; Duyf, B.J.; Hilliker, A.J. The role of heterochromatin in the expression of a heterochromatic gene, the rolled locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1993, 134, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, M.G.; Hedrick, A.; Grigliatti, T.A.; Wakimoto, B.T. The effect of modifiers of position-effect variegation on the variegation of heterochromatic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1991, 128, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, N.; Honda, B.; Whitehead, I.; Grigliatti, T.; Wakimoto, B.; Brock, H.; Lloyd, V.; Sinclair, D. Suppressors of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster affect expression of the heterochromatic gene light in the absence of a chromosome rearrangement. Genome 1998, 41, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.Y.; Emtage, P.C.R.; Duyf, B.J.; Hilliker, A.J.; Eissenberg, J.C. Heterochromatin Protein 1 Is Required for the Normal Expression of Two Heterochromatin Genes in Drosophila. Genetics 2000, 155, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, S.R.; Sinclair, D.A.R.; Fitzpatrick, K.A.; Honda, B.M. A Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Two Proximal Heterochromatic Genes on Chromosome 3 of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2005, 169, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prozzillo, Y.; Monache, F.D.; Ferreri, D.; Cuticone, S.; Dimitri, P.; Messina, G. The True Story of Yeti, the "Abominable" Heterochromatic Gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messina, G.; Atterrato, M.T.; Fanti, L.; Giordano, E.; Dimitri, P. Expression of human Cfdp1 gene in Drosophila reveals new insights into the function of the evolutionarily conserved BCNT protein family. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Celauro, E.; Atterrato, M.T.; Giordano, E.; Iwashita, S.; Dimitri, P. The Bucentaur (BCNT) protein family: A long-neglected class of essential proteins required for chromatin/chromosome organization and function. Chromosoma 2014, 124, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Prozzillo, Y.; Bizzochi, G.; Marsano, R.M.; Dimitri, P. The Green Valley of Drosophila melanogaster Constitutive Heterochromatin: Protein-Coding Genes Involved in Cell Division Control. Cells 2022, 11, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, K.A.; Gracheva, E.; Elgin, S.C.R. A Distinct Type of Heterochromatin Within Drosophila melanogaster Chromosome 4. Genetics 2007, 175, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska, L.; Beltran-Nebot, M.; Ule, J.; Jenner, R. Regulatory feedback from nascent RNA to chromatin and transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

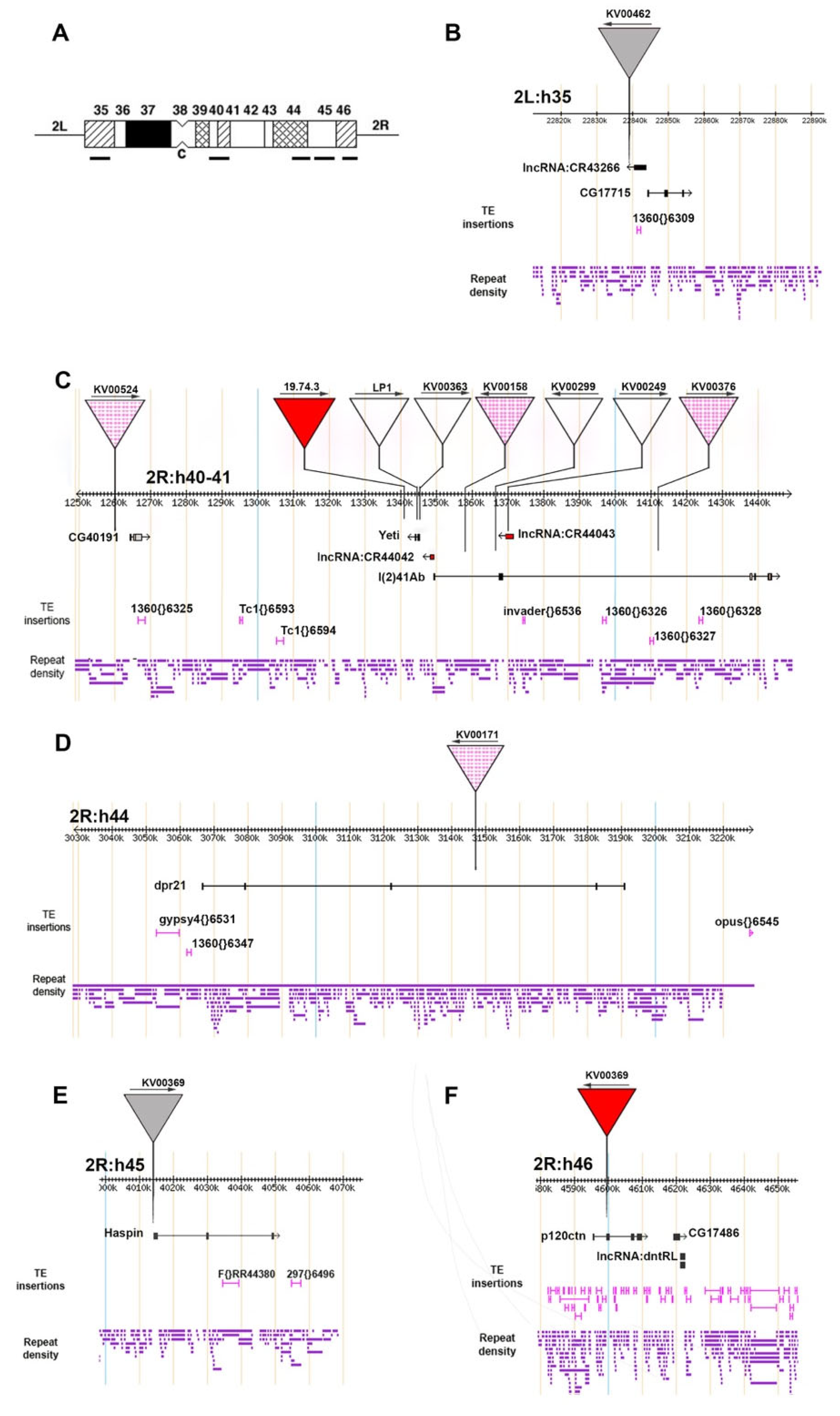

| Line | P-Element | P-Element Position | Affected Gene(s) | Gene Position | Insert Position Relative to Nearby Genes | Sensitivity to Suppressors | Chromatin State (Gene) | Chromatin State (Insertion Site) | Natural TE Insertions (+/− 5 kb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KV00462 | P{SUPor-P} | 2L:22839699 [−] | lnRNA:CR43266 CG17715 | 2L:22840517..22843668 [−] 2L:22844220..22854541 [+] | 818 bp downstream 4521 bp upstream | Y | 1 1,2,7 | 7 | 1360 |
| KV00524 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1260501 [+] | CG40191 | 2R:1264140..1267747 [+] | 3639 bp upstream | Y/N | 1,7 | 7 | 1360 |
| 19.74.3 | P{Fab7-w#un1} | 2R:1341511 [+] | Yeti (CG40218) | 2R:1343403..1345119 [−] | 1892 bp upstream | Y | 1 | NR | ND |
| LP1 | P{Fab7-w#un1} | 2R:1345084 [+] | Yeti (CG40218) | 2R:1343403..1345119 [−] | Start codon | N | 1 | 1 | |
| KV00363 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1345097 [+] | Yeti (CG40218) | 2R:1343403..1345119 [−] | 5′UTR | N | 1 | 1 | |
| KV00158 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1358001 [−] | l(2)41Ab (CG41265) | 2R:1349392..1443935 [+] | 1st intron | Y/N | NR | NR | invader1 1360 (3 copies) |
| KV00299 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1366708 [+] | l(2)41Ab (CG41265) | 2R:1349392..1443935 [+] | 1st intron | N | NR | NR | |
| KV00249 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1370175 [+] | l(2)41Ab (CG41265) lnRNA:CR44043 | 2R:1349392..1443935 [+] 2R:1368921..1371468 [−] | 2nd intron Gene body | N | NR ND | NR | |
| KV00376 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:1412310 [+] | l(2)41Ab (CG41265) | 2R:1349392..1443935 [+] | 2nd intron | Y/N | NR | NR | |
| KV00171 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:3147095 [−] | dpr21 (CG42596) | 2R:3066499..3191011 [+] | Intron 5 | Y/N | ND | ND | Gypsy4 1360 |
| KV00384 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R: 4014047 [+] | Haspin (CG40080) | 2R:4014111..4049342 [+] | 64 bp upstream | Y | 1 | NR | F 297 |
| KV00369 | P{SUPor-P} | 2R:4593333 [−] | p120ctn (CG17484) | 2R:4595288..4609492 [+] | 1955 bp upstream | Y | 1,2,7 | 7 | Doc3 (2 copies) Doc 1360 (5 copies) INE-1 (5 copies) Diver (2 copies) Cr1a Burdock Gypsy12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messina, G.; Celauro, E.; Marsano, R.M.; Prozzillo, Y.; Dimitri, P. Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes 2023, 14, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010012
Messina G, Celauro E, Marsano RM, Prozzillo Y, Dimitri P. Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes. 2023; 14(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessina, Giovanni, Emanuele Celauro, Renè Massimiliano Marsano, Yuri Prozzillo, and Patrizio Dimitri. 2023. "Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster" Genes 14, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010012
APA StyleMessina, G., Celauro, E., Marsano, R. M., Prozzillo, Y., & Dimitri, P. (2023). Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes, 14(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010012









