Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurement of Hearing
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Frequencies of the Genotypes and Alleles of the Mutations in the GJB2 Gene
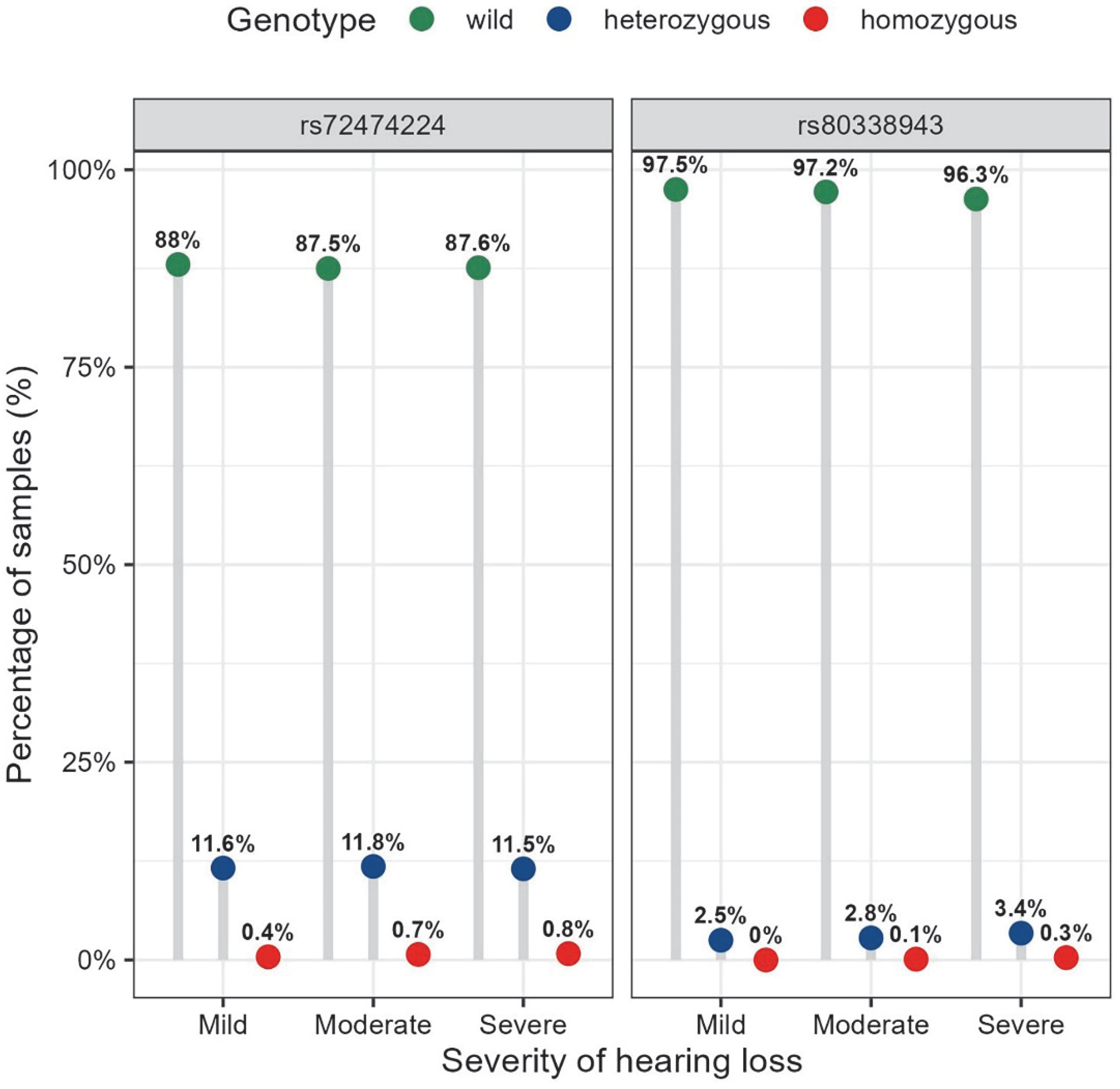
3.3. Distribution of Audiogram Shapes for the Different Genotypes of rs72474224 (c.109G>A) and rs80338943 (c.235delC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- WHO. World Report on Hearing; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2019 Hearing Loss Collaborators. Hearing loss prevalence and years lived with disability, 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 397, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, N.E. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 630, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.B.; Chen, Z.B.; Wei, Q.J.; Lu, Y.J.; Xing, G.Q.; Cao, X. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes analysis of DFNB1 locus in Chinese sporadic hearing impairment population. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, P.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Kang, D.; et al. GJB2 mutation spectrum in 2063 Chinese patients with nonsyndromic hearing impairment. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, A.P.; de Oliveira, F.M.; de Carvalho, G.Q.; Medrano, R.F.; da Silva-Costa, S.M.; Sartorato, E.L.; de Oliveira, C.A. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the GJB2 and GJB6 genes are associated with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 318727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Camp, G.; Smith, R.J.H. Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Snoeckx, R.L.; Huygen, P.L.; Feldmann, D.; Marlin, S.; Denoyelle, F.; Waligora, J.; Mueller-Malesinska, M.; Pollak, A.; Ploski, R.; Murgia, A.; et al. GJB2 mutations and degree of hearing loss: A multicenter study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn hearing screening—A silent revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, T.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Tseng, L.H.; Yang, T.H.; Chen, P.L.; Wu, C.C.; Hsu, C.J. Prediction Model for Audiological Outcomes in Patients with GJB2 Mutations. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsell, D.P.; Dunlop, J.; Stevens, H.P.; Lench, N.J.; Liang, J.N.; Parry, G.; Mueller, R.F.; Leigh, I.M. Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 1997, 387, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.K.; Chang, K.W. GJB2-associated hearing loss: Systematic review of worldwide prevalence, genotype, and auditory phenotype. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E34–E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Oza, A.M.; Del Castillo, I.; Duzkale, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Pandya, A.; Kang, H.P.; Mar-Heyming, R.; Guha, S.; Moyer, K.; et al. Consensus interpretation of the p.Met34Thr and p.Val37Ile variants in GJB2 by the ClinGen Hearing Loss Expert Panel. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2019, 21, 2442–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, P.M.; Harris, D.J.; Comer, B.C.; Askew, J.W.; Fowler, T.; Smith, S.D.; Kimberling, W.J. Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) that cause autosomal recessive (DFNB1) hearing loss. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Usami, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Kelley, P.M.; Kimberling, W.J. Prevalent connexin 26 gene (GJB2) mutations in Japanese. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, S.A.; Saunders, K.; Osborn, A.H.; Arnold, A.; Wunderlich, J.; Kelly, T.; Collins, V.; Wilcox, L.J.; McKinlay Gardner, R.J.; Kamarinos, M.; et al. High frequency hearing loss correlated with mutations in the GJB2 gene. Hum. Genet. 2000, 106, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Chen, D.; Sun, L.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Pang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, T. The homozygous p.V37I variant of GJB2 is associated with diverse hearing phenotypes. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Sun, X.; Song, N.; Ramaswamy, S.; Abou Tayoun, A.N.; Peng, Z. Comprehensive interpretation of single-nucleotide substitutions in GJB2 reveals the genetic and phenotypic landscape of GJB2-related hearing loss. Hum. Genet. 2023, 142, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.K.; Schrijver, I.; Chang, K.W. Connexin-26-associated deafness: Phenotypic variability and progression of hearing loss. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2010, 12, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Z.; Pandya, A.; Angeli, S.; Telischi, F.F.; Arnos, K.S.; Nance, W.E.; Balkany, T. Audiological features of GJB2 (connexin 26) deafness. Ear Hear. 2005, 26, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, J.; Yao, P.; Li, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, L.; Min, X.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study of retired workers. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiao, L.; Cao, L.; Zhou, M.; Kong, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; He, M.; et al. Association between shift work and hearing loss: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study. Hear. Res. 2019, 384, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Yi, G.; Chen, Z.; et al. Association of occupational noise exposure, bilateral hearing loss with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in Chinese adults. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 235, 113776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report of the Informal Working Group on Prevention of Deafness and Hearing Impairment Programme Planning, Geneva, 18–21 June 1991. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/58839 (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Jiang, J.; He, S.; Liu, K.; Yu, K.; Long, P.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; et al. Multiple plasma metals, genetic risk and serum complement C3, C4: A gene-metal interaction study. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, C.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Peng, T.; et al. A genome wide association study of genetic loci that influence tumour biomarkers cancer antigen 19-9, carcinoembryonic antigen and α fetoprotein and their associations with cancer risk. Gut 2014, 63, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, P.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; He, S.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Qiu, G.; Yu, K.; Liu, K.; Jiang, J.; et al. Circulating folate concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease: A prospective cohort study in Chinese adults and a Mendelian randomization analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, B.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, P. The Relationship between the p.V37I Mutation in GJB2 and Hearing Phenotypes in Chinese Individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Huang, D.; Kang, D.; et al. The prevalence of the 235delC GJB2 mutation in a Chinese deaf population. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2007, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Che, T.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Wu, H. Molecular epidemiology of Chinese Han deaf patients with bi-allelic and mono-allelic GJB2 mutations. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Z.; Xia, X.J.; Ke, X.M.; Ouyang, X.M.; Du, L.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Angeli, S.; Telischi, F.F.; Nance, W.E.; Balkany, T.; et al. The prevalence of connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations in the Chinese population. Hum. Genet. 2002, 111, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, C.L.; Hsu, Y.C. GJB2 mutation spectrum in the Taiwanese population and genotype-phenotype comparisons in patients with hearing loss carrying GJB2 c.109G>A and c.235delC mutations. Hear. Res. 2022, 413, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.F.; Ji, Y.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Lan, L.; Han, M.K.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Rao, S.; Han, D.; Wang, Q.J. Phenotype-genotype correlation in 295 Chinese deaf subjects with biallelic causative mutations in the GJB2 gene. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2011, 15, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Guan, J.; Lan, L.; Yang, J.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, C.; Xie, L.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; et al. Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Post-Lingual and/or Milder Hearing Loss for the Patients with the GJB2 c.235delC Homozygous Mutation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 647240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, K.B.; Khalaily, L.; Noy, Y.; Kamal, L.; Koffler-Brill, T.; Taiber, S. The noncoding genome and hearing loss. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Ji, J.; Wan, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. An overview of research trends and genetic polymorphisms for noise-induced hearing loss from 2009 to 2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 34754–34774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | Total (n = 9910) |
|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 67.2 (7.6) |
| Age group (%) | |
| <60 | 1548 (15.6) |
| 60–69 | 4765 (48.1) |
| 70–79 | 3054 (30.8) |
| ≥80 | 543 (5.5) |
| Gender (%) | |
| Female | 5197 (52.4) |
| Male | 4713 (47.6) |
| Severity of hearing loss (%) | |
| Normal | 4168 (42.1) |
| Mild | 3806 (38.4) |
| Moderate | 1581 (16.0) |
| Severe-profound | 355 (3.6) |
| SNPs | Nucleotide Change | Protein Change | Clinical Significance | Overall (n = 9910) | Hearing Loss | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Group (n = 4168) | Patients Group (n = 5742) | ||||||
| rs111033222 | c.11G>A | p.G4D | Conflicting | ||||
| Genotype | C/C | 9854 (99.4) | 4143 (99.4) | 5711 (99.5) | 0.797 a | ||
| T/C | 56 (0.6) | 25 (0.6) | 31 (0.5) | ||||
| Allele | C | 19,764 (99.7) | 8311 (99.7) | 11,453 (99.7) | 0.797 a | ||
| T | 56 (0.3) | 25 (0.3) | 31 (0.3) | ||||
| rs2274084 | c.79G>A | p.V27I | Benign | ||||
| Genotype | C/C | 4391 (44.3) | 1854 (44.5) | 2537 (44.2) | 0.680 a | ||
| T/C | 4518 (45.6) | 1906 (45.7) | 2612 (45.5) | ||||
| T/T | 1001 (10.1) | 408 (9.8) | 593 (10.3) | ||||
| Allele | C | 13,300 (67.1) | 5614 (67.3) | 7686 (66.9) | 0.546 a | ||
| T | 6520 (32.9) | 2723 (32.7) | 3798 (33.1) | ||||
| rs3751385 | c.*84T>C | - | Benign | ||||
| Genotype | A/A | 2157 (21.8) | 850 (20.4) | 1307 (22.8) | 0.017a | ||
| A/G | 4985 (50.3) | 2142 (51.4) | 2843 (49.5) | ||||
| G/G | 2768 (27.9) | 1176 (28.2) | 1592 (27.7) | ||||
| Allele | A | 9299 (46.9) | 3842 (46.1) | 5457 (47.5) | 0.048 a | ||
| G | 10,521 (53.1) | 4494 (53.9) | 6027 (52.5) | ||||
| rs72474224 | c.109G>A | p.V37I | Pathogenic | ||||
| Genotype | C/C | 8718 (88.0) | 3674 (88.1) | 5044 (87.8) | <0.001 b | ||
| T/C | 1161 (11.7) | 491 (11.8) | 670 (11.7) | ||||
| T/T | 31 (0.3) | 3 (0.1) | 28 (0.5) | ||||
| Allele | C | 18,597 (93.8) | 7839 (94.0) | 10,758 (93.7) | 0.313 a | ||
| T | 1223 (6.2) | 497 (6.0) | 726 (6.3) | ||||
| rs80338943 | c.235delC | p.Leu79fs | Pathogenic | ||||
| Genotype | AG/AG | 9665 (97.5) | 4078 (97.8) | 5587 (97.3) | 0.118 b | ||
| A/AG | 243 (2.5) | 90 (2.2) | 153 (2.7) | ||||
| A/A | 2 (0.02) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.03) | ||||
| Allele | AG | 19,573 (98.8) | 8246 (98.9) | 11,327 (98.6) | 0.083 a | ||
| A | 247 (1.2) | 90 (1.1) | 157 (1.4) | ||||
| rs2274083 | c.341A>G | p.E114G | Benign/Likely benign | ||||
| Genotype | T/T | 5284 (53.3) | 2249 (54.0) | 3035 (52.9) | 0.423 a | ||
| C/T | 4025 (40.6) | 1678 (40.3) | 2347 (40.9) | ||||
| C/C | 601 (6.1) | 241 (5.8) | 360 (6.3) | ||||
| Allele | T | 14,593 (73.6) | 6176 (74.1) | 8417 (73.3) | 0.216 a | ||
| C | 5227 (26.3) | 2160 (25.9) | 3067 (26.7) | ||||
| rs111033188 | c.368C>A | p.T123N | Benign/Likely benign | ||||
| Genotype | G/G | 9828 (99.2) | 4134 (99.2) | 5694 (99.2) | 0.965 b | ||
| T/G | 80 (0.8) | 33 (0.8) | 47 (0.8) | ||||
| T/T | 2 (0.02) | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.02) | ||||
| Allele | G | 19,736 (99.6) | 8301 (99.6) | 11,435 (9.6) | 0.942 a | ||
| T | 84 (0.4) | 35 (0.4) | 49 (0.4) | ||||
| rs397516878 | c.571T>C | p.F191L | Uncertain | ||||
| Genotype | A/A | 9899 (99.9) | 4163 (99.9) | 5736 (99.9) | 0.871 b | ||
| A/G | 11 (0.1) | 5 (0.1) | 6 (0.1) | ||||
| Allele | A | 19,809 (99.9) | 8331 (99.9) | 11,478 (99.95) | 0.871 b | ||
| G | 11 (0.1) | 5 (0.1) | 6 (0.05) | ||||
| rs76838169 | c.608T>C | p.I203T | Benign | ||||
| Genotype | A/A | 9298 (93.8) | 3929 (94.3) | 5369 (93.5) | 0.289 a | ||
| A/G | 598 (6.0) | 234 (5.6) | 364 (6.3) | ||||
| G/G | 14 (0.1) | 5 (0.1) | 9 (0.2) | ||||
| Allele | A | 19,194 (96.8) | 8092 (97.1) | 11,102 (96.7) | 0.122 a | ||
| G | 626 (3.2) | 244 (2.9) | 382 (3.3) | ||||
| Hearing Loss | Medical ID | Age (Years) | Gender | Better Ear (dB) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 kHz | 1 kHz | 2 kHz | 4 kHz | 8 kHz | PTA 0.5–4 kHz | ||||
| Normal | 106846 | 58 | Female | 15 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 11.25 |
| Normal | 105802 | 59 | Female | 15 | 5 | 25 | 40 | 60 | 21.25 |
| Normal | 90678 | 68 | Male | 25 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 21.25 |
| Mild | 78353 | 60 | Male | 20 | 25 | 25 | 40 | 65 | 27.5 |
| Mild | 70091 | 61 | Female | 25 | 25 | 20 | 50 | 45 | 30 |
| Mild | 70740 | 61 | Female | 30 | 30 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 32.5 |
| Mild | 11011 | 63 | Female | 15 | 15 | 50 | 50 | 70 | 32.5 |
| Mild | 4888 | 64 | Female | 25 | 30 | 40 | 45 | 75 | 35 |
| Mild | 60195 | 64 | Female | 25 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 70 | 28.75 |
| Mild | 107326 | 64 | Female | 25 | 30 | 35 | 55 | 65 | 36.25 |
| Mild | 54382 | 66 | Male | 20 | 30 | 40 | 45 | 95 | 33.75 |
| Mild | 101181 | 66 | Male | 30 | 35 | 35 | 40 | 65 | 35 |
| Mild | 11321 | 67 | Male | 20 | 30 | 35 | 60 | 85 | 36.25 |
| Mild | 67746 | 69 | Female | 25 | 25 | 25 | 45 | 90 | 30 |
| Mild | 39311 | 71 | Male | 15 | 15 | 30 | 60 | 25 | 30 |
| Mild | 59571 | 74 | Female | 15 | 15 | 40 | 60 | 70 | 32.5 |
| Mild | 53680 | 76 | Male | 20 | 20 | 30 | 35 | 90 | 26.25 |
| Moderate | 54632 | 56 | Female | 35 | 35 | 35 | 60 | 90 | 41.25 |
| Moderate | 79049 | 61 | Female | 35 | 40 | 50 | 45 | 55 | 42.5 |
| Moderate | 16099 | 67 | Male | 20 | 30 | 60 | 70 | 85 | 45 |
| Moderate | 28532 | 67 | Male | 35 | 35 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 50 |
| Moderate | 90158 | 68 | Male | 40 | 50 | 50 | 65 | 55 | 51.25 |
| Moderate | 94371 | 68 | Male | 30 | 45 | 65 | 75 | 100 | 53.75 |
| Moderate | 42832 | 77 | Male | 15 | 30 | 60 | 70 | 90 | 43.75 |
| Moderate | 100741 | 77 | Female | 20 | 40 | 55 | 50 | 80 | 41.25 |
| Moderate | 116341 | 78 | Male | 40 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 85 | 47.5 |
| Moderate | 107144 | 79 | Male | 20 | 25 | 55 | 70 | 90 | 42.5 |
| Moderate | 5826 | 80 | Male | 40 | 50 | 65 | 85 | 90 | 60 |
| Severe | 56456 | 64 | Male | 50 | 55 | 65 | 90 | 110 | 65 |
| Severe | 115724 | 73 | Male | 60 | 70 | 70 | 75 | 110 | 68.75 |
| Severe | 93245 | 74 | Male | 60 | 60 | 70 | 70 | 100 | 65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Kong, W.; He, M.; Sun, Y. Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort. Genes 2023, 14, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112007
Yuan L, Wang X, Liu X, Chen S, Kong W, He M, Sun Y. Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort. Genes. 2023; 14(11):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112007
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Lanlai, Xiaohui Wang, Xiaozhou Liu, Sen Chen, Weijia Kong, Meian He, and Yu Sun. 2023. "Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort" Genes 14, no. 11: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112007
APA StyleYuan, L., Wang, X., Liu, X., Chen, S., Kong, W., He, M., & Sun, Y. (2023). Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort. Genes, 14(11), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112007







