The Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome: From Genetics to Prognostic–Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
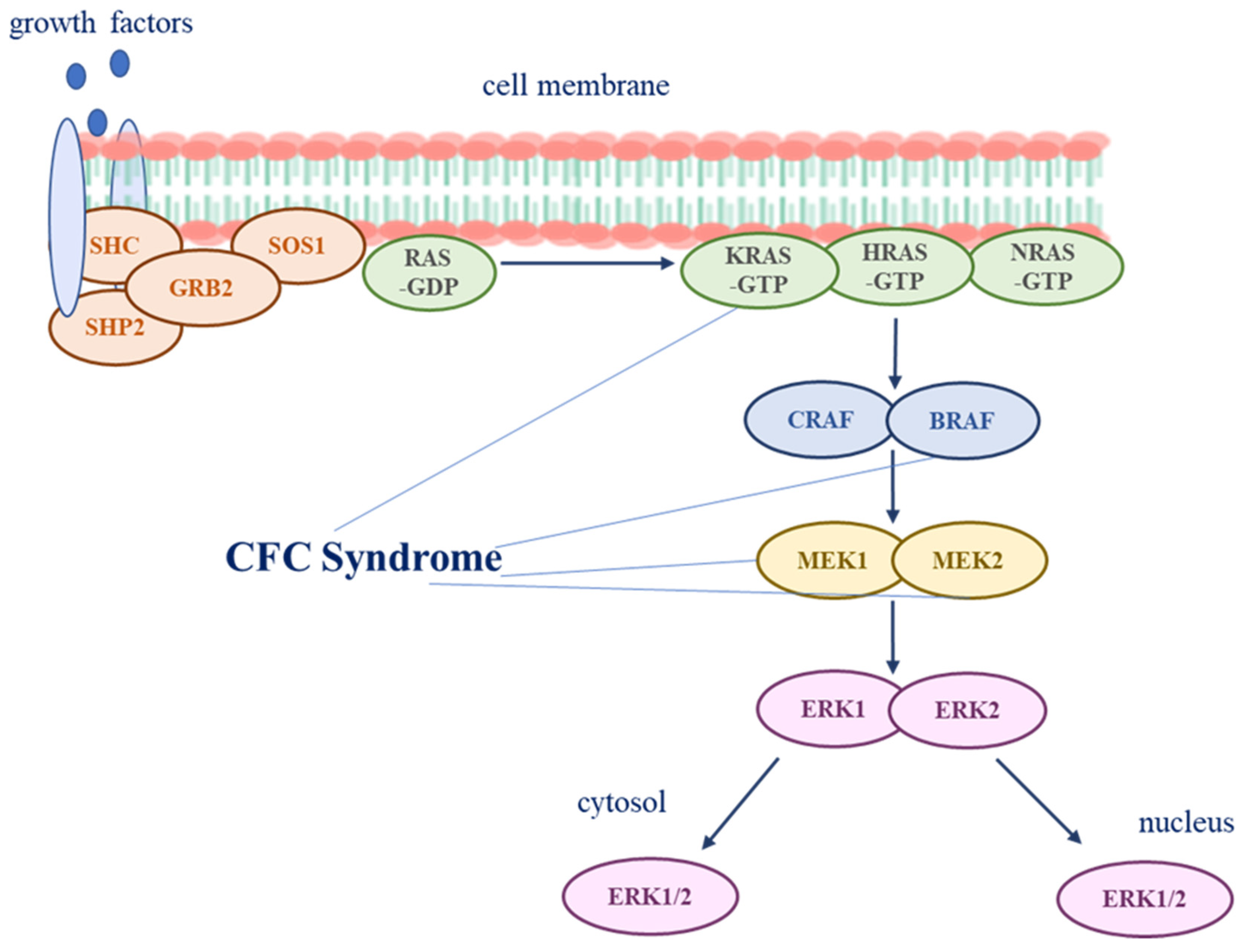
3. Pathogenesis
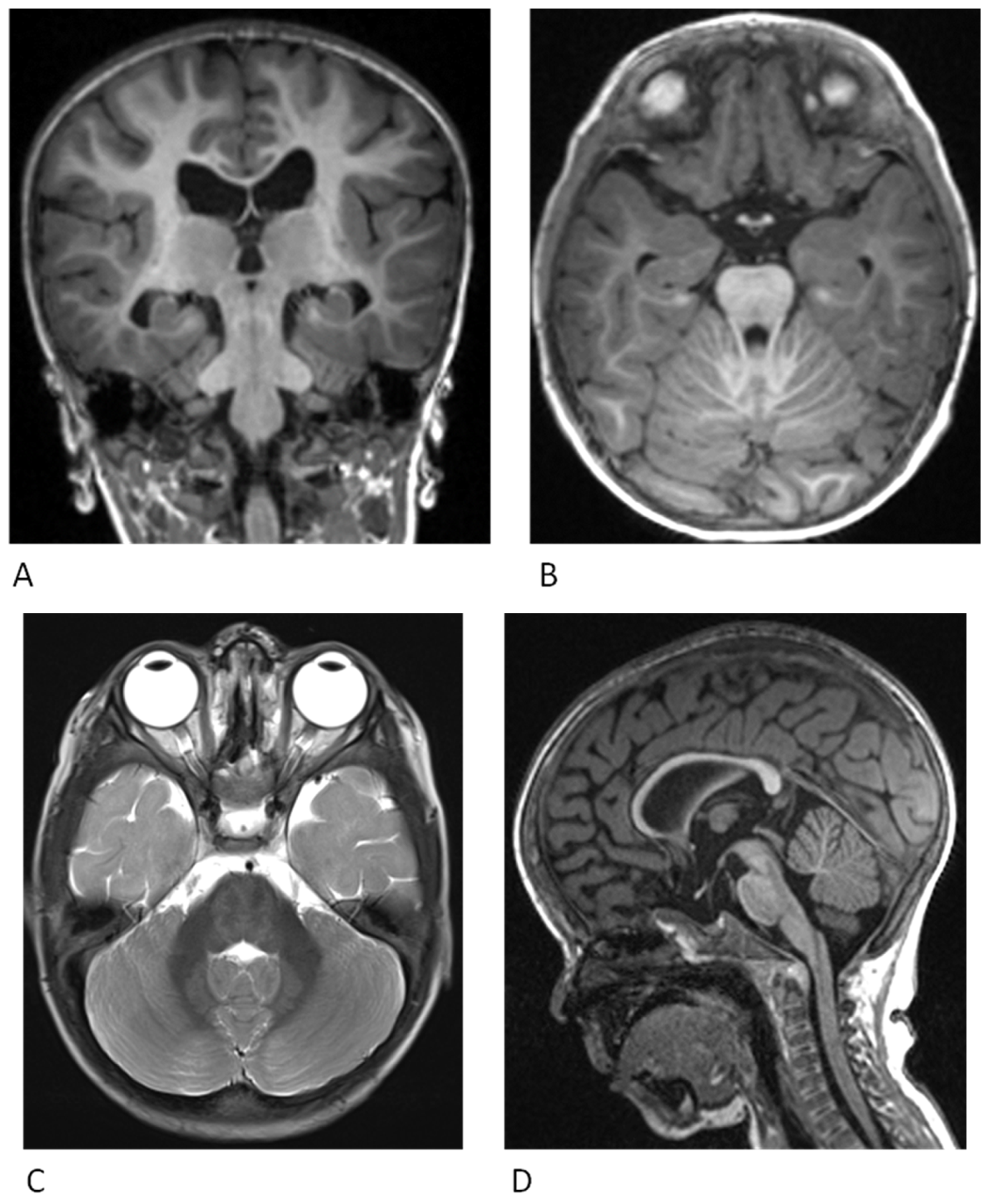
4. Neurological Findings
4.1. Cardiac Findings
4.2. Ectodermal Findings
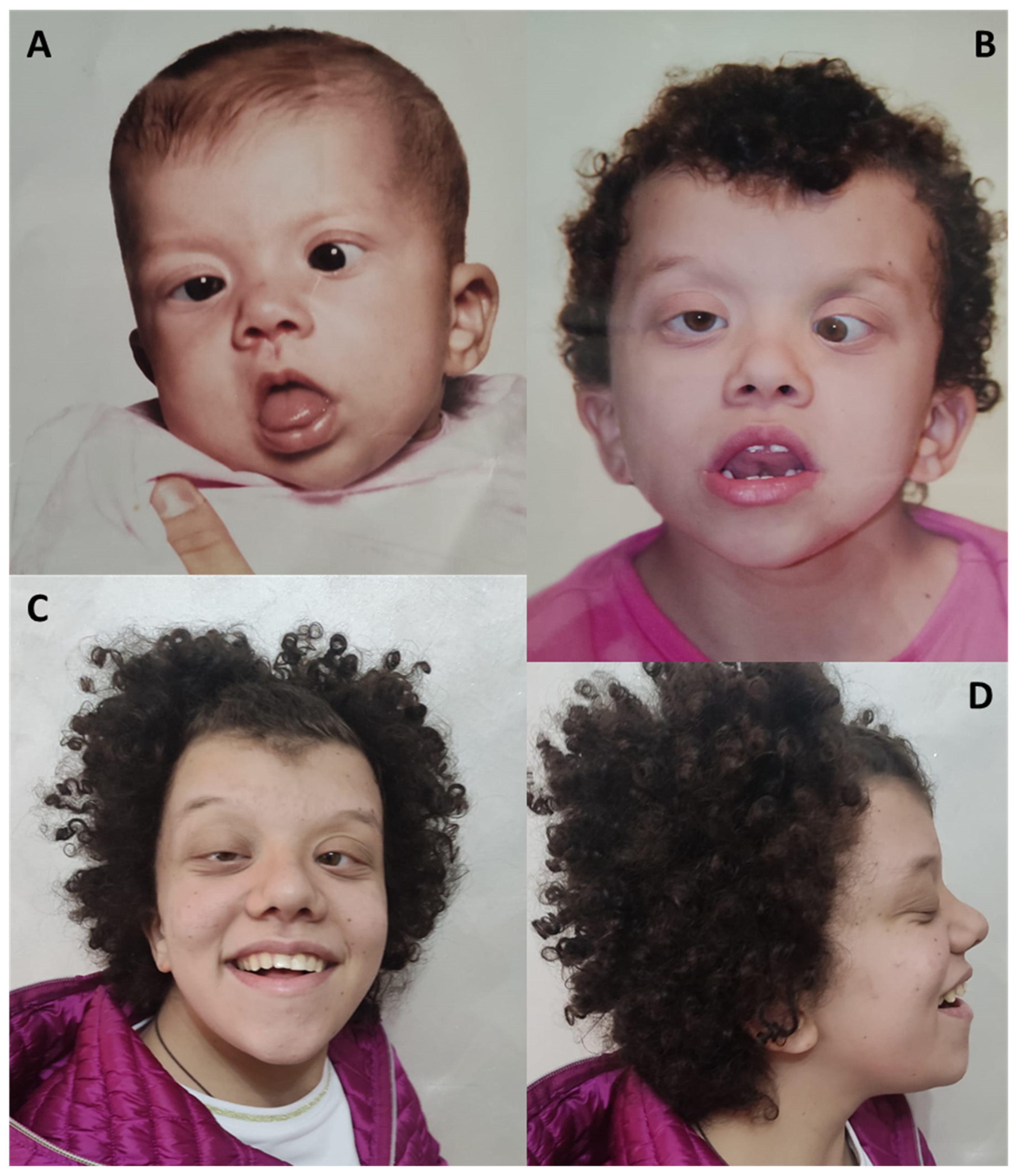
4.3. Craniofacial Findings
4.4. Gastrointestinal and Growth Findings
4.5. Additional Features
5. Diagnosis
Current Consensus Guidelines Strategy Include the Following
- Multigene panel for common RASopathy genes that includes BRAF, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, KRAS and YWHAZ usually detects up to 90% of individuals with CFC and it is the preferred initial test.
- Individual single-gene testing is recommended if panel testing is not available, beginning with BRAF, MAP2K1, and MAP2K2, and KRAS.
- If these molecular genetic tests are negative, a more comprehensive genetic sequencing including exome and genome sequencing should be performed [5].
6. Treatment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hebron, K.E.; Hernandez, E.R.; Yohe, M.E. The RASopathies: From pathogenetics to therapeutics. Dis. Models Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Kuriyama, S.; Kawame, H.; Okamoto, N.; Kurosawa, K.; Ohashi, H.; Mizuno, S.; Ogata, T.; Kure, S.; et al. Prevalence and clinical features of Costello syndrome and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome in Japan: Findings from a nationwide epidemiological survey. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2012, 158, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.K.M.; Leprivier, G. The impact of oncogenic RAS on redox balance and implications for cancer development. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, M. Clinical overview on RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, K.A. Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pierpont, E.I.; Kenney-Jung, D.L.; Shanley, R.; Zatkalik, A.L.; Whitmarsh, A.E.; Kroening, S.J.; Roberts, A.E.; Zenker, M. Neurologic and neurodevelopmental complications in cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome are associated with genotype: A multinational cohort study. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney-Jung, D.L.; Rogers, D.J.; Kroening, S.J.; Zatkalik, A.L.; Whitmarsh, A.E.; Roberts, A.E.; Zenker, M.; Gambardella, M.L.; Contaldo, I.; Leoni, C.; et al. Infantile epileptic spasms syndrome in children with cardiofaciocutanous syndrome: Clinical presentation and associations with genotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.K.; Hiatt, S.M.; Whalen, S.; Keren, B.; Ruivenkamp, C.; van Haeringen, A.; Chen, M.-J.; Cooper, G.M.; Korf, B.R.; Chang, C. A YWHAZ Variant Associated With Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome Activates the RAF-ERK Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpont, M.E.M.; Magoulas, P.L.; Adi, S.; Kavamura, M.I.; Neri, G.; Noonan, J.; Pierpont, E.I.; Reinker, K.; Roberts, A.E.; Shankar, S.; et al. Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous Syndrome: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management Guidelines. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1149–e1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, M.; Aoki, Y.; Gelb, B.D. The molecular genetics of RASopathies: An update on novel disease genes and new disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasaki, C.; Estep, A.L.; Marais, R.; Rauen, K.A.; Patton, E.E. Kinase-activating and kinase-impaired cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome alleles have activity during zebrafish development and are sensitive to small molecule inhibitors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.; Rosenberg, J.; Blaser, S.; Rauen, K.A. Neurological complications of cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizaki, K.; Sugai, K.; Saito, Y.; Nakagawa, E.; Sasaki, M.; Aoki, Y.; Matsubara, Y. Cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome with infantile spasms and delayed myelination. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakusawa, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Abe, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Endo, W.; Inui, T.; Iwaki, M.; Watanabe, S.; Togashi, N.; Nara, T.; et al. A girl with Cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome complicated with status epilepticus and acute encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Abe, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Matsubara, Y. Epilepsy in RAS/MAPK syndrome: Two cases of cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome with epileptic encephalopathy and a literature review. Seizure 2012, 21, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, D.I.; Gambardella, M.L.; Veltri, S.; Contaldo, I.; Chillemi, G.; Veredice, C.; Quintiliani, M.; Leoni, C.; Onesimo, R.; Verdolotti, T.; et al. Epilepsy and BRAF Mutations: Phenotypes, Natural History and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Genes 2021, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, M.; Baldassari, S.; Tochigi, Y.; Kośla, K.; Buffelli, F.; Torella, A.; Severino, M.; Paladini, D.; Mandarà, L.; Riva, A.; et al. Loss of Wwox Perturbs Neuronal Migration and Impairs Early Cortical Development. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuray, C.; Maroofian, R.; Scala, M.; Sultan, T.; Pai, G.S.; Mojarrad, M.; Khashab, H.E.; deHoll, L.; Yue, W.; Alsaif, H.S.; et al. Early-infantile onset epilepsy and developmental delay caused by bi-allelic GAD1 variants. Brain 2020, 143, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, A.; Efthymiou, S.; O’Connor, E.; Mendes, M.I.; Jennings, M.; Maroofian, R.; Davagnanam, I.; Mankad, K.; Lopez, M.R.; Salpietro, V.; et al. De Novo and Bi-allelic Pathogenic Variants in NARS1 Cause Neurodevelopmental Delay Due to Toxic Gain-of-Function and Partial Loss-of-Function Effects. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niestroj, L.-M.; Perez-Palma, E.; Howrigan, D.P.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, F.; Saarentaus, E.; Nürnberg, P.; Stevelink, R.; Daly, M.J.; Palotie, A.; et al. Epilepsy subtype-specific copy number burden observed in a genome-wide study of 17 458 subjects. Brain 2020, 143, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, P.; Piccini, G.; Caciolo, C.; Perrino, F.; Gambardella, M.L.; Mallardi, M.; Cesarini, L.; Leoni, C.; Leone, D.; Fossati, C.; et al. Behavioral profile in RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanson, J.E.; Annerén, G.; Aoki, Y.; Armour, C.M.; Bondeson, M.-L.; Cave, H.; Gripp, K.W.; Kerr, B.; Nystrom, A.-M.; Sol-Church, K.; et al. Cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome: Does genotype predict phenotype? Am. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 157, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauen, K.A.; Tidyman, W.E.; Estep, A.L.; Sampath, S.; Peltier, H.M.; Bale, S.J.; Lacassie, Y. Molecular and functional analysis of a novel MEK2 mutation in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome: Transmission through four generations. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 152, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, D.; Salpietro, V.; Phadke, R.; Pitt, M.; Gentile, G.; Massoud, A.; Batten, L.; Bashamboo, A.; Mcelreavey, K.; Saggar, A.; et al. Whole exome sequencing reveals a MLL de novo mutation associated with mild developmental delay and without “hairy elbows”: Expanding the phenotype of Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome. J. Genet. 2015, 94, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthymiou, S.; Salpietro, V.; Malintan, N.; Poncelet, M.; Kriouile, Y.; Fortuna, S.; De Zorzi, R.; Payne, K.; Henderson, L.B.; Cortese, A.; et al. Biallelic mutations in neurofascin cause neurodevelopmental impairment and peripheral demyelination. Brain 2019, 142, 2948–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpietro, V.; Efthymiou, S.; Manole, A.; Maurya, B.; Wiethoff, S.; Ashokkumar, B.; Cutrupi, M.C.; Dipasquale, V.; Manti, S.; Botia, J.A.; et al. A loss-of-function homozygous mutation in DDX59 implicates a conserved DEAD-box RNA helicase in nervous system development and function. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Goldberg-Strassler, D.; Gripp, K.; Thacker, M.; Leoni, C.; Stevenson, D. Function and disability in children with Costello syndrome and Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, E.; Sifakis, S.; Sol-Church, K.; Klein-Zighelboim, E.; Stabley, D.L.; Raissaki, M.; Gripp, K.W.; Kalmanti, M. CNS imaging is a key diagnostic tool in the evaluation of patients with CFC syndrome: Two cases and literature review. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.N.; Gripp, K.W. Central nervous system involvement in individuals with RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, A.B.; Limongelli, G.; Versacci, P.; Adorisio, R.; Kaski, J.P.; Blandino, R.; Maiolo, S.; Monda, E.; Putotto, C.; De Rosa, G.; et al. The heart in RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Blandino, R.; Delogu, A.B.; De Rosa, G.; Onesimo, R.; Verusio, V.; Marino, M.V.; Lanza, G.A.; Rigante, D.; Tartaglia, M.; et al. Genotype-cardiac phenotype correlations in a large single-center cohort of patients affected by RASopathies: Clinical implications and literature review. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Chen, Z.; Chen, M.H.; Choudhury, S. RASopathies and cardiac manifestations. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1176828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentici, M.L.; Sarkozy, A.; Pantaleoni, F.; Carta, C.; Lepri, F.; Ferese, R.; Cordeddu, V.; Martinelli, S.; Briuglia, S.; Digilio, M.C.; et al. Spectrum of MEK1 and MEK2 gene mutations in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome and genotype–phenotype correlations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, C. RASopathies and the skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavamura, M.I.; Leoni, C.; Neri, G. Dermatological manifestations, management, and care in RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessis, D.; Morice-Picard, F.; Bourrat, E.; Abadie, C.; Aouinti, S.; Baumann, C.; Best, M.; Bursztejn, A.-C.; Capri, Y.; Chiaverini, C.; et al. Dermatological manifestations in cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome: A prospective multicentric study of 45 mutation-positive patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Allanson, J.; Jadico, S.K.; Kavamura, M.I.; Noonan, J.; Opitz, J.M.; Young, T.; Neri, G. The cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, M.; Urban, J.; Zhu, G.; Rybak, I.; Terrell, J.R.; Qi, L.; McPherson, J.D.; Marghoob, A.A.; Rauen, K.A. RAS pathway influences the number of melanocytic nevi in cardiofaciocutaneous and Costello syndromes. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Guerriero, C.; Onesimo, R.; Coco, V.; Di Ruscio, C.; Acampora, A.; Esposito, I.; Romano, A.; Tartaglia, M.; Genuardi, M.; et al. Melanocytic nevi in RASopathies: Insights on dermatological diagnostic handles. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e83–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.H.; McKenzie, J.; Frieden, I.J.; Rauen, K.A. Dermatological findings in 61 mutation-positive individuals with cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onesimo, R.; Sforza, E.; Giorgio, V.; Viscogliosi, G.; Kuczynska, E.M.; Margiotta, G.; Perri, L.; Limongelli, D.; Proli, F.; De Rose, C.; et al. The “FEEDS (FEeding Eating Deglutition Skills)” over Time Study in Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome. Genes 2023, 14, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onesimo, R.; Giorgio, V.; Viscogliosi, G.; Sforza, E.; Kuczynska, E.; Margiotta, G.; Iademarco, M.; Proli, F.; Rigante, D.; Zampino, G.; et al. Management of nutritional and gastrointestinal issues in RASopathies: A narrative review. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, C.; Romeo, D.M.; Pelliccioni, M.; Di Già, M.; Onesimo, R.; Giorgio, V.; Flex, E.; Tedesco, M.; Tartaglia, M.; Rigante, D.; et al. Musculo-skeletal phenotype of Costello syndrome and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome: Insights on the functional assessment status. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, C.; Viscogliosi, G.; Onesimo, R.; Bisanti, C.; Massese, M.; Giorgio, V.; Corbo, F.; Tedesco, M.; Acampora, A.; Cipolla, C.; et al. Characterization of bone homeostasis in individuals affected by cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siano, M.A.; Pivonello, R.; Salerno, M.; Falco, M.; Mauro, C.; De Brasi, D.; Klain, A.; Sestito, S.; De Luca, A.; Pinna, V.; et al. Endocrine system involvement in patients with RASopathies: A case series. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1030398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crincoli, E.; Leoni, C.; Viscogliosi, G.; Onesimo, R.; Mattei, R.; Tartaglia, M.; Catania, F.; Rizzo, S.; Zampino, G.; Salerni, A. Systematic ophthalmologic evaluation in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome: A genotype-endophenotype correlation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2023, 191, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Triumbari, E.K.A.; Vollono, C.; Onesimo, R.; Podagrosi, M.; Giorgio, V.; Kuczynska, E.; Veltri, S.; Tartaglia, M.; Zampino, G. Pain in individuals with RASopathies: Prevalence and clinical characterization in a sample of 80 affected patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, Y.; Narumi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Niihori, T.; Kure, S.; Fujieda, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Aoki, Y. Leukemia in Cardio-facio-cutaneous (CFC) syndrome: A patient with a germline mutation in BRAF proto-oncogene. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2007, 29, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, C.P.; Franke, L.; Peters, H.; Kohlschmidt, N.; Kazmierczak, B.; Finckh, U.; Bier, A.; Eichhorn, B.; Blank, C.; Kraus, C.; et al. Cancer spectrum and frequency among children with Noonan, Costello, and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndromes. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niihori, T.; Aoki, Y.; Narumi, Y.; Neri, G.; Cavé, H.; Verloes, A.; Okamoto, N.; Hennekam, R.C.M.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Wieczorek, D.; et al. Germline KRAS and BRAF mutations in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rahawan, M.M.; Chute, D.J.; Sol-Church, K.; Gripp, K.W.; Stabley, D.L.; McDaniel, N.L.; Wilson, W.G.; Waldron, P.E. Hepatoblastoma and heart transplantation in a patient with cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2007, 143, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, G.; Gross, A.; Livinski, A.; Kratz, C.P.; Stewart, D.R. Cancer incidence and surveillance strategies in individuals with RASopathies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauen, K.A.; Maeda, Y.; Egense, A.; Tidyman, W.E. Familial cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome: Vertical transmission of the BRAF p. G464R pathogenic variant and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2021, 185, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurcă, M.C.; Iuhas, O.A.; Puiu, M.; Chiriţă-Emandi, A.; Andreescu, N.I.; Petcheşi, C.D.; Jurcă, A.D.; Magyar, I.; Jurcă, S.I.; Kozma, K.; et al. Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome—A longitudinal study of a case over 33 years: Case report and review of the literature. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 62, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.N.; John, A.M.; Handler, M.Z.; Schwartz, R.A. Neurofibromatosis type 1: New developments in genetics and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.E.; March, M.E.; Seiler, C.; Matsuoka, L.S.; Kim, S.E.; Kao, C.; Rubin, A.I.; Battig, M.R.; Khalek, N.; Schindewolf, E.; et al. Lymphatic disorders caused by mosaic, activating KRAS variants respond to MEK inhibition. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e155888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, A.; Carli, D.; Giorgio, E.; Villar, A.M.; Cardaropoli, S.; Carbonara, C.; Campagnoli, M.F.; Galletto, P.; Palumbo, M.; Olivieri, S.; et al. MEK Inhibition in a Newborn with RAF1-Associated Noonan Syndrome Ameliorates Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy but Is Insufficient to Revert Pulmonary Vascular Disease. Genes 2021, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andelfinger, G.; Marquis, C.; Raboisson, M.-J.; Théoret, Y.; Waldmüller, S.; Wiegand, G.; Gelb, B.D.; Zenker, M.; Delrue, M.-A.; Hofbeck, M. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Noonan Syndrome Treated by MEK-Inhibition. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2237–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisinski, K.B.; Flamand, Y.; Wilson, M.A.; Luke, J.J.; Tawbi, H.A.; Hong, F.; Mitchell, E.P.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Chen, H.; Gray, R.J.; et al. Trametinib in Patients With NF1-, GNAQ-, or GNA11-Mutant Tumors: Results From the NCI-MATCH ECOG-ACRIN Trial (EAY131) Subprotocols S1 and S2. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, e2200421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Morozumi, N.; Yoshikiyo, K.; Maeda, H.; Aoki, Y. C-type natriuretic peptide improves growth retardation in a mouse model of cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Moriya, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Miyagawa-Tomita, S.; Niihori, T.; Oba, D.; Ono, M.; Kure, S.; Ogura, T.; Matsubara, Y.; et al. New BRAF knockin mice provide a pathogenetic mechanism of developmental defects and a therapeutic approach in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6553–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, K.A.; Alsaegh, A.; Ben-Shachar, S.; Berman, Y.; Blakeley, J.; Cordeiro, I.; Elgersma, Y.; Evans, D.G.; Fisher, M.J.; Frayling, I.M.; et al. First International Conference on RASopathies and Neurofibromatoses in Asia: Identification and advances of new therapeutics. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiessner, M.; Maroofian, R.; Ni, M.-Y.; Pedroni, A.; Müller, J.S.; Stucka, R.; Beetz, C.; Efthymiou, S.; Santorelli, F.M.; Alfares, A.A.; et al. Biallelic variants in HPDL cause pure and complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia. Brain 2021, 144, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworschak, G.C.; Punetha, J.; Kalanithy, J.C.; Mingardo, E.; Erdem, H.B.; Akdemir, Z.C.; Karaca, E.; Mitani, T.; Marafi, D.; Fatih, J.M.; et al. Biallelic and monoallelic variants in PLXNA1 are implicated in a novel neurodevelopmental disorder with variable cerebral and eye anomalies. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epi25 Collaborative. Sub-genic intolerance, ClinVar, and the epilepsies: A whole-exome sequencing study of 29,165 individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkervoort, S.; Kutzner, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Lornage, X.; Rendu, J.; Stojkovic, T.; Baets, J.; Neuhaus, S.B.; Tanboon, J.; Maroofian, R.; et al. Pathogenic Variants in the Myosin Chaperone UNC-45B Cause Progressive Myopathy with Eccentric Cores. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 1078–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari, S.; Musante, I.; Iacomino, M.; Zara, F.; Salpietro, V.; Scudieri, P. Brain Organoids as Model Systems for Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 590119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.M.; Punetha, J.; Zheng, C.; Mazaheri, N.; Rad, A.; Efthymiou, S.; Petersen, A.; Dehghani, M.; Pehlivan, D.; Partlow, J.N.; et al. Homozygous Missense Variants in NTNG2, Encoding a Presynaptic Netrin-G2 Adhesion Protein, Lead to a Distinct Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, F.; Morabito, R.; Mormina, E.; Alafaci, C.; Marino, S.; Laganà, A.; Vinci, S.L.; Briguglio, M.; Calamuneri, A.; Gaeta, M.; et al. 3T Double Inversion Recovery Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Diagnostic advantages in the evaluation of cortical development anomalies. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpietro, V.; Zollo, M.; Vandrovcova, J.; Ryten, M.; Botia, J.A.; Ferrucci, V.; Manole, A.; Efthymiou, S.; Al Mutairi, F.; Bertini, E.; et al. The phenotypic and molecular spectrum of PEHO syndrome and PEHO-like disorders. Brain 2017, 140, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, M.; Polizzi, A.; Schepis, C.; Morano, M.; Strano, S.; Belfiore, G.; Palmucci, S.; Foti, P.V.; Pirrone, C.; Roggini, M.; et al. Cutis tricolor: A literature review and report of five new cases. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2016, 6, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Salpietro, V.; Phadke, R.; Hargreaves, I.P.; Batten, L.; McElreavy, K.; Pitt, M.; Mankad, K.; Wilson, C.; Cutrupi, M.C.; et al. Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2D and optic nerve atrophy further expand the spectrum associated with selenoprotein biosynthesis deficiency. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | OMIM Number | Prevalence | Inheritance | CFC Phenotypic Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRAF | *164757 | 75% |
| Moderate to severe polymorphic seizures (+exons 11–16) 57% Moderate ID 89% Motor delay and hypotonia (unable to walk, needing support) 29% Cardiac disease 72% Greater risk of skin abnormalities Ocular hypertelorism, optic nerve hypoplasia Tumors (+melanoma, thyroid, colorectal, and ovarian cancers, benign nevi, premalignant colon polyps 8% Pulmonary stenosis 50% |
| MAP2K1 | *176872 | 25% | De novo missense heterozygous variants | Moderate to severe polymorphic seizures (+p.Y130C/H/N variant, exon 3) 61% Mild ID 84% Motor delay and hypotonia (unable to walk, needing support) 71% Cardiac disease (lower frequency, NA) Macrocephaly, high forehead, bitemporal constriction, hypoplasia of the supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures Musculoskeletal abnormalities |
| MAP2K2 | *601263 | 25% |
| Lower risk of seizure occurrence and less severe seizure types 30% Mild ID 25% Motor delay and hypotonia (unable to walk, needing support) 13% Cardiac disease 64% Macrocephaly, high forehead, bitemporal constriction, hypoplasia of the supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures |
| KRAS | *190070 | 2% |
| No epilepsy Neurodevelopmental delay Coarse face Cardiac defects |
| YWHAZ | *601288 | Rarely, NA | De novo missense heterozygous variants | Developmental delay, behavioural disorders ID Short stature Motor and speech delay Triangular facies, ptosis Seizures Feeding problems |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scorrano, G.; David, E.; Calì, E.; Chimenz, R.; La Bella, S.; Di Ludovico, A.; Di Rosa, G.; Gitto, E.; Mankad, K.; Nardello, R.; et al. The Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome: From Genetics to Prognostic–Therapeutic Implications. Genes 2023, 14, 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122111
Scorrano G, David E, Calì E, Chimenz R, La Bella S, Di Ludovico A, Di Rosa G, Gitto E, Mankad K, Nardello R, et al. The Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome: From Genetics to Prognostic–Therapeutic Implications. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122111
Chicago/Turabian StyleScorrano, Giovanna, Emanuele David, Elisa Calì, Roberto Chimenz, Saverio La Bella, Armando Di Ludovico, Gabriella Di Rosa, Eloisa Gitto, Kshitij Mankad, Rosaria Nardello, and et al. 2023. "The Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome: From Genetics to Prognostic–Therapeutic Implications" Genes 14, no. 12: 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122111
APA StyleScorrano, G., David, E., Calì, E., Chimenz, R., La Bella, S., Di Ludovico, A., Di Rosa, G., Gitto, E., Mankad, K., Nardello, R., Mangano, G. D., Leoni, C., & Ceravolo, G. (2023). The Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome: From Genetics to Prognostic–Therapeutic Implications. Genes, 14(12), 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122111







