Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships and Unveiling Novel Genetic Diversity among Slow and Pygmy Lorises, including Resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
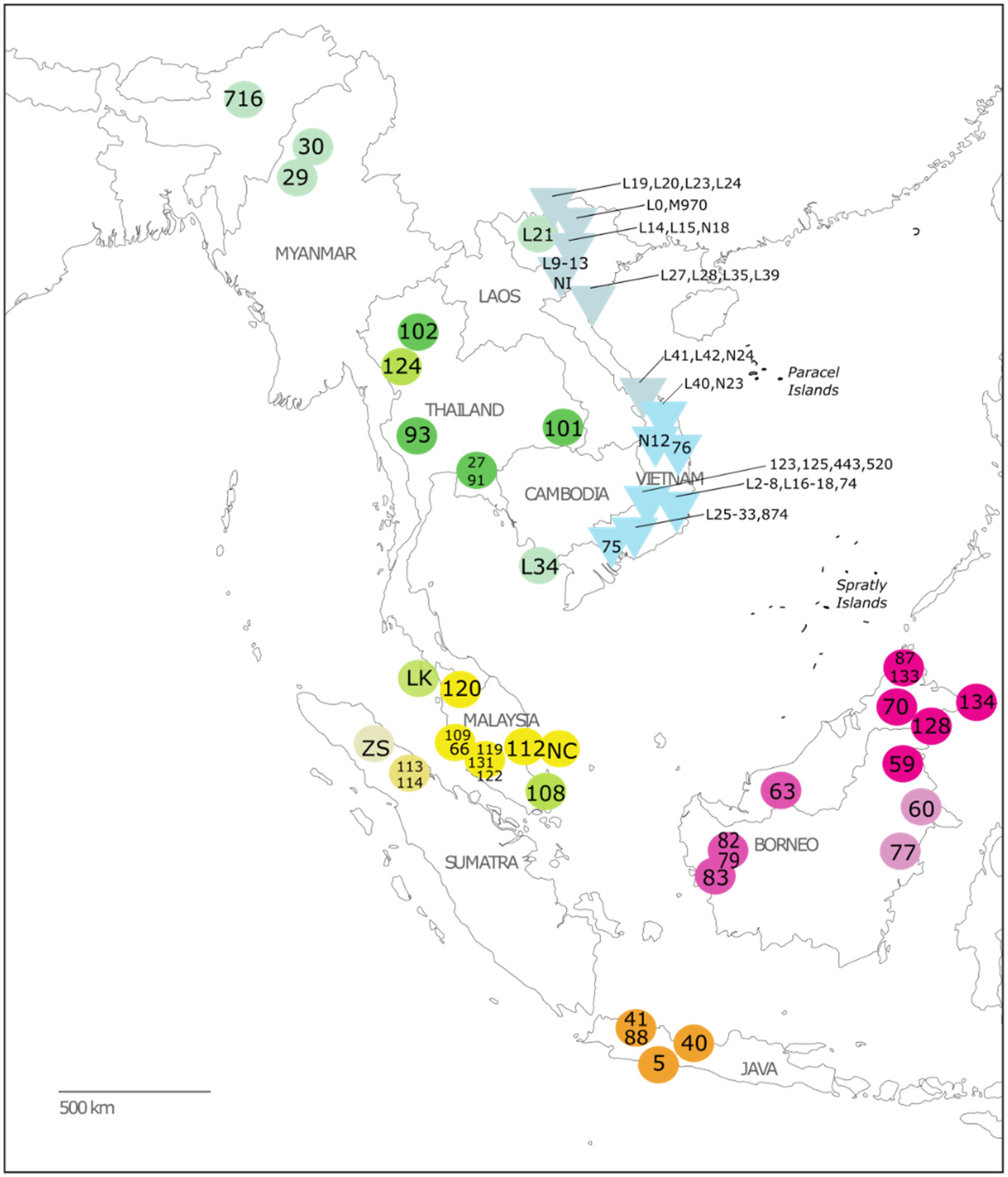
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Molecular Data Collection
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
| Species Name | English Name | Specimen No. | Map ID | Provider | Provenance | Clade | Reference | Genbank Acc. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | AMNH20870 | 26 | AMNH | Zoo origin | 1-m | This study | OQ518055 OQ555566 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | FMNH98478 | 131 | FMNH | Malaysia, Bentong | 1-m | This study | OQ518069 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | NMNH283915 | 116 | NMNH | Malaysia | 1-m | This study | OQ518063 OQ555488 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | NMNH300000 | 66 | NMNH | Malaysia, Selangor | 1-m | This study | OQ518056 OQ555477 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | NMNH355347 | 109 | NMNH | Malaysia, Selangor | 1-m | This study | OQ518058 |
| N. coucang insularis | Sunda slow loris | NC040292 | NC | J. Rovie- Ryan | Malaysia, Tioman Island | 1-m | [49] | NC040292 |
| N. coucang malayanus | Sunda slow loris | NMNH488075 | 112 | NMNH | Malaysia, Pahang | 1-m | This study | OQ518062 OQ555486 |
| N. coucang malayanus | Sunda slow loris | NMNH488076 | 120 | NMNH | Malaysia, Perak | 1-m | This study | OQ518066 OQ555489 |
| N. coucang malayanus | Sunda slow loris | NMNH488078 | 119 | NMNH | Malaysia, Selangor | 1-m | This study | OQ518065 OQ555478 |
| N. coucang malayanus | Sunda slow loris | NMNH488079 | 122 | NMNH | Malaysia, Selangor | 1-m | This study | OQ518068 OQ555491 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | aDNA716 | 716 | NHMUK | India, Kohima, Naga Hills, Assam | 1-nb | This study | OQ518145 OQ555539 OQ555565 |
| N. bengalensis+ | Bengal slow loris | AJ309867 | AJ | Unknown | Unknown | 1-nb | [50] | AJ309867 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | AMNH112990 | 30 | AMNH | N. Burma, Chindwin River below Haibum, Sagaing | 1-nb | This study | OQ518075 OQ555497 OQ555542 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | AMNH112991 | 29 | AMNH | N. Burma, Singkaling Hkamti, Sagaing | 1-nb | This study | OQ518074 OQ555496 OQ555541 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | KC977312 | KC9 | H. Somura | Japan, Nasu World Monkey Park | 1-nb | [51] | KC977312 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | L21 | L21 | M. Le | Vietnam, Sa Pa | 1-nb | This study | OQ518071 OQ555519 OQ555560 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | L34 | L34 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Phú Quốc Island | 1-nb | This study | OQ518073 OQ555532 OQ555561 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH300015 | 99 | NMNH | Thailand | 1-nb | This study | OQ518077 OQ555482 OQ555550 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | AMNH240010 | 27 | AMNH | Thailand, Chanthaburi, E Base Khao Sai Dao Tai | 1-tb | This study | OQ518085 OQ555540 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | KC757405 | KC7 | H. Schulze | Unknown (zoo origin) | 1-tb | [52] | KC757405 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH296513 | 93 | NMNH | Thailand, Kanchanaburi | 1-tb | This study | OQ518086 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH355064 | 102 | NMNH | Thailand, Chiang Mai | 1-tb | This study | OQ518088 OQ555484 OQ555552 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH535153 | 101 | NMNH | Thailand, Ubon Ratchathani | 1-tb | This study | OQ518087 OQ555483 OQ555551 |
| N. hilleri | Sumatran slow loris | NMNH267400 | 114 | NMNH | Sumatra, Siantar | 1-h | This study | OQ518054 OQ555487 OQ555554 |
| N. hilleri | Sumatran slow loris | NMNH270595 | 113 | NMNH | Sumatra, Siantar | 1-h | This study | OQ518053 OQ555553 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | LANGKAWI | LK | B. Md Zain | Malaysia, Langkawi Island | 1 | [32] | OQ466050 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH114151 | 108 | NMNH | Malaysia, Johor Lama | 1 | This study | OQ518078 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | NMNH258870 | 91 | NMNH | E Thailand, Chanthaburi | 1 | This study | OQ518076 OQ555481 OQ555549 |
| N. bengalensis | Bengal slow loris | FMNH99616 | 124 | FMNH | Thailand, Tak, Mae Sod, Ban Mae Lamao | 1 | This study | OQ518079 OQ555492 OQ555555 |
| N. coucang tenasserimensis | Sunda slow loris | NMNH84389 | 105 | NMNH | Thailand | 1 | This study | OQ518052 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | NMNH14290 | 95 | NMNH | Unknown | n | This study | OQ555476 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | NJAV | NJ | H. Schulze | Java | 2 | [21] | KP410612 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | N3 | N3 | H. Schulze | Java | 2 | [21] | KP410601 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | AMNH106013 | 59 | AMNH | Borneo, Peleben, Timur | 3 | This study | OQ518097 OQ555543 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | FMNH108856 | 133 | FMNH | Borneo, Sabah, Mt. Kinabalu | 3 | This study | OQ518099 OQ555494 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | NMNH292553 | 87 | NMNH | Borneo, Sabah, Mt. Kinabalu | 3 | This study | OQ518100 OQ555547 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | NMNH317188 | 70 | NMNH | Borneo, Sabah, Ranau | 3 | This study | OQ518098 OQ555479 OQ555546 |
| N. menagensis | Philippine slow loris | FMNH129502 | 134 | FMNH | Philippines, Tawi Tawi | 3 | This study | OQ518102 |
| N. menagensis | Philippine slow loris | FMNH85926 | 128 | FMNH | Borneo, Sabah, Tawau | 3 | This study | OQ518101 OQ555493 OQ555556 |
| N. bancanus | Sody’s slow loris | NMNH142237 | 82 | NMNH | Borneo, W Kalimantan, Sanggau | 4 | This study | OQ518092 OQ555480 |
| N. borneanus | Bornean slow loris | AMNH17133 | 61 | AMNH | Zoo origin | 4 | This study | OQ518090 OQ555545 |
| N. borneanus | Bornean slow loris | NMNH142232 | 83 | NMNH | Borneo, W Kalimantan, Landak River | 4 | This study | OQ518093 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | AMNH16616 | 34 | AMNH | Likely zoo or trade origin, tag notes ‘Singapore’ | 4 | This study | OQ518094 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | NMNH142239 | 79 | NMNH | Borneo, W Kalimantan, Sanggau | 4 | This study | OQ518095 |
| N. menagensis | Phillippine slow loris | AMNH32649 | 63 | AMNH | Borneo, Ft. Kapit | 4 | This study | OQ518091 |
| N. kayan | Kayan slow loris | AMNH106012 | 60 | AMNH | Borneo, Peleben, Timur, Sungai Tajan | 5 | This study | OQ518089 OQ555544 |
| N. menagensis | Phillippine slow loris | NMNH198857 | 77 | NMNH | Borneo, E Kalimantan, Samarinda | 5 | This study | OQ518096 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | AMNH101509 | 41 | AMNH | Java, Soemedang | 6 | This study | OQ518084 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | AMNH102027 | 5 | AMNH | Java, Tasikmalaja, Tjamis | 6 | This study | OQ518080 OQ555567 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | AMNH102845 | 40 | AMNH | Java, Cheribon | 6 | This study | OQ518081 |
| N. javanicus | Javan slow loris | NMNH521836 | 88 | NMNH | Java, Tjilegong | 6 | This study | OQ518083 OQ555474 OQ555548 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | NCOU751 | 751 | Singapore Zoo | Malaysian Peninsula | 7 | [21] | KP410655 |
| N. coucang | Sunda slow loris | ZSM3 | ZS | ZSM | Sumatra, Batang Kwis | 7 | [21] | KP410591 |
| X. intermedius | Northern pygmy loris | L0 | L0 | Huấn | Vietnam, Na Hang Nature Reserve, Tuyên Quang | 8 | This study | OQ518127 OQ555498 OQ555557 |
| X. intermedius | Northern pygmy loris | KX397281 | KX | Q. Ni | China, Geiju Zoo | 8 | [53] | KX397281 |
| X. intermedius | Northern pygmy loris | L41 | L41 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Mương Lọ, Nam Đồng, Thừa Thiên Huế | 8 | This study | OQ518142 OQ555536 OQ555562 |
| X. intermedius | Northern pygmy loris | L42 | L42 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Nam Đồng, Thừa Thiên Huế | 8 | This study | OQ518143 OQ555537 OQ555563 |
| X. intermedius | Northern pygmy loris | HZM1001 | N24 | Vũ Ngọc Thành | Vietnam, Nam Giang, Quảng Nam | 8 | This study | OQ518144 OQ555538 |
| X. pygmaeus | Southern pygmy loris | HZM1000 | N23 | Vũ Ngọc Thành | Vietnam, Chaval, Nam Giang, Quảng Nam | 9 | This study | OQ555564 |
| X. pygmaeus | Southern pygmy loris | L2 | L2 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Lâm Đồng | 9 | This study | OQ518109 OQ555500 OQ555558 |
| X. pygmaeus | Southern pygmy loris | L6 | L6 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Lâm Đồng | 9 | This study | OQ518113 OQ555504 OQ555559 |
| X. pygmaeus | Southern pygmy loris | L40 | L40 | M. Blair | Vietnam, Thương Nhạt, Nam Đồng, Thừa Thiên Huế | 9 | This study | OQ555535 |
| L. tardigradus | Red slender loris | NC012763 | - | Outgroup | [54] | NC012763 | ||
| G. moholi | Mohol bushbaby | KC757396 | - | Outgroup | [52] | KC757396 |
3. Results
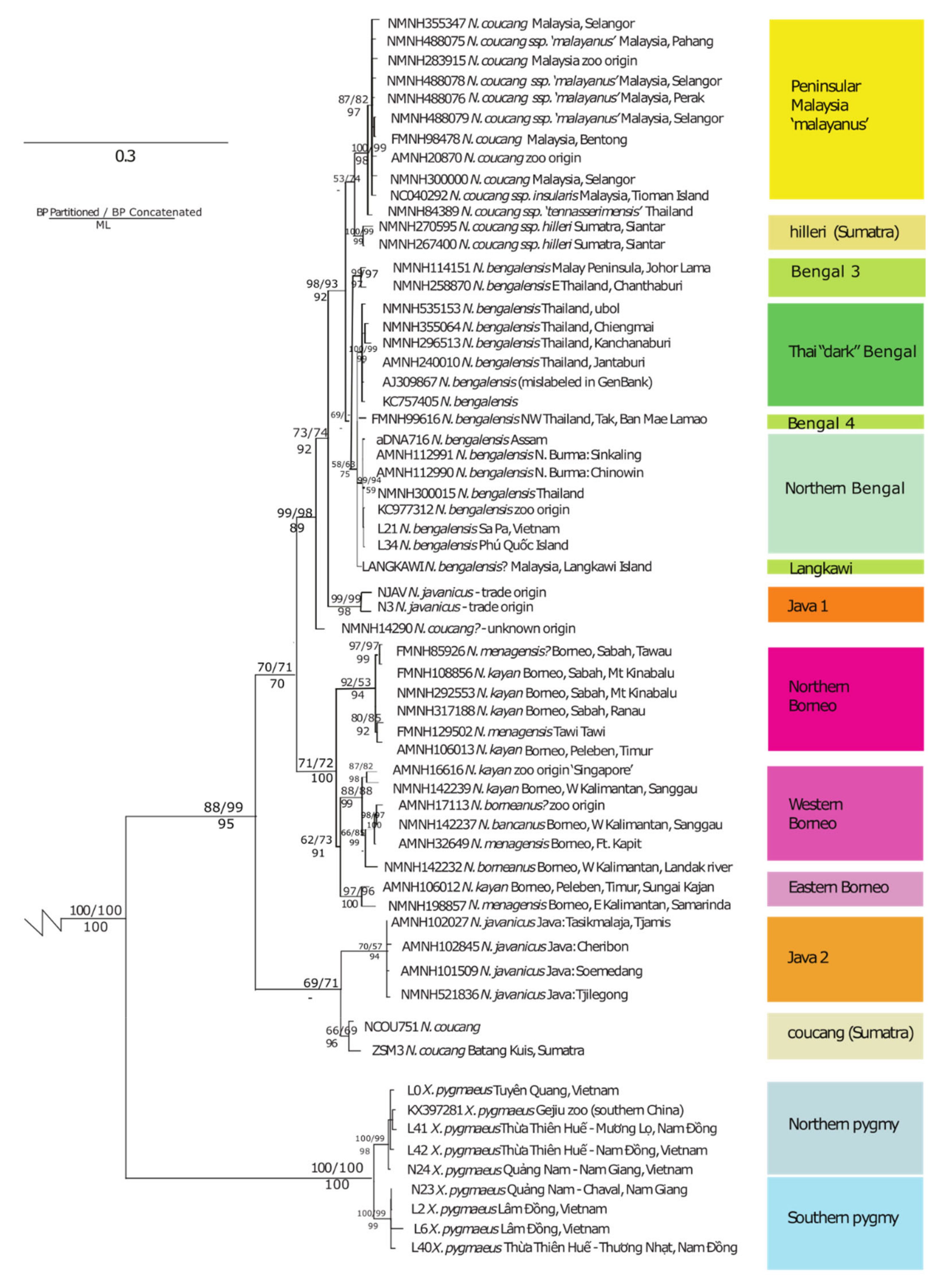
3.1. Inference of Phylogenetic Relationships
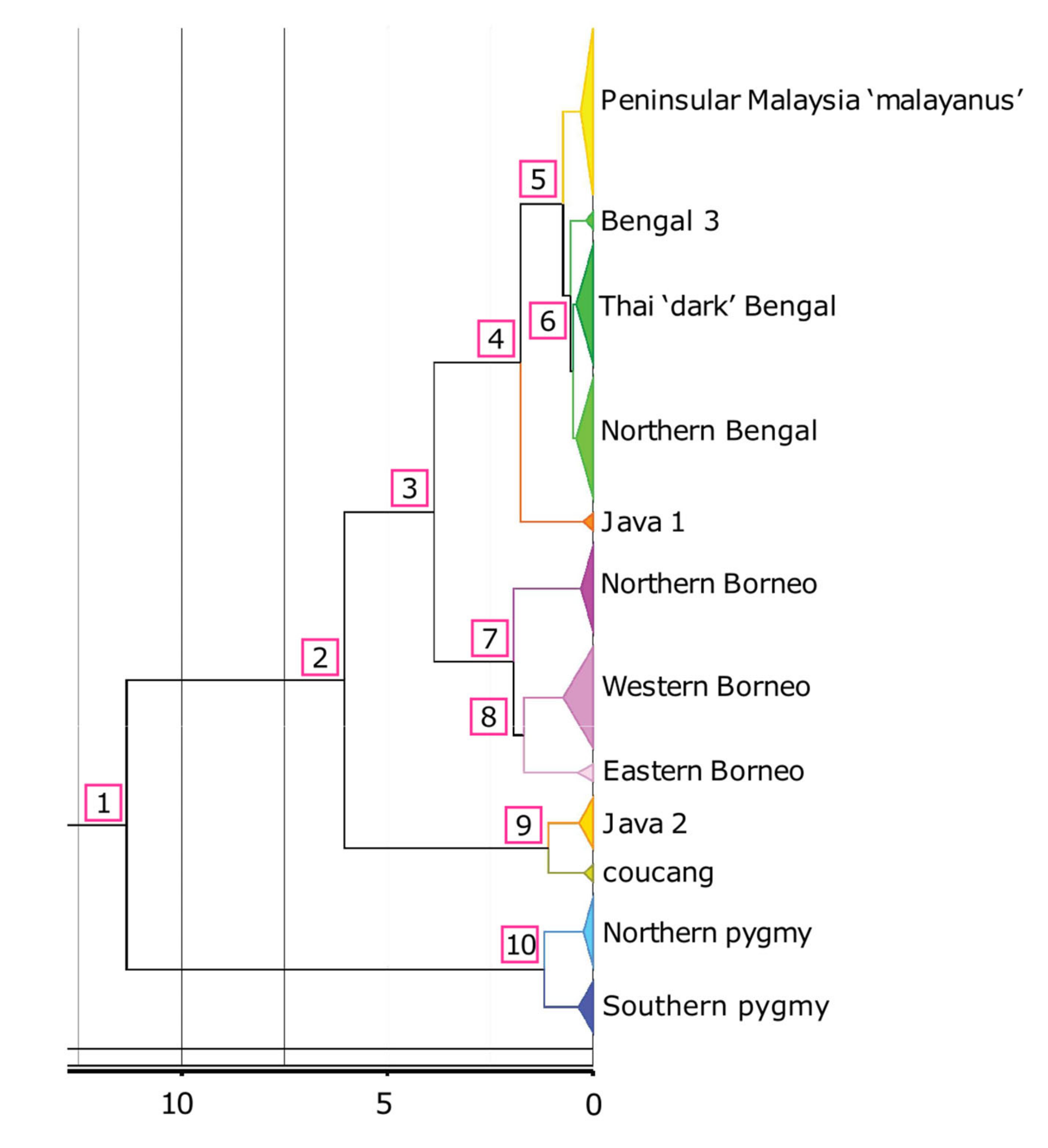
3.2. Divergence Dating
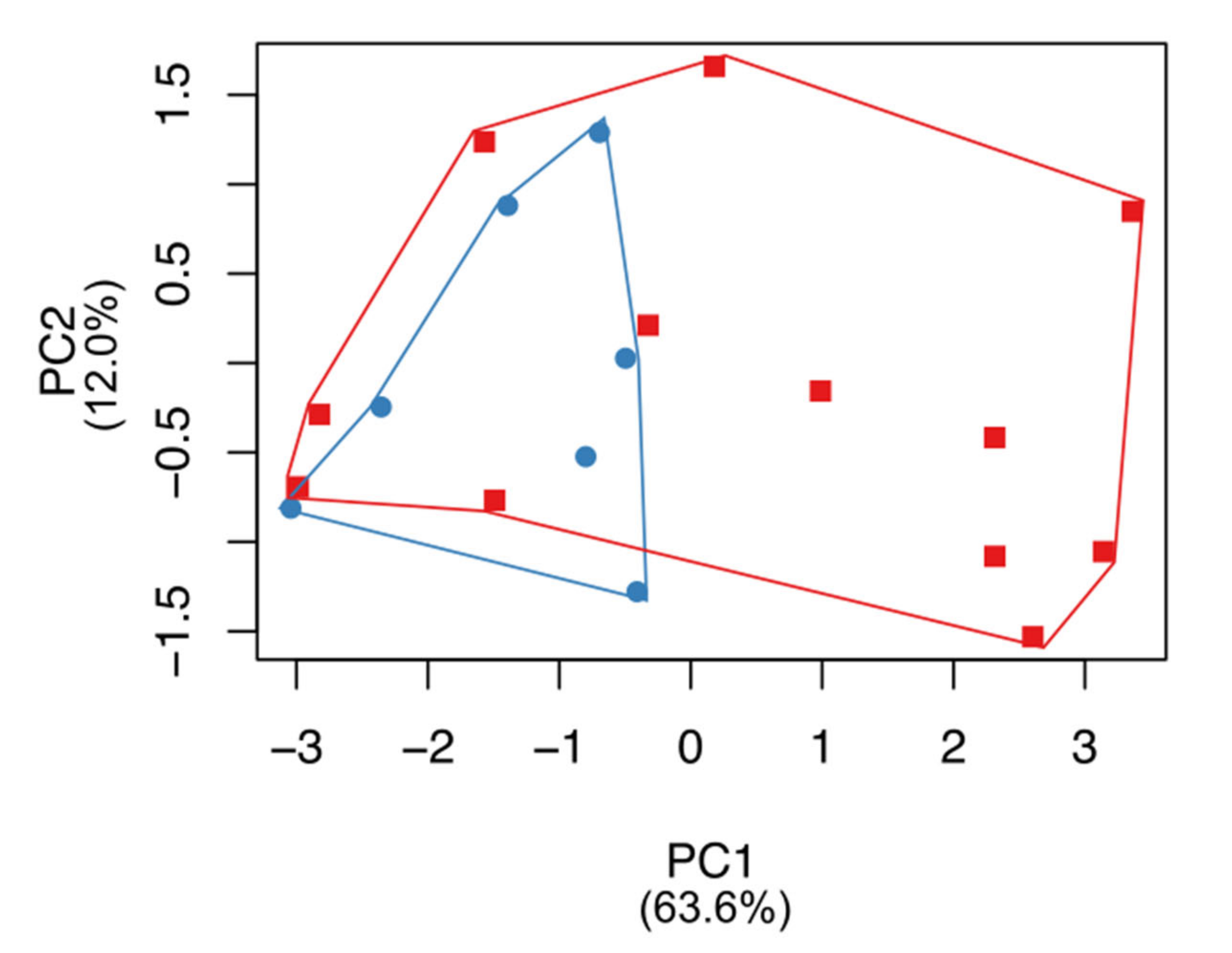
3.3. Craniometric Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Pygmy Lorises: Ancient Divergence and Novel Diversity
Redescription of X. intermedius and X. pygmaeus
4.2. Support for Additional Diversity within Nycticebus
4.3. Placement of N. javanicus
4.4. Historical Wildlife Trade and Issues of Known Provenance
4.5. Informing Conservation Management
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, E.; Speller, C.F. Novel Substrates as Sources of Ancient DNA: Prospects and Hurdles. Genes 2017, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guschanski, K.; Krause, J.; Sawyer, S.; Valente, L.M.; Bailey, S.; Finstermeier, K.; Savolainen, V. Next-Generation Museomics Disentangles One of the Largest Primate Radiations. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrell, A.S.; Disotell, T.R.; Bergey, C.M. The use of museum specimens with high-throughput DNA sequencers. J. Hum. Evol. 2015, 79, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, L.; Roos, C.; Blair, M.E. Molecular Advances in Lorisid Taxonomy and Phylogeny. Evolution, Ecology and Conservation of Lorises and Pottos.; Nekaris, K.A.I., Burrows, A.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 57–66. ISBN 9781108429023. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, M.E.; Sterling, E.J.; Hurley, M.M. Taxonomy and conservation of Vietnam’s primates: A review. Am. J. Primatol. 2011, 73, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.M. The role of taxonomy in species conservation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, C.; Boonratana, R.; Supriatna, J.; Fellowes, J.; Groves, C.; Nash, S.; Mittermeier, R.A. An Updated Taxonomy and Conservation Status Review of Asian Primates. Asian Primates 2014, 4, 2–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Nijman, V. CITES proposal highlights rarity of Asian nocturnal primates (Lorisidae: Nycticebus). Folia Primatol. 2007, 78, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekaris, K.A.I. Extreme Primates: Ecology and Evolution of Asian Lorises. Evol. Anthr. 2014, 23, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijman, V.; Spaan, D.; Rode-Margono, E.J.; Wirdateti, K.A.I.N. Changes in the primate trade in Indonesian wildlife markets over a 25-year period: Fewer apes and langurs, more macaques, and slow lorises. Am. J. Primatol. 2017, 79, e22517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thạch, H.M.; Le, M.D.; Vu, N.B.; Panariello, A.; Sethi, G.; Sterling, E.J.; Blair, M.E. Slow Loris Trade in Vietnam: Exploring Diverse Knowledge and Values. Folia Primatol. 2018, 89, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Groves, C. Asian lorises: Taxonomic problems caused by illegal trade. In Conservation of Primates in Vietnam; Nadler, T., Streicher, U., Ha, T.L., Eds.; Frankfurt Zoological Society: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2004; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon, M.; Streicher, U.; Loung, H.; Tran, T.; Tran, M.; Vo, B.; Cronin, A. Survival of reintroduced pygmy slow loris Nycticebus pygmaeus in South Vietnam. Endanger. Species Res. 2014, 25, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.E.; Le, M.D.; Thach, H.M.; Panariello, A.; Vu, N.B.; Birchette, M.G.; Sethi, G.; Sterling, E.J. Applying systems thinking to inform studies of wildlife trade in primates. Am. J. Primatol. 2017, 79, e22715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, C.; Maryanto, I. Craniometry of slow lorises (genus Nycticebus) of insular Southeast Asia. In Primates of the Oriental Night; Shekelle, M., Maryanto, I., Groves, C., Schulze, H., Fitch-Snyder, H., Eds.; LIPI Press: Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta, Indonesia, 2008; pp. 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Munds, R.; Nekaris, K.A.I.; Ford, S. Taxonomy of the Bornean Slow Loris, with new Species Nycticebus kayan (Primates, Lorisidae). Am. J. Primatol. 2013, 75, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C.; Vu, N.T.; Walter, L.; Nadler, T. Molecular systematics of Indochinese primates. Vietnam. J. Primatol. 2007, 1, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Nijman, V. A new genus name for pygmy lorises, Xanthonycticebus gen. nov. (Mammalia, Primates). Zoosystematics Evol. 2022, 98, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydekker, R. On two lorises. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1904, 2, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Jaffe, S. Unexpected diversity within the Javan slow loris trade: Implications for slow loris taxonomy. Contrib. Zool. 2007, 76, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, L.; Nekaris, K.A.; Perkin, A.; Bearder, S.K.; Pimley, E.R.; Schulze, H.; Streicher, U.; Nadler, T.; Kitchener, A.C.; Zischler, H.; et al. Remarkable ancient divergences amongst neglected lorisiform primates. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 175, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, J.C. Sluggards and Drunkards? A History of the Discovery and Description of the Afro-Asian Lorisidae. In Ecology and Conservation of Lorises and Pottos; Nekaris, K.A.I., Burrows, A.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, H. Conservation Database for Lorises (Loris, Nycticebus) and Pottos (Arctocebus, Perodicticus), Prosimian Primates. Available online: www.loris-conservation.org/database (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Streicher, U. Seasonal changes in colouration and fur pattern in the pygmy loris (Nycticebus pygmaeus). In Conservation of Primates in Vietnam; Nadler, T., Streicher, U., Ha, T.L., Eds.; Frankfurt Zoological Society: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2004; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, C. Taxonomy and biogeography of primates in Vietnam and neighbouring regions. In Conservation of Primates in Vietnam; Nadler, T., Streicher, U., Ha, T.L., Eds.; Frankfurt Zoological Society: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2004; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Meijaard, E.; Groves, C. The geography of mammals and rivers in Mainland Southeast Asia. In Primate Biogeography: Progress and Prospects; Lehman, S.M., Fleagle, J.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 305–330. [Google Scholar]
- Bett, N.N.; Blair, M.E.; Sterling, E.J. Ecological niche conservatism in Doucs (Genus Pygathrix). Int. J. Primatol. 2012, 33, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, N.T.; Mootnick, A.R.; Vu, N.T.; Nadler, T.; Roos, C. A new species of crested gibbon, from the central Annamite mountain range. Vietnam. J. Primatol. 2010, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- White, L.; Edwards, A. Methods for assessing the status of animal populations. In Conservation Research in the African Rain Forests: A Technical Handbook; White, L., Edwards, A., Eds.; Wildlife Conservation Society: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 91–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Blackham, G.V.; Nijman, V. Conservation implications of low encounter rates of five nocturnal primate species (Nycticebus spp.) in Asia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, C.; Nekaris, K.A.I.; Streicher, U.; Leung, L. Field surveys of the threatened pygmy slow loris (Nycticebus pygmaeus) using local knowledge in Mondulkiri Province, Cambodia. Oryx 2011, 45, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md-Zain, B.M.; Mohhoyua, K.S.; Aifat, N.R.; Yaakop, S.; Rovie-Ryan, J.J.; Mohd-Ridwan, A.R.; Blair, M.E.; Abdul-Latiff, M.A.B. Molecular Data Confirms the Presence of Nycticebus bengalensis on Langkawi Island, Malaysia. Biodiversitas 2019, 20, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C.; Helgen, K.M.; Miguez, R.P.; Thant, N.M.L.; Lwin, N.; Lin, A.K.; Yi, K.M.; Soe, P.; Hein, Z.M.; Myint, M.N.N.; et al. Mitogenomic phylogeny of the Asian colobine genus Trachypithecus with special focus on Trachypithecus phayrei (Blyth, 1847) and description of a new species. Zool Res. 2020, 41, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Desalle, R. Mitochondrial DNA extraction and sequencing of formalin-fixed archival snake tissue. Mitochondrial DNA 2008, 19, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, M.J.; Meyers, G.L.; Kolokotronis, S.-O.; Leslie, M.S.; Martin, A.P.; Amato, G. Barcoding bushmeat: Molecular identification of Central African and South American harvested vertebrates. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 1389–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M.; Kocher, T.D.; Wilson, A.C. Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 32, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Raxworthy, C.J.; Mccord, W.P.; Mertz, L. A molecular phylogeny of tortoises (Testudines: Testudinidae) based on mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2006, 40, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohland, N.; Hofreiter, M. Comparison and optimization of ancient DNA extraction. Biotechniques 2006, 42, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Bui, M.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J.A.A.; Ronquist, F.; Huelsenback, J.P.; Nieves-Aldrey, J.L. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of combined data. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandley, M.C.; Schmitz, A.; Reeder, T.W. Partitioned Bayesian analyses, partition choice, and the phylogenetic relationships of scincid lizards. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partition models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PloS Biol. 2006, 4, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, L.; Disotell, T.R.; Masters, J.C. A multilocus phylogeny reveals deep lineages within African galagids (Primates: Galagidae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovie-Ryan, J.J.; Gani, M.; Gan, H.M.; Bolongon, G.G.; Cheng, T.C.; Razak, N.; Rosli, N.; Aziz, M.A.; Matkasim, K. Rediscovery of Nycticebus coucang insularis Robinson, 1917 (Primates: Lorisidae) at Tioman Island and its Mitochondrial Genetic Assessment. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 2533–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnason, U.; Gullberg, A.; Burguete, A.S.; Janke, A. Molecular estimates of primate divergences and new hypotheses for primate dispersal and the origin of modern humans. Hereditas 2000, 133, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somura, H.; Hori, H.; Manome, Y. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial DNAs of 12S rRNA, 16S rRNA, and cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 (COI) regions in slow lorises (Genus Nycticebus) may contribute to improved identification of confiscated specimens. ISRN Zool. 2012, 2012, 498731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstermeier, K.; Zinner, D.; Brameier, M.; Meyer, M.; Kreuz, E.; Hofreiter, M.; Roos, C. A mitogenomic phylogeny of living primates. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, E69504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.; He, X.; Xie, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence for the Nycticebus pygmaeus (Primates, Lorisidae). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2016, 8, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, A.; Rakotondraparany, F.; Munechika, I.; Hasegawa, M.; Horai, S. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of prosimians based on complete sequences of mitochondrial DNAs. Gene 2009, 441, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, J.E.; Weisrock, D.W.; Embry, S.L.; Fiorentino, I.; Balhoff, J.P.; Kappeler, P.; Wray, G.A.; Willard, H.F.; Yoder, A.D. Development and application of a phylogenomic toolkit: Resolving the evolutionary history of Madagascar’s lemurs. Genome. Res. 2008, 18, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Tian, H.Y.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shao, Y.; Xiong, Z.-J.; Qi, X.-G.; Cooper, D.N.; et al. Functional genomics analysis reveals the evolutionary adaptation and demographic history of pygmy lorises. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2123030119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munds, R.A.; Titus, C.L.; Eggert, L.S.; Blomquist, G.E. Using a multi-gene approach to infer the complicated phylogeny and evolutionary history of lorises (Order Primates: Family Lorisidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 127, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, P.; Johnson, W.E.; Roos, C.; Seuanez, H.N.; Horvath, J.E.; Moreira, M.A.M.; Kessing, B.; Pontius, J.; Roelke, M.; Rumpler, Y.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of living primates. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, C.T.H. Conservation of the Slow Loris: Using Molecular Approaches to Study Genetic Diversity of Populations in Vietnam. Department of Genetics. Bachelor’s Honors Thesis, Vietnam National University, Hanoi University of Science, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2015; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Ravosa, M.J. Cranial allometry and geographic variation in slow lorises (Nycticebus). Am. J. Primatol. 1998, 45, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhote, J.L. On a collection of mammals made by Dr Vassal in Annam. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1907, 77, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, V.T. Sur une nouvelle espèce de Nycticebus au Vietnam. Zool. Anz. 1960, 164, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, C. Systematics of the genus Nycticebus. In Taxonomy, Anatomy, Reproduction. Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Primatology; Beigert, J., Leutenegger, W., Eds.; S Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1971; Volume 1, pp. 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Chen, Z.P.; Shi, L.M. Phylogeny of the Slow Lorises (Genus Nycticebus)—An Approach Using Mitochondrial-DNA Restriction Enzyme Analysis. Int. J. Primatol. 1993, 14, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, L.; Freed, B.Z. Description and survey of three Nycticebus species in Bolikhamxay Province, Laos. Primate Eye 1997, 63, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Brandon-Jones, D.; Eudey, A.A.; Geissmann, T.; Groves, C.P.; Melnick, D.J.; Morales, J.C.; Shekelle, M.; Stewart, C.-B. Asian primate classification. Int. J. Primatol. 2004, 25, 97–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, J.W. Field sightings of the pygmy loris, Nycticebus pygmaeus, in Laos. Folia Primatol. 1994, 63, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, R.H.; Hurley, M.M. A biogeographic synthesis of the amphibians and reptiles of Indochina. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2011, 360, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, E.J.; Hurley, M.M. Le Duc Minh. Vietnam: A Natural History; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, M.E.; Sterling, E.J.; Dusch, M.; Raxworthy, C.; Pearson, R.G. Ecological divergence and speciation in Eulemur sister species. J. Evol. Biol. 2013, 26, 1790–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Bearder, S.K. The strepsirrhine primates of Asia and Mainland Africa: Diversity shrouded in darkness. In Primates in Perspective, 2nd ed.; Campbell, C., Fuentes, A., Mackinnon, K.C., Bearder, S.K., Stumpf, R.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 24–45. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, C. Systematics of Tarsiers and Lorises. Primates 1998, 39, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Pan, D.; Groves, C.; Wang, Y.X.; Narushima, E.; Fitch-Snyder, H.; Crow, P.; Thanh, V.N.; Ryder, O.; Zhang, H.W.; et al. Molecular phylogeny of Nycticebus inferred from mitochondrial genes. Int. J. Primatol. 2006, 27, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubback, T.R.; Chasem, F.N.; Tan, C.L.; Elphick, H.; Forbes, J.T. Report of the Wild Animals and Wild Birds Committee; Government Printing Office: Singapore, 1933.
- Hornaday, W.T. The Experiences of a Hunter and Naturalist in India, Ceylon, the Malay Peninsula and Borneo; Oxford University Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, F. The beastly business of regulating the wildlife trade in colonial Singapore. In Nature Contained: Environmental Histories of Singapore; Barnard, T., Ed.; National University of Singapore Press: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, D.H. Ecology, biology and conservation status of prosimian species in Vietnam. Folia Primatol. 1998, 69 (Suppl. 1), 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/en (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- MARD. Decision 628. Urgent Conservation Action Plan for Primates in Vietnam to 2025, Vision to 2030; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD), 87; The Prime Minister of Government, Socialist Republic of Vietnam: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2017.
- Campera, M.; Brown, E.; Imron, M.A.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Unmonitored releases of small animals? The importance of considering natural dispersal, health, and human habituation when releasing a territorial mammal threatened by wildlife trade. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 242, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongrit, C.; Markviriya, D.; Laithong, P.; Khudamrongsawat, J. Species Identification and Unlocking Hidden Genetic Diversity of Confiscated Slow Lorises (Nycticebus spp.) Based on Mitochondrial DNA Markers. Folia Primatol. 2020, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | n | |
| 1 | 0.0056 | 0.0132 | 0.05 | 0.0483 | 0.043 | 0.0537 | 0.0372 | 0.1218 | 0.1256 | 0.0218 |
| 2 | 0.0009 | - | - | - | - | 0.0772 | 0.0936 | 0.1176 | - | |
| 3 | 0.0038 | 0.033 | 0.0304 | 0.0653 | - | 0.1216 | 0.125 | 0.0487 | ||
| 4 | 0.0065 | 0.0246 | 0.0661 | - | 0.1192 | 0.1231 | 0.0568 | |||
| 5 | 0.0054 | 0.062 | - | 0.1121 | 0.0955 | 0.0712 | ||||
| 6 | 0.0026 | - | 0.1121 | 0.1126 | 0.0873 | |||||
| 7 | 0.0044 | 0.0987 | 0.1231 | - | ||||||
| 8 | 0.0069 | 0.0187 | 0.16 | |||||||
| 9 | 0.0057 | 0.1209 | ||||||||
| n | - |
| Node | Age (mya) | HPD | Node | Age (mya) | HPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.34 | 8.59–14.17 | Bengal 3 MRCA | 0.17 | 0.05–0.33 |
| 2 | 6.04 | 4.02–8.39 | ‘Dark’ Bengal MRCA | 0.41 | 0.24–0.61 |
| 3 | 3.86 | 2.55–5.41 | Northern Bengal MRCA | 0.41 | 0.23–0.61 |
| 4 | 1.76 | 1.07–2.67 | Java 1 MRCA | 0.24 | 0–0.39 |
| 5 | 0.73 | 0.46–1.06 | Northern Borneo MRCA | 0.3 | 0.15–0.49 |
| 6 | 0.55 | 0.35–0.81 | Western Borneo MRCA | 0.73 | 0.42–1.10 |
| 7 | 1.93 | 1.28–2.77 | Eastern Borneo MRCA | 0.38 | 0.10–0.80 |
| 8 | 1.68 | 1.09–2.38 | Java 2 MRCA | 0.34 | 0.12–0.68 |
| 9 | 1.08 | 0.46–1.90 | N. coucang (Sumatra) MRCA | 0.22 | 0.05–0.47 |
| 10 | 1.18 | 0.66–1.82 | Northern pygmy MRCA | 0.22 | 0.11–0.40 |
| ‘malayanus’ MRCA * | 0.30 | 0.14–0.51 | Southern pygmy MRCA | 0.35 | 0.17–0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blair, M.E.; Cao, G.T.H.; López-Nandam, E.H.; Veronese-Paniagua, D.A.; Birchette, M.G.; Kenyon, M.; Md-Zain, B.M.; Munds, R.A.; Nekaris, K.A.-I.; Nijman, V.; et al. Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships and Unveiling Novel Genetic Diversity among Slow and Pygmy Lorises, including Resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius. Genes 2023, 14, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030643
Blair ME, Cao GTH, López-Nandam EH, Veronese-Paniagua DA, Birchette MG, Kenyon M, Md-Zain BM, Munds RA, Nekaris KA-I, Nijman V, et al. Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships and Unveiling Novel Genetic Diversity among Slow and Pygmy Lorises, including Resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius. Genes. 2023; 14(3):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030643
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlair, Mary E., Giang T. H. Cao, Elora H. López-Nandam, Daniel A. Veronese-Paniagua, Mark G. Birchette, Marina Kenyon, Badrul M. Md-Zain, Rachel A. Munds, K. Anne-Isola Nekaris, Vincent Nijman, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships and Unveiling Novel Genetic Diversity among Slow and Pygmy Lorises, including Resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius" Genes 14, no. 3: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030643
APA StyleBlair, M. E., Cao, G. T. H., López-Nandam, E. H., Veronese-Paniagua, D. A., Birchette, M. G., Kenyon, M., Md-Zain, B. M., Munds, R. A., Nekaris, K. A.-I., Nijman, V., Roos, C., Thach, H. M., Sterling, E. J., & Le, M. D. (2023). Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships and Unveiling Novel Genetic Diversity among Slow and Pygmy Lorises, including Resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius. Genes, 14(3), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030643







