Ovule Transcriptome Analysis Discloses Deregulation of Genes and Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Limonium Species (Plumbaginaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Ovule Extraction
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.4. Processing, Mapping, and Quantification of Illumina Reads
2.5. Differentially Expressed Genes Detection
2.6. Functional Annotation
2.7. Transcription Factors (TFs) Involved in Plant Reproduction
2.8. Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression
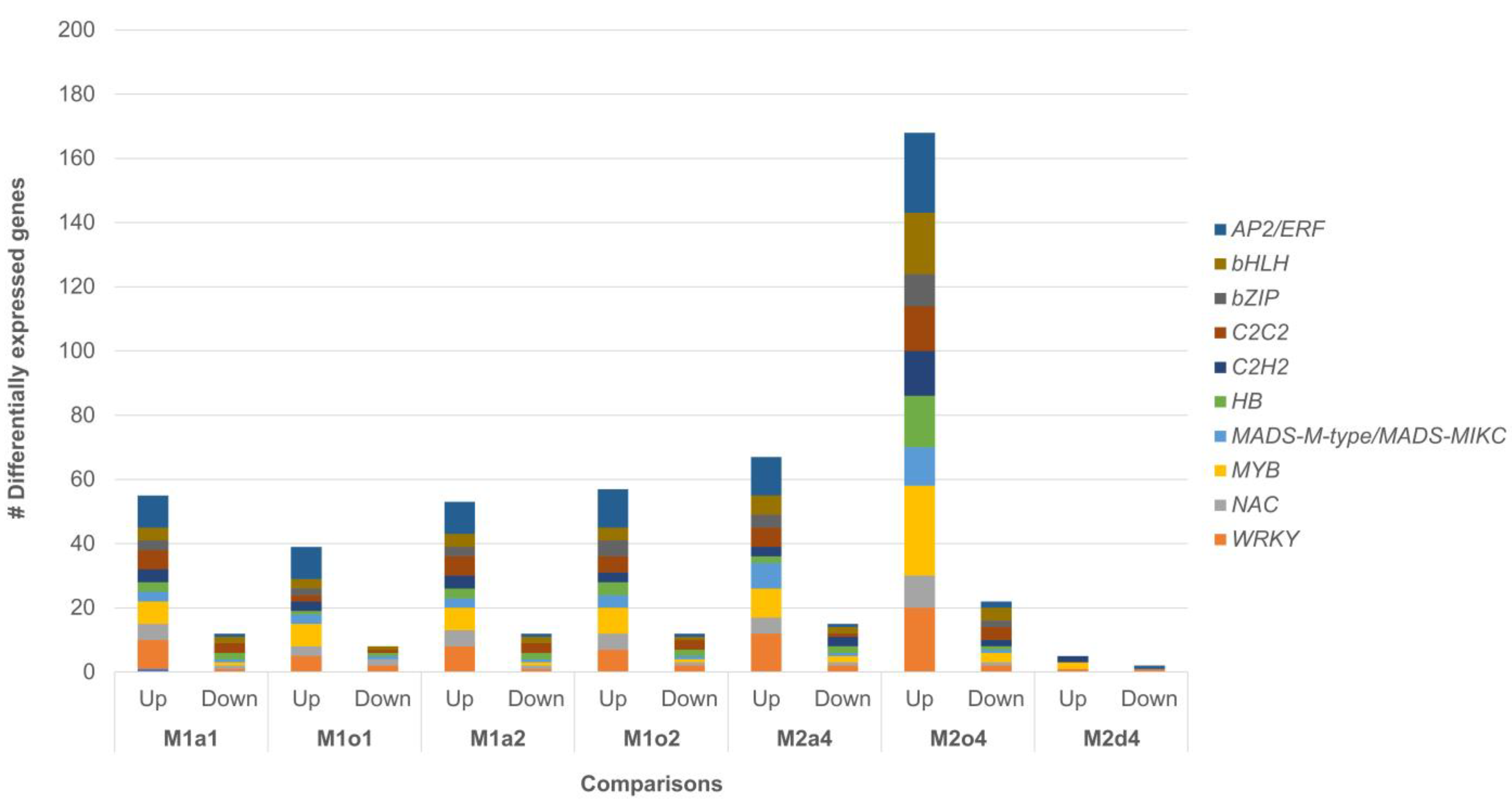
3.2. Overall Differential Expression Analysis
3.3. DEGs Potentially Implicated in Apomixis Regulation
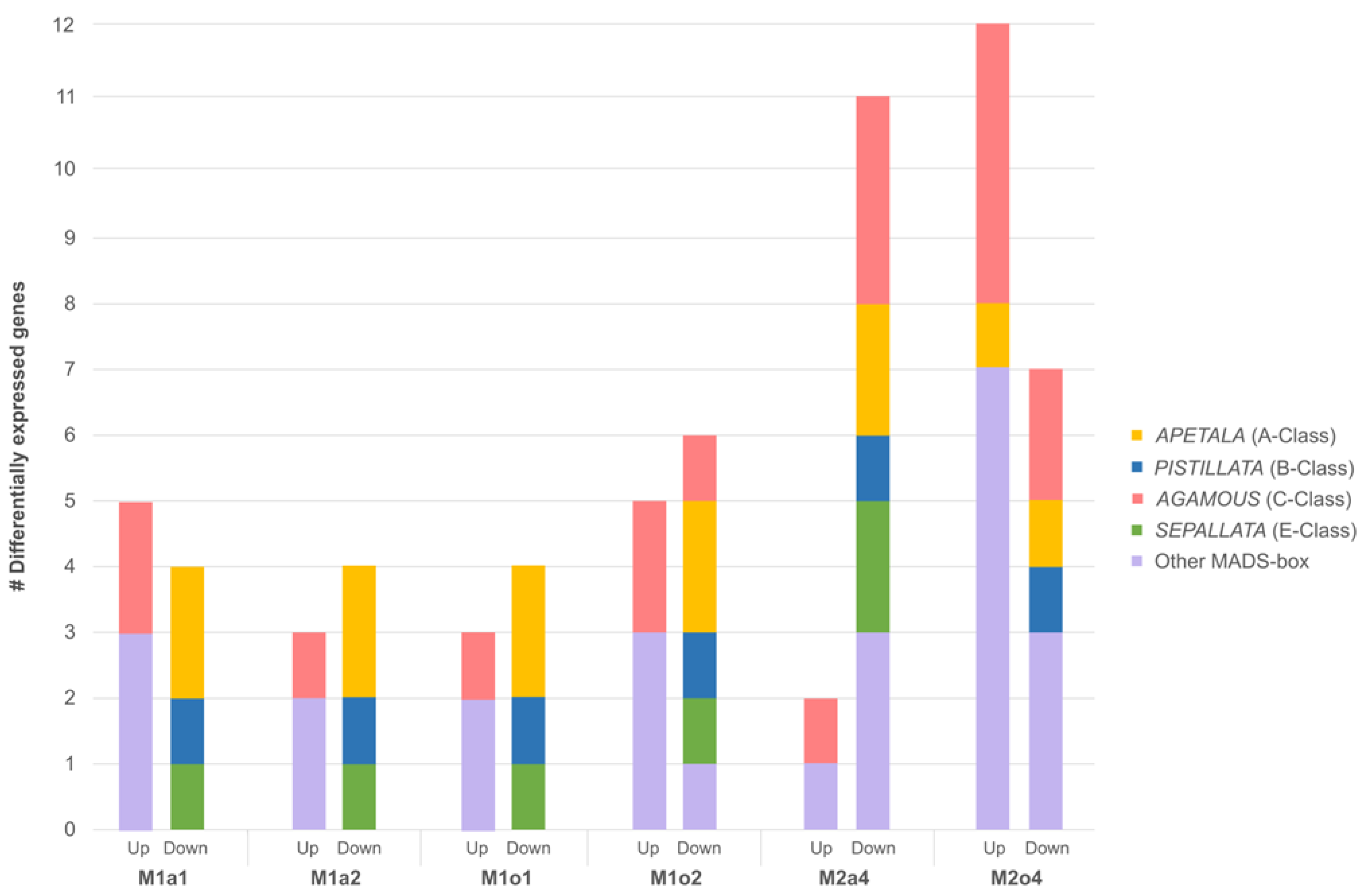
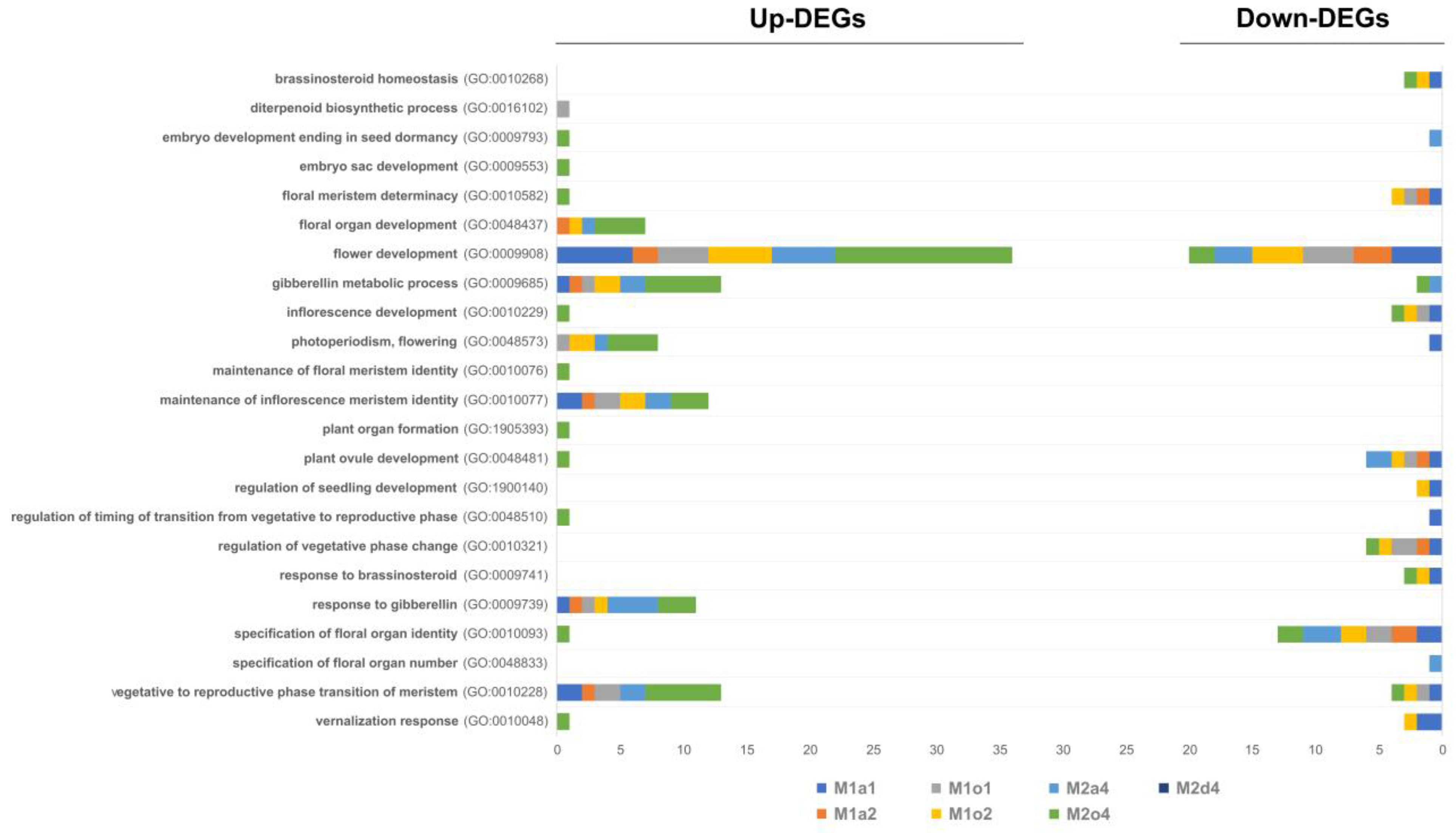
3.4. Floral-Related DEGs
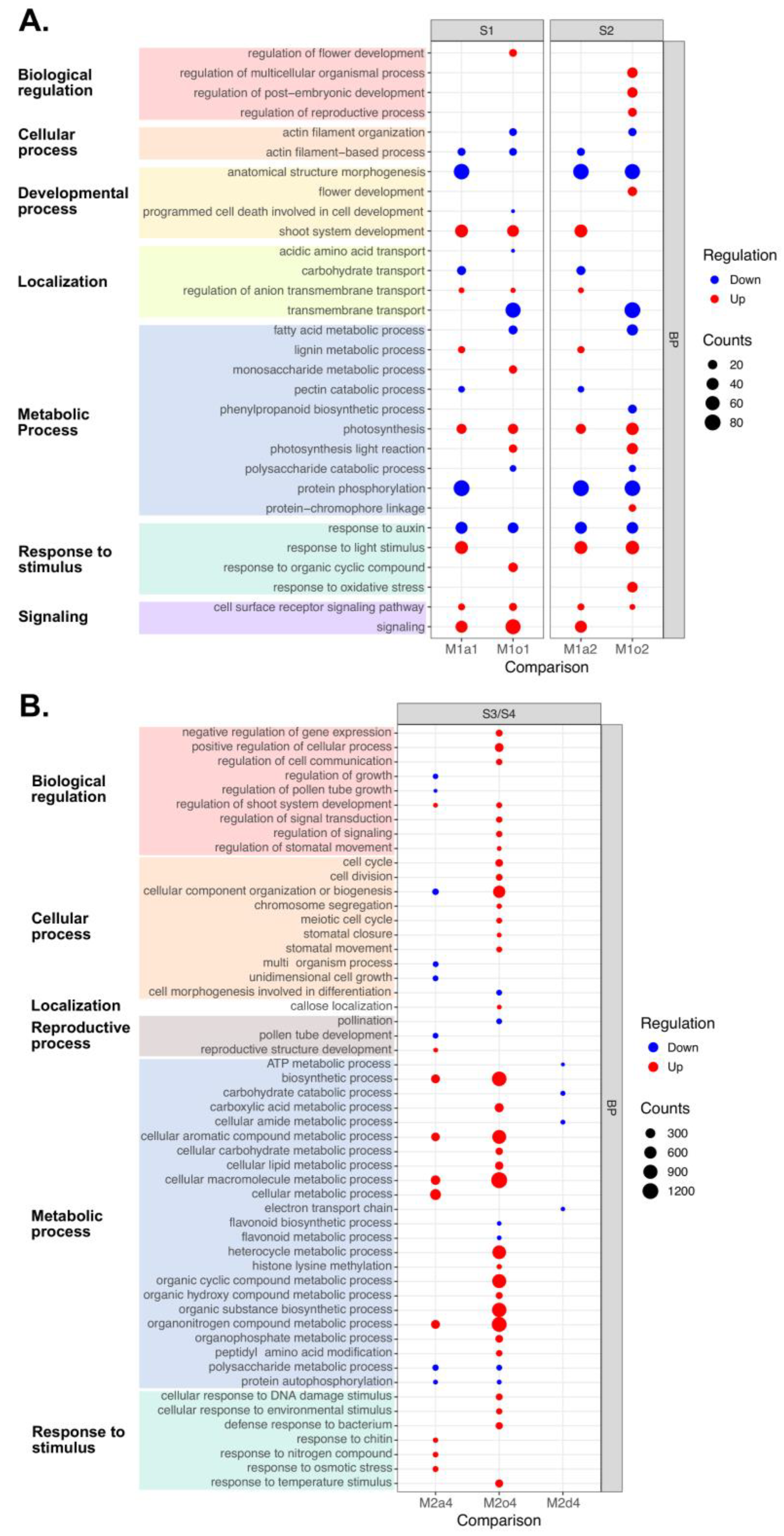
3.5. General GO Enrichment
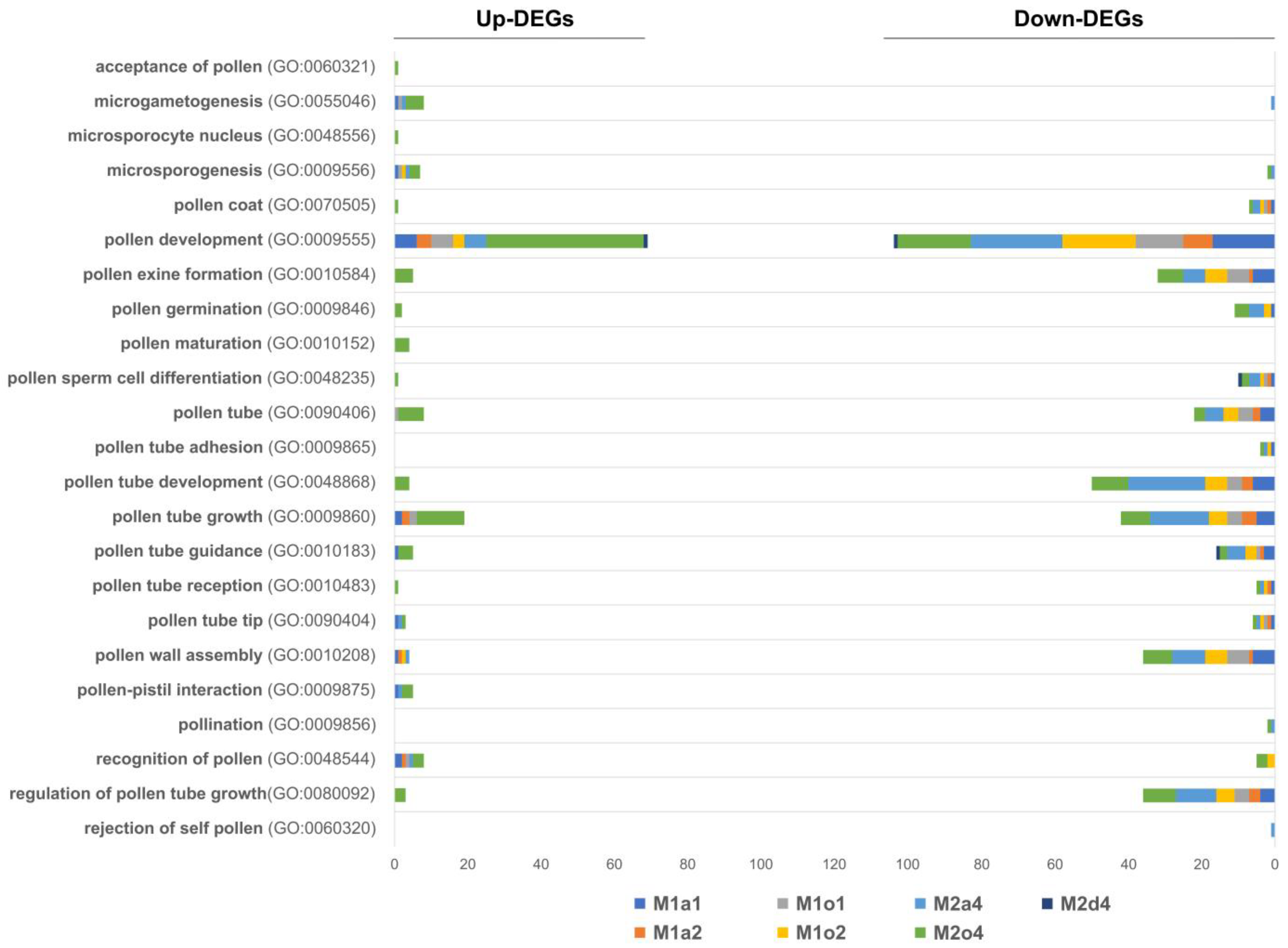
3.6. GO Enrichment in Floral and Pollen-Related DEGs
4. Discussion
4.1. Differential Regulation of HKG and Metabolic Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Plants
4.2. Feminization of Apomicts Is Related to Down-Regulation of Floral Genes Specifying Stamens
4.3. Male Sterility Appears to Be Linked with Downregulation of Genes Connected to Pollen Wall Formation and Assembly and Pollen Tube Growth
4.4. Pollen-Stigma Interactions
4.5. Up-Regulation of Specific Genes Related with Embryo Formation in the Apomicts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hojsgaard, D.; Greilhuber, J.; Pellino, M.; Paun, O.; Sharbel, T.F.; Hörandl, E. Emergence of apospory and bypass of meiosis via apomixis after sexual hybridisation and polyploidisation. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asker, S.E.; Jerling, L. Apomixis in Plants, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, A.J. Plant Breeding Systems; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Koltunow, A.M.; Grossniklaus, U. Apomixis: A developmental perspective. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 547–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talent, N.; Dickinson, T.A. Endosperm formation in aposporous Crataegus. Rosaceae, Spiraeoideae, tribe Pyreae): Parallels to Ranunculaceae and Poaceae. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogler, G.A. Gametophytic apomixis. In Embryology of Angiosperms, Johri, B.M., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 475–518. [Google Scholar]
- Naumova, T.N.; Mershchikova, I. Apomixis in Angiosperms: Nucellar and Integumentary Embryony; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Whitton, J.; Sears, C.J.; Baack, E.; Otto, S.P. The dynamic nature of apomixis in the angiosperms. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 169, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, I.C.; Van Dijk, P.J. Crosses between sexual and apomictic dandelions (Taraxacum). I. The inheritance of apomixis. Heredity 1999, 83, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirmans, P.G.; Den Nijs, J.C.; Van Tienderen, P.H. Male sterility in triploid dandelions: Asexual females vs. asexual hermaphrodites. Heredity 2006, 96, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.L.; Choe, G.; Ritland, K.; Whitton, J. Cryptic sex within male-sterile polyploid populations of the easter daisy, Townsendia hookeri. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 169, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róis, A.S.; Teixeira, G.; Sharbel, T.F.; Fuchs, J.; Martins, S.; Espírito-Santo, D.; Caperta, A.D. Male fertility versus sterility, cytotype, and DNA quantitative variation in seed production in diploid and tetraploid sea lavenders (Limonium sp., Plumbaginaceae) reveal diversity in reproduction modes. Sex Plant Reprod. 2012, 25, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róis, A.S.; Sádio, F.; Paulo, O.S.; Teixeira, G.; Paes, A.P.; Espírito-Santo, D.; Caperta, A.D. Phylogeography and modes of reproduction in diploid and tetraploid halophytes of Limonium species (Plumbaginaceae): Evidence for a pattern of geographical parthenogenesis. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, A.P.S.; Cortez, P.A.; Teixeira, S.P.; Oliveira, P.E.; Carmello-Guerreiro, S.M. Unusual diversity of apomictic mechanisms in a species of Miconia, Melastomataceae. Plant Syst. Evol. 2018, 304, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A. The genesis of some Scandinavian species of Calamagrostis. Hereditas 1946, 32, 131–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czapik, R. Problems of apomictic reproduction in the families Compositae and Rosaceae. Folia Geobot. 1996, 31, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcaccia, G.; Albertini, E. Apomixis in plant reproduction: A novel perspective on an old dilemma. Plant Reprod. 2013, 26, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, M.L.; Koltunow, A.M. The genetic control of apomixis: Asexual seed formation. Genetics 2014, 197, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, J.G. Asynchronous expression of duplicate genes in angiosperms may cause apomixis, bispory, tetraspory, and polyembryony. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1997, 61, 51–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Martínez, G.; Vielle-Calzada, J.P. Apomixis in flowering plants: Developmental and evolutionary considerations. Curr. Top. Dev. 2019, 131, 565–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A. Controlling apomixis: Shared features and distinct characteristics of gene regulation. Genes 2020, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brukhin, V. Molecular and genetic regulation of apomixis. Russ. J. Genet. 2017, 53, 943–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo de Arias, M.; Gao, L.; Sherwood, D.A.; Dwivedi, K.K.; Price, B.J.; Jamison, M.; Kowalis, B.M.; Carman, J.G. Whether gametophytes are reduced or unreduced in angiosperms might be determined metabolically. Genes 2020, 11, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, S.I.R.; Róis, A.S.; Caperta, A.D. Limonium homoploid and heteroploid intra- and interspecific crosses unveil seed anomalies and neopolyploidy related to sexual and/or apomictic reproduction. Taxon 2018, 67, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, M. Die gattung Limonium im südwestmediterranen Raum. Mitt. Bot. Staatssamml. Münch. 1978, 14, 361–626. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrouille, M.J.; Stace, C.A. Pattern of variation of agamospermous Limonium (Plumbaginaceae) in the British Isles. Nordic J. Bot. 1985, 5, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.; Ingrouille, M.J.; Lledó, M.D. The taxonomic treatment of agamosperms in the genus Limonium Mill. (Plumbaginaceae). Folia Geobot. 1998, 33, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caperta, A.D.; Conceição, S.I.; Róis, A.S.; Loureiro, J.; Castro, S. Cytogenetic features of sexual and asexual Limonium taxa (Plumbaginaceae). Taxon 2018, 67, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.G. Dimorphism and monomorphism in the Plumbaginaceae: II. Pollen and stigmata in the genus Limonium. Ann. Bot. 1953, 17, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.G. The evolution, functioning and breakdown of heteromorphic incompatibility systems. I. The Plumbaginaceae. Evolution 1966, 20, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição, S.I.R.; Fernandes, J.; Borges da Silva, E.; Caperta, A.D. Reproductive output and insect behavior in hybrids and apomicts from Limonium ovalifolium and L. binervosum complexes (Plumbaginaceae) in an open cross-pollination experiment. Plants 2021, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, F. Contributo all’embriologia delle Plumbaginaceae. Nuov. Giorn. Bot. Ital. 1940, 47, 349–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, F. Triploidia e apomissia in Statice oleaefolia Scop. var. confusa Godr. Caryologia 1949, 2, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmqvist, H.; Grazi, E. Studies on variation in embryo sac development. Bot. Not. 1964, 118, 329–360. [Google Scholar]
- Conceição, S.I.R.; Róis, A.S.; Caperta, A.D. Nonreduction via meiotic restitution and pollen heterogeneity may explain residual male fertility in triploid marine halophyte Limonium algarvense (Plumbaginaceae). Caryologia 2019, 72, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrouille, M.J.; Stace, C.A. The Limonium binervosum aggregate (Plumbaginaceae) in the British Isles. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1986, 92, 177–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Guacchio, E.; Erben, M.; Caputo, P. The neglected name Statice auriculifolia (Plumbaginaceae) and its related names: A long history of nomenclatural intricacy. Taxon 2019, 68, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soneson, C.; Delorenzi, M.A. Comparison of methods for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.R.; Burge, G.K.; Seelye, J.F.; Hopping, M.E.; Grant, J.E. Production of inter-specific hybrids between Limonium perezii (Stapf) Hubb. and Limonium sinuatum (L.) Mill. Euphytica 1998, 102, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Wingett, S.W.; Andrews, S. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gribskov, M. Comprehensive evaluation of de novo transcriptome assembly programs and their effects on differential gene expression analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Seppey, M.; Simão, F.A.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO applications from quality assessments to gene prediction and phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, O.; Hara, Y.; Kuraku, S. gVolante for standardizing completeness assessment of genome and transcriptome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3635–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2010; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lun, A.T.L.; Smyth, G.K. Differential expression analysis of complex RNA-seq experiments using edgeR. In Statistical Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data. Frontiers in Probability and the Statistical Sciences; Datta, S., Nettleton, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, T.A.; Droettboom, M.; Lee, A.; Hunter, J.H.; Sales de Andrade, E.; Hoffman, T.; Stansby, D.; Klymak, J.; Varoquaux, N.; Hedegaard, N.J.; et al. matplotlib/matplotlib: REL: v3.3.3 (Version v3.3.3). Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Wu, C.H. Protein Bioinformatics Databases and Resources. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1558, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ex, F.; Jacob, Y.; Martienssen, R.A. Multiple roles for small RNAs during plant reproduction. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, R.; Cucinotta, M.; Mendes, M.A.; Underwood, C.J.; Colombo, L. The emerging role of small RNAs in ovule development, a kind of magic. Plant Reprod. 2021, 34, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinta, G.; Khan, A.; Abd Elgawad, H.; Verma, V.; Srivastava, A.K. Unveiling the redox control of plant reproductive development during abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, E.; Østergaard, L. Distinct and dynamic auxin activities during reproductive development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.; Vivian-Smith, A.; Offringa, R.; Sundberg, E. Auxin homeostasis in Arabidopsis ovules is anther-dependent at maturation and changes dynamically upon fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambacher, S.; Hahn, M.; Schotta, G. Epigenetic regulation of development by histone lysine methylation. Heredity 2010, 105, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.R.; Klose, R.J. Understanding the relationship between DNA methylation and histone lysine methylation. BBA 2014, 1839, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, R.; Agarwal, P.; Ray, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kapoor, S. MADS-box gene family in rice: Genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelán-Muñoz, N.; Herrera, J.; Cajero-Sánchez, W.; Arrizubieta, M.; Trejo, C.; García-Ponce, B.; de la Sánchez, M.P.; Álvarez-Buylla, E.R.; Garay-Arroyo, A. MADS-Box genes are key components of genetic regulatory networks involved in abiotic stress and plastic developmental responses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.; Sohail, A.; Ahmad, R.; Cheng, S.; Cao, L.; Wu, W. The roles of MADS-Box genes from root growth to maturity in Arabidopsis and rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, P.; Browse, J. Male sterility in Arabidopsis induced by overexpression of a MYC5-SRDX chimeric repressor. Plant J. 2015, 81, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouider, S.; Borges, F.; LeBlanc, C.; Ungru, A.; Schnittger, A.; Martienssen, R.; Colot, V.; Bouyer, D. Male fertility in Arabidopsis requires active DNA demethylation of genes that control pollen tube function. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.; Rosli, H.G.; Pombo, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Banf, M.; Dai, X.; Martin, G.B.; Giovannoni, J.J.; et al. iTAK: A program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J.G. Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supek, F.; Bošnjak, M.; Škunca, N.; Šmuc, T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of Gene Ontology terms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pupilli, F.; Barcaccia, G. Cloning plants by seeds: Inheritance models and candidate genes to increase fundamental knowledge for engineering apomixis in sexual crops. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 159, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polegri, L.; Calderini, O.; Arcioni, S.; Pupilli, F. Specific expression of apomixis-linked alleles revealed by comparative transcriptomic analysis of sexual and apomictic Paspalum simplex Morong flowers. JXB 2010, 61, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharbel, T.F.; Voigt, M.L.; Corral, J.M.; Galla, G.; Kumlehn, J.; Klukas, C.; Schreiber, F.; Vogel, H.; Rotter, B. Apomictic and sexual ovules of Boechera display heterochronic global gene expression patterns. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellino, M.; Hojsgaard, D.; Hörandl, E.; Sharbel, T.F. Chasing the apomictic factors in the Ranunculus auricomus complex: Exploring gene expression patterns in microdissected sexual and apomictic ovules. Genes 2020, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.D.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Guimarães, L.A.; Silva, F.R.; Carneiro, V.T.C. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR expression studies in the apomictic and sexual grass Brachiaria brizantha. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, B.; Conner, J.A.; Ozias-Akins, P. Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression analysis in apomictic and sexual Cenchrus ciliaris. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, C.; Benoit, M.; Détourné, G.; Simon, L.; Poulet, A.; Jung, M.; Veluchamy, A.; Latrasse, D.; Le Goff, S.; Cotterell, S.; et al. Arabidopsis ATRX modulates H3.3 occupancy and fine-tunes gene expression. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1773–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Podio, M.; Conner, J.; Ozias-Akins, P. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris) eggs unveils apomictic parthenogenesis signatures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Monfil, V.; Durán-Figueroa, N.; Arteaga-Vázquez, M.; Demesa-Arévalo, E.; Autran, D.; Grimanelli, D.; Slotkin, R.K.; Martienssen, R.A.; Vielle-Calzada, J.-P. Control of female gamete formation by a small RNA pathway in Arabidopsis. Nature 2010, 464, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Schmid, M.W.; Klostermeier, U.C.; Qi, W.; Guthörl, D.; Sailer, C.; Waller, M.; Rosenstiel, P.; Grossniklaus, U. Apomictic and sexual germline development differ with respect to cell cycle, transcriptional, hormonal and epigenetic regulation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.; Rogers, R.; Muralla, R.; Meinke, D. Requirement of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for gametogenesis and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 44, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemlyanskaya, E.V.; Omelyanchuk, N.A.; Ubogoeva, E.V.; Mironova, V.V. Deciphering auxin-ethylene crosstalk at a systems level. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, A.R.; Thomas, S.G.; Wilson, Z.A.; Hedden, P. Gibberellin control of stamen development: A fertile field. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mara, C. Regulatory mechanisms for floral homeotic gene expression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, E.S.; Meyerowitz, E.M. The war of the whorls: Genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature 1991, 353, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, C.A. Determination of sexual organ development. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2010, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sather, D.N.; Jovanovic, M.; Golenberg, E.M. Functional analysis of B and C class floral organ genes in spinach demonstrates their role in sexual dimorphism. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronk, Q.; Müller, N.A. Default sex and single gene sex determination in dioecious plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cui, M.; Yang, L.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D. Genetic and biochemical mechanisms of pollen wall development. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Hong, Z.; Sivaramakrishnan, M.; Mahfouz, M.; Verma, D.P.S. Callose synthase (CalS5) is required for exine formation during microgametogenesis and for pollen viability in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 42, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Zinkl, G.M.; Swanson, R.J.; Maruyama, D.; Preuss, D. Callose (beta-1,3 glucan) is essential for Arabidopsis pollen wall patterning, but not tube growth. BMC Plant Biol. 2005, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Han, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, T. GLUCAN SYNTHASE-LIKE 5 (GSL5) plays an essential role in male fertility by regulating callose metabolism during microsporogenesis in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töller, A.; Brownfield, L.; Neu, C.; Twell, D.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Dual function of Arabidopsis glucan synthase-like genes GSL8 and GSL10 in male gametophyte development and plant growth. Plant J. 2008, 54, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Rim, Y.; Han, X.; Cho, W.K.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.-Y. Arabidopsis glucan synthase-like 10 functions in male gametogenesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrice, T.N.; Vogler, H.; Draeger, C.; Munglani, G.; Gupta, S.; Herger, A.G.; Knox, P.; Grossniklaus, U.; Ringli, C. LRX proteins play a crucial role in pollen grain and pollen tube cell wall development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sede, A.R.; Borassi, C.; Wengier, D.L.; Mecchia, M.A.; Estevez, J.M.; Muschietti, J.P. Arabidopsis pollen extensins LRX are required for cell wall integrity during pollen tube growth. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, D.; Vekemans, X.; Castric, V.; Glémin, S. Plant self-incompatibility systems: A molecular evolutionary perspective. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nettancourt, D. The basic features of self-Incompatibility. In Incompatibility and Incongruity in Wild and Cultivated Plants, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaba, M.; Dwyer, K.; Hendershot, J.; Vrebalov, J.; Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Self-incompatibility in the genus Arabidopsis: Characterization of the S locus in the outcrossing A. lyrata and its autogamous relative A. thaliana. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.; Rajewski, A.; He, J.; Castaneda, O.G.; Litt, A.; Kaloshian, I. Classification and phylogenetic analyses of the Arabidopsis and tomato G-type lectin receptor kinases. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ge, W.; Li, L.; Hou, D.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Bai, Q.; Li, X.; Mu, S.; Gao, J. Analysis of MADS-Box gene family reveals conservation in floral organ ABCDE model of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ying, H.; Helliwell, C.A.; Taylor, J.M.; Peacock, W.J.; Denis, E.S. FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) regulates development pathways throughout the life cycle of Arabidopsis. PNAS 2011, 108, 6680–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Weigel, D. Move on up, it’s time for change–Mobile signals controlling photoperiod-dependent flowering. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2371–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, S.; Kampmann, G.; Chandler, J.; Apel, K. FPF1 modulates the competence to flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 1999, 18, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.C.; Bracko, O.; Park, M.S.; Schawb, R.; Chun, H.J.; Park, K.M.; Seo, J.S.; Grbic, V.; Balasubramanian, S.; Schmid, M.; et al. Control of lateral organ development and flowering time by the Arabidopsis thaliana MADS-box Gene AGAMOUS-LIKE6. Plant J. 2010, 62, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, L.A.; de Dusi, D.M.A.; Masiero, S.; Resentini, F.; Gomes, A.C.M.M.; Silveira, E.D.; Florentino, L.H.; Rodrigues, J.C.M.; Colombo, L.; Carneiro, V.T. BbrizAGL6 Is differentially expressed during embryo sac formation of apomictic and sexual Brachiaria brizantha plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.E.; Lehti, M.D.; Fernandez, D.E. The MADS-domain protein AGAMOUS-like 15 accumulates in embryonic tissues with diverse origins. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakare, D.; Tang, W.; Hill, K.; Perry, S.E. The MADS-domain transcriptional regulator AGAMOUS-LIKE15 promotes somatic embryo development in Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlova, R.; Boeren, S.; Russinova, E.; de Vries, S. The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 protein complex includes Brassinosteroid-Insensitive1. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Gu, A.; Zhang, J.; Luo, S.; Gao, X.; Zhao, J.; Pan, X.; Shen, S. Gene characterization and molecular pathway analysis of reverse thermosensitive genic male sterility in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
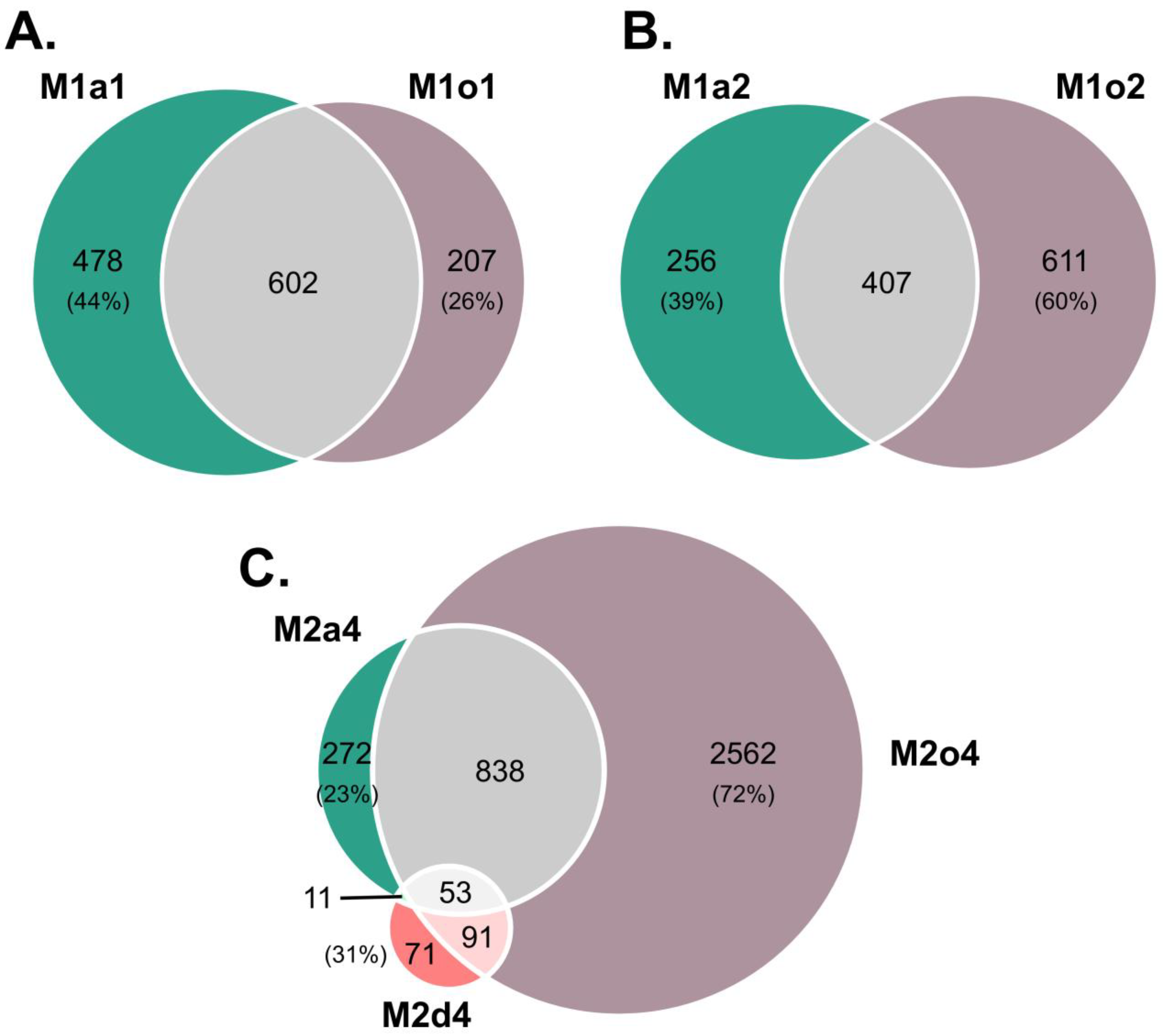
| Test Samples (T) | Control Samples (c) | Comparison | All DEGs | Annotated DEGs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Stage (Rep) | Species | Stage (Rep) | Total | Up (%) | Down (%) | ||
| L. multiflorum (M) [Apomictic] | Apomictic vs. sexual | |||||||
| S1 (R1) | L. auriculifolium (a) [Sexual] | S1 (R1) | M1a1 | 3517 | 1080 | 453 (42%) | 627 (58%) | |
| S2 (R1) | M1a2 | 2785 | 663 | 295 (44%) | 368 (56%) | |||
| S2 (R1-5) | S3/S4 (R1) | M2a4 | 4400 | 1174 | 489 (42%) | 685 (58%) | ||
| S1 (R1-4) | L. ovalifolium (o) [Sexual] | S1 (R1) | M1o1 | 3068 | 809 | 371 (46%) | 438 (54%) | |
| S2 (R1) | M1o2 | 3054 | 1018 | 419 (41%) | 599 (59%) | |||
| S2 (R1-5) | S3/S4 (R1) | M2o4 | 12,839 | 3544 | 2827 (80%) | 717 (20%) | ||
| Apomictic vs. facultative apomictic | ||||||||
| S2 (R1-5) | L. dodartii (d) [Facultative apomictic] | S4 (R1-3) | M2d4 | 806 | 226 | 41 (18%) | 185 (82%) | |
| Between stages comparisons (same species) | ||||||||
| S2 (R1-5) | L. multiflorum (M) [Apomictic] | S1 (R1-4) | M2m1 | 1096 | 387 | 379 (98%) | 8 (2%) | |
| L. auriculifolium (A) [Sexual] | S2 (R1) | L. auriculifolium (a) [Sexual] | S1 (R1) | A2a1 | 796 | 276 | 40 (14%) | 236 (86%) |
| S3/S4 (R1) | A4a1 | 351 | 111 | 93 (84%) | 18 (16%) | |||
| S2 (R1) | A4a2 | 1346 | 471 | 356 (76%) | 115 (24%) | |||
| L. ovalifolium (O) [Sexual] | S2 (R1) | L. ovalifolium (o) [Sexual] | S1 (R1) | O2o1 | 693 | 208 | 189 (91%) | 19 (9%) |
| S3/S4 (R1) | O4o1 | 2067 | 711 | 395 (56%) | 316 (44%) | |||
| S2 (R1) | O4o2 | 1650 | 526 | 228 (43%) | 298 (57%) | |||
| Between species comparisons (sexual) | ||||||||
| S1 (R1) | L. auriculifolium (a) [Sexual] | S1 (R1) | O1a1 | 616 | 200 | 34 (17%) | 166 (83%) | |
| S2 (R1) | S2 (R1) | O2a2 | 1242 | 367 | 273 (74%) | 94 (26%) | ||
| S3/S4 (R1) | S3/S4 (R1) | O4a4 | 1611 | 550 | 257 (47%) | 293 (53%) | ||
| Reproduction | Species | Stages | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3/S4 | ||
| Apomictic | L. multiflorum (M) | 933936 | 115775 | - |
| Facultative apomictic | L. dodartii (d) | - | - | 103,345 |
| Sexual | L. auriculifolium (A/a) | 60,143 | 48,851 | 61,550 |
| L. ovalifolium (O/o) | 67,207 | 76,395 | 20,133 | |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Log2FC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1a1 | M1a2 | M1o1 | M1o2 | M2a4 | M2o4 | M2d4 | |||
| TRINITY_DN12562_c0_g1 | A1 | Elongation factor 1-α | 10.09 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9323_c2_g1 | ACR11 | ACT domain-containing protein ACR11 | 7.81 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN594_c3_g1 | ACT1 | Actin-1 | 7.09 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3478_c1_g1 | ACT11 | Actin-11 | −4.39 | −2.32 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN13623_c0_g1 | EXPA11 | Expansin-A11 | −5.35 | −5.85 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2256_c1_g1 | EXPA13 | Expansin-A13 | −2.28 | −2.07 | −2.17 | −3.78 | |||
| TRINITY_DN27728_c0_g1 | EXPA15 | Expansin-A15 | 6,5 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN151736_c0_g1 | EXPA16 | Expansin-A16 | −4.77 | −2.4 | −2.06 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN12567_c0_g1 | EXPA20 | Expansin-A20 | −2.08 | 7.23 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN21891_c0_g1 | EXPA6 | Expansin-A6 | −2.41 | −2.42 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN5240_c0_g1 | EXPA8 | Expansin-A8 | −5.09 | −3.65 | −3.79 | −4.76 | −2.76 | −3.16 | |
| TRINITY_DN10654_c0_g1 | GAPC1 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GAPC1, cytosolic | 8.03 | 2.95 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN10775_c0_g1 | GAPC2 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GAPC2, cytosolic | −2.67 | −2.02 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN638_c0_g1 | HSP90-6 | Heat shock protein 90-6, mitochondrial | 9.87 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN28088_c0_g2 | RALFL19 | Probable ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 24 | −7.67 | −4.99 | −4.97 | −7.43 | −4.92 | −4.37 | |
| TRINITY_DN521_c0_g6 | TUBB5 | Tubulin β-5 chain | −2.46 | −3.5 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN159888_c0_g1 | TUBB6 | Tubulin β-6 chain | −2.58 | −2.21 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2826_c0_g1 | TUBB8 | Tubulin β-8 chain | 11.41 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2332_c0_g1 | TUBB9 | Tubulin β-9 chain | 8.91 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6957_c0_g1 | UBC10 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 10 | 8.36 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN193932_c0_g1 | UBC11 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 11 | 6.39 | 2.72 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN184540_c0_g1 | UBC19 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 19 | −3.31 | −3.22 | −3.64 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN6909_c0_g1 | UBC29 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 29 | 3.03 | 2.14 | 3.94 | 4.14 | 14.61 | ||
| TRINITY_DN2966_c0_g1 | UBC33 | Probable ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 33 | 2.1 | 5.58 | 9.74 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN43968_c0_g1 | UBC35 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 35 | 3.13 | 6.36 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN10935_c1_g1 | UBC4 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 4 | 7.32 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10551_c0_g1 | UBC8 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 8 | 2.06 | 2.34 | 6.99 | ||||
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Log2FC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1a1 | M1a2 | M1o1 | M1o2 | M2a4 | M2o4 | |||
| TRINITY_DN28291_c0_g2 | AGL15 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL15 | −4.08 | 7.12 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN13295_c0_g1 | AGL16 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL16 | 2.14 | 2.21 | 9.13 | |||
| TRINITY_DN610_c1_g1 | AGL42 | MADS-box protein AGL42 | 2.15 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2793_c0_g2 | AGL6 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL6 | 7.9 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN3873_c0_g1 | AGL65 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL65 | −2.29 | −2.62 | −3.28 | |||
| TRINITY_DN12180_c0_g1 | AGL66 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL66 | −4.72 | −3.81 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN342_c0_g2 | AGL8 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL8 | 4.02 | 2.86 | 4.34 | 2.59 | 6.91 | |
| TRINITY_DN72066_c0_g2 | ANR1 | MADS-box transcription factor ANR1 | 6.03 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN9027_c0_g3 | AP1 | Floral homeotic protein APETALA 1 | −7.1 | −7.24 | −7.17 | −6.32 | ||
| TRINITY_DN2754_c0_g1 | AP2 | Floral homeotic protein APETALA 2 | 2.14 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN7779_c0_g1 | AP3 | Floral homeotic protein APETALA 3 | −8.66 | −6.05 | −6.98 | −8.55 | −4.17 | −3.22 |
| TRINITY_DN46144_c0_g1 | ATH1 | Homeobox protein ATH1 | 3 | 7.07 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN27333_c1_g1 | BLH8 | BEL1-like homeodomain protein 8 | 7.15 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN1609_c0_g1 | BRI1 | Protein BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1 | −2.45 | −2.2 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN17115_c0_g1 | CCA1 | Protein CCA1 | 7.18 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN11983_c0_g1 | CDF2 | Cyclic dof factor 2 | 2.81 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2531_c1_g2 | COL5 | Zinc finger protein CONSTANS-LIKE 5 | 2.15 | 2.71 | 2.27 | |||
| TRINITY_DN26110_c0_g1 | CSTF77 | Cleavage stimulation factor subunit 77 | 2.13 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN22923_c0_g1 | ELF6 | Probable lysine-specific demethylase ELF6 | 5.1 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN3347_c0_g1 | EMF2 | Polycomb group protein EMBRYONIC FLOWER 2 | 2.89 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN7896_c0_g2 | FLC | MADS-box protein FLOWERING LOCUS C | 8.63 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN5378_c0_g1 | FPA | Flowering time control protein FPA | 3.27 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN184585_c0_g1 | FPF1 | Flowering-promoting factor 1 | 2.72 | 2.94 | 3.9 | 2.94 | 3.58 | |
| TRINITY_DN7899_c0_g1 | FT | Protein FLOWERING LOCUS T | 2.06 | 2.37 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN344_c1_g2 | GA2 | Ent-kaur-16-ene synthase, chloroplastic | 3.21 | 7.82 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN2317_c0_g2 | GA2OX6 | Gibberellin 2-β-dioxygenase 6 | 3.87 | 3.85 | 3.72 | 11.51 | ||
| TRINITY_DN38605_c0_g1 | GA2OX8 | Gibberellin 2-β-dioxygenase 8 | −4,06 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN13033_c0_g1 | GA3OX1 | Gibberellin 3-β-dioxygenase 1 | 2.87 | 8 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN8333_c0_g1 | GA3OX2 | Gibberellin 3-β-dioxygenase 2 | 11.4 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN17736_c0_g1 | GASA1 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 1 | 4.81 | 2.37 | 2.98 | 5.17 | ||
| TRINITY_DN10114_c0_g1 | GASA11 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 11 | 2.56 | 2.1 | 2.79 | 2.59 | 9.79 | |
| TRINITY_DN31284_c0_g1 | GASA14 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 14 | −2.5 | −4.11 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN185389_c0_g1 | GASA3 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 3 | −5.19 | −4.01 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN5658_c0_g1 | GASA6 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 6 | −4.47 | −2.13 | −2.06 | −4.55 | −4.83 | −5.73 |
| TRINITY_DN1467_c0_g1 | GASA7 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 7 | −7.76 | −6.05 | −7.43 | −7.99 | −4.99 | −4.24 |
| TRINITY_DN8938_c0_g1 | GASA9 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 9 | −2.47 | −2.33 | −2.99 | |||
| TRINITY_DN21137_c0_g1 | GID1C | Gibberellin receptor GID1C | 2.77 | 7.5 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN37680_c0_g1 | JMJ14 | Probable lysine-specific demethylase JMJ14 | 11.2 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN7266_c0_g2 | LD | Homeobox protein LUMINIDEPENDENS | 2.16 | 2.68 | 3.09 | 7.25 | ||
| TRINITY_DN6935_c0_g1 | MSI4 | WD-40 repeat-containing protein MSI4 | 10.21 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN34495_c0_g1 | NFYB2 | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit B-2 | 2.4 | 2.58 | 2.59 | |||
| TRINITY_DN18038_c0_g1 | NFYB3 | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit B-3 | 2.17 | 8.27 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN35701_c0_g2 | NFYC1 | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit C-1 | 2.59 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN1267_c0_g1 | PEX4 | Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensin-like protein 4 | −8.5 | −5.05 | −5.26 | −8.04 | −4.31 | −3.62 |
| TRINITY_DN6353_c0_g1 | PHYA | Phytochrome A | 2.15 | 2.39 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN21387_c0_g1 | PHYB | Phytochrome B | −2.28 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN7954_c0_g1 | PI | Floral homeotic protein PISTILLATA | −8.44 | −6.51 | −7.06 | −8.3 | −3.54 | −3.36 |
| TRINITY_DN12744_c0_g2 | SEP1 | Developmental protein SEPALLATA 1 | −7.94 | −7.09 | −7.56 | −8.08 | −2.8 | |
| TRINITY_DN31040_c0_g1 | SEP3 | Developmental protein SEPALLATA 3 | −2.37 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2251_c0_g1 | SOC1 | MADS-box protein SOC1 | 4.05 | 2.9 | 3.46 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 12.47 |
| TRINITY_DN6192_c0_g1 | SPL15 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 15 | 10.17 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN6705_c0_g1 | SPL3 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 3 | −3.84 | −3.38 | −4.54 | −2.82 | ||
| TRINITY_DN14821_c0_g1 | SPL4 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 4 | −3.38 | −2.18 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN57302_c0_g1 | SRF6 | Protein STRUBBELIG-RECEPTOR FAMILY 6 | −4.07 | −3.28 | −4.01 | −3.91 | ||
| TRINITY_DN46547_c0_g1 | SRF8 | Protein STRUBBELIG-RECEPTOR FAMILY 8 | 7.42 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2130_c0_g1 | SRR1 | Protein SENSITIVITY TO RED LIGHT REDUCED 1 | 12.09 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN29363_c0_g1 | SVP | MADS-box protein SVP | −3.8 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN5406_c1_g1 | UBC1 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 1 | 7.86 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN16649_c0_g1 | ULT1 | Protein ULTRAPETALA 1 | −2.18 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN13113_c0_g1 | VRN1 | B3 domain-containing transcription factor VRN1 | −3.2 | −2.14 | −2.41 | −2.73 | ||
| TRINITY_DN8011_c0_g1 | WNK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | 8.81 | |||||
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Log2FC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1a1 | M1a2 | M1o1 | M1o2 | M2a4 | M2o4 | M2d4 | |||
| Aminoacyl-tRNA | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN2761_c0_g1 | AO | L-aspartate oxidase, chloroplastic | 2.11 | 2.61 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN4987_c0_g1 | EDD1 | Glycine--tRNA ligase, chloroplastic/mitochondrial 2 | 12.19 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN157005_c0_g1 | GDH2 | Glycine cleavage system H protein 2, mitochondrial | −3.49 | −2.94 | −2.46 | −2.49 | −2.5 | ||
| TRINITY_DN2155_c4_g1 | GLDP1 | Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) 1, mitochondrial | 2.29 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10603_c0_g1 | GLDP2 | Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) 2, mitochondrial | 4.14 | 7.09 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2985_c0_g1 | GRDP2 | Glycine-rich domain-containing protein 2 | −2.18 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6537_c0_g1 | PSS1 | CDP-diacylglycerol--serine O-phosphatidyltransferase 1 | 9.39 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN20064_c0_g1 | RBG3 | Glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 3, mitochondrial | −2.44 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8570_c0_g1 | RBG4 | Glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 4, mitochondrial | 3.75 | 8.48 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8373_c0_g1 | RBG5 | Glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 5, mitochondrial | 9.41 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN27069_c0_g1 | RZ1A | Glycine-rich RNA-binding protein RZ1A | 2.24 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14144_c0_g1 | UGLYAH | (S)-ureidoglycine aminohydrolase | 2.79 | 2.01 | 3.21 | 7.94 | |||
| Ethylene | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN15258_c0_g1 | AIL5 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor AIL5 | −2.78 | −3.27 | −3.23 | −2.23 | 8.8 | ||
| TRINITY_DN51613_c0_g1 | ANT | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor ANT | 6.87 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN13736_c0_g1 | CRF2 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor CRF2 | −3.02 | −2.65 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN68_c0_g2 | EIN2 | Ethylene-insensitive protein 2 | 2.15 | 2.3 | 11.11 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN2468_c0_g1 | ERF010 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF010 | 3.25 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9993_c0_g1 | ERF014 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF014 | −2.01 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1685_c1_g1 | ERF018 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF018 | 2.98 | 3.3 | 3.09 | 2.52 | |||
| TRINITY_DN18951_c0_g1 | ERF034 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF034 | −3.47 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7978_c0_g2 | ERF054 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF054 | 3.29 | 3.21 | 4.29 | 3.91 | 10.81 | ||
| TRINITY_DN455_c0_g2 | ERF061 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF061 | 2.36 | 10.86 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN74944_c0_g3 | ERF071 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF071 | −2.59 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2504_c1_g1 | ERF109 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF109 | 2.63 | 3.22 | 4.14 | 10.25 | |||
| TRINITY_DN12655_c0_g1 | ERF114 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF114 | 9.96 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN40207_c0_g1 | ERF118 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF118 | −2.01 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN15135_c0_g1 | ERF1A | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 1A | 11.43 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN5700_c2_g1 | ERF2 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 2 | 2.19 | 10.77 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN10435_c0_g1 | ERF5 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 5 | 7.93 | 7.95 | 7.89 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN4039_c0_g2 | ERF9 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 9 | 2.46 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9095_c0_g1 | ERS1 | Ethylene response sensor 1 | 9.71 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2665_c0_g1 | RAP2-13 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-13 | 10.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN40774_c0_g3 | RAP2-3 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-3 | −5.92 | −4.04 | −5.69 | −5.82 | −2.5 | ||
| TRINITY_DN1497_c0_g1 | RAP2-4 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-4 | 4.08 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2_c1_g1 | RAP2-6 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-6 | 2.25 | 2.3 | 2.41 | 11.76 | |||
| TRINITY_DN12350_c0_g1 | RAP2-7 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor RAP2-7 | 6.43 | 4.91 | 6.54 | 4.61 | 4.12 | 9.24 | |
| TRINITY_DN5947_c0_g1 | RTE1 | Protein REVERSION-TO-ETHYLENE SENSITIVITY1 | 10.91 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN29694_c0_g1 | SHN3 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor SHINE 3 | −3.72 | −3.93 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN4330_c3_g1 | TINY | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor TINY | 9.64 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN148_c3_g1 | WRI1 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor WRI1 | −2.13 | −2.63 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN5382_c0_g1 | AT4G13040 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor-like protein At4g13040 | 9.5 | ||||||
| Lysine | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN6270_c0_g1 | AATL1 | Lysine histidine transporter-like 8 | 2.04 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8133_c0_g1 | ASHR1 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ASHR1 | 10.07 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4218_c0_g3 | ATX2 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATX2 | 7.65 | −3.53 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN3010_c0_g1 | ATX4 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATX4 | 11.71 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN209_c0_g2 | ATX5 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATX5 | 7.64 | 7.46 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN1076_c0_g1 | ATXR2 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATXR2 | 10.78 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1656_c0_g1 | ATXR3 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATXR3 | 2.13 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN11945_c0_g1 | ATXR4 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATXR4 | 9.06 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN15991_c0_g1 | ATXR5 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATXR5 | −3.1 | 6.81 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN22923_c0_g1 | ELF6 | Probable lysine-specific demethylase ELF6 | 5.1 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6877_c1_g1 | EMB3003 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component 5 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. chloroplastic | −2.46 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14929_c0_g1 | EZA1 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZA1 | 2.92 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN37680_c0_g1 | JMJ14 | Probable lysine-specific demethylase JMJ14 | 11.2 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3464_c0_g3 | JMJ25 | Lysine-specific demethylase JMJ25 | 8.39 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3267_c0_g1 | JMJ30 | Lysine-specific demethylase JMJ30 | −2.4 | −2.16 | 9.65 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN1796_c2_g1 | LHT1 | Lysine histidine transporter 1 | 4.61 | 3.22 | 2.51 | 3.81 | 4.38 | 10.07 | |
| TRINITY_DN1796_c0_g3 | LHT2 | Lysine histidine transporter 2 | 9.7 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6877_c1_g2 | LTA2 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component 4 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. chloroplastic | −2.23 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN92_c0_g1 | OVA5 | Lysine--tRNA ligase. chloroplastic/mitochondrial | 2.08 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN22984_c0_g1 | SUVH6 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase. H3 lysine-9 specific SUVH6 | −2.35 | 7.17 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN393_c0_g2 | SUVH9 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase family member SUVH9 | 10.36 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN18492_c0_g1 | SUVR1 | Probable inactive histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUVR1 | 10.33 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10785_c0_g1 | SUVR3 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUVR3 | 7.14 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN27123_c0_g1 | SUVR4 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUVR4 | 9.46 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN22651_c0_g1 | AT1G25530 | Lysine histidine transporter-like 6 | 10.9 | 2.27 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN21036_c0_g1 | AT4G26910 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex 2. mitochondrial | 9.63 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1947_c0_g1 | AT5G55070 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex 1. mitochondrial | 9.52 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN971_c1_g3 | AT4G35180 | Lysine histidine transporter-like 7 | 8.3 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN40168_c0_g1 | AT3G11710 | Lysine--tRNA ligase. cytoplasmic | 7.18 | ||||||
| Tryptophan | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN10705_c0_g1 | TAA1 | L-tryptophan--pyruvate aminotransferase 1 | 7.41 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6324_c0_g2 | TAR2 | Tryptophan aminotransferase-related protein 2 | −4.07 | −2.65 | −3.72 | −4.13 | −3.64 | ||
| TRINITY_DN18489_c0_g3 | TSB2 | Tryptophan synthase β chain 2. chloroplastic | 2.13 | 7.83 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN257_c0_g2 | AT3G04600 | Tryptophan--tRNA ligase. cytoplasmic | 10.25 | ||||||
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | M1a1 | M1a2 | M1o1 | M1o2 | M2a4 | M2o4 | M2d4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pollen development (GO:0009555) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN5448_c0_g1 | NAS3 | Nicotianamine synthase 3 | −3.49 | −4.95 | −3.84 | −3.52 | |||
| TRINITY_DN95402_c0_g1 | PS1 | FHA domain-containing protein PS1 | −2.61 | −2.08 | −2.42 | 8.49 | |||
| TRINITY_DN38119_c0_g1 | KDSB | 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase, mitochondrial | 2.07 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10816_c0_g1 | TMK3 | Receptor-like kinase TMK3 | −3.51 | −2.75 | −2.57 | −3.57 | |||
| TRINITY_DN923_c0_g1 | CALS5 | Callose synthase 5 | −2.91 | −2.05 | −3.3 | −3.49 | |||
| TRINITY_DN111580_c0_g2 | CYP73A5 | Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase | 2.6 | 2.57 | 3.63 | 2.01 | |||
| TRINITY_DN41226_c0_g1 | PAL1 | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase 1 | −2.27 | −2.65 | −3.8 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN2633_c0_g1 | CALS9 | Callose synthase 9 | 2.08 | 2.07 | 9.17 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN1417_c2_g1 | FAB1B | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase FAB1B | 2.35 | 2.38 | 2.68 | 3.2 | |||
| TRINITY_DN1233_c4_g1 | AT4G39110 | Probable receptor-like protein kinase At4g39110 | −8.01 | −4.86 | −4.65 | −7.56 | −4.44 | −3.74 | |
| TRINITY_DN3115_c1_g1 | ATL73 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL73 | −2.87 | −2.93 | −2.79 | −2.45 | 8.09 | ||
| TRINITY_DN6027_c0_g1 | LRP1 | Protein LATERAL ROOT PRIMORDIUM 1 | −2.64 | −2.92 | −2.65 | −2.47 | |||
| TRINITY_DN5863_c0_g1 | LCB2A | Long chain base biosynthesis protein 2a | 2.81 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7884_c0_g1 | XRI1 | Protein XRI1 | −4.22 | −3.9 | −2.9 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN4445_c0_g1 | CEP1 | KDEL-tailed cysteine endopeptidase CEP1 | −6.27 | −7.42 | −6.31 | −5.23 | |||
| TRINITY_DN8949_c0_g1 | SWEET13 | Bidirectional sugar transporter SWEET13 | −2.61 | −2.07 | −2.58 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN10107_c0_g1 | ABCB25 | ABC transporter B family member 25, mitochondrial | 2.48 | 2.73 | 2.35 | 8.62 | |||
| TRINITY_DN27954_c0_g3 | LECRK42 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase IV.2 | 3.43 | −2.54 | −3.02 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN8056_c1_g1 | CALS11 | Callose synthase 11 | 3.3 | 3.44 | 3.29 | 8.01 | |||
| TRINITY_DN4094_c0_g1 | NMT1 | Phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase 1 | 2.15 | 2.43 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN17932_c0_g1 | WRKY2 | Probable WRKY transcription factor 2 | −2.02 | −2.22 | −2.23 | 7.15 | |||
| TRINITY_DN12987_c0_g1 | PIN5 | Auxin efflux carrier component 5 | 2.41 | 10 | 3.48 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN4445_c0_g1 | CEP1 | KDEL-tailed cysteine endopeptidase CEP1 | |||||||
| TRINITY_DN5448_c0_g1 | NAS3 | Nicotianamine synthase 3 | |||||||
| TRINITY_DN3873_c0_g1 | AGL65 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL65 | −2.29 | −2.62 | −3.28 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN47156_c0_g1 | IPK2B | Inositol polyphosphate multikinase β | 3.28 | 7.44 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2407_c1_g1 | BZIP34 | Basic leucine zipper 34 | −5.18 | −2.68 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN12180_c0_g1 | AGL66 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL66 | −4.72 | −3.81 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN15991_c0_g1 | ATXR5 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ATXR5 | −3.1 | 6.81 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN9971_c0_g1 | MYB80 | Transcription factor MYB80 | 4.46 | 8.63 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN10584_c0_g1 | MCM7 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 | −2.04 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN5641_c0_g1 | LOX3 | Lipoxygenase 3, chloroplastic | 2.93 | 2.75 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN23341_c0_g1 | D6PKL3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D6PKL3 | 2.16 | 8.44 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN11273_c0_g1 | MCM4 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM4 | −4.4 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN440_c0_g1 | MCM8 | Probable DNA helicase MCM8 | 12.61 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3132_c0_g1 | PGDH1 | D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase 1, chloroplastic | 11.73 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN12133_c0_g1 | MRS2-2 | Magnesium transporter MRS2-2 | 11.26 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7153_c0_g1 | APD2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase APD2 | 11.16 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4731_c0_g3 | MYB101 | Transcription factor MYB101 | 11.05 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1371_c0_g1 | RGTB1 | Geranylgeranyl transferase type-2 subunit β 1 | 11.03 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2976_c0_g1 | AT2G21870 | Probable ATP synthase 24 kDa subunit. mitochondrial | 9.59 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN11362_c1_g1 | WRKY35 | Probable WRKY transcription factor 35 | 9.53 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN166676_c0_g1 | CER26L | Protein ECERIFERUM 26-like | 9.43 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9251_c0_g1 | FAS1 | Chromatin assembly factor 1 subunit FAS1 | 9.15 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN17928_c0_g2 | CYP94B3 | Cytochrome P450 94B3 | −2.3 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1593_c0_g1 | DSE1 | Protein DECREASED SIZE EXCLUSION LIMIT 1 | 3.87 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN41732_c1_g1 | GAPCP1 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GAPCP1, chloroplastic | −2.38 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN968_c1_g1 | CDKA-1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase A-1 | 8.61 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN114534_c0_g1 | LCB2B | Long chain base biosynthesis protein 2b | 8.44 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN39521_c0_g1 | RUK | Serine/threonine-protein kinase RUNKEL | 8.41 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN30938_c0_g1 | XPO1 | Protein EXPORTIN 1A | 2.82 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN54834_c0_g2 | KIN7A | Kinesin-like protein KIN-7A | 7.81 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN29594_c0_g1 | PTD | Protein PARTING DANCERS | 7.27 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3033_c0_g4 | P5CSA | Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase A | 2.7 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN31412_c0_g1 | RGP1 | UDP-arabinopyranose mutase 1 | 7.16 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14808_c0_g1 | RTEL1 | Regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 homolog | 6.99 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN49207_c0_g1 | SRS1 | Protein SHI RELATED SEQUENCE 1 | 6.96 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN29704_c0_g5 | SRS5 | Protein SHI RELATED SEQUENCE 5 | 6.81 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9646_c0_g1 | ATRX | Protein CHROMATIN REMODELING 20 | 2.32 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN21539_c0_g1 | BHLH91 | Transcription factor bHLH91 | 6.74 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN826_c0_g2 | TULP7 | Tubby-like F-box protein 7 | 2.15 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4508_c0_g1 | MPK4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | 2.09 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN161_c0_g2 | NEDD1 | Protein NEDD1 | 2.22 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6156_c0_g1 | PKSA | Type III polyketide synthase A | −3.61 | −6.78 | −6.63 | −3.39 | −2.98 | ||
| TRINITY_DN31801_c4_g1 | GPAT1 | Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1 | −4.13 | −4.38 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN17166_c0_g1 | 4CL3 | 4-coumarate--CoA ligase 3 | −4.44 | −2.69 | −4.06 | −3.78 | −2.43 | ||
| TRINITY_DN16998_c0_g1 | ZAT2 | Zinc finger protein ZAT2 | −4.9 | −4.15 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN15578_c0_g1 | LRL1 | Transcription factor LRL1 | −3.39 | 6.94 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN4588_c0_g2 | ABCG31 | ABC transporter G family member 31 | −2.72 | −3.81 | −2.13 | −2.53 | −2.22 | 10.04 | |
| TRINITY_DN45712_c0_g1 | FAR2 | Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 2, chloroplastic | −3.28 | −6.24 | −6.93 | −4.07 | −2.8 | ||
| TRINITY_DN9952_c0_g1 | ABCG26 | ABC transporter G family member 26 | −3.28 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN15838_c0_g1 | TIP5-1 | Probable aquaporin TIP5-1 | −2.48 | −2.82 | 8.26 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN6869_c0_g1 | A6 | Probable glucan endo-1,3-β-glucosidase A6 | −2.6 | −7.57 | −7.88 | −2.61 | −2.95 | ||
| TRINITY_DN156774_c0_g1 | ABCG9 | ABC transporter G family member 9 | −2.19 | −3.86 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN31379_c0_g1 | TKPR1 | Tetraketide α-pyrone reductase 1 | −4.21 | −4.43 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN3196_c3_g1 | EMS1 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EMS1 | −2.05 | −2.34 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN176325_c0_g1 | COPT1 | Copper transporter 1 | −3.79 | −3.86 | −3.99 | −3.76 | −2.12 | ||
| TRINITY_DN4485_c0_g1 | CYP704B1 | Cytochrome P450 704B1 | −2.52 | ||||||
| microsporogenesis (GO:0009556) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN5204_c0_g1 | PLC2 | Phosphoinositide phospholipase C 2 | 3.07 | 2.44 | 3.37 | 2.07 | 3.53 | ||
| TRINITY_DN3196_c3_g1 | EMS1 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EMS1 | −2.05 | −2.34 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN6537_c0_g1 | PSS1 | CDP-diacylglycerol--serine O-phosphatidyltransferase 1 | 9.39 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN2003_c0_g1 | FH14 | Formin-like protein 14 | 2.33 | ||||||
| pollen germination (GO:0009846) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN373_c0_g1 | CSLD1 | Cellulose synthase-like protein D1 | −3.31 | −4.72 | −3.45 | −2.22 | |||
| TRINITY_DN19056_c0_g1 | IP5P13 | Type I inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 13 | −2.38 | −3.35 | −2.36 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN4602_c0_g1 | JGB | Protein JINGUBANG | −4 | −4.06 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8465_c0_g1 | CSLD4 | Cellulose synthase-like protein D4 | −3.89 | −3.71 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN46361_c0_g1 | PTF2 | Plant-specific TFIIB-related protein PTF2 | 9.36 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN19056_c0_g3 | IP5P12 | Type I inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 12 | 6.94 | ||||||
| pollination (GO:0009856) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN6022_c0_g1 | ARPN | Basic blue protein | −5.23 | −3.65 | |||||
| pollen tube growth (GO:0009860) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN8457_c0_g3 | AT1G03010 | BTB/POZ domain-containing protein At1g03010 | −4.41 | −4.84 | −4.35 | −3.42 | 2.01 | ||
| TRINITY_DN5849_c0_g1 | XI-E | Myosin-11 | 2.14 | 4.3 | 3.52 | 7.48 | |||
| TRINITY_DN691_c0_g2 | ARAC5 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC5 | −3.62 | −2.02 | −2.9 | −3.64 | −2.65 | ||
| TRINITY_DN11455_c0_g1 | CBL1 | Calcineurin B-like protein 1 | 2.24 | 4.42 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN1267_c0_g1 | PEX4 | Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensin-like protein 4 | −8.5 | −5.05 | −5.26 | −8.04 | −4.31 | −3.62 | |
| TRINITY_DN677_c0_g2 | NPF8.2 | Protein NRT1/PTR FAMILY 8,2 | −2.24 | −2.05 | −2.36 | −2.43 | |||
| TRINITY_DN7934_c0_g1 | ABCG28 | ABC transporter G family member 28 | −2.78 | −3.68 | −4.42 | 7.31 | |||
| TRINITY_DN5923_c0_g1 | OASA1 | Cysteine synthase 1 | 2.1 | 2.13 | 9.71 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN8399_c0_g1 | RIC5 | CRIB domain-containing protein RIC5 | −4.82 | −4.6 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8450_c0_g1 | PPME1 | Pectinesterase PPME1 | −4.77 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN5260_c2_g1 | PEX1 | Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensin-like protein 1 | −4.49 | −3.64 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN16608_c0_g2 | RIC6 | CRIB domain-containing protein RIC6 | −4.2 | −3.93 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN184921_c0_g1 | AGC1-5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase AGC1-5 | −4.13 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN35118_c0_g1 | CNGC18 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 18 | −3.97 | 6.14 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN14636_c1_g1 | CNGC7 | Putative cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 7 | −3.93 | −4.53 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN15772_c0_g3 | CXE18 | Probable carboxylesterase 18 | −3.71 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8917_c0_g2 | TOPP8 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1 isozyme 8 | −3.98 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN12354_c0_g2 | KLCR2 | Protein KINESIN LIGHT CHAIN-RELATED 2 | −3.52 | −3.57 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN43059_c0_g1 | TCTP1 | Translationally-controlled tumor protein 1 | −2.39 | 6.64 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN145_c0_g1 | AT2G41970 | Probable protein kinase At2g41970 | −2.03 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8899_c0_g3 | ARAC11 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC11 | −2 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3041_c0_g3 | CDI | Protein CDI | 11.87 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10453_c0_g1 | AGC1-7 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase AGC1-7 | 11.84 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7093_c0_g1 | PIGA | Phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit A | 10.57 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1136_c1_g1 | FIM5 | Fimbrin-5 | 10.5 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN17922_c0_g2 | WIP2 | Zinc finger protein WIP2 | −2.58 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6837_c0_g1 | XI-C | Myosin-9 | 9.53 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN9379_c0_g1 | SBT3.1 | Subtilisin-like protease SBT3.1 | −2.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN12065_c0_g1 | MIRO1 | Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1 | 8.43 | ||||||
| pollen tube adhesion (GO:0009865) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN14184_c0_g1 | HS1 | Stress-response A/B barrel domain-containing protein HS1 | −3.03 | −2.2 | −2.58 | −2.22 | |||
| pollen-pistil interaction (GO:0009875) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN2016_c0_g1 | MPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | 2.1 | 2.21 | 4.22 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN4521_c0_g1 | MAA3 | Probable helicase MAGATAMA 3 | 12.13 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14556_c0_g1 | MKK9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 9 | 9.61 | ||||||
| pollen maturation (GO:0010152) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN8479_c0_g1 | DRP1C | Dynamin-related protein 1C | 13.13 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN13085_c0_g1 | AFB2 | Protein AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX 2 | 9.73 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6009_c0_g1 | RPK2 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase RPK2 | 3.81 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3540_c1_g1 | PDR2 | Probable manganese-transporting ATPase PDR2 | 2.12 | ||||||
| pollen tube guidance (GO:0010183) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN6442_c0_g1 | A39 | Aspartic proteinase 39 | −2.79 | −3.46 | −3.7 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN253_c1_g1 | COBL10 | COBRA-like protein 10 | −8.86 | −5.63 | −5.6 | −8.42 | −4.18 | ||
| TRINITY_DN22116_c0_g1 | MIK2 | MDIS1-interacting receptor like kinase 2 | 2.62 | 8.29 | −2.01 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN17193_c0_g1 | MIK1 | MDIS1-interacting receptor like kinase 1 | −4.33 | −3.54 | −3.34 | −4.58 | |||
| TRINITY_DN253_c0_g2 | COBL11 | COBRA-like protein 11 | −4.68 | −3.27 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN30272_c0_g1 | GEX3 | Protein GAMETE EXPRESSED 3 | −2.97 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN20396_c0_g1 | LIP2 | Receptor-like kinase LIP2 | 9.71 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7012_c0_g1 | SIZ1 | E3 SUMO-protein ligase SIZ1 | 2.21 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN5591_c0_g1 | POD1 | Protein POLLEN DEFECTIVE IN GUIDANCE 1 | 2.11 | ||||||
| pollen wall assembly (GO:0010208) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN6156_c0_g1 | PKSA | Type III polyketide synthase A | −3.61 | −6.78 | −6.63 | −3.39 | −2.98 | ||
| TRINITY_DN17166_c0_g1 | 4CL3 | 4-coumarate--CoA ligase 3 | −4.44 | −2.69 | −4.06 | −3.78 | −2.43 | ||
| TRINITY_DN923_c0_g1 | CALS5 | Callose synthase 5 | −2.91 | −2.05 | −3.3 | −3.49 | |||
| TRINITY_DN4588_c0_g2 | ABCG31 | ABC transporter G family member 31 | −2.72 | −3.81 | −2.13 | −2.53 | −2.22 | 10.04 | |
| TRINITY_DN45712_c0_g1 | FAR2 | Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 2. chloroplastic | −3.28 | −6.24 | −6.93 | −4.07 | −2.8 | ||
| TRINITY_DN9952_c0_g1 | ABCG26 | ABC transporter G family member 26 | −3.28 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6869_c0_g1 | A6 | Probable glucan endo-1,3-β-glucosidase A6 | −2.6 | −7.57 | −7.88 | −2.61 | −2.95 | ||
| TRINITY_DN31379_c0_g1 | TKPR1 | Tetraketide α-pyrone reductase 1 | −4.21 | −4.43 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN156774_c0_g1 | ABCG9 | ABC transporter G family member 9 | −2.19 | −3.86 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN3259_c0_g1 | AHL16 | AT-hook motif nuclear-localized protein 16 | 2.36 | 2.17 | 2.08 | 2.17 | |||
| TRINITY_DN6293_c0_g2 | CYP703A2 | Cytochrome P450 703A2 | −3.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4485_c0_g1 | CYP704B1 | Cytochrome P450 704B1 | −2.52 | ||||||
| pollen tube reception (GO:0010483) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN2319_c0_g2 | FER | Receptor-like protein kinase FERONIA | −3.33 | −2.02 | −2.9 | −2.85 | −3.99 | ||
| TRINITY_DN1919_c0_g1 | EVN | Dolichol kinase EVAN | 3.02 | ||||||
| pollen exine formation (GO:0010584) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN6156_c0_g1 | PKSA | Type III polyketide synthase A | −3.61 | −6.78 | −6.63 | −3.39 | −2.98 | ||
| TRINITY_DN17166_c0_g1 | 4CL3 | 4-coumarate--CoA ligase 3 | −4.44 | −2.69 | −4.06 | −3.78 | −2.43 | ||
| TRINITY_DN45712_c0_g1 | FAR2 | Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 2. chloroplastic | −3.28 | −6.24 | −6.93 | −4.07 | −2.8 | ||
| TRINITY_DN6869_c0_g1 | A6 | Probable glucan endo-1,3-β-glucosidase A6 | −2.6 | −7.57 | −7.88 | −2.61 | −2.95 | ||
| TRINITY_DN4186_c0_g1 | QRT3 | Polygalacturonase QRT3 | −4.02 | −3.09 | −4.76 | −4.77 | |||
| TRINITY_DN1609_c0_g1 | BRI1 | Protein BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1 | −2.45 | −2.2 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN10341_c0_g1 | PKSB | Type III polyketide synthase B | −2.2 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN31379_c0_g1 | TKPR1 | Tetraketide α-pyrone reductase 1 | −4.21 | −4.43 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN9952_c0_g1 | ABCG26 | ABC transporter G family member 26 | −3.28 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6293_c0_g2 | CYP703A2 | Cytochrome P450 703A2 | −3.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN17210_c0_g1 | IRX9H | Probable β-1,4-xylosyltransferase IRX9H | 10.62 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8740_c0_g1 | SHT | Spermidine hydroxycinnamoyl transferase | 9.57 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4485_c0_g1 | CYP704B1 | Cytochrome P450 704B1 | −2.52 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN42106_c0_g1 | SSL13 | Protein STRICTOSIDINE SYNTHASE-LIKE 13 | 8.48 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN558_c0_g1 | CDKG1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase G1 | 3.14 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN53293_c1_g1 | TKPR2 | Tetraketide α-pyrone reductase 2 | 6.87 | ||||||
| pollen sperm cell differentiation (GO:0048235) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN176325_c0_g1 | COPT1 | Copper transporter 1 | −3.79 | −3.86 | −3.99 | −3.76 | −2.12 | ||
| TRINITY_DN16998_c0_g1 | ZAT2 | Zinc finger protein ZAT2 | −4.9 | −4.15 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN31801_c4_g1 | GPAT1 | Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1 | −4.13 | −4.38 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN40616_c0_g1 | QRT2 | Polygalacturonase QRT2 | 6.55 | −2.45 | |||||
| recognition of pollen (GO:0048544) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN10463_c0_g1 | SD129 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-29 | 3.45 | 3.42 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN6512_c0_g1 | SD16 | Receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-6 | 2.13 | 2.14 | 2.61 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN5252_c0_g2 | AT5G24080 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At5g24080 | 2.26 | −2.9 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN38630_c0_g1 | SD11 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-1 | −2.08 | 8.92 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN2975_c0_g2 | SD18 | Receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-8 | −3.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN21172_c0_g1 | RDR6 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 6 | −2.18 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN10167_c0_g1 | AT5G03700 | PAN domain-containing protein At5g03700 | −2.38 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN151527_c0_g1 | AT4G27290 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g27290 | 7.03 | ||||||
| microsporocyte nucleus (GO:0048556) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN42827_c0_g1 | ARID1 | AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1 | 10.37 | ||||||
| pollen tube development (GO:0048868) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN10227_c0_g2 | CSLC12 | Probable xyloglucan glycosyltransferase 12 | −5.27 | −3.31 | −4.36 | −5.35 | −3.3 | ||
| TRINITY_DN2830_c0_g1 | EDA30 | Protein EMBRYO SAC DEVELOPMENT ARREST 30 | 11.59 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN16425_c0_g1 | LPPG | Lipid phosphate phosphatase γ | 11.3 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN1186_c1_g2 | KCS5 | 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase 5 | −3.15 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN65496_c0_g1 | E1-β-2 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit β-3, chloroplastic | 9.78 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14636_c1_g1 | CNGC7 | Putative cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 7 | −3.93 | −4.53 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8450_c0_g1 | PPME1 | Pectinesterase PPME1 | −4.77 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN691_c0_g2 | ARAC5 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC5 | −3.62 | −2.02 | −2.9 | −3.64 | −2.65 | ||
| TRINITY_DN5487_c0_g1 | ROPGEF12 | Rop guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 | −5.33 | −2.79 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN923_c0_g1 | CALS5 | Callose synthase 5 | −2.91 | −2.05 | −3.3 | −3.49 | |||
| TRINITY_DN16608_c0_g2 | RIC6 | CRIB domain-containing protein RIC6 | −4.2 | −3.93 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN145_c0_g1 | AT2G41970 | Probable protein kinase At2g41970 | −2.03 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN184921_c0_g1 | AGC1-5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase AGC1-5 | −4.13 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN43059_c0_g1 | TCTP1 | Translationally-controlled tumor protein 1 | −2.39 | 6.64 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN1241_c0_g1 | MGP4 | UDP-D-xylose:L-fucose α-1,3-D-xylosyltransferase MGP4 | 2.88 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN14184_c0_g1 | HS1 | Stress-response A/B barrel domain-containing protein HS1 | −3.03 | −2.2 | −2.58 | −2.22 | |||
| TRINITY_DN5260_c2_g1 | PEX1 | Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensin-like protein 1 | −4.49 | −3.64 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8399_c0_g1 | RIC5 | CRIB domain-containing protein RIC5 | −4.82 | −4.6 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN12354_c0_g2 | KLCR2 | Protein KINESIN LIGHT CHAIN-RELATED 2 | −3.52 | −3.57 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8899_c0_g3 | ARAC11 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC11 | −2 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN17193_c0_g1 | MIK1 | MDIS1-interacting receptor like kinase 1 | −4.33 | −3.54 | −3.34 | −4.58 | |||
| TRINITY_DN1267_c0_g1 | PEX4 | Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensin-like protein 4 | −8.5 | −5.05 | −5.26 | −8.04 | −4.31 | −3.62 | |
| TRINITY_DN35118_c0_g1 | CNGC18 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 18 | −3.97 | 6.14 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN30272_c0_g1 | GEX3 | Protein GAMETE EXPRESSED 3 | −2.97 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN15772_c0_g3 | CXE18 | Probable carboxylesterase 18 | −3.71 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN8917_c0_g2 | TOPP8 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1 isozyme 8 | −3.98 | ||||||
| microgametogenesis (GO:0055046) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN3449_c0_g1 | PIRL3 | Plant intracellular Ras-group-related LRR protein 3 | 2.7 | 2.74 | 3.21 | 2.39 | |||
| TRINITY_DN15578_c0_g1 | LRL1 | Transcription factor LRL1 | −3.39 | 6.94 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN4115_c0_g1 | MYB35 | Transcription factor MYB35 | 10.32 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN593_c1_g2 | KIN12A | Kinesin-like protein KIN-12A | 8.1 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN7491_c0_g1 | AUG6 | AUGMIN subunit 6 | 2.54 | ||||||
| rejection of self pollen (GO:0060320) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN124729_c0_g1 | SPH5 | S-protein homolog 5 | −3.04 | ||||||
| acceptance of pollen (GO:0060321) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN12342_c0_g1 | SEC5A | Exocyst complex component SEC5A | 2.66 | ||||||
| pollen coat (GO:0070505) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN4588_c0_g2 | ABCG31 | ABC transporter G family member 31 | −2.72 | −3.81 | −2.13 | −2.53 | −2.22 | 10.04 | |
| TRINITY_DN156774_c0_g1 | ABCG9 | ABC transporter G family member 9 | −2.19 | −3.86 | |||||
| regulation of pollen tube growth (GO:0080092) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN28088_c0_g2 | RALFL19 | Protein RALF-like 19 | −7.67 | −4.99 | −4.97 | −7.43 | −4.92 | −4.37 | |
| TRINITY_DN6629_c0_g1 | PRK4 | Pollen receptor-like kinase 4 | −6.87 | −5.12 | −4.56 | −6.56 | −4.64 | −3.32 | |
| TRINITY_DN5487_c0_g1 | ROPGEF12 | Rop guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 | −5.33 | −2.79 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN151480_c0_g1 | CPK24 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 24 | −4.88 | −2.89 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN8879_c0_g1 | CPK17 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 17 | −4.85 | −2.86 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN14172_c0_g1 | PRK3 | Pollen receptor-like kinase 3 | −3.48 | 6.87 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN9330_c2_g1 | ROPGEF9 | Rop guanine nucleotide exchange factor 9 | −3.05 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN6638_c1_g2 | ROPGEF14 | Rop guanine nucleotide exchange factor 14 | −2.1 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN37662_c0_g1 | RABA4D | Ras-related protein RABA4d | 7.85 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN4047_c0_g1 | AT1G60420 | Probable nucleoredoxin 1 | 2.01 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN3873_c0_g1 | AGL65 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL65 | −2.29 | −2.62 | −3.28 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN12180_c0_g1 | AGL66 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL66 | −4.72 | −3.81 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN923_c0_g1 | CALS5 | Callose synthase 5 | −2.91 | −2.05 | −3.3 | −3.49 | |||
| TRINITY_DN1233_c4_g1 | AT4G39110 | Probable receptor-like protein kinase At4g39110 | −8.01 | −4.86 | −4.65 | −7.56 | −4.44 | −3.74 | |
| pollen tube tip (GO:0090404) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN14105_c0_g1 | ALA3 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase 3 | 2.51 | 3.12 | 10.21 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN5561_c0_g1 | ANX2 | Receptor-like protein kinase ANXUR2 | −7.96 | −4.9 | −5.05 | −7.4 | −4.33 | −3.5 | |
| pollen tube (GO:0090406) | |||||||||
| TRINITY_DN41664_c0_g1 | ZAR1 | Receptor protein kinase-like protein ZAR1 | −2.54 | −2.17 | −2.01 | −2.43 | |||
| TRINITY_DN6369_c0_g1 | PLT1 | Putative polyol transporter 1 | −2.03 | −2.04 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN29983_c0_g1 | AT4G36180 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g36180 | −3.9 | −2.83 | −4.51 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN6280_c0_g1 | STP8 | Sugar transport protein 8 | −4.78 | −2.96 | −4.96 | −4.45 | 10.23 | ||
| TRINITY_DN4295_c0_g1 | INT2 | Probable inositol transporter 2 | 2.38 | 2.79 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN15838_c0_g1 | TIP5-1 | Probable aquaporin TIP5-1 | −2.48 | −2.82 | 8.26 | ||||
| TRINITY_DN12736_c0_g1 | LLG2 | GPI-anchored protein LLG2 | −4.35 | −2.64 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN165958_c0_g1 | GATL4 | Probable galacturonosyltransferase-like 4 | −4.18 | −4.06 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN11246_c1_g1 | GNL2 | ARF guanine-nucleotide exchange factor GNL2 | −2.8 | −2.87 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN63597_c0_g1 | MDIS2 | Protein MALE DISCOVERER 2 | −2.26 | 9.33 | |||||
| TRINITY_DN9084_c0_g1 | SUC3 | Sucrose transport protein SUC3 | 11.54 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN18602_c0_g1 | SAUR62 | Auxin-responsive protein SAUR62 | 9.11 | ||||||
| TRINITY_DN38341_c0_g1 | STP7 | Sugar transport protein 7 | 2.55 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caperta, A.D.; Fernandes, I.; Conceição, S.I.R.; Marques, I.; Róis, A.S.; Paulo, O.S. Ovule Transcriptome Analysis Discloses Deregulation of Genes and Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Limonium Species (Plumbaginaceae). Genes 2023, 14, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040901
Caperta AD, Fernandes I, Conceição SIR, Marques I, Róis AS, Paulo OS. Ovule Transcriptome Analysis Discloses Deregulation of Genes and Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Limonium Species (Plumbaginaceae). Genes. 2023; 14(4):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040901
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaperta, Ana D., Isabel Fernandes, Sofia I. R. Conceição, Isabel Marques, Ana S. Róis, and Octávio S. Paulo. 2023. "Ovule Transcriptome Analysis Discloses Deregulation of Genes and Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Limonium Species (Plumbaginaceae)" Genes 14, no. 4: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040901
APA StyleCaperta, A. D., Fernandes, I., Conceição, S. I. R., Marques, I., Róis, A. S., & Paulo, O. S. (2023). Ovule Transcriptome Analysis Discloses Deregulation of Genes and Pathways in Sexual and Apomictic Limonium Species (Plumbaginaceae). Genes, 14(4), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040901









