Stacking Multiple Genes Improves Resistance to Chilo suppressalis, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Nilaparvata lugens in Transgenic Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
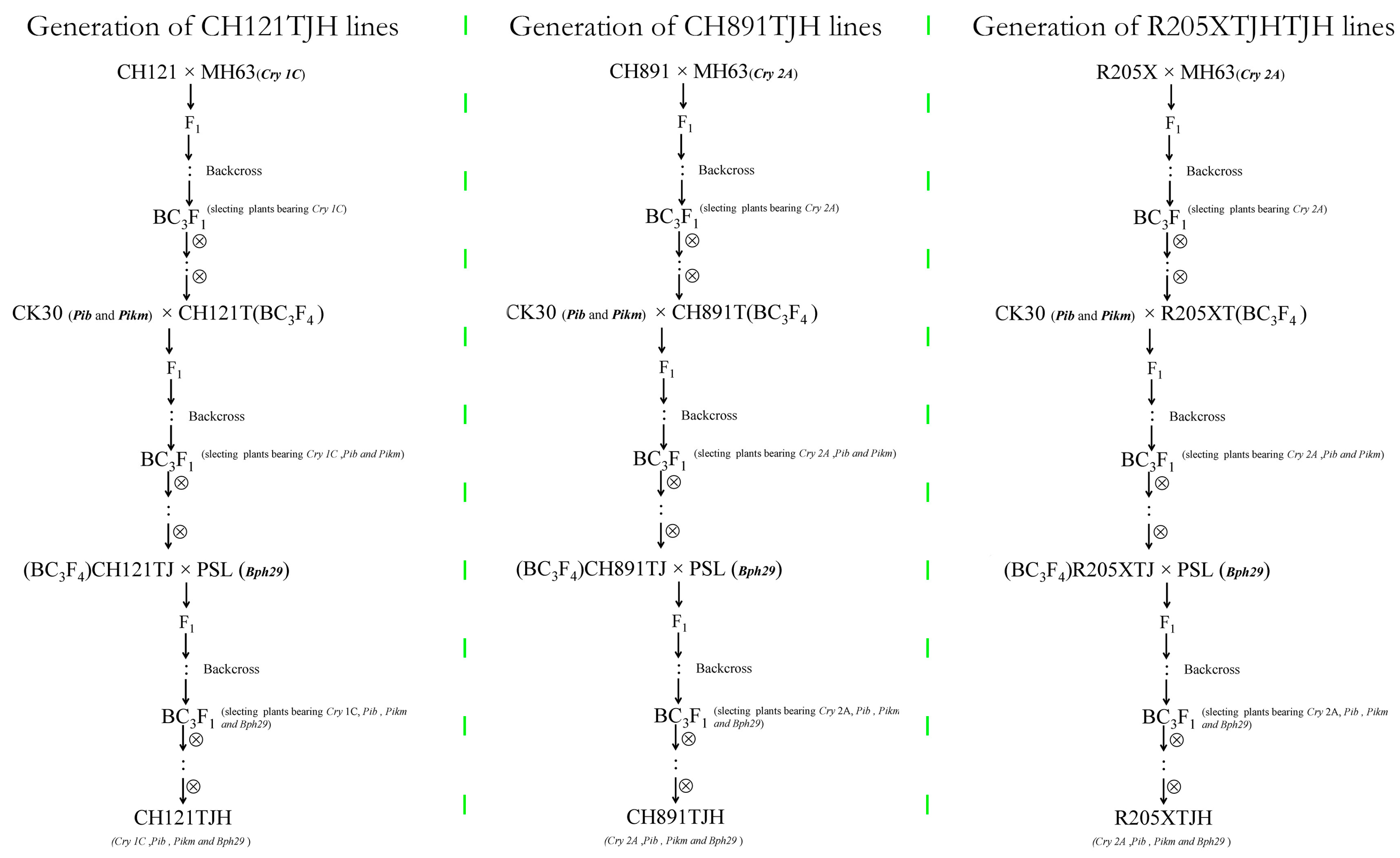
2.1. Plant Materials
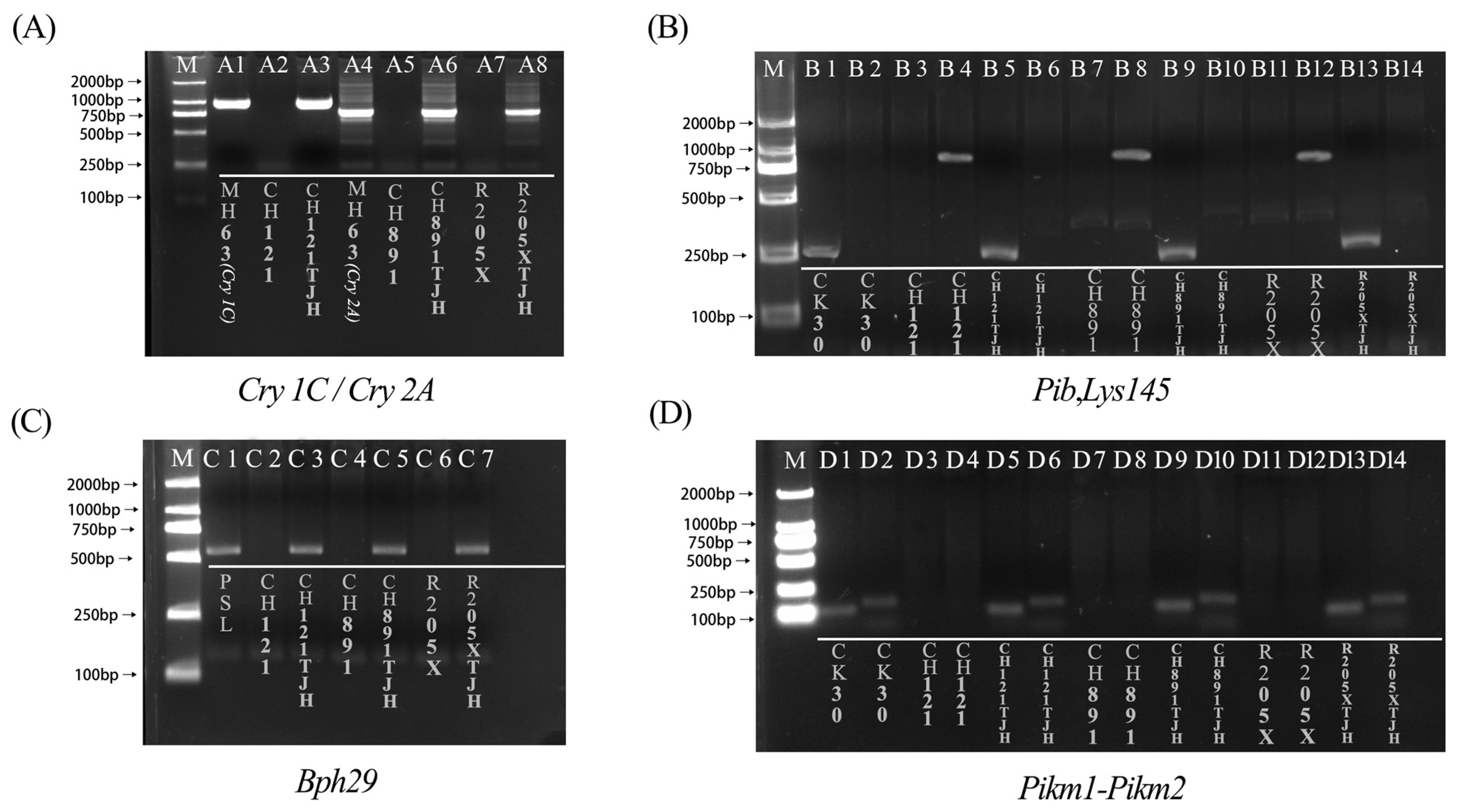
2.2. Molecular Marker-Assisted Detection
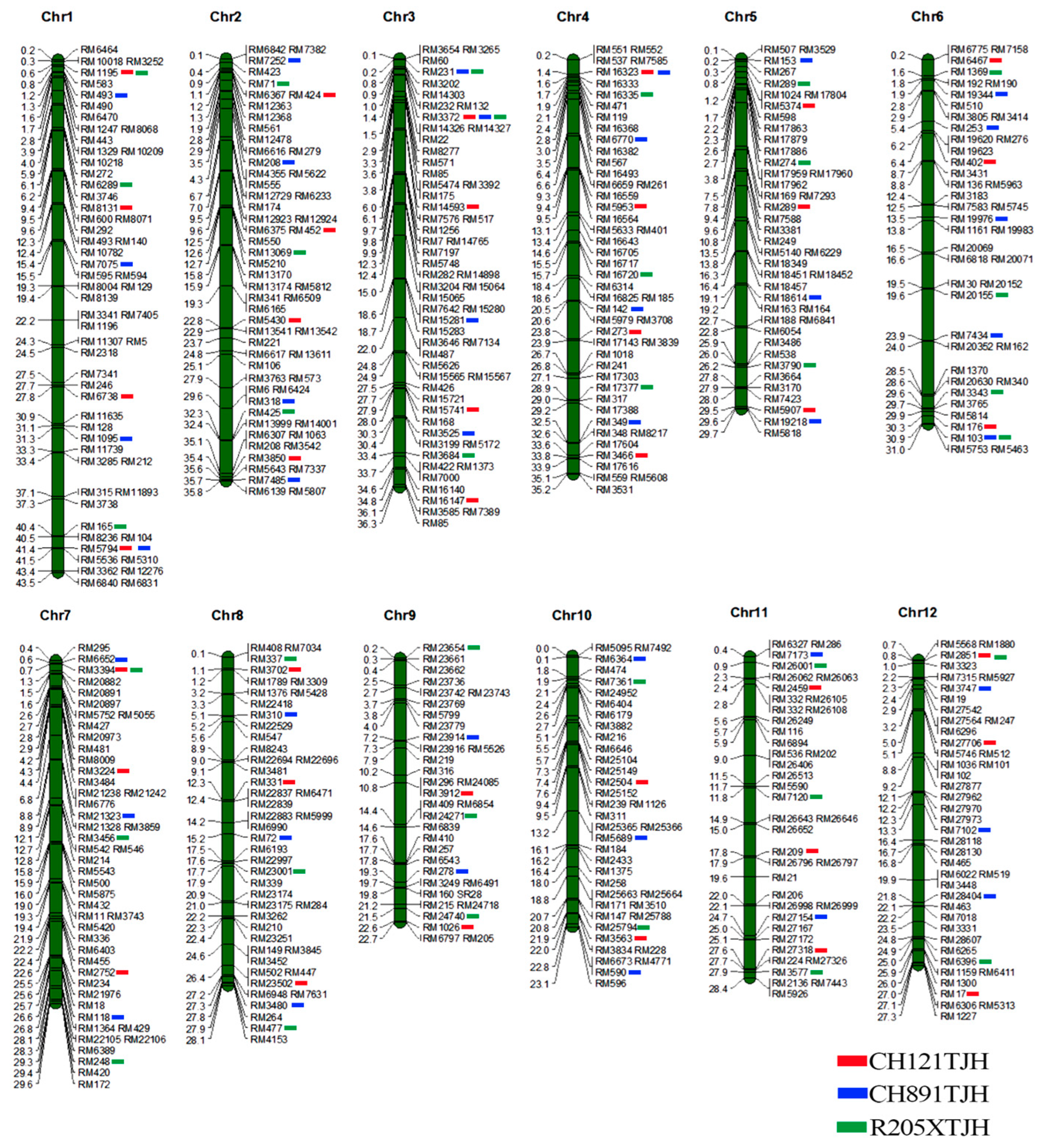
2.3. Genetic Background Detection Based on SSR Markers
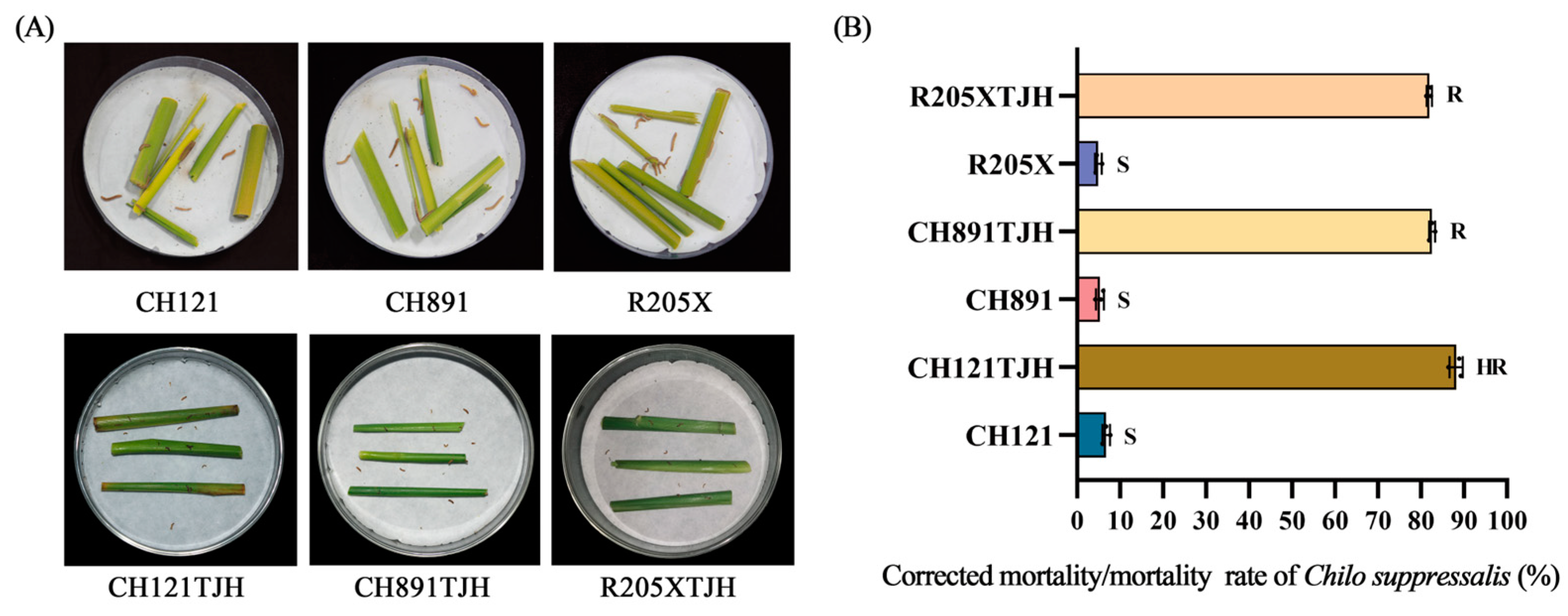
2.4. Insect Resistance in the Laboratory
larval × 100%
negative controls rice)/(1 − larval mortality of negative controls rice) × 100%
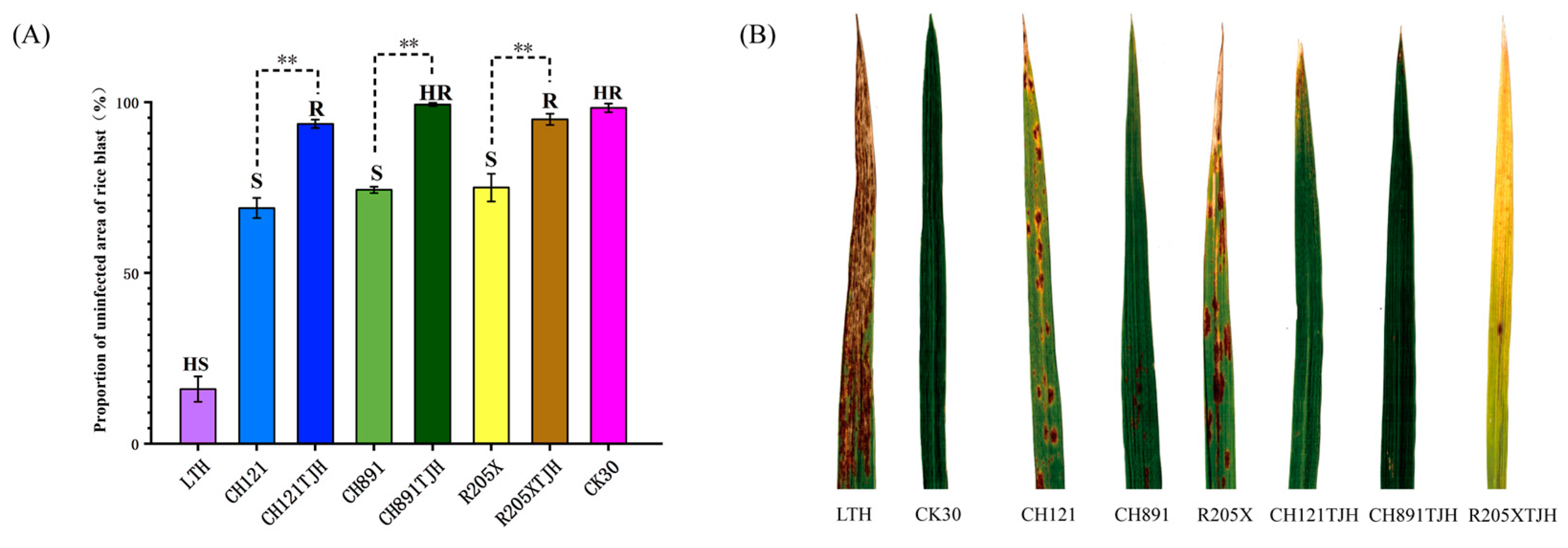
2.5. Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance at the Seedling Stage
2.6. Identification of Resistance to N. lugens at the Seedling Stage
2.7. Measurement of Agronomic Traits
3. Results
3.1. Resistance Gene Stacking Analysis
3.2. Analysis of Genetic Background Recovery Rate
3.3. Assessment of Resistance to C. suppressalis
3.4. Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance at the Seedling Stage
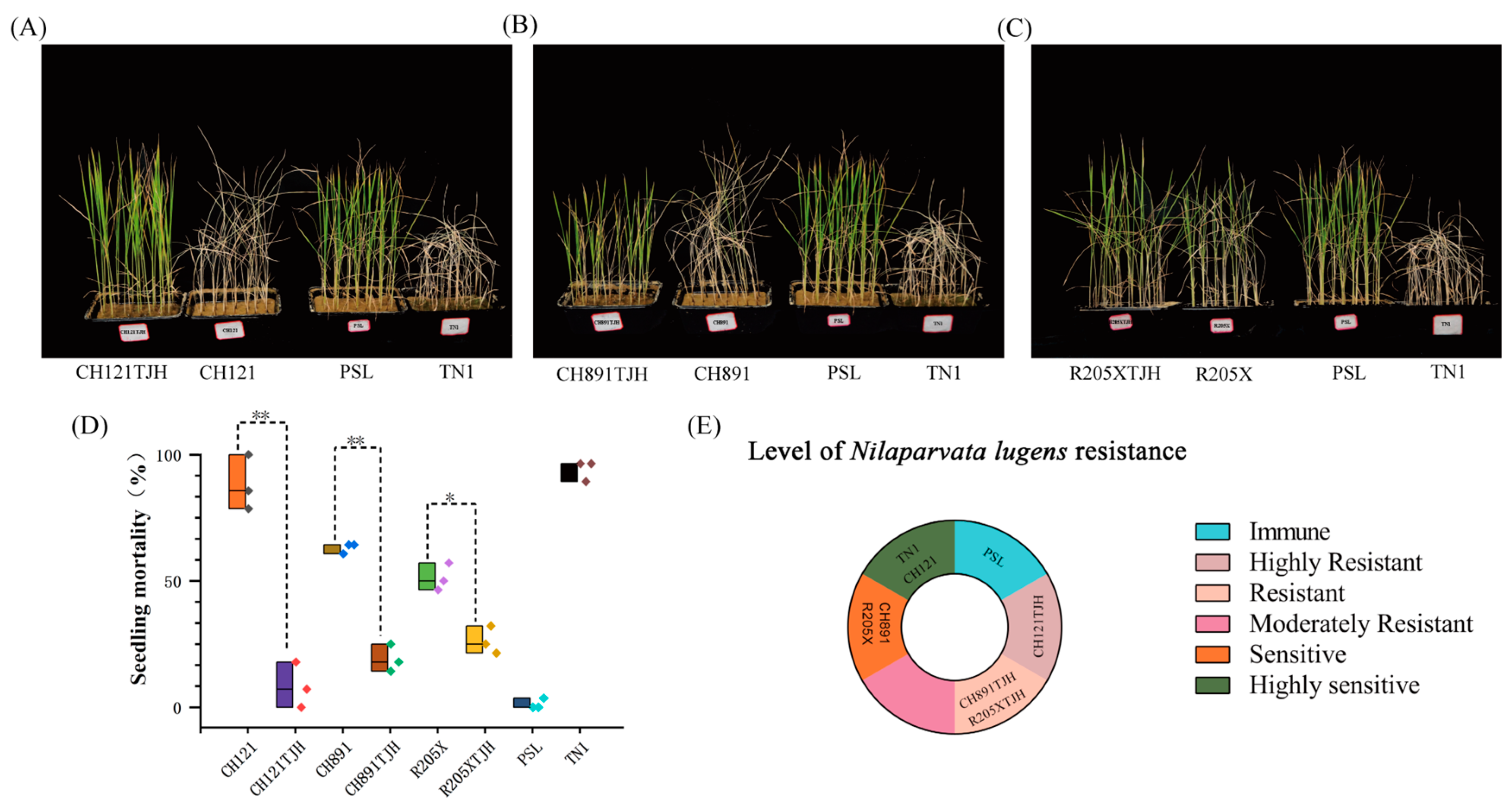
3.5. Assessment of N. lugens Resistance at the Seedling Stage
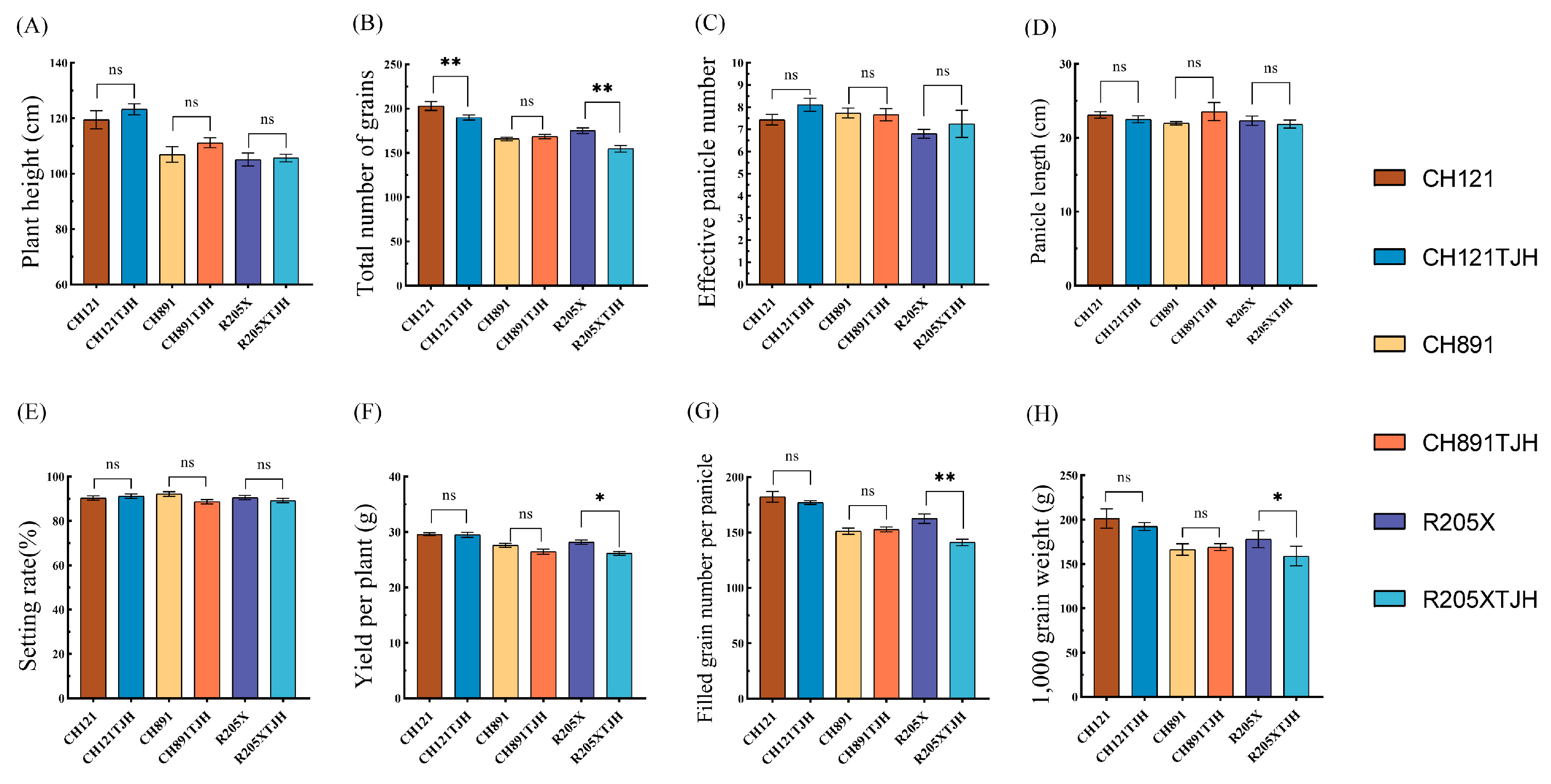
3.6. Analysis of Agronomic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caron, P.; Ferrero de Loma-Osorio, G.; Ferroni, M.; Lehmann, B.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Sokona, Y. Global Food Security: Pool Collective Intelligence. Nature 2022, 612, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litsinger, J.A.; Canapi, B.L.; Bandong, J.P.; Cruz, C.D.; Apostol, R.F.; Pantua, P.C.; Lumaban, M.D.; Alviola, A.L.; Raymundo, F.; Libetario, E.M.; et al. Rice Crop Loss from Insect Pests in Wetland and Dryland Environments of Asia with Emphasis on the Philippines. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2011, 8, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pan, S.; Cai, M.; Li, C.; Zhan, M.; Wang, J.; Mohamed, I.; Cao, C. Assessment of yield advantages of Bt-MH63 with cry1C* or cry2A* genes over MH63 (Oryza sativa L.) under different pest control modes. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S.; Jena, K.K. Advances in Genetics, Genomics and Control of Rice Blast Disease. Conf. Proc. 2009, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.D.; Cabunagan, R.C.; Cabauatan, P.Q.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, I.R.; Ho, V.C.; Nguyen, H.H. Yellowing syndrome of rice: Etiology, current status and future challenges. Omonrice 2007, 15, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Du, B.; Chen, R. Insect Resistance. In Genetics and Genomics of Rice; Zhang, Q., Wing, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, H.B.; Shirke, M.D.; Singh, S.; Rajamani, A.; Hittalmani, S.; Wang, G.L.; Gowda, M. Indica Rice Genome Assembly, Annotation and Mining of Blast Disease Resistance Genes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnadass, A.; Fernandes, P.; Avelino, J.; Habib, R. Plant Species Diversity for Sustainable Management of Crop Pests and Diseases in Agroecosystems: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdon, J.J.; Barrett, L.G.; Rebetzke, G.; Thrall, P.H. Guiding Deployment of Resistance in Cereals Using Evolutionary Principles. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Sun, X.; Mumm, R.H. Optimized Breeding Strategies for Multiple Trait Integration:II. Process Efficiency in Event Pyramiding and Trait Fixation. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witcombe, J.; Hash, C. Resistance Gene Deployment Strategies in Cereal Hybrids Using Marker-assisted Selection: Gene Pyramiding, Three-way Hybrids, and Synthetic Parent Populations. Euphytica 2000, 112, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermerris, W.; Saballos, A.; Ejeta, G.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R.; Carpita, N.C. Molecular Breeding to Enhance Ethanol Production from Corn and Sorghum Stover. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, S142–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgotra, R.K.; Gupta, B.B.; Millwood, R.J.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Stewart, C.N. Introgression of Bacterial Leaf Blight Resistance and Aroma Genes Using Functional Marker-assisted Selection in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 2012, 187, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, S.G.; Ma, Y.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, K.D.; Zhu, L.H. Marker-assisted Selection and Pyramiding for Three Blast Resistance Genes, Pi-d(t)1, Pi-b, Pi-ta2, in Rice. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao = Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 20, 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, W.; Zhao, J.; Jin, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y. Diverse Genetic Basis of Field-evolved Resistance to Bt Cotton in Cotton Bollworm from China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10275–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, K.K.; Osborn, T.C. Simple plant DNA isolation procedures. In Plant Genomes: Methods for Genetic and Physical Mapping, 1st ed.; Beckmann, J.S., Osborn, T.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesenberg-Smith, K.A.; Pessarakli, M.M.; Wolk, D.M. Assessment of DNA Yield and Purity:An Overlooked Detail of PCR Troubleshooting. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2012, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, S.; Jia, Y. Sequence Variation at the Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pi-km Locus: Implications for the Development of Allele Specific Markers. Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjellstrom, R.; Conaway-Bormans, C.A.; McClung, A.M.; Marchetti, M.A.; Shank, A.R.; Park, W.D. Development of DNA Markers Suitable for Marker Assisted Selection of Three Pi Genes Conferring Resistance to Multiple Pyricularia grisea Pathotypes. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, F.; Chevalet, C.; Mulsant, P. Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 1992, 132, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A. Larval Movements of Chilo partellus (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) within and between Plants: Timing, Density Responses and Survival. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1992, 82, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tzin, V.; Romeis, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses to Understand the Dynamic Responses of Rice Plants to Attack by the Rice Stem Borer Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Ke, K.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Han, L.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Hua, H.X.; Peng, Y.F. Comparison of Three Transgenic Bt Rice Lines for Insecticidal Protein Expression and Resistance Against a Target Pest, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashizawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Moriwaki, J.; Hirayae, K.A. Refined Inoculation Method to Evaluate False Smut Resistance in Rice. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2011, 77, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackill, D.J.; Bonman, J.M. Inheritance of Blast Resistance in Near-isogenic Lines of Rice. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, R.; Heinrichs, E.A.; Medrano, F.G. Greenhouse Techniques to Identify Field Resistance to the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Stål)(Homoptera: Delphacidae), in Rice Cultivars. Crop Prot. 1986, 5, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyen-Sampong, M. Assessment of On-Farm Losses in Rice Due to Insect Pests. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 1988, 9, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Vossen, J.H.; Visser, R.G.; Jacobsen, E. Functional stacking of three resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans in potato. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amian, A.A.; Papenbrock, J.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Hassan, F. Enhancing transgenic pea (Pisum sativum L.) resistance against fungal diseases through stacking of two antifungal genes (chitinase and glucanase). GM Crops 2011, 2, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehryar, K.; Khan, R.S.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, S.A.; Imdad, S.; Bibi, A.; Nakamura, I. Transgene stacking as effective tool for enhanced disease resistance in plants. Mol. Biotechnol. 2020, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.C.; Liu, M.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.C. Generation of insect-resistant and glyphosate-tolerant rice by introduction of a T-DNA containing two Bt insecticidal genes and an EPSPS gene. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, S.B.; Riazuddin, S.; Loc, N.T.; Gatehouse, A.M.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Christou, P. Expression of multiple insecticidal genes confers broad resistance against a range of different rice pests. Mol. Breed. 2001, 7, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, F.; Chesson, A.; Colquhoun, I.; Constable, A.; Davies, H.V.; Engel, K.H.; Smith, M. Unintended effects and their detection in genetically modified crops. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 1089–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, H.J.; Krens, F.A.; Jacobsen, E. Do cisgenic plants warrant less stringent oversight? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribaut, J.M.; Hoisington, D. Marker-assisted Selection:New Tools and Strategies. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, N.; Ramanathan, N.; Pukalenthy, B.; Chandran, S.; Manickam, D.; Adhimoolam, K.; Nalliappan, G.K.; Manickam, S.; Rajasekaran, R.; Sampathrajan, V.; et al. Development of β-carotene, Lysine, and Tryptophan-rich Maize (Zea mays) Inbreds Through Marker-assisted Gene Pyramiding. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Rao, G.J.; Varier, M.; Prakash, A.; Prasad, D. Improved Tapaswini Having Four BB Resistance Genes Pyramided with Six Genes/QTLs, Resistance/Tolerance to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Rice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, R.W. Marker-Assisted Dissection of Adaptedness in Cultivation. In Principles of Plant Breeding, 2nd ed.; Allard, R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Toronto, Canada, 1999; Volume 11, pp. 136–154. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A.; Sorrells, M.E. Genic Microsatellite Markers in Plants: Features and Applications. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2004, 23, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.; Dakshinamurthi, V.; Ramasamy, S.; Manickam, S.; Kaliyaperumal, A.K.; Raha, S.; Raveendran, M. Introgression of Submergence Tolerance into CO 43, a Popular Rice Variety of India, through Marker-assisted Backcross Breeding. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2018, 54, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, G.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Puteh, A.B.; Rahim, H.A.; Latif, M.A. Marker-assisted Introgression of Broad-spectrum Blast Resistance Genes into the Cultivated MR219 Rice Variety. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2810–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Varity | Type | Provided by | R.Gene | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MH63(CRY1C) | Donor parents | Huazhong Agricultural University, China | CRY1C | Chilo suppressalis |
| MH63(CRY2A) | Donor parents | Huazhong Agricultural University, China | CRY2A | C. suppressalis |
| CK30 | Donor parents | Sichuan Agricultural University, China | Pib Pikm | Magnaporthe oryzae |
| PSL | Donor parents | Chengdu Institute of Biology, China | Bph29 | Nilaparvata lugens |
| CH121 | Acceptor parents | Jiangxi Agricultural University, China | / | / |
| CH891 | Acceptor parents | Jiangxi Agricultural University, China | / | / |
| R205X | Acceptor parents | Jiangxi Agricultural University, China | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Song, L.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, D.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, C.; et al. Stacking Multiple Genes Improves Resistance to Chilo suppressalis, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Nilaparvata lugens in Transgenic Rice. Genes 2023, 14, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14051070
Li B, Chen Z, Chen H, Wang C, Song L, Sun Y, Cai Y, Zhou D, Ouyang L, Zhu C, et al. Stacking Multiple Genes Improves Resistance to Chilo suppressalis, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Nilaparvata lugens in Transgenic Rice. Genes. 2023; 14(5):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14051070
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bai, Zhongkai Chen, Huizhen Chen, Chunlei Wang, Liyan Song, Yue Sun, Yicong Cai, Dahu Zhou, Linjuan Ouyang, Changlan Zhu, and et al. 2023. "Stacking Multiple Genes Improves Resistance to Chilo suppressalis, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Nilaparvata lugens in Transgenic Rice" Genes 14, no. 5: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14051070
APA StyleLi, B., Chen, Z., Chen, H., Wang, C., Song, L., Sun, Y., Cai, Y., Zhou, D., Ouyang, L., Zhu, C., He, H., & Peng, X. (2023). Stacking Multiple Genes Improves Resistance to Chilo suppressalis, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Nilaparvata lugens in Transgenic Rice. Genes, 14(5), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14051070








