Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Expression Analysis Suggest Its Roles in Responses to Cercospora Leaf Spot in Sugar Beet (Beta Vulgaris L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties Analysis of BvBBXs
2.2. Chromosome Localization Analysis of BvBBXs
2.3. Domain Analysis of BvBBXs
2.4. Analysis of Gene Structures and Conserved Motifs of BvBBx Genes
2.5. Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis BvBBXs
2.6. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of BvBBXs’ Promoters
2.7. Analisis of BvBBx Genes’ Potential Role in Leaf Spot Disease Resistance
2.7.1. Infection Experiment
2.7.2. Sampling Treatment
2.7.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of B-Box Gene Family in Sugar Beet Genome
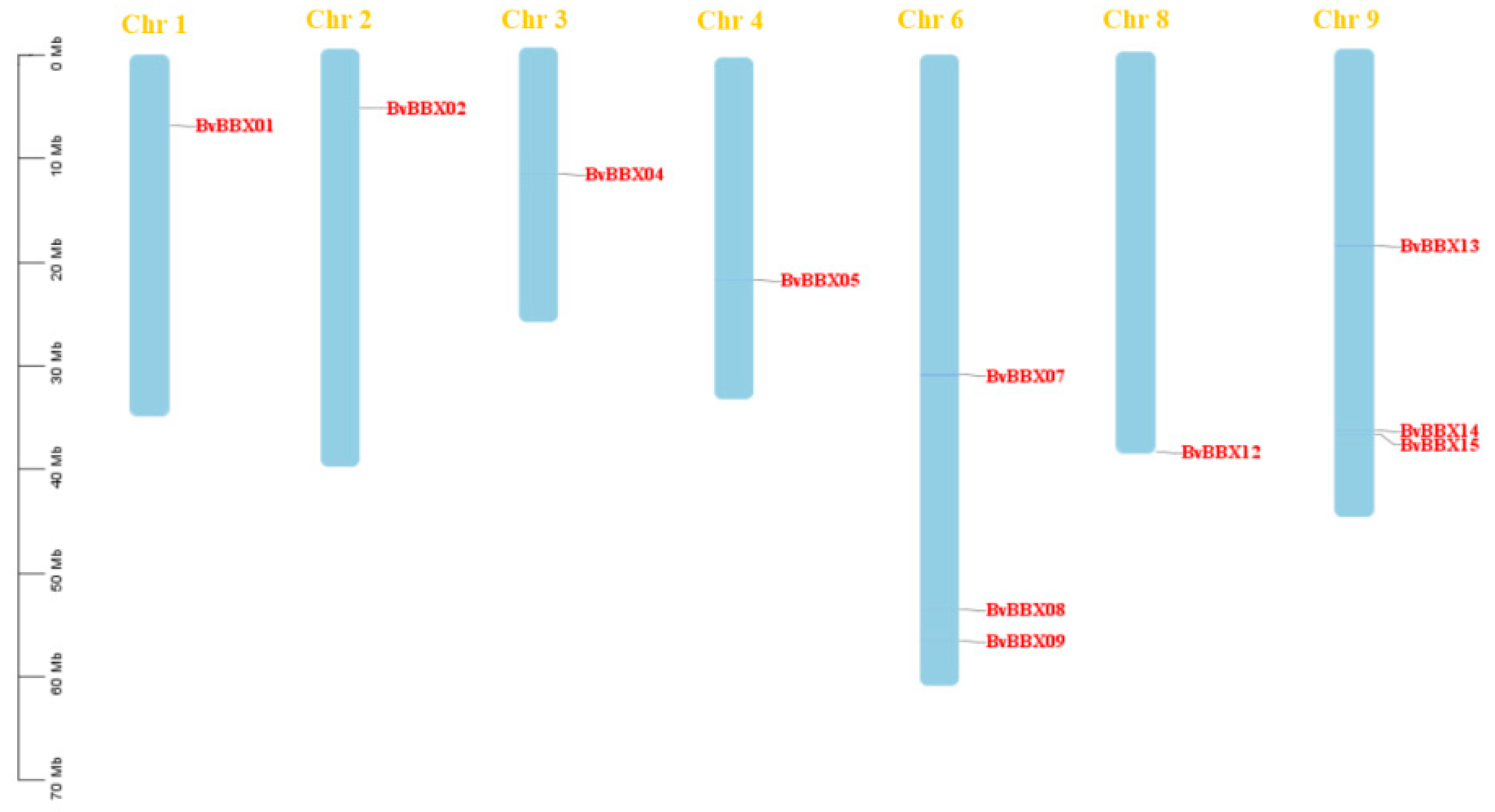
3.2. Chromosome Localization Analysis of B-Box Gene Family in Sugar Beet
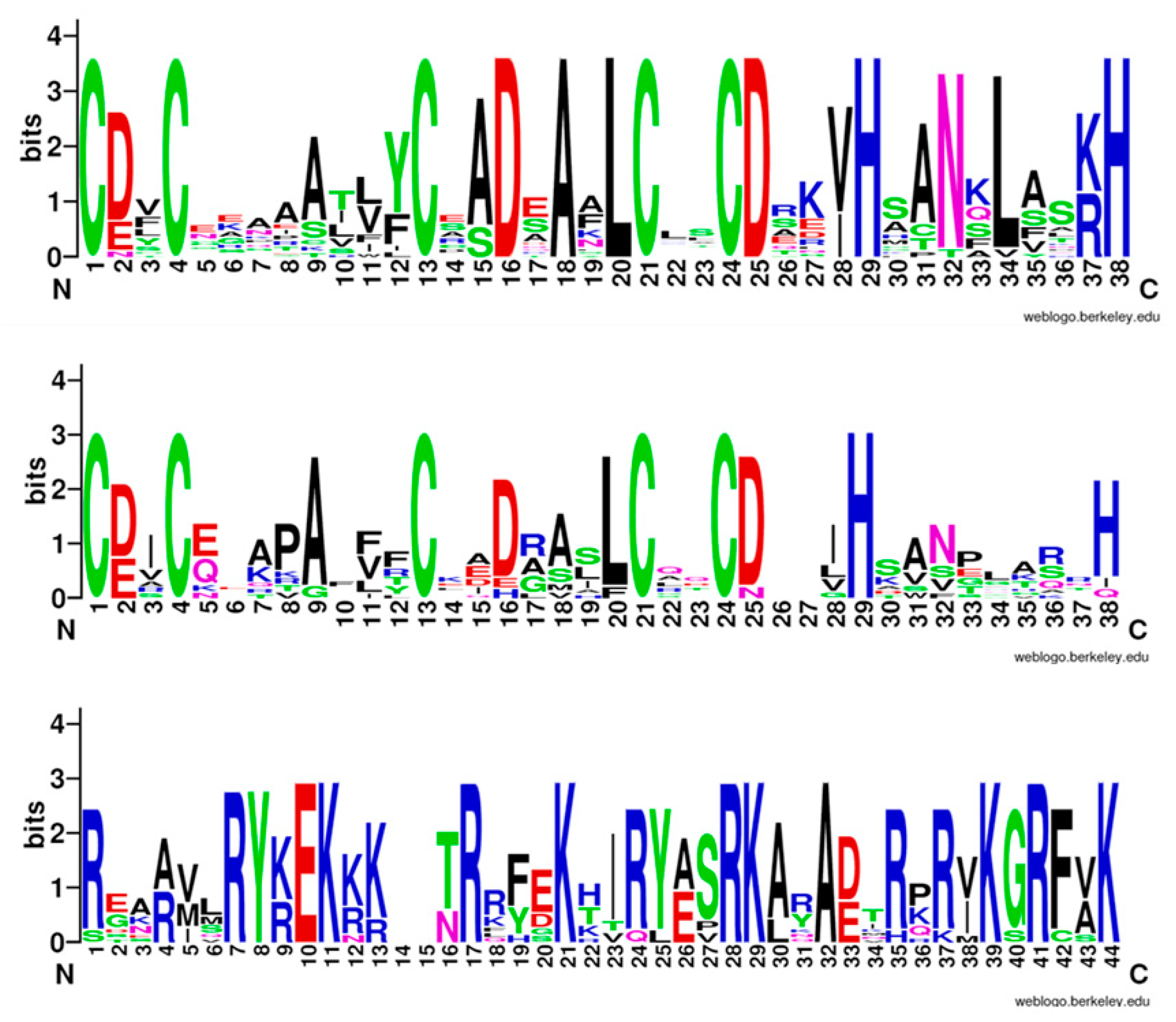
3.3. Domain Analysis of Sugar Beet B-Box Family Members
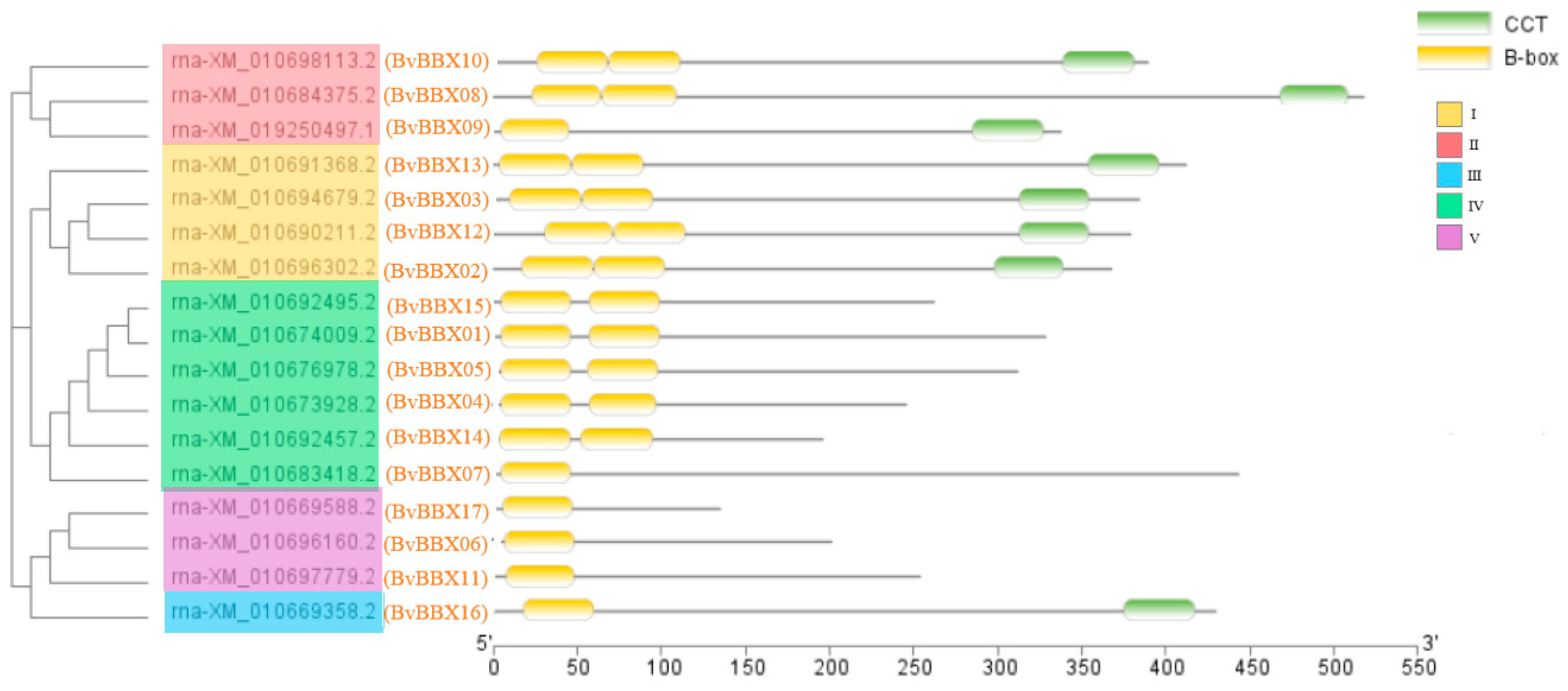
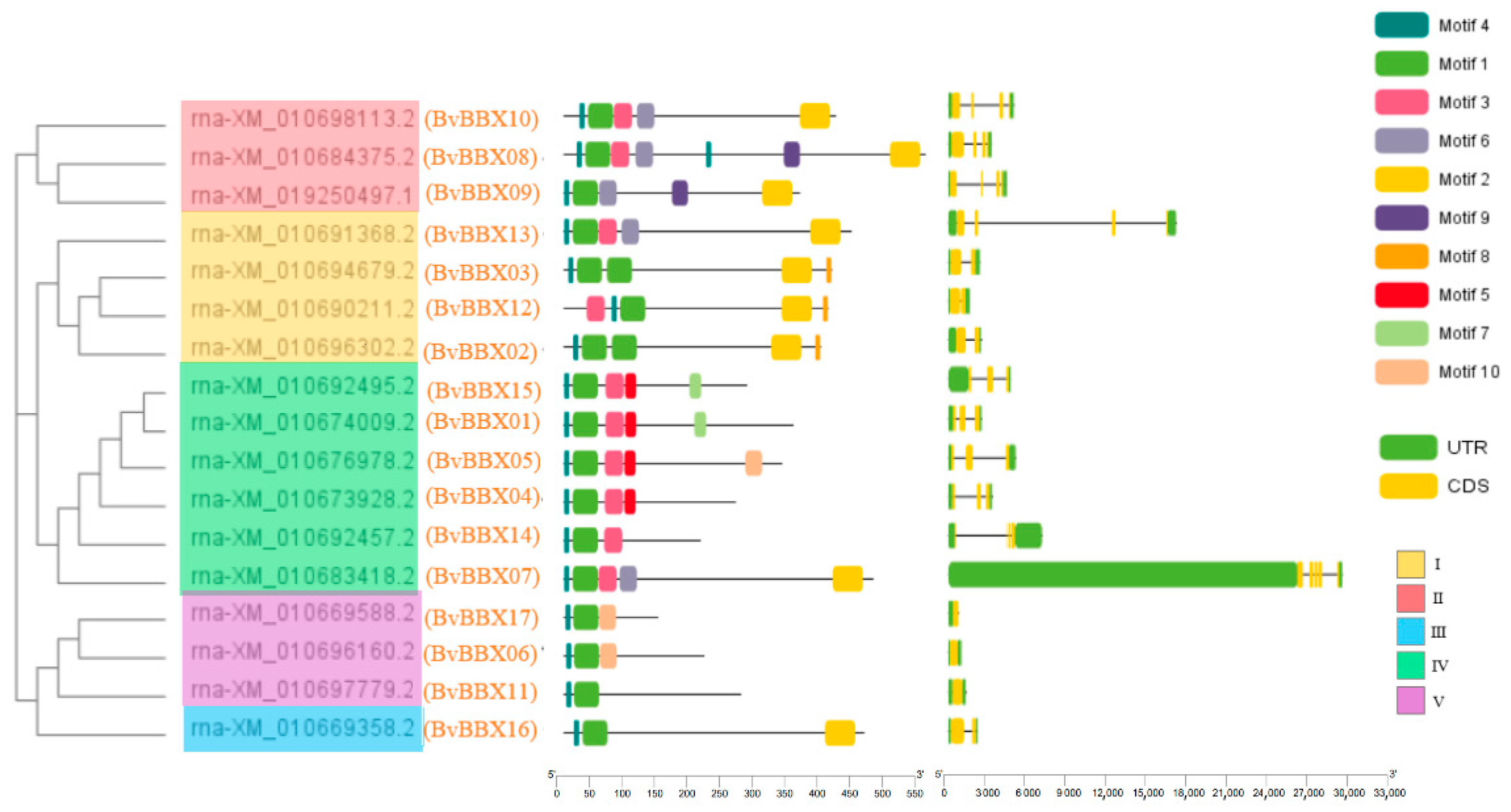
3.4. Analysis of Gene Structure and Protein Conserved Motifs of Sugar Beet B-Box Family Members
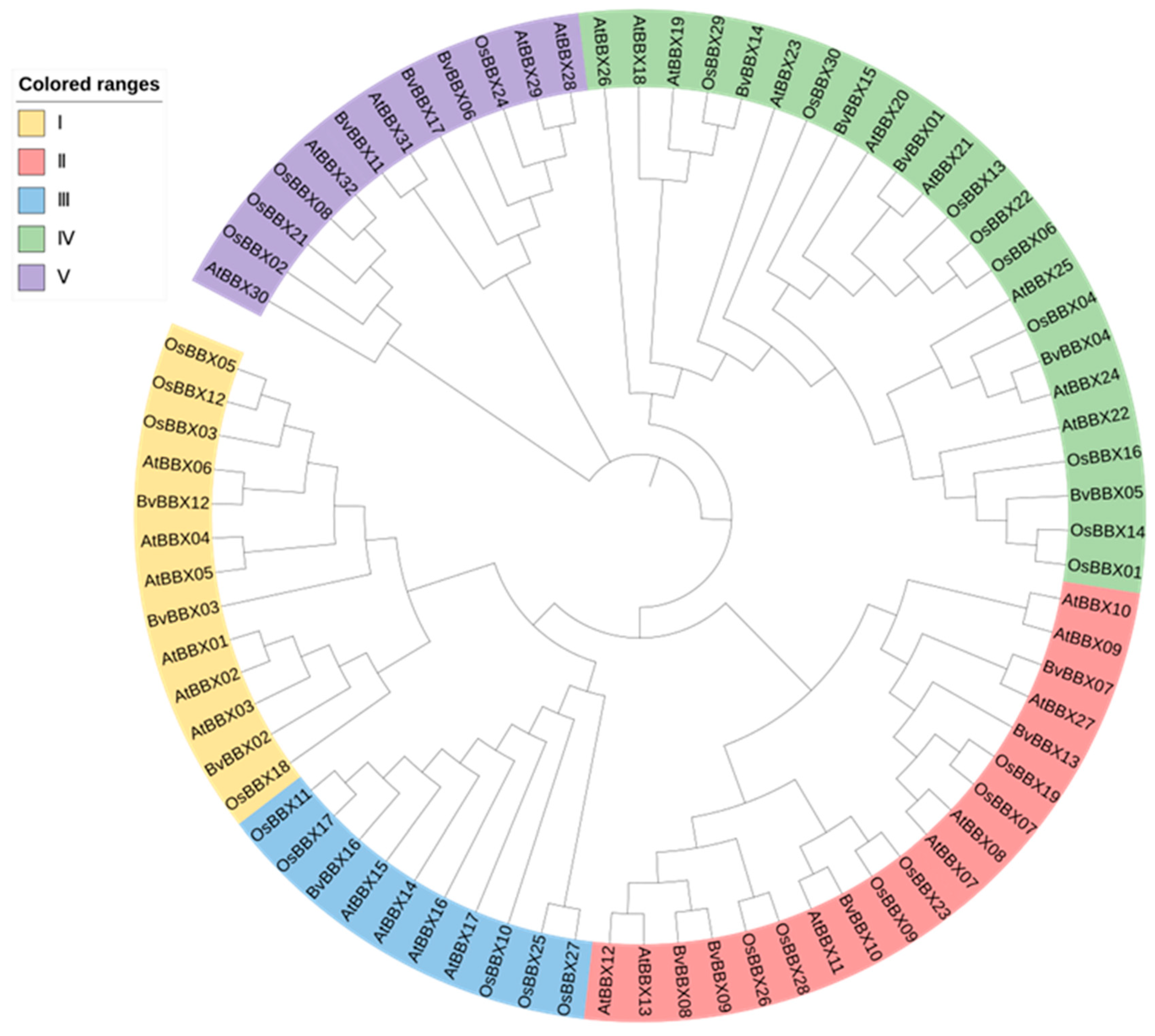
3.5. Classification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Family Members
3.6. Cis-Acting Element Analysis
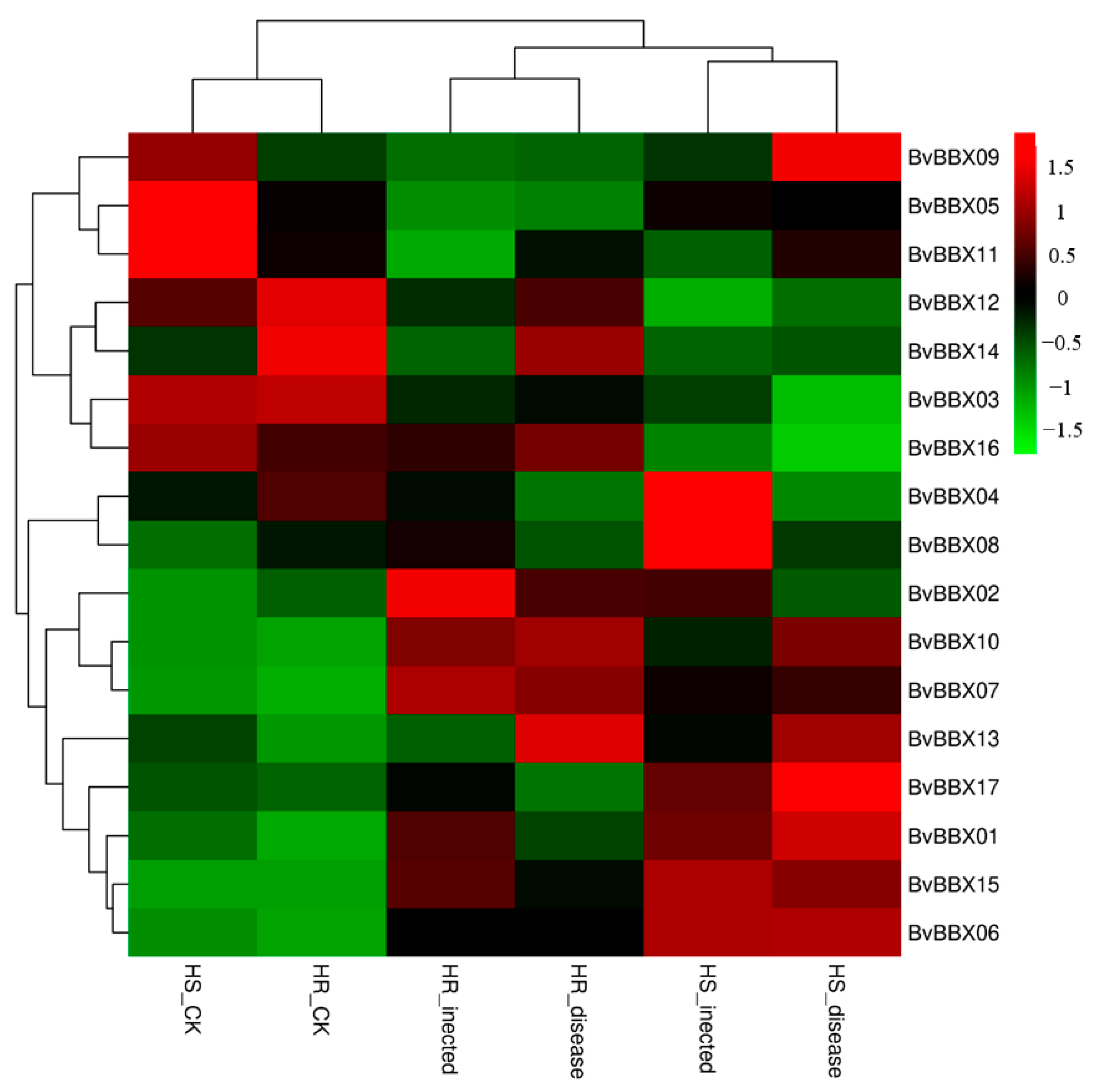
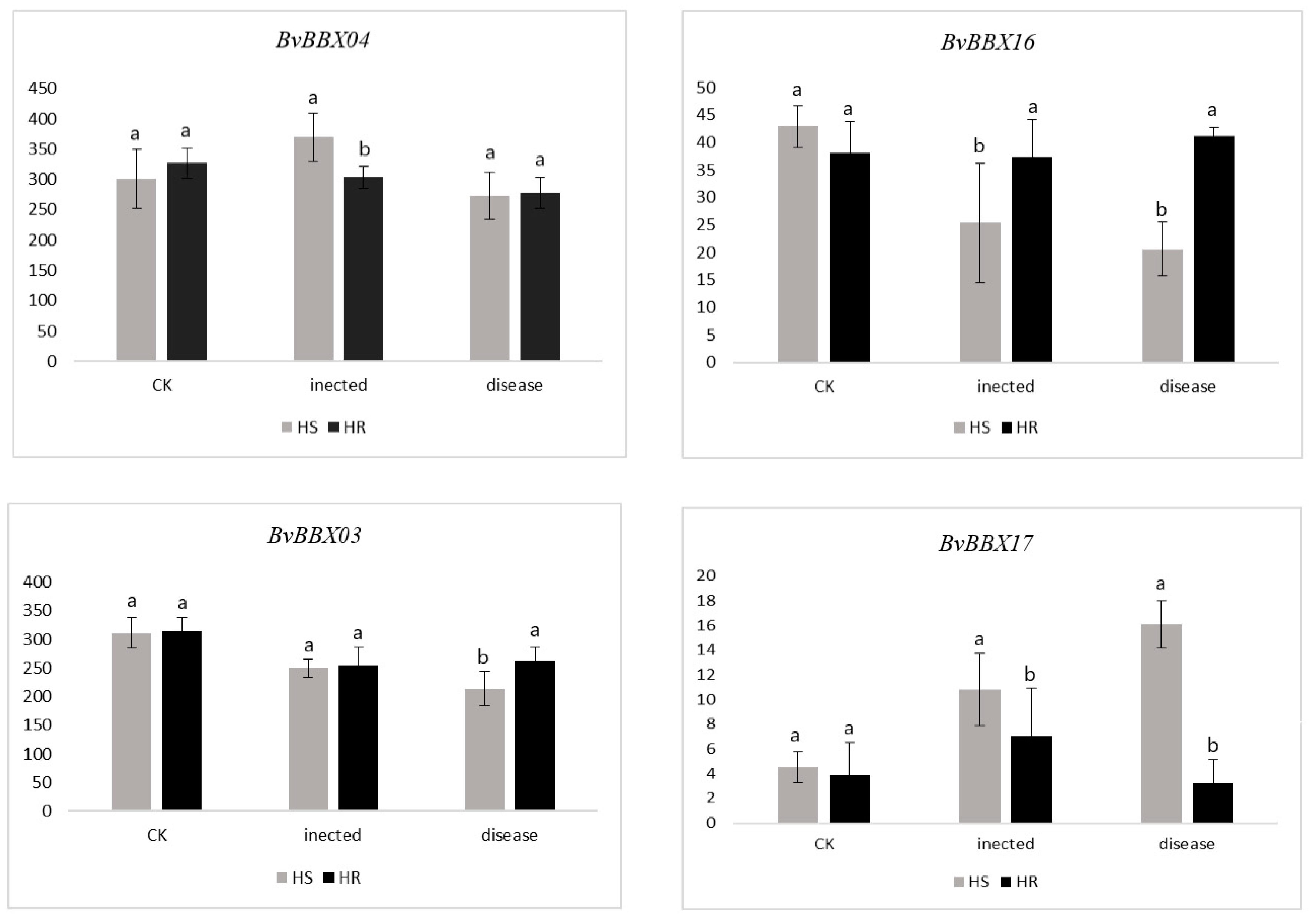
3.7. Expression Analysis of BvBBXs Gene in Highly Resistant and Susceptible Varieties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Ding, F.; Pan, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Peng, H.; et al. Research progress of zinc finger protein transcription factor family in plants. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2020, 40, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, R.; Kronmiller, B.; Maszle, D.R.; Coupland, G.; Holm, M.; Mizuno, T.; Wu, S.-H. The Arabidopsis B-Box Zinc Finger Family. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3416–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klug, A.; Schwabe, J.W.R. Zinc Fingers. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, K.; Adamczyk, J.; Krężel, A. Metal Binding Properties, Stability and Reactivity of Zinc Fingers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 367, 18–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocco, C.D.; Botto, J.F. BBX Proteins in Green Plants: Insights into Their Evolution, Structure, Feature and Functional Diversification. Gene 2013, 531, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Holm, M.; Deng, X.W. The B-Box Domain Protein BBX21 Promotes Photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Hettiarachchi, G.H.C.M.; Deng, X.-W.; Holm, M. Arabidopsis CONSTANS-LIKE3 Is a Positive Regulator of Red Light Signaling and Root Growth. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valverde, F.; Mouradov, A.; Soppe, W.; Ravenscroft, D.; Samach, A.; Coupland, G. Photoreceptor Regulation of CONSTANS Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering. Science 2004, 303, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ping, Q.; Cheng, P.; Huang, F.; Ren, L.; Cheng, H.; Guan, Z.; Fang, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Jiang, J. The Heterologous Expression in Arabidopsis Thaliana of a Chrysanthemum Gene Encoding the BBX Family Transcription Factor CmBBX13 Delays Flowering. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Ortiz, M.; Lin, C.; Liu, B. CONSTANS-LIKE 7 Regulates Branching and Shade Avoidance Response in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangappa, S.N.; Botto, J.F. The BBX Family of Plant Transcription Factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, S.B.; Meister, R.; Xu, Q.; Urwin, C.P.; Tripodi, F.A.; Screen, S.E.; Anil, V.S.; Zhu, S.; Morrell, J.A.; Liu, G.; et al. Expression of the Arabidopsis Thaliana BBX32 Gene in Soybean Increases Grain Yield. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Li, R.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. A B-Box Zinc Finger Protein, MdBBX10, Enhanced Salt and Drought Stresses Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tu, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Rao, L. Heat Stress-Induced BBX18 Negatively Regulates the Thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2679–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Takano, T. Salt Tolerance-related Protein STO Binds to a Myb Transcription Factor Homologue and Confers Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Imtiaz, M.; Lan, H.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, M.; Fei, Z.; et al. A Zinc Finger Protein Regulates Flowering Time and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Chrysanthemum by Modulating Gibberellin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2038–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takuhara, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, S. Low-Temperature-Induced Transcription Factors in Grapevine Enhance Cold Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmani, A.; Jing, X.-Q.; Shi, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Zhou, M.-R.; Wei, X.-Y.; Chen, Q.-Q.; Li, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-T.; Chen, K.-M. Characterization of B-BOX Gene Family and Their Expression Profiles under Hormonal, Abiotic and Metal Stresses in Poaceae Plants. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Gao, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huo, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, N.; et al. IbBBX24 Promotes the Jasmonic Acid Pathway and Enhances Fusarium Wilt Resistance in Sweet Potato. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Sun, D.; Liu, W.; Gu, F.; Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. CONSTANS-Like 9 (OsCOL9) Interacts with Receptor for Activated C-Kinase 1(OsRACK1) to Regulate Blast Resistance through Salicylic Acid and Ethylene Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaracis, G.N.; Pavli, O.I.; Biancardi, E. Cercospora Leaf Spot Disease of Sugar Beet. Sugar Tech 2010, 12, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Weng, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, W. The Rice B-Box Zinc Finger Gene Family: Genomic Identification, Characterization, Expression Profiling and Diurnal Analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of B-box gene family in wheat. Acta Crop. Sin. 2021, 47, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Lou, K.; Wang, X.; LIU, Y.; CHen, Q. Genome-wide sequence identification and expression analysis of B-box gene family in Tanghaoru forest strawberry. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Characterization of B-Box Gene Family and Its Roles in Responses to Light Quality and Cold Stress in Tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 698525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Feng, C.; Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Jiao, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of the B-BOX Genes That Respond to Multiple Ripening Related Signals in Sweet Cherry Fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hua, R.; Liu, H.; Sui, S. CpBBX19, a B-Box Transcription Factor Gene of Chimonanthus Praecox, Improves Salt and Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Genes 2021, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolser, D.; Staines, D.M.; Pritchard, E.; Kersey, P. Ensembl Plants: Integrating Tools for Visualizing, Mining, and Analyzing Plant Genomics Data. In Plant Bioinformatics; Methods in Molecular Biology; Edwards, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1374, ISBN 978-1-4939-3166-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Coin, L.; Durbin, R.; Finn, R.D.; Hollich, V.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Khanna, A.; Marshall, M.; Moxon, S.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; et al. The Pfam Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D138–D141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s Conserved Domain Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The Proteomics Server for in-Depth Protein Knowledge and Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple Sequence Alignment Using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2003, 1, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Yin, J.; Wang, S.; Fang, Z.; Ma, D.; Gao, D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Mining of Wheat B-BOX Zinc Finger (BBX) Gene Family Provides New Insights into Light Stress Responses. Crop Pasture Sci. 2021, 72, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M. PlantCARE, a Database of Plant Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements and a Portal to Tools for in Silico Analysis of Promoter Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Katoh, H.; Takayanagi, T.; Suzuki, S. Characterization of Thermotolerance-Related Genes in Grapevine (Vitis Vinifera). J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y. Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogenetic Analysis, and Expression Profiling of the BBX Family Genes in Pear. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, R.; Dai, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the B-Box Gene Family in the Apple (Malus Domestica Borkh). Genome. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Meng, Z. Expression Analysis of Genes Encoding Double B-Box Zinc Finger Proteins in Maize. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2017, 17, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, H.; Fu, X.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, S. Comprehensive Identification and Expression Analysis of B-Box Genes in Cotton. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reagent | Amount |
|---|---|
| TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (2×) | 10 μL |
| PCR Forward Primer (10 μM) | 0.8 μL |
| PCR Reverse Primer (10 μM) | 0.8 μL |
| ROX Reference Dye (50×) | 0.4 μL |
| DNA Templates | 2 μL |
| Sterile Water | Filling to 20 μL |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| BvBBX01 | AGACGCGCCGAAAAAGAAAA | GGGCGTTCCTATTCCCTCG |
| BvBBX02 | AAAAGATTTAGCGTTGACCACC | TGTTGATGGTCTATGTGAGTCCC |
| BvBBX03 | CTTCTGCTGCTTGCAAACCT | GATGAGCGCTTACACTGTGAC |
| BvBBX04 | CTGATGGTTTGCGGCAAGAG | ACTGACCTGATCTGCACATTT |
| BvBBX05 | TGATGGGATGACACGAACGG | TCATCACGCCATGTGGAACA |
| BvBBX06 | GCAACGACGTATTGCGAGTC | CCAGATGCAGTCCAAGGTGT |
| BvBBX07 | TTTTTCCCGTGCTGTGTGGG | CAAGACAATTGAACTCCGTACCA |
| BvBBX08 | TTCCGGATTCGTCTTGATCCC | ATGTTCACCCTTTTGCTTGGT |
| BvBBX09 | TTCCACACTGACCATCCCAC | TGCCTTCAGGGATGTGATCG |
| BvBBX10 | TTCCACACTGACCATCCCAC | TGCGAGACTGAAGATGTTACCT |
| BvBBX11 | CCACCACCGTACCTTTCTCC | TTCCGGCGAAGACGATTCTC |
| BvBBX12 | TCAACTTTCCTTTATCTCAACCACA | CGAATTCGTGTTTCCGTCTGG |
| BvBBX13 | ACCTCAATGCATCAAATCTTCCA | TCCAGATTTTGCGGGTTCAGT |
| BvBBX14 | ACAACAAGGAGATCTTTCGGGG | GGCTCGGTAACCCTGTAAACT |
| BvBBX15 | TGTTTCTCGATGCTAATTCGAGG | CGACATGCATGAAAAGCAAACG |
| BvBBX16 | TCCCATGGGTAGACCATTTGC | GGCCAACCCAAAACTAACTGC |
| BvBBX17 | TCTATGCCTTGCAATAGCCCT | CCCAAGTTCGGGCCTACTTT |
| BvActin | ACTGGTATTGTGCTTGACTC | ATGAGATAATCAGTGAGATC |
| Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Accession Number | Protein Length | pI | MW (Da) | Chr. Location | Exon No. | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvBBX01 | LOC104888895 | XM_010674009.2 | 328 | 6.06 | 35915.31 | 1 | 3 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX02 | LOC104907374 | XM_010696302.2 | 368 | 5.41 | 40858.69 | 2 | 2 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX03 | LOC104906002 | XM_010694679.2 | 384 | 6.1 | 41702.13 | 2 un | 2 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX04 | LOC104888829 | XM_010673928.2 | 246 | 4.94 | 27226.69 | 3 | 3 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX05 | LOC104891303 | XM_010676978.2 | 312 | 5.44 | 33737.74 | 4 | 3 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX06 | LOC104907254 | XM_010696160.2 | 201 | 4.12 | 22061.55 | 4 un | 1 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX07 | LOC104896645 | XM_010683418.2 | 443 | 6.7 | 49495.5 | 6 | 6 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX08 | LOC104897491 | XM_010684375.2 | 517 | 5.64 | 57633.24 | 6 | 4 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX09 | LOC104897745 | XM_019250497.1 | 338 | 4.58 | 37833.16 | 6 | 4 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX10 | LOC104908945 | XM_010698113.2 | 389 | 5.99 | 41552.96 | 7 un | 1 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX11 | LOC104908648 | XM_010697779.2 | 254 | 5.92 | 27896.79 | 7 un | 4 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX12 | LOC104902431 | XM_010690211.2 | 379 | 5.99 | 41552.96 | 8 | 2 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX13 | LOC104903341 | XM_010691368.2 | 412 | 4.97 | 44928.89 | 9 | 6 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX14 | LOC104904254 | XM_010692457.2 | 196 | 5.75 | 21583.28 | 9 | 6 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX15 | LOC104904288 | XM_010692495.2 | 262 | 5.77 | 29046.26 | 9 | 3 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX16 | LOC104884672 | XM_010669358.2 | 430 | 5.64 | 48855.67 | Un | 2 | Nucleus. |
| BvBBX17 | LOC104884884 | XM_010669588.2 | 135 | 4.33 | 14743.74 | Un | 1 | Nucleus. |
| Cis-Acting Element | Number of Genes | Functions of Cis-Acting Element |
|---|---|---|
| CAAT-box | 17 | common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| TATA-box | 17 | core promoter element around −30 of transcription start |
| Box 4 | 16 | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| ABRE | 16 | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| G-box | 13 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| ARE | 13 | cis-acting regulatory element essential for anaerobic induction |
| TCT-motif | 11 | part of a light-responsive element |
| CGTCA-motif | 10 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| TGACG-motif | 10 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| O2-site | 9 | cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation |
| TCA-element | 9 | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| I-box | 8 | part of a light-responsive element |
| GATA-motif | 8 | part of a light-responsive element |
| GT1-motif | 8 | light-responsive element |
| MBS | 7 | MYB binding site involved in drought inducibility |
| TGA-element | 6 | auxin-responsive element |
| TC-rich repeats | 6 | cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| CAT-box | 5 | cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression |
| WUN-motif | 5 | wound-responsive element |
| P-box | 5 | gibberellin-responsive element |
| AE-box | 5 | part of a module for light response |
| CCAAT-box | 5 | MYBHv1 binding site |
| LTR | 5 | cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| TCCC-motif | 5 | part of a light-responsive element |
| MRE | 4 | MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness |
| ACE | 4 | cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness |
| ATCT-motif | 3 | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Ding, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y. Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Expression Analysis Suggest Its Roles in Responses to Cercospora Leaf Spot in Sugar Beet (Beta Vulgaris L.). Genes 2023, 14, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061248
Song H, Ding G, Zhao C, Li Y. Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Expression Analysis Suggest Its Roles in Responses to Cercospora Leaf Spot in Sugar Beet (Beta Vulgaris L.). Genes. 2023; 14(6):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061248
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, He, Guangzhou Ding, Chunlei Zhao, and Yanli Li. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Expression Analysis Suggest Its Roles in Responses to Cercospora Leaf Spot in Sugar Beet (Beta Vulgaris L.)" Genes 14, no. 6: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061248
APA StyleSong, H., Ding, G., Zhao, C., & Li, Y. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification of B-Box Gene Family and Expression Analysis Suggest Its Roles in Responses to Cercospora Leaf Spot in Sugar Beet (Beta Vulgaris L.). Genes, 14(6), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061248






