Morphological and Molecular Identification of Hard Ticks in Hainan Island, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Tick Collection
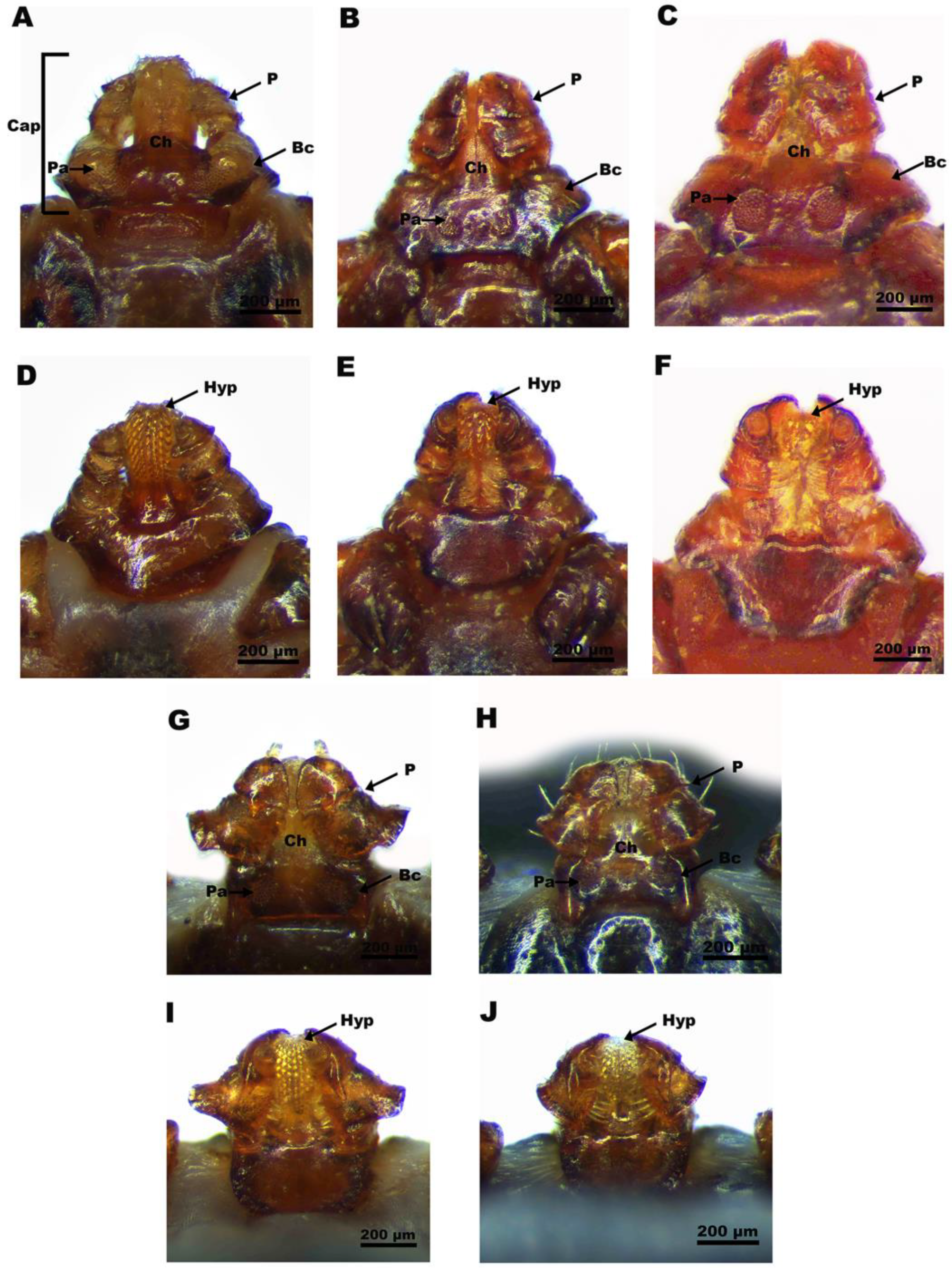
2.2. Morphological Identification and Photography
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification of the Tick cox1 and 16S rRNA Genes
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. DNA Polymorphism Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Features of Tick Species
3.2. Molecular Identification and Classification of Ticks by Nucleotide BLAST
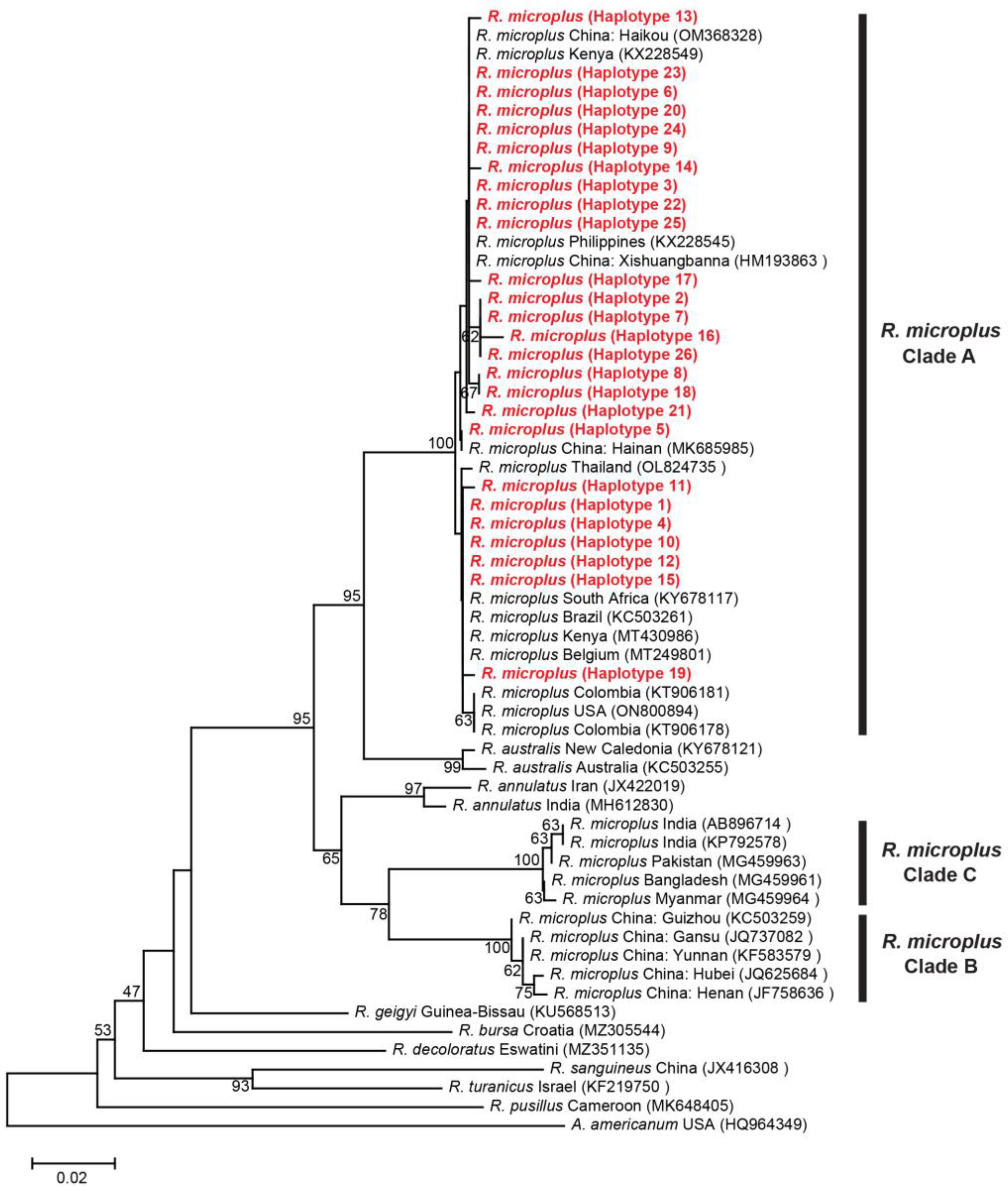
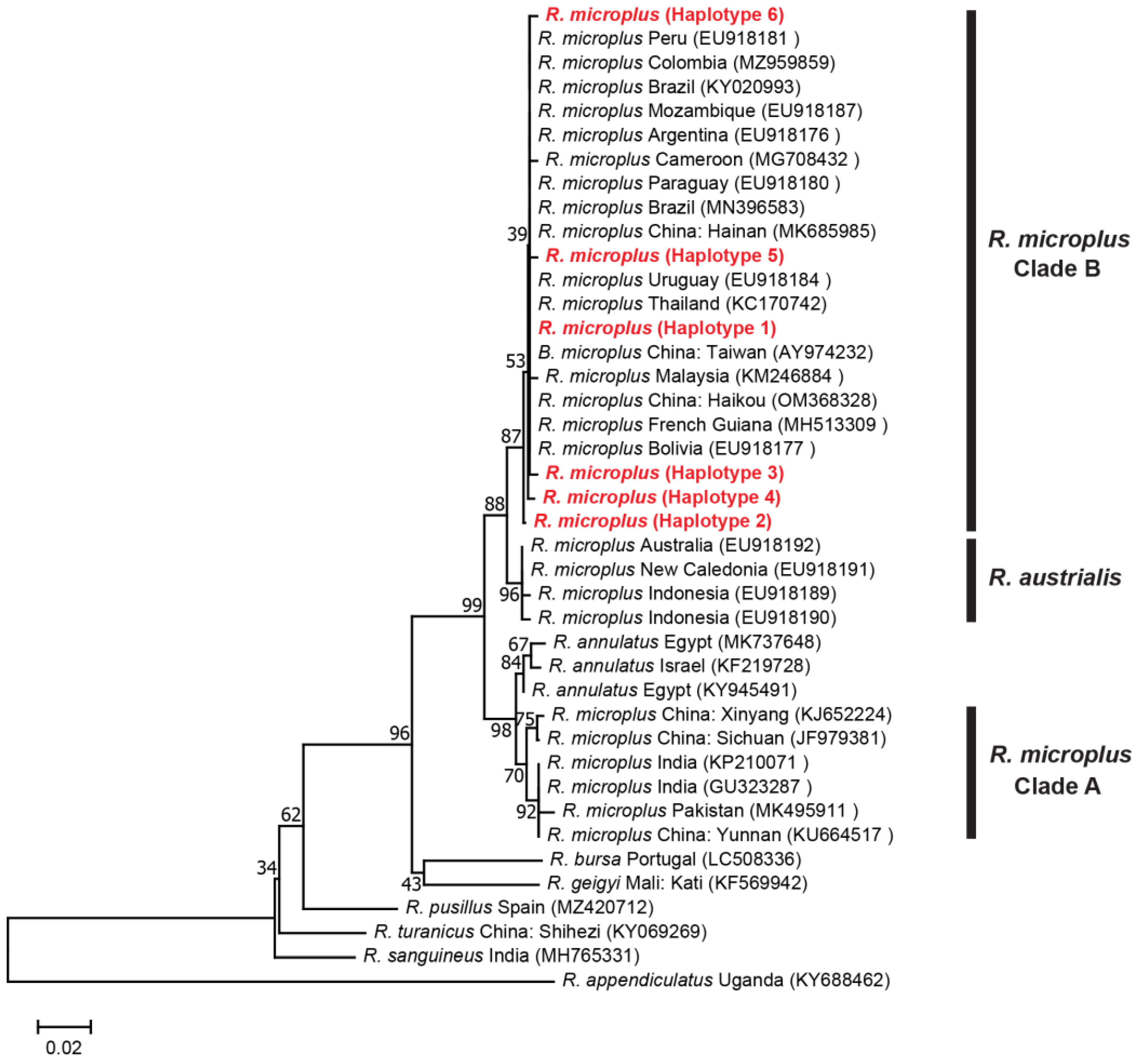
3.2.1. Genetic Distances and Phylogenetic Analyses for R. microplus
3.2.2. Genetic Distances and Phylogenetic Analyses for R. sanguineus
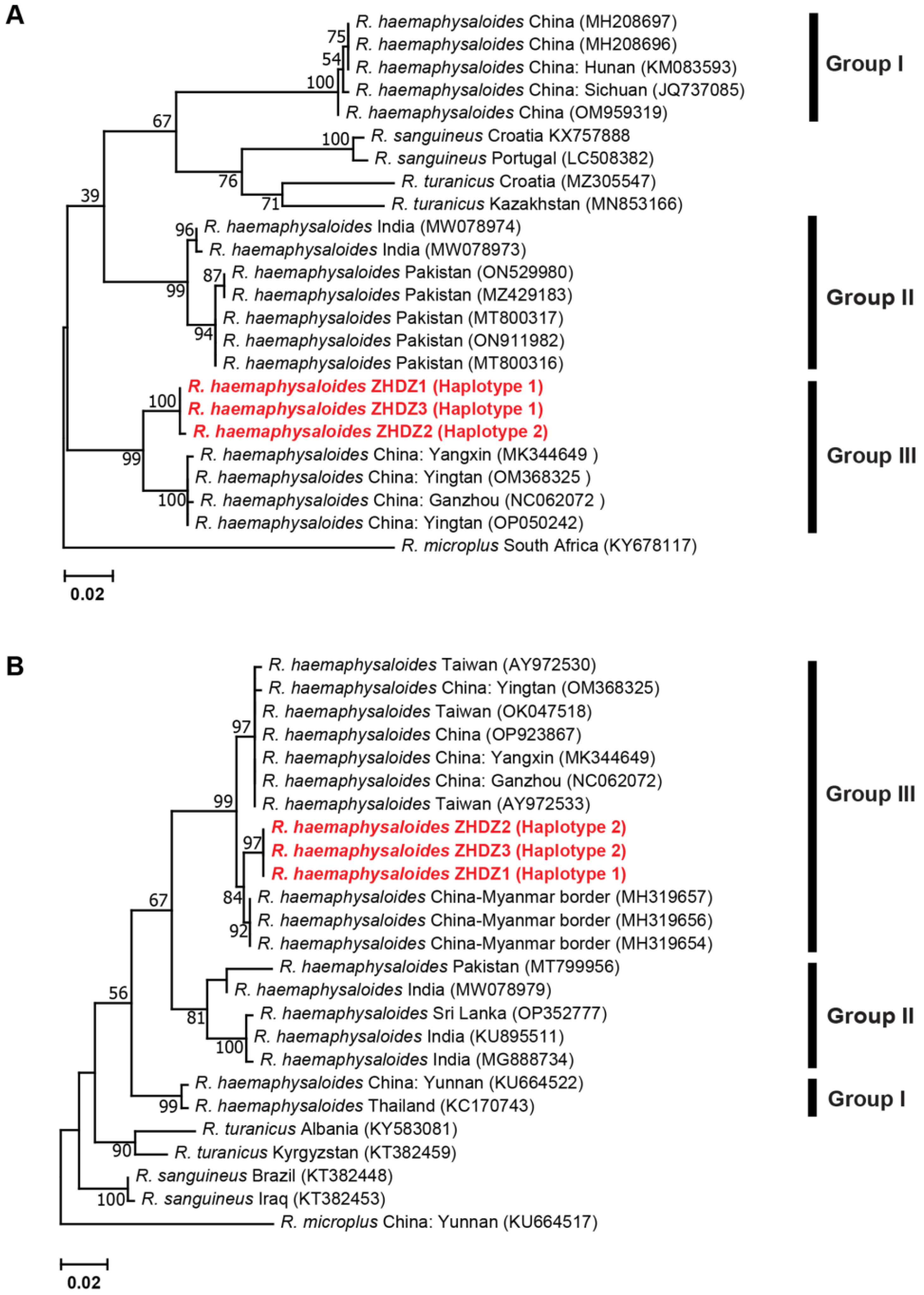
3.2.3. Genetic Distances and Phylogenetic Analyses for R. haemaphysaloides
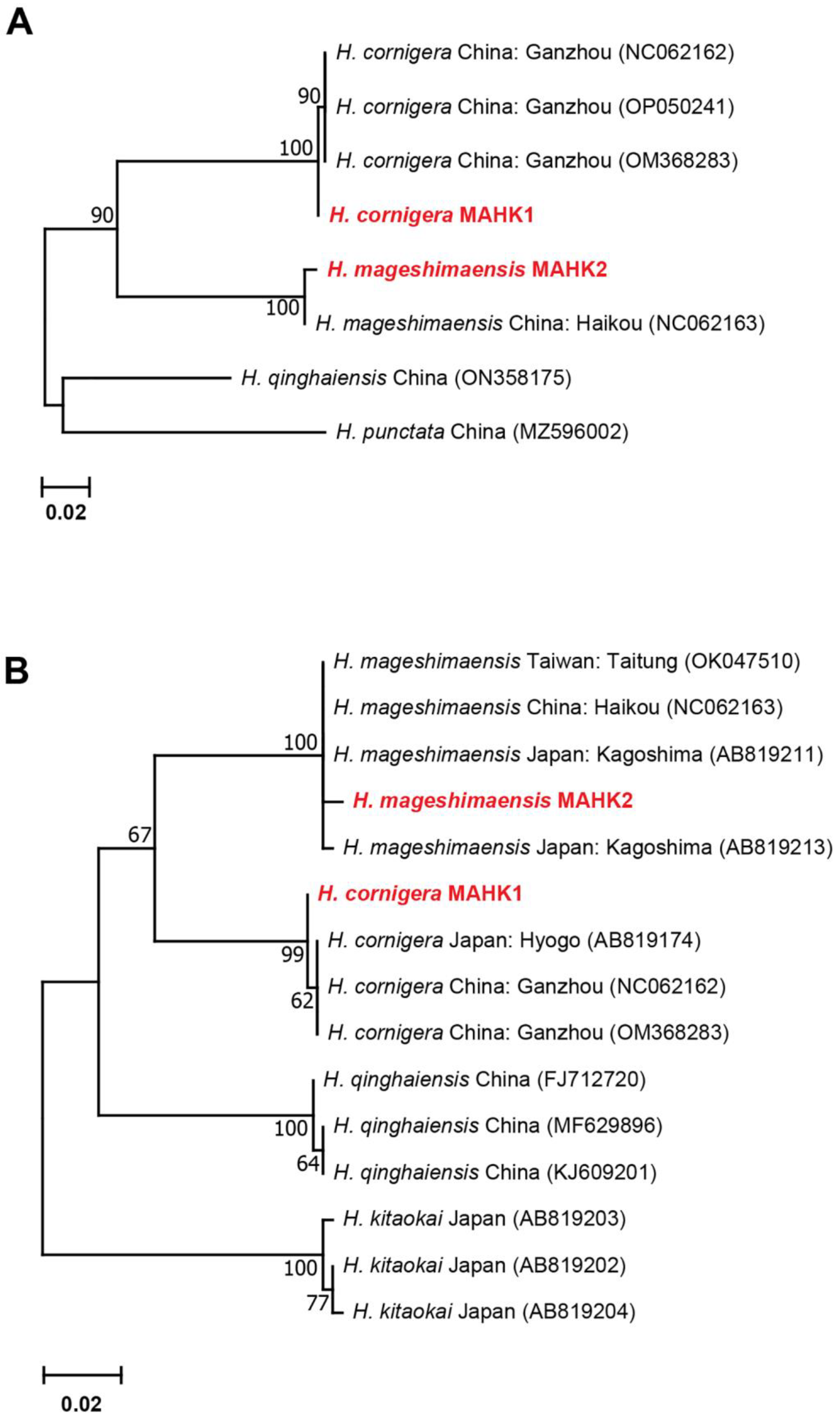
3.2.4. Genetic Distances and Phylogenetic Analyses for Haemaphysalis spp.
3.3. Genetic Diversity and Haplotype Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wikel, S.K. Tick modulation of host immunity: An important factor in pathogen transmission. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: An emerging infectious threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A One Health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Randolph, S.E. Drivers, dynamics, and control of emerging vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Lancet 2012, 380, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.Q.; Liu, K.; Li, X.L.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, H.W.; Sun, R.X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Zuo, S.Q.; et al. Emerging tick-borne infections in mainland China: An increasing public health threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Gong, X. Aishajiang·Abula: Hard tick and tick-borne diseases. Xinjiang Xu Mu Ye 2010, 9, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Regional distribution profiles of tick-borne pathogens in China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2012, 5, 445–447. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, K.; Li, X.D. Analysis of multiple infections of tick-borne diseases such as forest encephalitis, Lyme disease and spotted fever. World Latest Med. Inf. 2017, 17, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, J.Z. Ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea) in China: Geographical distribution, host diversity, and specificity. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 102, e21544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Shafy, S.; El Namaky, A.H.; Zeina, H.A.A.; Ghazy, A.A. Description of immature stages of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus Sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) using scanning electron microscopy. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Res. 2015, 1, 12–30. [Google Scholar]
- Amrutha, B.M.; Kumar, K.G.A.; Kurbet, P.S.; Varghese, A.; Deepa, C.K.; Pradeep, R.K.; Nimisha, M.; Asaf, M.; Juliet, S.; Ravindran, R.; et al. Morphological and molecular characterization of Rhipicephalus microplus and Rhipicephalus annulatus from selected states of southern India. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.L.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.; Latif, A.; Pegram, R.G.; Preston, P.M. Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa: A Guide to Identification of Species; Bioscience Reports: Edinburgh, UK, 2003; pp. 1–227. [Google Scholar]
- Paguem, A.; Manchang, K.; Kamtsap, P.; Renz, A.; Schaper, S.; Dobler, G.; Bakkes, D.K.; Chitimia-Dobler, L. Ticks and rickettsiae associated with wild animals sold in bush meat markets in Cameroon. Pathogens 2023, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, V.L.; Tay, S.T.; Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Tan, T.K.; Lim, Y.A.; Ong, B.L.; Panchadcharam, C.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Molecular characterisation of the tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Malaysia: New insights into the cryptic diversity and distinct genetic assemblages throughout the world. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tantrawatpan, C.; Vaisusuk, K.; Chatan, W.; Pilap, W.; Suksavate, W.; Andrews, R.H.; Petney, T.N.; Saijuntha, W. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analyses of ixodid ticks infesting cattle in northeast Thailand: The discovery of Rhipicephalus microplus clade C and the rarely detected R. haemaphysaloides. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 86, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sándor, A.D.; Milchev, B.; Takács, N.; Kontschán, J.; Szekeres, S.; Hornok, S. Five ixodid tick species including two morphotypes of Rhipicephalus turanicus on nestlings of Eurasian eagle owl (Bubo bubo) from south-eastern Bulgaria. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, J. Molecular identification and genetic analysis of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato of dogs in Nigeria, West Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 85, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Kontschán, J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; de Mera, I.G.; Tomanović, S.; de la Fuente, J. Contributions to the morphology and phylogeny of the newly discovered bat tick species, Ixodes ariadnae in comparison with I. vespertilionis and I. simplex. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Li, X.S.; Yin, S.Q.; Zhu, D.; Xue, J.B.; Li, S.G. High genetic diversity in hard ticks from a China-Myanmar border county. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.W.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhao, W. Seasonal succession of ticks in small wild animals in Chengmai county of Hainan province. Chin. J. Public Health 2012, 28, 1620. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.H.; Bai, Z.J.; Cai, J.; Fang, M.Y. Investigation and analysis of epiparasitic ticks on domestic animals in Qiongzhong area, Hainan province. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2008, 6, 544–545. [Google Scholar]
- Communicable Disease Center. Pictorial Keys to Arthropods, Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals of Public Health Significance; CDC: Doha, Qatar, 1966; pp. 1–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré, S. Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. Lect. Math. Life Sci. (Am. Math. Soc.) 1986, 17, 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.C.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Krücken, J.; Rehman, A.; Nijhof, A.M. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Myanmar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduma, E.G.; Emery, D.; Githaka, N.W.; Nguu, E.K.; Bishop, R.P.; Šlapeta, J. Molecular evidence confirms occurrence of Rhipicephalus microplus Clade A in Kenya and sub-Saharan Africa. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 76, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Sándor, A.D.; Tomanović, S.; Beck, R.; D’Amico, G.; Kontschán, J.; Takács, N.; Görföl, T.; Bendjeddou, M.L.; Földvári, G.; et al. East and west separation of Rhipicephalus sanguineus mitochondrial lineages in the Mediterranean Basin. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nava, S.; Beati, L.; Venzal, J.M.; Labruna, M.B.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Petney, T.; Saracho-Bottero, M.N.; Tarragona, E.L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Silva, M.M.S.; et al. Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806): Neotype designation, morphological re-description of all parasitic stages and molecular characterization. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkes, D.K.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Matloa, D.; Oosthuysen, M.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Mans, B.J.; Matthee, C.A. Integrative taxonomy and species delimitation of Rhipicephalus turanicus (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae). Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Chandra, S.; Halliday, B. The “tropical lineage” of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato identified as Rhipicephalus linnaei (Audouin, 1826). Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Halliday, B.; Chandra, S.; Alanazi, A.D.; Abdel-Shafy, S. Rhipicephalus linnaei (Audouin, 1826) recognised as the “tropical lineage” of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato: Neotype designation, redescription, and establishment of morphological and molecular reference. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Giannelli, A.; Parisi, A.; Otranto, D. Morphological and genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato from the New and Old Worlds. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caetano, R.L.; Vizzoni, V.F.; Bitencourth, K.; Carriço, C.; Sato, T.P.; Pinto, Z.T.; De Oliveira, S.V.; Amorim, M.; Voloch, C.M.; Gazeta, G.S. Ultrastructural morphology and molecular analyses of tropical and temperate “Species” of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae) in Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zemtsova, G.E.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Reeves, W.K.; Hahn, M.; Snellgrove, A.; Levin, M.L. Phylogeography of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato and its relationships with climatic factors. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 69, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doi, K.; Nishida, K.; Kato, T.; Hayama, S.I. Effects of introduced sika deer (Cervus nippon) and population control activity on the distribution of Haemaphysalis ticks in an island environment. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 11, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Hou, X.; Ge, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Shao, R.; Holmes, E.C.; Lei, C.; Shi, M. The diversity and evolutionary relationships of ticks and tick-borne bacteria collected in China. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, T.; Tatsuzawa, S. Questing height of nymphs of the bush tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis, and its closely related species, H. mageshimaensis: Correlation with body size of the host. Parasitology 2004, 128, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, V.L.; Prakash, B.K. First genetic characterization of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato in Peninsular Malaysia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 75, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Wu, L.; Cai, H.; Mu, L.; Yu, J.F.; Fu, S.Y.; Si, X.Y. Genetic diversity analysis of Dermacentor nuttalli within Inner Mongolia, China. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Intirach, J.; Lv, X.; Han, Q.; Lv, Z.-Y.; Chen, T. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Hard Ticks in Hainan Island, China. Genes 2023, 14, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081592
Intirach J, Lv X, Han Q, Lv Z-Y, Chen T. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Hard Ticks in Hainan Island, China. Genes. 2023; 14(8):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081592
Chicago/Turabian StyleIntirach, Jitrawadee, Xin Lv, Qian Han, Zhi-Yue Lv, and Tao Chen. 2023. "Morphological and Molecular Identification of Hard Ticks in Hainan Island, China" Genes 14, no. 8: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081592
APA StyleIntirach, J., Lv, X., Han, Q., Lv, Z.-Y., & Chen, T. (2023). Morphological and Molecular Identification of Hard Ticks in Hainan Island, China. Genes, 14(8), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081592








