Variation in the Local Grey Mullet Populations (Mugil cephalus) on the Western Pacific Fringe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Variations and Population Structures of Adult Grey Mullets
3.2. Selection on GPI and PGDH
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Differentiation in Mugil cephalus
4.2. Genetic Variation among the Migratory Groups
4.3. Genetic Variation among Non-Migratory Populations
4.4. Occurrence of Juvenile Grey Mullet
4.5. Selection during Life Stages
4.6. Linkage Disequilibrium between GPI-A and PGDH
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowen, B.W.; Gaither, M.R.; DiBattista, J.D.; Iacchei, M.; Andrews, K.R.; Grant, W.S.; Toonen, R.J.; Briggs, J.C. Comparative phylogeography of the ocean planet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7962–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, D.O.; Clarke, L.M.; Munch, S.B.; Wagner, G.N. Spatial and temporal scales of adaptive divergence in marine fishes and the implications for conservation. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.W.; Bor, H.; Wu, J.X.; Shieh, B.S.; Lin, H.D. Population Structure and Phylogeography of Marine Gastropods Monodonta labio and M. confusa (Trochidae) along the Northwestern Pacific Coast. Diversity 2023, 15, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Gao, T.X.; Wu, S.F.; Zhang, Y.P. Pleistocene isolation in the Northwestern Pacific marginal seas and limited dispersal in a marine fish, Chelon haematocheilus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1845). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.J.; Ai, W.M.; Chen, H.; Lin, H.D. Phylogeography and genetic population structure of the spadenose shark (Scoliodon macrorhynchos) from the Chinese coast. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Li, H.; Lin, H.D.; Ding, S.; Miyamoto, M.M. Phylogeography of the inshore fish, Bostrychus sinensis, along the Pacific coastline of China. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 96, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhao, J.; Tang, W.Q.; Liu, D.; Yang, J.Q.; Lin, H.D. Phylogeography of Tridentiger bifasciatus (Gobiidae) in the northwestern Pacific. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 935251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Yi, M.R.; He, X.B.; Lin, P.S.; Liu, W.H.; Luo, Z.S.; Lin, H.D.; Yan, Y.R. Genetic diversity and population structure of cutlassfish (Lepturacanthus savala) along the coast of mainland China, as inferred by mitochondrial and microsatellite DNA markers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.C.; Lai, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, I.C.; Lin, H.D.; Wang, W.K. Phylogeographic Structuring of the Kuroshio-Type Prawn Macrobrachium japonicum (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) in Taiwan and Ryukyu Islands. Diversity 2022, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Yi, M.R.; Gu, S.; He, X.B.; Luo, Z.S.; Kang, B.; Lin, H.D.; Yan, Y.R. Composition, demographic history, and population structures of Trichiurus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 875042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.M. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus Linnaeus 1758) Fishery Synopsis 1, Division of Fisheries and Oceanography; CSIRO: Mebourne, Australia, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.M. The grey mullet. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Rev. 1966, 4, 301–335. [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Panfili, J.; Durand, J.D. A global review of the cosmopolitan flathead mullet Mugil cephalus Linnaeus 1758 (Teleostei: Mugilidae), with emphasis on the biology, genetics, ecology and fisheries aspects of this apparent species complex. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2012, 22, 641–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.W. Larval development, growth, and spawing of striped mullet (Mugil cephahis) along the south Atlantic coast of the United States. Fish Bull. 1958, 58, 501–519. [Google Scholar]
- Nordile, F.G.; Szelistowski, W.A.; Nordile, W.C. Ontogenesis of osmotic regulation in the striped mullet, Mugil cephalus L. J. Fish Biol. 1982, 20, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, C.R.; Ray, G.C.; Douglass, J.; Freund, R. A Field Guide to Atlantic Coast Fishes of North America; Houghton and Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.C.; Han, Y.S.; Tzeng, W.N. Evidence of flathead mullet Mugil cephalus L. spawning in waters northeast of Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2007, 46, 717–725. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.N.; Jamandre, B.W.; Hsu, C.C.; Tzeng, W.N.; Durand, J.D. Plio-Pleistocene sea level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern Pacific promoted speciation in the globally-distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C.; Kawasaki, T. Characteristics of the life history of gray mullet from Taiwan waters. Fish. Sci. 1995, 61, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, F.; Peng, S.M. Genetic variation analysis of Mugil cephalus in China Sea based on mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamandre, B.W.; Durand, J.D.; Tzeng, W.N. Phylogeography of the flathead mullet Mugil cephalus in the north-west Pacific as inferred from the mtDNA control region. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 75, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livi, S.; Sola, L.; Crosetti, D. Phylogeographic relationships among worldwide populations of the cosmopolitan marine species, the striped gray mullet (Mugil cephalus), investigated by partial cytochrome b gene sequences. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Weng, C.; Lee, S. Distinguishing two types of gray mullet, Mugil cephalus L. (Mugiliformes: Mugilidae), by using glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI) allozymes with special reference to enzyme activities. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2001, 171, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, C.W.; You, C.F.; Tzeng, W.N. The migratory environmental history of freshwater resident flathead mullet Mugil cephalus L. in the Tanshui River, northern Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2010, 49, 504–514. [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano, M.J.; Shaw, C.R. Separation and visualization of enzymes on gels. In Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Techniques. Vol. II. Zone Electrophoresis (ed. Smith I); Year Book Medical Publishers: Chicago, IL, USA, 1976; pp. 185–209. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, J.A.; Salini, J.P. Techniques of starch-gel electrophoresis of penaeid prawn enzymes (Penaeus spp. and Metapenaeus spp.). CSIRO Div. Fish. Oceanogr. 1980, 116, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, C.T.; Lee, S.C.; Hui, C.F.; Chen, C.T. Tissue-specific isozymes in fishes of the subfamily Sparinae (Perciformes: Sparidae) from the coastal waters of Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 1995, 34, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Shaklee, J.B.; Allendorf, F.W.; Morizot, D.C.; Whitt, G.S. Gene nomenclature for protein-coding loci in fish. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 1990, 119, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, J.L.; Prowell, D.P. Genetic estimates of population structure and gene flow: Limitations, lessons and new directions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices, Version 2.9.3. 2001. Available online: http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.htm (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Rousset, F. genepop’007: A complete re-implementation of the genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 1984, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.A.; Nichols, R.A. Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 263, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antao, T.; Lopes, A.; Lopes, R.J.; Beja-Pereira, A.; Luikart, G. LOSITAN: A workbench to detect molecular adaptation based on a FST-outlier method. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foll, M.; Gaggiotti, O. A genome-scan method to identify selected loci appropriate for both dominant and codominant markers: A Bayesian perspective. Genetics 2008, 180, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Genetic distance between populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.O.D.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Wen, W.; Falush, D. Documentation for the Structure Software, Version 2; Department of Human Genetics, University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Piry, S.; Luikart, G.; Cornuet, J.M. Computer note. BOTTLENECK: A computer program for detecting recent reductions in the effective size using allele frequency data. J. Hered. 1999, 90, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Burke, J.S.; Fitzhugh, G.R. Early life history patterns of Atlantic North American flatfish: Likely (and unlikely) factors controlling recruitment. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1991, 27, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, R.F.; Allendorf, F.W.; Knudsen, K.L. Superior developmental stability of heterozygotes at enzyme loci in salmonid fishes. Am. Nat. 1984, 124, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.R.; Capula, M.; Crosetti, D.; Sola, L.; Campton, D.E. Allozyme variation in global populations of striped mullet, Mugil cephalus (Pisces: Mugilidae). Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campton, D.E.; Mahmoudi, B. Allozyme variation and population structure of striped mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Florida. Copeia 1991, 1991, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugama, K.; Benzie, J.A.H.; Bailment, E. Genetic variation and population structure of the giant tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon, in Indonesia. Aquaculture 2002, 205, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamuris, Z.; Apostolidis, A.P.; Triantaphyllidis, C. Genetic protein variation in red mullet (Mullus barbatus) and striped red mullet (M. surmuletus) populations from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 1998, 130, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.W.; Zhang, C.I.; Kang, H.J.; Wu, L.J.; Lian, L.J. Impact of fishing exploitation and climate change on the grey mullet Mugil cephalus stock in the Taiwan Strait. Mar. Coast Fish 2017, 9, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Chang, J.T. Allozyme variation in the large-scale mullet Liza macrolepis (Periformes: Mugilidae) from coastal water of western Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 1996, 35, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Tang, B.J. Low mtDNA variation and shallow population structure of the Chinese pomfret Pampus chinensis along the China coast. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.E.; Kim, J.K.; Li, C. A new perspective on biogeographic barrier in the flathead grey mullet (Pisces: Mugilidae) from the northwest Pacific. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Fu, C.; Guo, L.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Jin, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, B. Species delimitation and historical biogeography in the genus Helice (Brachyura: Varunidae) in the Northwestern Pacific. Zool. Sci. 2009, 26, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Yan, Y.R.; Yi, M.R.; Luo, Z.S.; Wen, H.; Jiang, C.P.; Lin, H.D.; He, X.B. Genetic pattern and demographic history of cutlassfish (Trichiurus nanhaiensis) in South China Sea by the influence of Pleistocene climatic oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endler, J.A. Gene flow and population differentiation. Science 1973, 179, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatkin, M. Gene flow and geographic structure of natural populations. Science 1987, 236, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddoch, B.J. The adaptive significance of electrophoretic mobility in phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1993, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.A.; Harrison, R.G. Balancing selection on electrophoretic variation of phosphoglucose isomerase in two species of field cricket: Gryllus veletis and G. pennsylvanicus. Genetics 1997, 147, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R.J. Evolutionary genetics of Metridium senile. I. Kinetic differences in phosphoglucose isomerase allozymes. Biochem. Genet. 1981, 19, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesson, K.; Kautsky, N.; Tedcngren, M. Genotypic and phenotypic differences between Baltic and North Sea populations of Mytilus edulis evaluated through reciprocal transplantations II. Genetic variation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 59, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitton, J.B. Selection in Natural Populations; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlhoff, E.P.; Rank, N.E. Functional and physiological consequences of genetic variation at phosphoglucose isomerase: Heat shock protein expression is related to enzyme genotype in a montane beetle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10056–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, W.B. Adaptation at specific loci. II. Demographic and biochemical elements in the maintenance of the Colias Pgi polymorphism. Genetics 1983, 103, 691–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnicka-Półtorak, A.; Celiński, K.; Chudzińska, E. Genetic differentiation between generations of Pinus sylvestris natural population: A case study from the last European primeval forest. Aust. J. Forest. Sci. 2017, 134, 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Deli, T.; Guizeni, S.; Ben, A.L.; Said, K.; Chatti, N. Chaotic genetic patchiness in the pelagic teleost fish Sardina pilchardus across the Siculo-Tunisian Strait. Mar. Biol. Res. 2020, 16, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, P.W.; Cockerham, C.C. Partial inbreeding: Equilibrium heterozygosity and the heterozygosity paradox. Evolution 1986, 40, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.H. A general model to account for enzyme variation in natural population. II. Characterization of the fitness function. Am. Nat. 1976, 110, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard Smith, J. Evolutionary Genetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lewontin, R.C. The Basis of Evolutionary Change; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Balakirev, E.I.; Rodrguez-Trelles, F.; Ayala, F.J. Molecular evolution of two linked genes, Est-6 and Sod, in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1999, 153, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, F.J.; Balakirev, E.S.; Sdez, A.G. Genetic polymorphism at two linked loci, Sod and Est-6, in Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 2002, 300, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



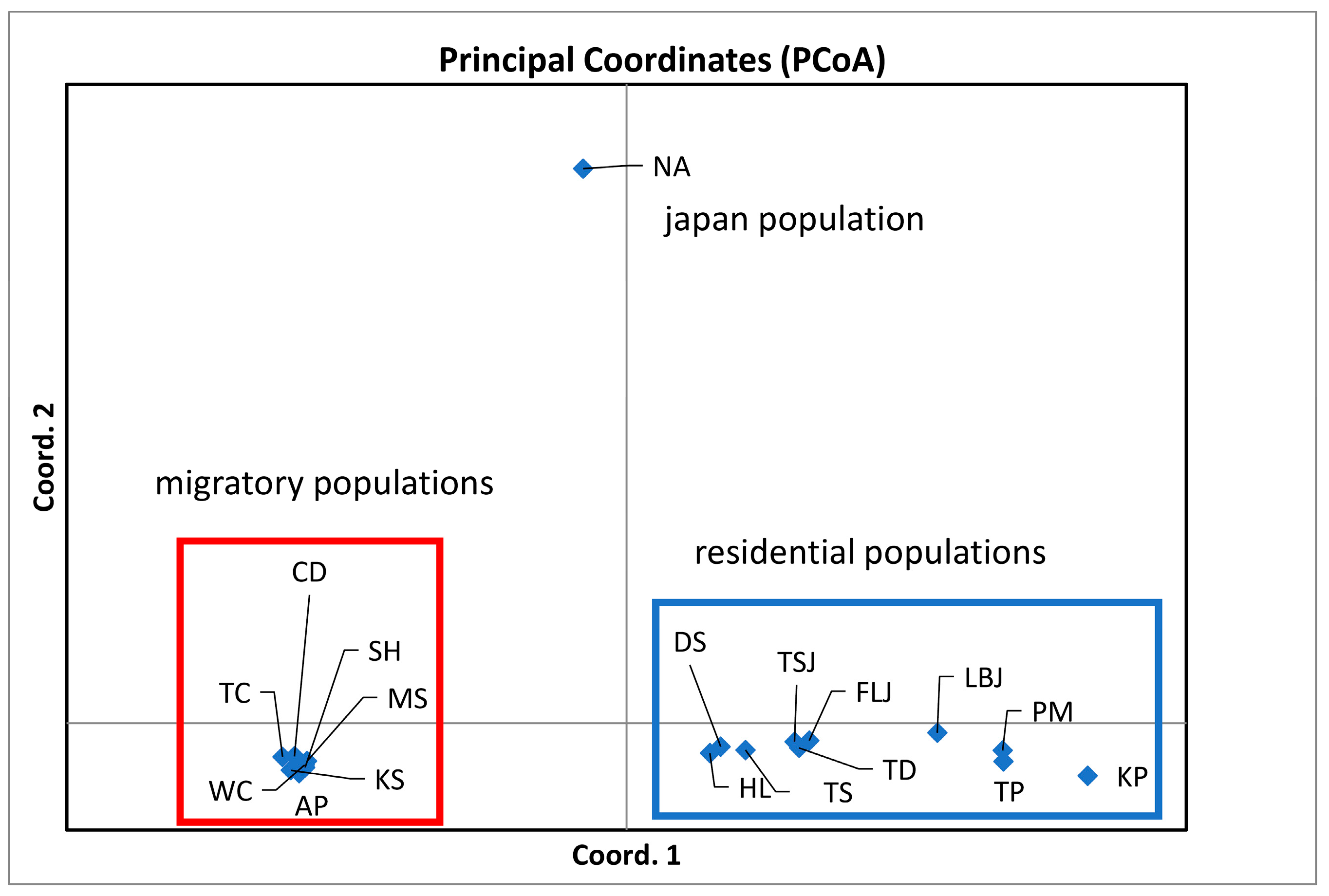


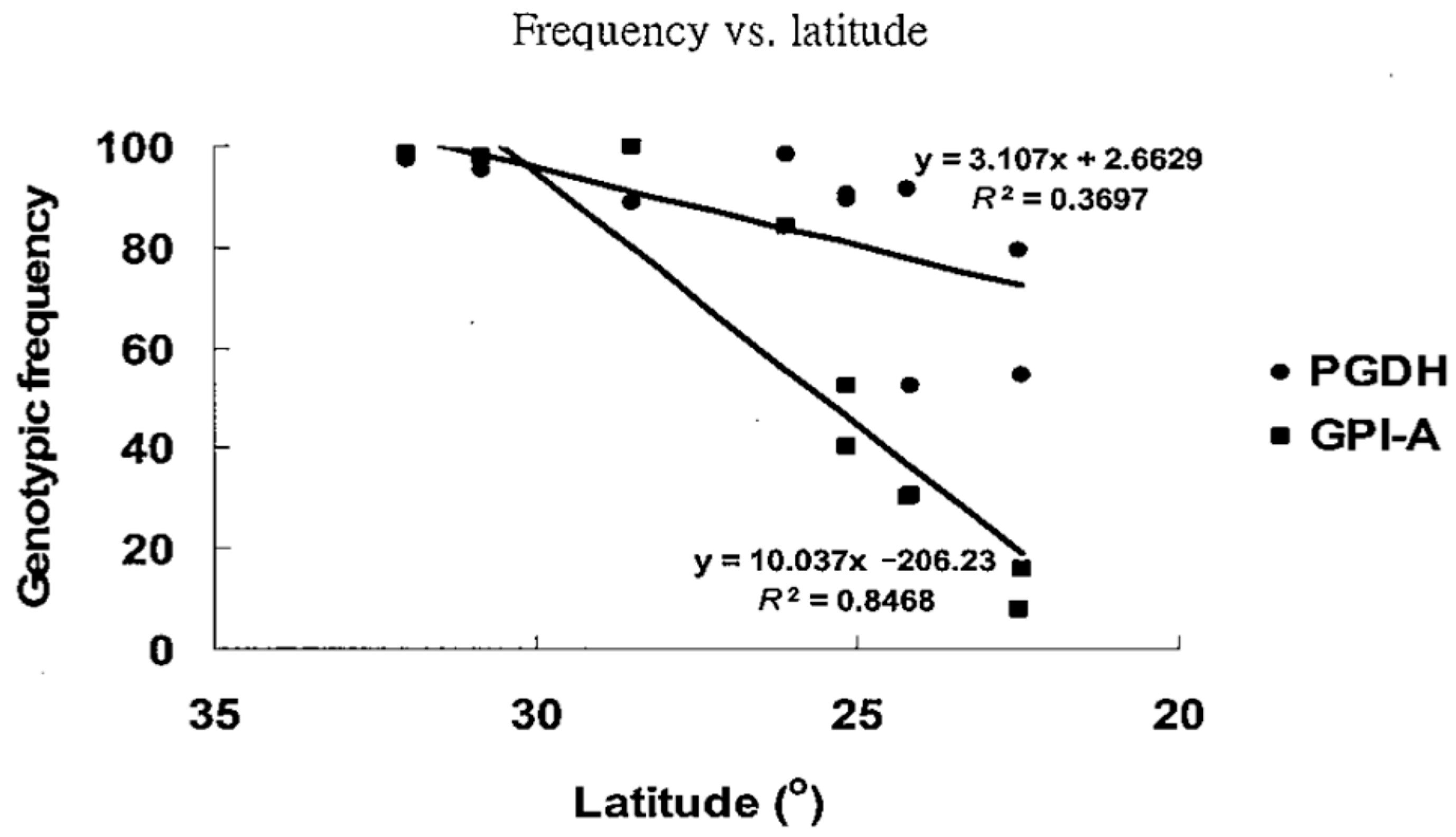
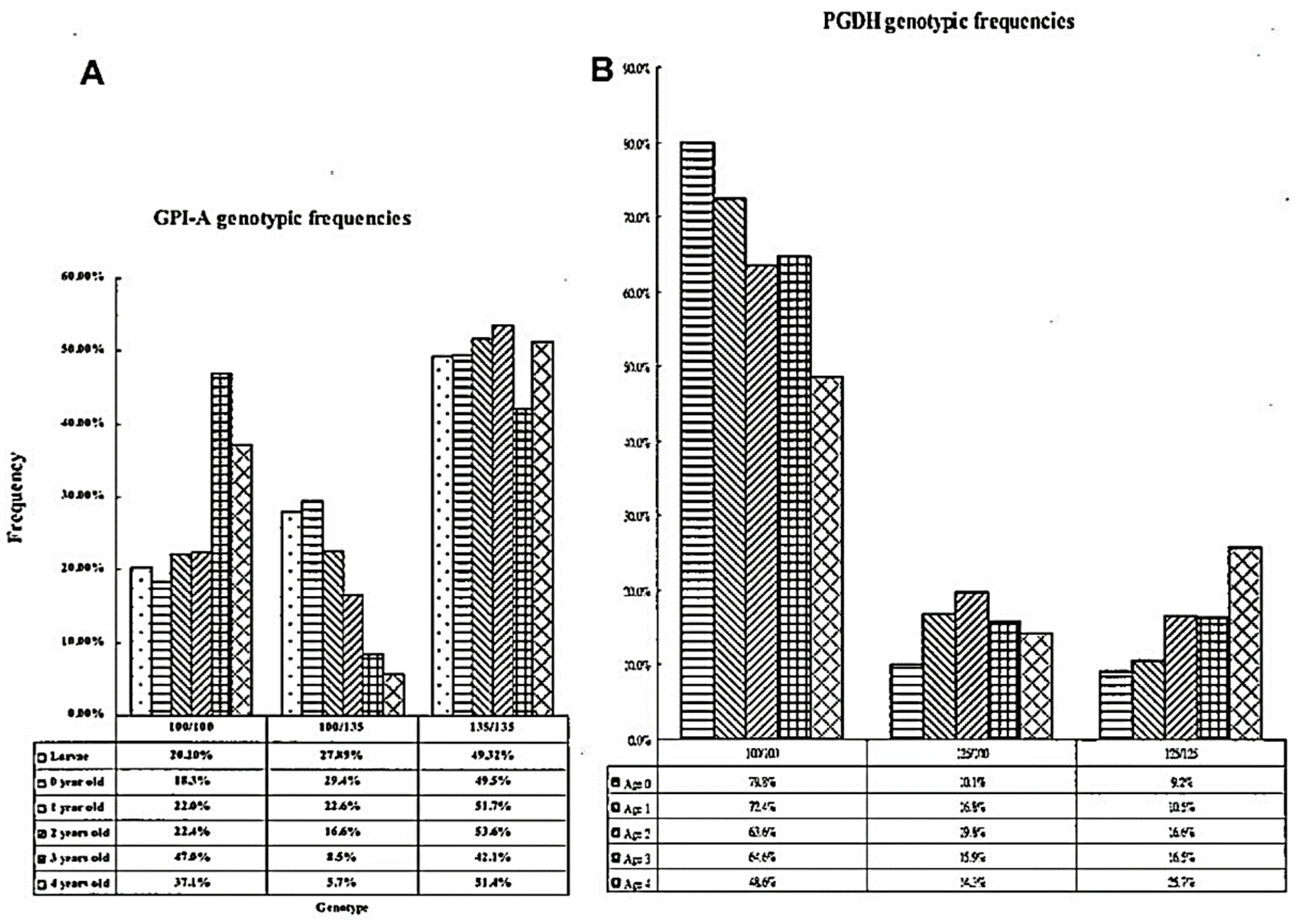
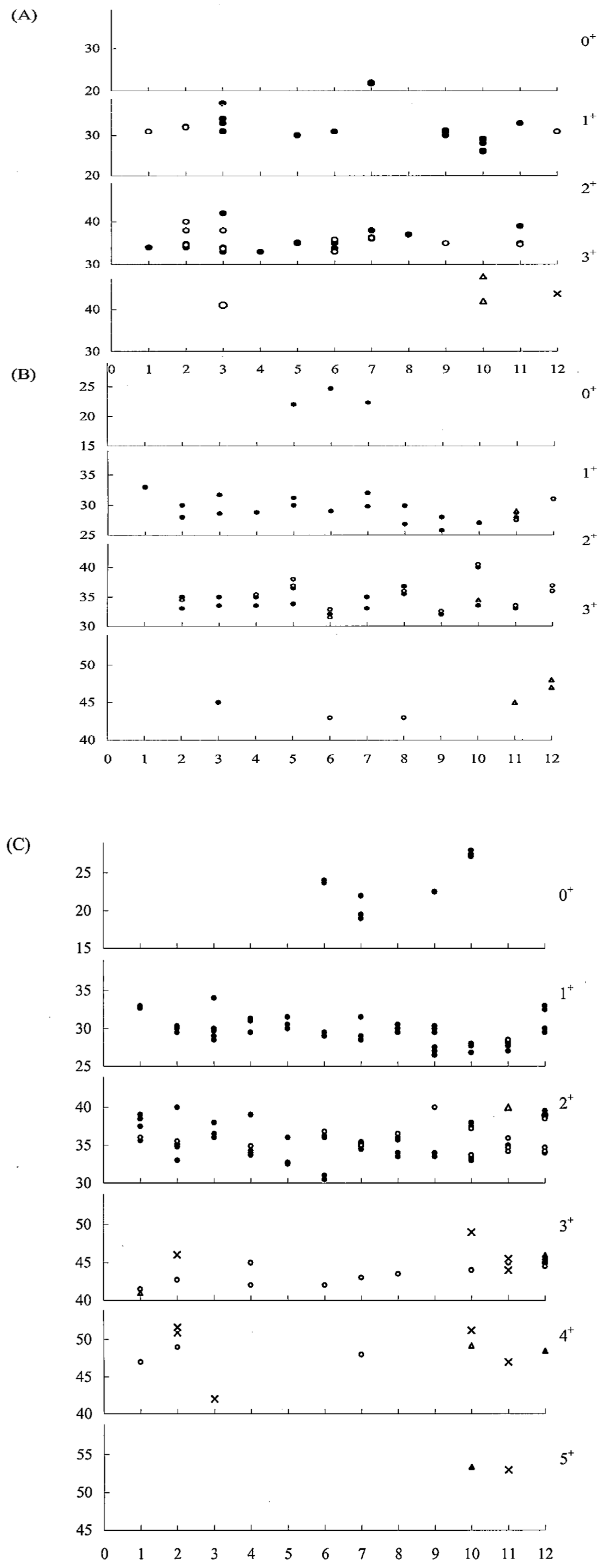
| Population | Abbreviation | N a | A b | AR c | Ho d | He e | Fis f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | |||||||
| Nagasaki | NA | 41 | 2.500 | 1.259 | 0.164 | 0.198 | 0.174 |
| Shanghai | SH | 22 | 2.286 | 1.382 | 0.058 | 0.093 | 0.383 |
| Tachen | TC | 9 | 2.000 | 1.231 | 0.111 | 0.111 | 0.000 |
| Matsu | MS | 48 | 2.167 | 1.125 | 0.031 | 0.031 | −0.007 |
| Dashi | DS | 50 | 2.000 | 1.201 | 0.132 | 0.143 | 0.083 |
| Tanshui | TS | 187 | 2.250 | 1.214 | 0.055 | 0.092 | 0.402 |
| Wuchi | WC | 25 | 2.000 | 1.119 | 0.066 | 0.065 | −0.017 |
| Tadu | TD | 42 | 2.200 | 1.186 | 0.080 | 0.132 | 0.390 |
| Peimen | PM | 73 | 2.167 | 1.247 | 0.100 | 0.131 | 0.235 |
| Anping | AP | 31 | 2.000 | 1.141 | 0.053 | 0.092 | 0.423 |
| Chiding | CD | 20 | 2.000 | 1.035 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.000 |
| Kaoshiung | KS | 131 | 2.500 | 1.123 | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.698 |
| Kaoping | KP | 44 | 3.000 | 1.207 | 0.215 | 0.442 | 0.515 |
| Tapong | TP | 540 | 2.333 | 1.283 | 0.049 | 0.083 | 0.407 |
| Hualien | HL | 28 | 2.000 | 1.155 | 0.142 | 0.215 | 0.340 |
| Juvenile | |||||||
| Fulung | FLJ | 426 | 2.800 | 1.159 | 0.059 | 0.127 | 0.532 |
| Tanshui | TSJ | 621 | 3.400 | 1.153 | 0.076 | 0.121 | 0.367 |
| Linbien | LBJ | 423 | 3.000 | 1.160 | 0.099 | 0.129 | 0.231 |
| Mean | 2.367 | 1.188 | 0.086 | 0.128 |
| Locus | Na a | AR b | HO c | HE d | FIS | FIT | FST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAAT | 3 | 1.153 | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.643 | 0.652 | 0.025 |
| CK-A | 2 | 1.102 | 0.024 | 0.023 | −0.031 | −0.002 | 0.029 |
| GPI-A | 5 | 2.415 | 0.185 | 0.296 | 0.454 | 0.570 | 0.214 |
| GPI-B | 4 | 1.481 | 0.031 | 0.031 | −0.029 | −0.018 | 0.011 |
| IDH-A | 2 | 1.007 | 0.001 | 0.001 | −0.002 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| IDH-B | 2 | 1.019 | 0.008 | 0.008 | −0.016 | 0.002 | 0.017 |
| LDH-A | 4 | 1.023 | 0.013 | 0.013 | −0.021 | 0.003 | 0.023 |
| LDH-B | 2 | 1.032 | 0.004 | 0.004 | −0.005 | −0.000 | 0.004 |
| MDH-A | 2 | 1.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | −0.000 | −0.003 |
| MPI | 4 | 1.09 | 0.026 | 0.025 | −0.016 | −0.001 | 0.015 |
| PGM-A | 4 | 1.055 | 0.003 | 0.003 | −0.002 | −0.002 | −0.000 |
| PGM-B | 2 | 1.026 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.246 | 0.250 | 0.004 |
| PGDH | 3 | 1.84 | 0.070 | 0.123 | 0.440 | 0.582 | 0.253 |
| Jackknifing over loci | |||||||
| Total | 0.452 ± 0.124 | 0.578 ± 0.130 | 0.218 ± 0.044 | ||||
| Bootstrapping over loci (95% confidence interval) | |||||||
| −0.008 ± 0.447 | 0.007 ± 0.564 | 0.012 ± 0.223 | |||||
| Bootstrapping over loci (99% confidence interval) | |||||||
| −0.024 ± 0.453 | −0.012 ± 0.569 | 0.011 ± 0.233 | |||||
| Scheme Category Description | % Var. | Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| One geographical group | |||
| Among populations within groups | 19.30 | FST = 0.193 | 0.000 |
| Within populations | 80.70 | ||
| Scenario I: Three geographical groups (Taiwan, Japan, and mainland China) | |||
| Among groups | 27.20 | FSC = 0.163 | 0.000 |
| Among populations within groups | 11.90 | FST = 0.390 | 0.000 |
| Within populations | 60.91 | FCT = 0.271 | 0.009 |
| Scenario II: Three geographical groups (NA); (WC, CD, KS, AP, SH, TC, and MS); (TS, DS, TD, HL, KP, PM, TP, TSJ, FLJ, and LBJ) | |||
| Among groups | 34.71 | FSC = 0.086 | 0.000 |
| Among populations within groups | 5.66 | FST = 0.403 | 0.000 |
| Within populations | 59.64 | FCT = 0.347 | 0.000 |
| Scenario III: Four ecological groups (NA); (WC, CD, KS, AP, SH, TC, and MS); (TS, DS, TD, HL, KP, PM, and TP); (TSJ, FLJ, and LBJ) | |||
| Among groups | 19.85 | FSC = 0.056 | 0.000 |
| Among populations within groups | 4.53 | FST = 0.243 | 0.000 |
| Within populations | 75.62 | FCT = 0.198 | 0.000 |
| Scenario IV: Three geographical groups (Taiwan vs. other populations) | |||
| Among groups | 18.70 | FSC = 0.243 | 0.000 |
| Among populations within groups | 19.77 | FST = 0.384 | 0.000 |
| Within populations | 61.53 | FCT = 0.186 | 0.000 |
| Scenario V: Residential and migratory, among 22 samples when GPI 100/100 and GPI 135/135 are treated separately | |||
| Among groups | 48.75 | FSC = 0.170 | 0.000 |
| Among populations in group | 8.75 | FST = 0.575 | 0.000 |
| Within population | 42.50 | FCT = 0.487 | 0.000 |
| Scenario VI: Taiwan, Japan, and mainland China groups when GPI loci are removed | |||
| Among groups | 1.34 | FSC = 0.116 | 0.000 |
| Among populations in group | 11.52 | FST = 0.128 | 0.000 |
| Within population | 87.15 | FCT = 0.013 | 0.000 |
| Scenario VII: Taiwan and Japan migratory groups | |||
| Among groups | 3.18 | FSC = 0.132 | 0.000 |
| Among populations in group | 12.86 | FST = 0.160 | 0.000 |
| Within population | 83.96 | FCT = 0.031 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, C.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Du, S.-Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Lin, H.-D. Variation in the Local Grey Mullet Populations (Mugil cephalus) on the Western Pacific Fringe. Genes 2024, 15, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101280
Kuo C-H, Lee S-C, Du S-Y, Huang C-S, Lin H-D. Variation in the Local Grey Mullet Populations (Mugil cephalus) on the Western Pacific Fringe. Genes. 2024; 15(10):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101280
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Chien-Hsien, Sin-Che Lee, Shin-Yi Du, Chao-Shen Huang, and Hung-Du Lin. 2024. "Variation in the Local Grey Mullet Populations (Mugil cephalus) on the Western Pacific Fringe" Genes 15, no. 10: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101280
APA StyleKuo, C.-H., Lee, S.-C., Du, S.-Y., Huang, C.-S., & Lin, H.-D. (2024). Variation in the Local Grey Mullet Populations (Mugil cephalus) on the Western Pacific Fringe. Genes, 15(10), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101280







