Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cross-Genomic Analysis of the RIPK Gene Family and the MLKL Gene
2.2. Molecular Cloning of Hl-RIPK5, Hl-RIPK7 and Hl-MLKL ORF cDNA
2.3. Phylogenetic Tree, Motif, and Structural Domain Analysis
2.4. Tissue Distribution and Ontogeny of Hl-RIPK5, Hl-RIPK7 and Hl-MLKL mRNA Expression
2.5. Primary Culture and Challenge of Coelomocytes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
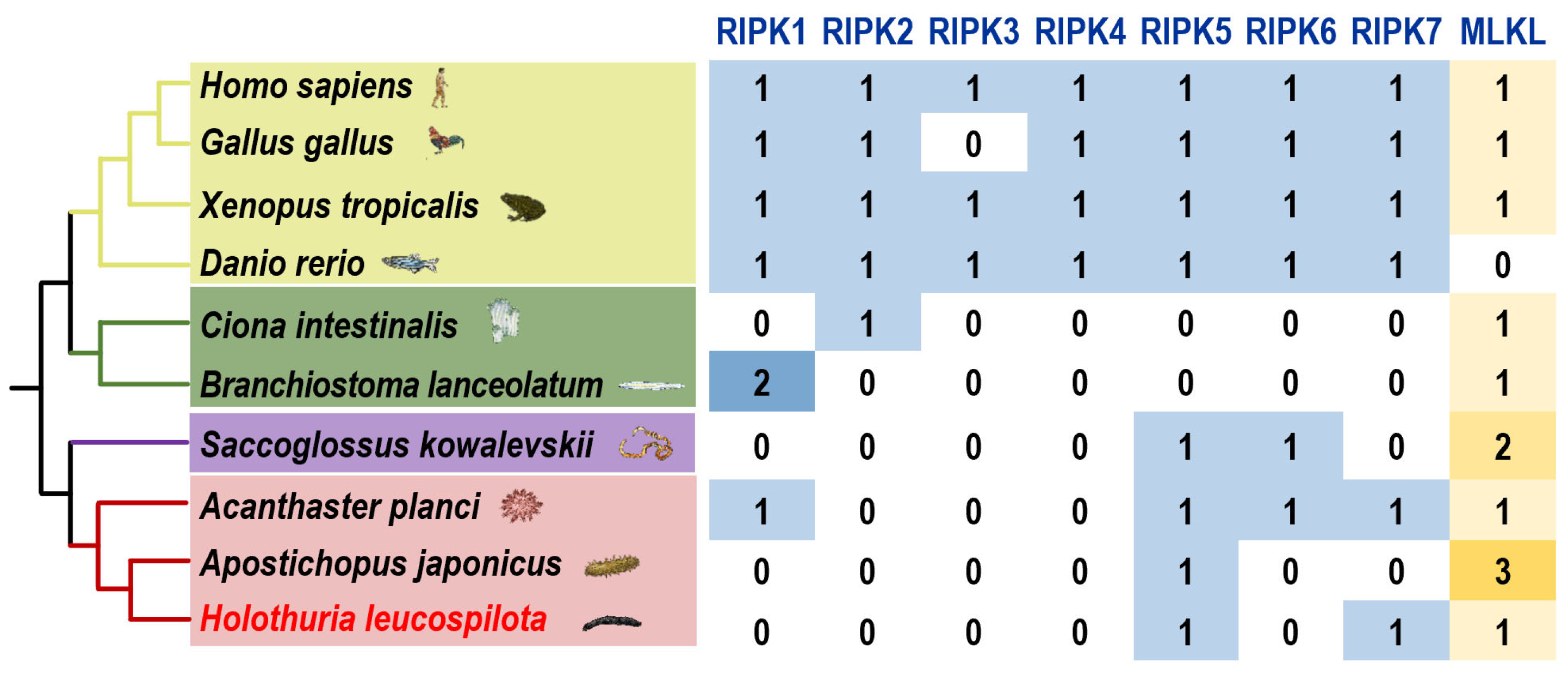
3.1. Screening of the Genes of the RIPK Family and MLKL
3.2. Molecular Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Hl-RIPK5, Hl-RIPK7 and Hl-MLKL
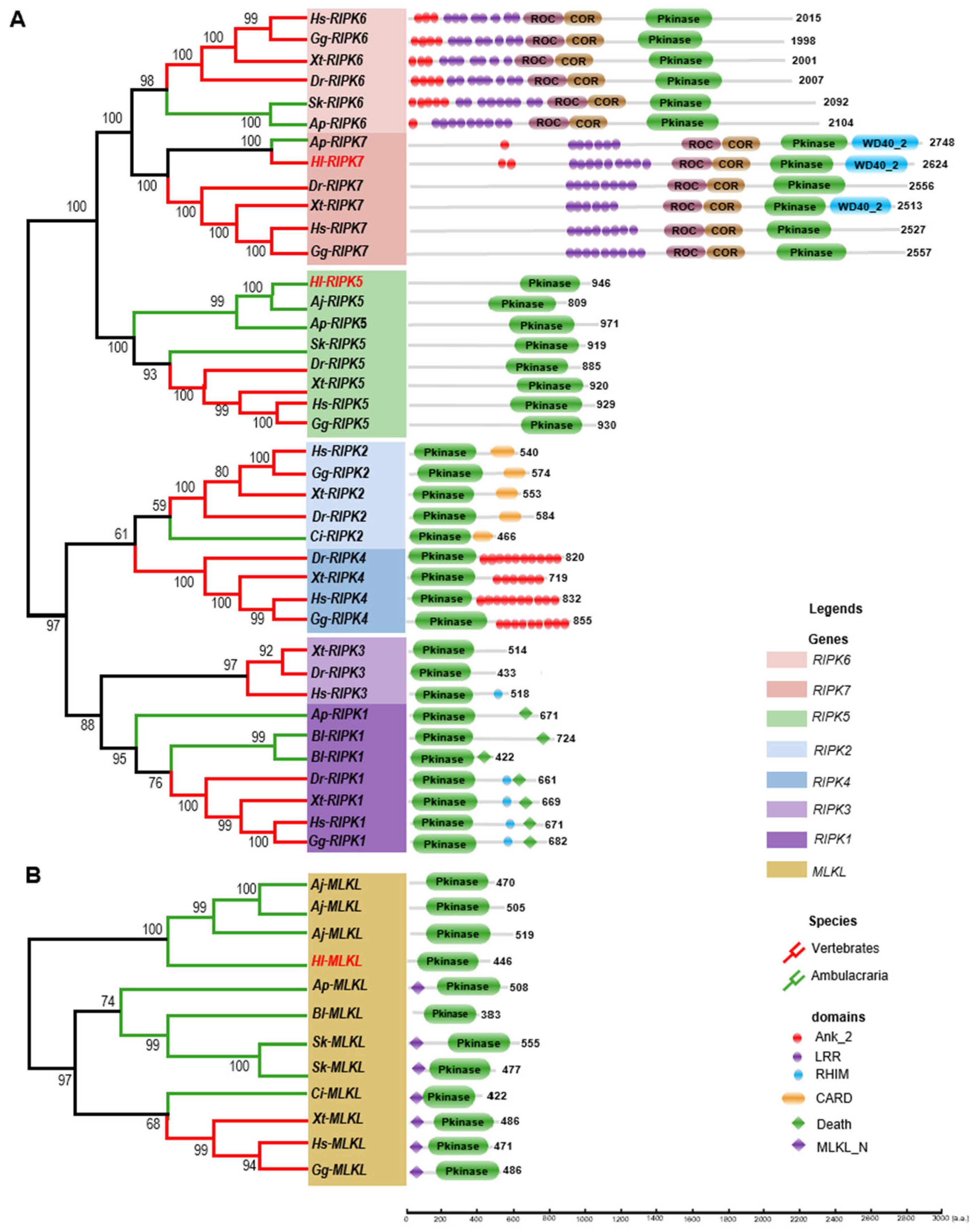
3.3. The Phylogenetic Tree and Functional Domain
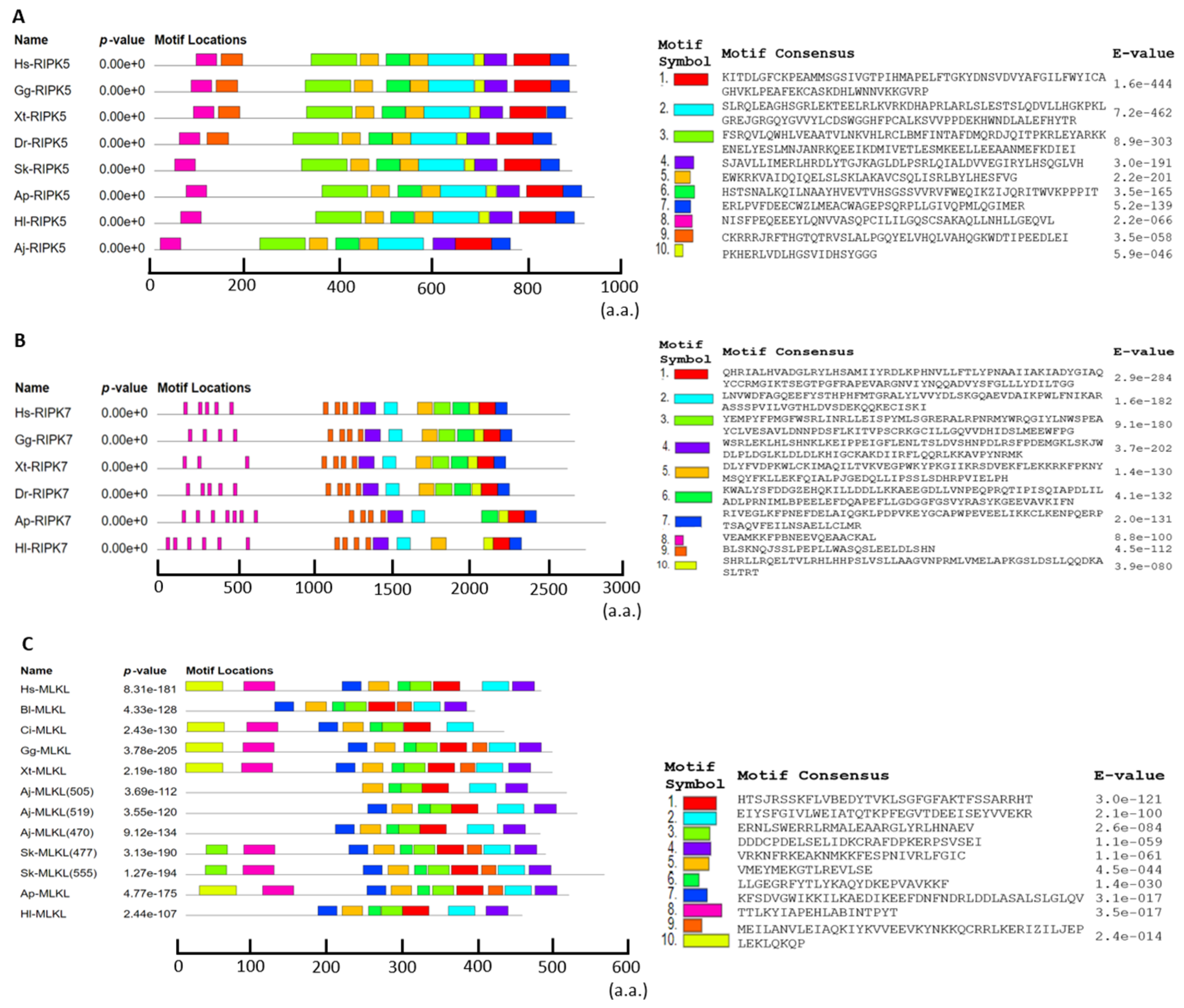
3.4. The Motif Patterns Analysis of RIPK5, RIPK7, and MLKL
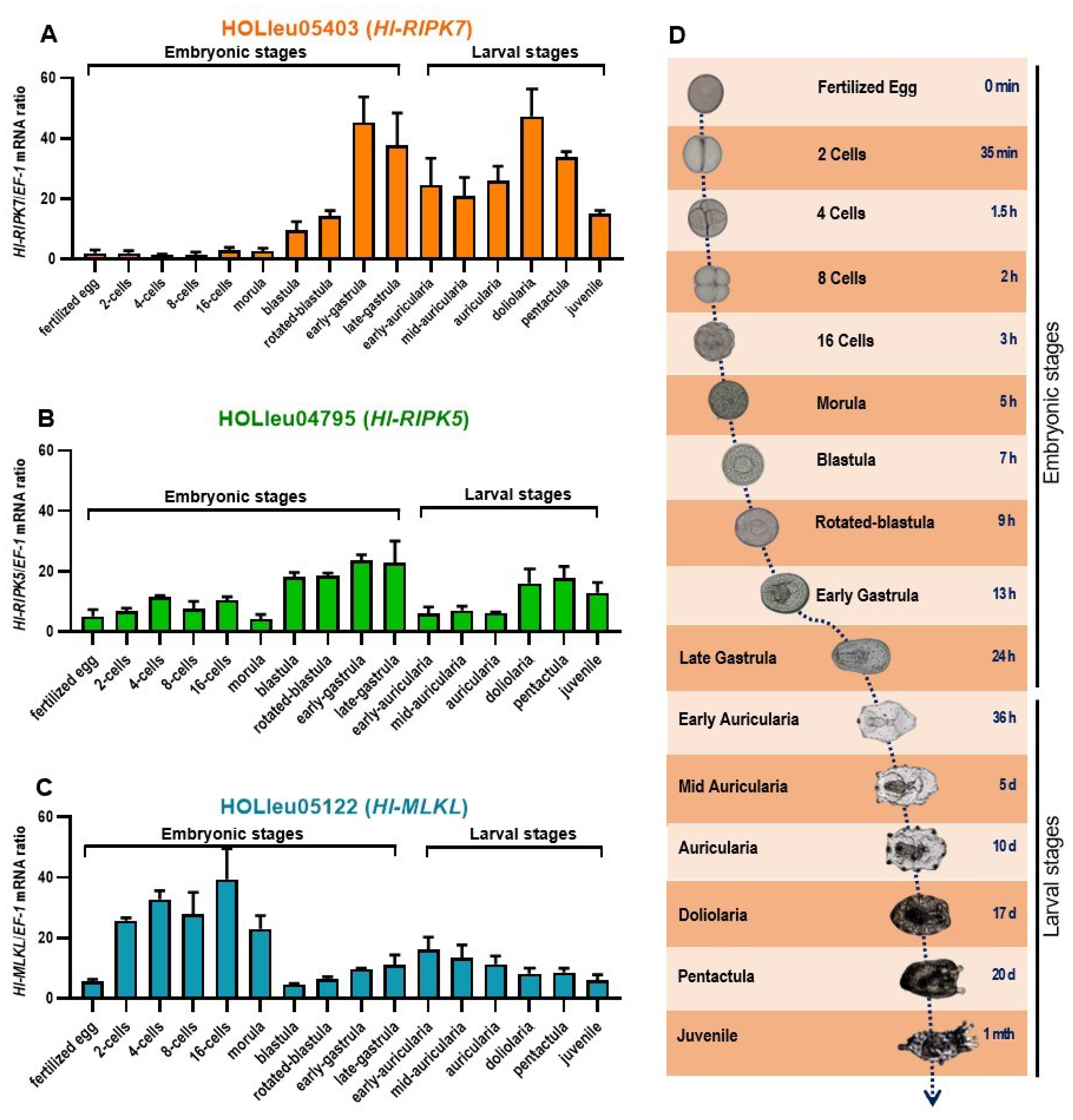
3.5. mRNA Expression Patterns of Hl-RIPK5, Hl-RIPK7, and Hl-MLKL in Adult Tissues and Different Developments
3.6. Primary Coelomocytes Transcript Response of Hl-RIPKs and Hl-MLKL during Environmental and Pathogenic Challenges
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Han, J. Receptor-interacting protein (RIP) kinase family. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, W.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Vandenabeele, P. RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and survival. Cell 2009, 138, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, X. RIP kinases as modulators of inflammation and immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, K.; Chan, F.K. Necroptosis-independent signaling by the RIP kinases in inflammation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Osorio, V.; Abdelwahab, Y.; Ros, U. The many faces of MLKL, the executor of necroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuny, G.D.; Degterev, A. RIPK protein kinase family: Atypical lives of typical kinases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 109, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger, B.Z.; Stanger, B.Z.; Leder, P.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, E.; Seed, B. RIP: A novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell 1995, 81, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mompean, M.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Laage, S.; Siemer, A.B.; Bozkurt, G.; Wu, H.; McDermott, A.E. The structure of the necrosome RIPK1-RIPK3 core, a human hetero-amyloid signaling complex. Cell 2018, 173, 1244–1253.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, L.G.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. RIP5 is a RIP-homologous inducer of cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Challa, S.; Moquin, D.; Genga, R.; Ray, T.D.; Guildford, M.; Chan, F.K. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009, 137, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Chen, S.; Liao, D.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, W.; Lei, X.; et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 2012, 148, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Ren, J.; Huang, D.; He, W.T.; Song, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Chen, P.; et al. Translocation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein to plasma membrane leads to necrotic cell death. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Huang, M.; Yang, X.; Hou, J. MLKL: Functions beyond serving as the Executioner of Necroptosis. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4759–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinlich, R.; Green, D.R. The two faces of receptor interacting protein kinase-1. Mol. Cell. 2014, 56, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Hulihan, M.M.; Kachergus, J.M.; Melrose, H.L.; Lincoln, S.J.; Hinkle, K.M.; Stone, J.T.; Ross, O.A.; Hauser, R.; Aasly, J.; et al. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 1: A paralog of LRRK2 and a candidate gene for Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 2007, 8, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimprich, A.; Biskup, S.; Leitner, P.; Lichtner, P.; Farrer, M.; Lincoln, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Uitti, R.J.; Calne, D.B.; et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 2004, 44, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ren, C.H.; Wong, N.K.; Yan, A.F.; Sun, C.Y.; Fan, D.D.; Luo, P.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, L.P.; Ruan, Y.; et al. The Holothuria leucospilota genome elucidates sacrificial organ expulsion and bioadhesive trap enriched with amyloid-patterned proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2213512120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.M.; Wu, X.F.; Feng, J.; Zhu, X.X.; Tang, D.S.; Jiang, X.; Pan, W.J.; Huang, J.S.; Chen, T.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in the tropical sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Ren, X.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, X.Y.; Lin, T.H.; Huang, J.S.; Guo, Z.Y.; Luo, L.; Ren, C.H.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the early body wall regeneration mechanism of the sea cucumber after artificially induced transverse fission. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Zixuan, E.; Pan, W.J.; Li, Z.; Lin, T.H.; Ren, C.H.; Luo, P.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.G.; et al. Metabolome and transcriptome association analysis reveals the link between pigmentation and nutrition utilization in the juveniles of sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, C.; Luo, P.; Jiang, X.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Fang, J.; Yu, S.; E, Z.; Diao, D.; et al. Pipeline for identification of genome-wide microsatellite markers and its application in assessing the genetic diversity and structure of the tropical sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 37, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, C. A review of the immune molecules in the sea cucumber. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Moynagh, P.N. RIP kinases: Key decision makers in cell death and innate immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Manning, G. Necroptosis and Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 743–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondelinger, Y.; Hulpiau, P.P.; Saeys, Y.; Bertrand, M.J.M.; Vandenabeele, P. An evolutionary perspective on the necroptotic pathway. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Huo, D.; Yu, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Cheng, C.; Jiang, X.; Ren, C. Transcriptomic analysis of sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota) coelomocytes revealed the echinoderm cytokine response during immune challenge. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, C.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, T.; et al. First echinoderm trehalase from a tropical sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota): Molecular cloning and mRNA expression in different tissues, embryonic and larval stages, and under a starvation challenge. Gene 2018, 665, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Pang, Y.; Li, Q. Comprehensive evolutionary analysis of lamprey TNFR-associated factors (TRAFs) and receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPKs) and insights into the functional characterization of TRAF3/6 and RIPK1. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; McQuade, T.; Siemer, A.B.; Napetschnig, J.; Moriwaki, K.; Hsiao, Y.S.; Damko, E.; Moquin, D.; Walz, T.; McDermott, A.; et al. The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell 2012, 150, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Quade, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Rizo, J. A plug release mechanism for membrane permeation by MLKL. Structure 2014, 22, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Su, L.; Rizo, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, X. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebeling, T.; Kunzendorf, U.; Krautwald, S. The role of RHIM in necroptosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, J. The structure of mouse RIPK1 RHIM-containing domain as a homo-amyloid and in RIPK1/RIPK3 complex. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.H.; Vincenz, C. The death domain superfamily: A tale of two interfaces? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Gómez, F.; Aponte-Rivera, F.; Méndez-Castaner, L.; García-Arrarás, J.E. Changes in holothurian coelomocyte populations following immune stimulation with different molecular patterns. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Ito, G.; Tomita, T. Physiological and pathological functions of LRRK2: Implications from substrate proteins. Neuronal Signal. 2018, 2, NS20180005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Rastegar, D.; Dzamko, N. Leucine Rich Repeat Kinase 2 and Innate Immunity. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Hansoul, S.; Nicolae, D.L.; Cho, J.H.; Duerr, R.H.; Rioux, I.D.; Brant, S.R.; Silverberg, M.S.; Taylor, K.D.; Barmada, M.M.; et al. Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.; McGovern, D.P.; Barrett, J.C.; Wang, K.; Radford-Smith, G.L.; Ahmad, T.; Lees, C.W.; Balschun, T.; Lee, J.; Roberts, R.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, M.K.; Tansey, M.G. Is LRRK2 the missing link between inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease? NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Murabe, N.; Amemiya, S.; Nakajima, Y. Nervous system development of the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, T.; Yu, Z.; Huo, D.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Jiang, X.; Ren, C. First echinoderm alpha-amylase from a tropical sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota): Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, cellular localization and functional production in a heterogenous E. coli system with codon optimization. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechel, S.; Meinhardt, A.; Unsicker, K.; von Bohlen Und Halbach, O. Expression of leucine-rich-repeat-kinase 2 (LRRK2) during embryonic development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Perera, N.D.; Chiam, M.D.F.; Cuic, B.; Wanniarachchillage, N.; Tomas, D.; Samson, A.L.; Cawthorne, W.; Valor, E.N.; Murphy, J.M.; et al. Necroptosis is dispensable for motor neuron degeneration in a mouse model of ALS. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, A.K.; Rosler, S.; Schenk, B.; Kowald, L.; van Wijk, S.J.L.; Fulda, S. Interferons transcriptionally up-regulate MLKL expression in cancer cells. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Martens, S.; Bridelance, J.; Roelandt, R.; Vandenabeele, P.; Takahashi, N. MLKL in cancer: More than a necroptosis regulator. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Mlkl knockout mice demonstrate the indispensable role of Mlkl in necroptosis. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Luo, P.; Hu, C.; Wong, N.K.; Ren, C. Evolutionarily ancient caspase-9 sensitizes immune effector coelomocytes to cadmium-induced cell death in the sea cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 927880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, R.; Huang, Q.; Rao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, R.; Peng, S.; Huang, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tang, D.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota. Genes 2024, 15, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101297
Chen R, Huang Q, Rao Y, Wang J, Yu R, Peng S, Huang K, Huang Y, Zhu X, Tang D, et al. Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota. Genes. 2024; 15(10):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101297
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Rong, Qianying Huang, Yingzhu Rao, Junyan Wang, Ruiming Yu, Shuangxin Peng, Kaiyi Huang, Yihang Huang, Xiangxing Zhu, Dongsheng Tang, and et al. 2024. "Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota" Genes 15, no. 10: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101297
APA StyleChen, R., Huang, Q., Rao, Y., Wang, J., Yu, R., Peng, S., Huang, K., Huang, Y., Zhu, X., Tang, D., Zhang, X., Lin, T., Chen, T., & Yan, A. (2024). Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota. Genes, 15(10), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101297




